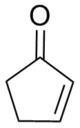
Cyclopentenone
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cyclopent-2-en-1-one | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.012 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H6O | |||
| Molar mass | 82.102 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 0.98 g·mL−1 | ||
| Boiling point | 150 °C (302 °F; 423 K) | ||
| almost insoluble in water | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Harmful | ||
| Flash point | 42 °C (108 °F; 315 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
2-Cyclopentenone is a ketone with chemical formula C5H6O and CAS number 930-30-3. It is structurally similar to cyclopentanone, with the additional feature of α-β unsaturation in the ring system. 2-Cyclopentenone contains two functional groups, a ketone and an alkene. It is a colorless liquid.
The term cyclopentenone may also refer to a structural motif wherein the cyclopentenone moiety is a subunit of a larger molecule. Cyclopentenones are found in a large number of natural products, including jasmone, the aflatoxins, and several prostaglandins.
Synthesis[]
2-Cyclopentenones can be synthesized in a number of ways. One of the routes involves elimination of α-bromo-cyclopentanone using lithium carbonate[1] and Claisen condensation-decarboxylation-isomerization cascades of unsaturated diesters as shown below.[2]

The acid-catalyzed dehydration of cyclopentanediols affords cyclopentenone.[3]
As a functional group, the synthesis of 2-cyclopentenones is accomplished in a variety of other ways, including the Nazarov cyclization reaction from divinyl ketones, Saegusa–Ito oxidation from cyclopentanones, ring-closing metathesis from the corresponding dienes, oxidation of the corresponding cyclic allylic alcohols, and the Pauson–Khand reaction from alkenes, alkynes, and carbon monoxide.[4]
Reactions[]
As an enone, 2-cyclopentenone undergoes the typical reactions of α-β unsaturated ketones, including nucleophilic conjugate addition, the Baylis–Hillman reaction, and the Michael reaction. Cyclopentenone also functions as an excellent dienophile in the Diels–Alder reaction, reacting with a wide variety of dienes. In one example, a Danishefsky-type diene is reacted with a cyclopentenone to yield a fused tricyclic system en route to the synthesis of coriolin.[5]

Occurrence[]
It has been isolated from pressure-cooked pork liver by simultaneous steam distillation and continuous solvent extraction.[6]
References[]
- ^ US EP1418166, Daisuke, Fukushima & Norihiko, Hirata, "Process for producing 2-bromocyclopentanone", published 2004-05-12
- ^ US EP1422212, Liang, Shelue; Haunert, Andrea & Huber-Dirr, Sylvia et al., "Process for preparing cyclopentenone", published 2004-11-25
- ^ Charles H. DePuy And K. L. Eilers (1962). "2-Cyclopentenone". Org. Synth. 42: 38. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.042.0038.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^ Müller, Reto. "Synthesis of cyclopentenones". Organic Chemistry Portal. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ Danishefsky, Samuel; Zamboni, Robert; Kahn, Michael; Etheredge, Sarah Jane (March 1980). "Total synthesis of dl-coriolin". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 102 (6): 2097–2098. doi:10.1021/ja00526a061.
- ^ Mussinan, Cynthia J.; Walradt, John P. (May 1974). "Volatile constituents of pressure cooked pork liver". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 22 (5): 827–831. doi:10.1021/jf60195a002.
- Enones
- Cyclopentenes