Democratic deficit
A democratic deficit (or democracy deficit) occurs when ostensibly democratic organizations or institutions (particularly governments) fall short of fulfilling the principles of democracy in their practices or operation where representative and linked parliamentary integrity becomes widely discussed.[1]
The phrase democratic deficit is cited as first being used by the Young European Federalists in their Manifesto in 1977,[2] which was drafted by Richard Corbett. The phrase was also used by David Marquand in 1979, referring to the then European Economic Community, the forerunner of the European Union.[3]
Examples[]
The UN Parliamentary Assembly has been proposed as a way of ameliorating a democractic deficit within the United Nations.[4]
Some scholars have argued that the ratification of European Union treaties by repeated referendums—such as those held in Ireland for the Treaty of Nice and the Treaty of Lisbon—is also associated with a democratic deficit.[5] Another problem in the EU is that voters vote more on the basis of national issues in the European parliamentary elections and that the election is more used by voters to punish their government in the middle of their term.[6] There is also insufficiently a European public opinion or European public sphere that votes against or rewards European politicians.[7] Another problem is the big influence of lobbying groups on European institutions.[8][9] The European Parliament was created to give more democratic legitimacy to the EU, but shares legislative power with the Council of the European Union, which has one vote per country.
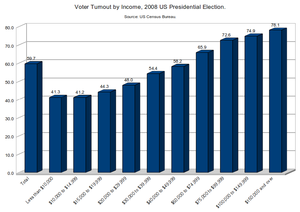
A study of the Columbia University concluded that policy in U.S. states is congruent with the majority only half the time. The largest influences were found to be legislative professionalization, term limits, and issue salience. Partisanship and interest groups affect the ideological balance of incongruence more than the aggregate degree thereof. Policy is found to be overresponsive to ideology and party, leading policy to be polarized relative to state electorates.[10] The large differences in voter turnout during the American elections for various income groups are also seen as a problem for the functioning of democracy.[11] Sanford Levinson argues that next to the fact that campaign financing and gerrymandering are seen as serious problems for democracy, also one of the root causes of the American democratic deficit lies in the United States Constitution itself,[12] for example there is a lack of representation in the Senate for highly populated states such as California.[13]
See also[]
- Defective democracy
- Democracy Index
- Democratic deficit in the European Union
- Direct democracy
- Elite theory
- Freedom deficit
- How Democratic Is the American Constitution?
- Political alienation
- Popular assembly
- Post-democracy
References[]
- ^ "A democratic deficit occurs when ostensibly democratic organizations or institutions, in fact, fall short of fulfilling what are believed to be the principles of democracy." Sanford Levinson, How the United States Constitution Contributes to the Democratic Deficit in America, 55 Drake L. Rev. 859, 860 (2007).
- ^ Richard (10 October 1977). "The first use of the term "democratic deficit"".
- ^ Marquand, David (1979). Parliament for Europe. Cape. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-224-01716-9.
The resulting 'democratic deficit' would not be acceptable in a Community committed to democratic principles.
Chalmers, Damian; et al. (2006). European Union law: text and materials. Cambridge University Press. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-521-52741-5.'Democratic deficit' is a term coined in 1979 by the British political scientist . . . David Marquand .
Meny, Yves (2003). "De La Democratie En Europe: Old Concepts and New Challenges". Journal of Common Market Studies. 41: 1–13. doi:10.1111/1468-5965.t01-1-00408. S2CID 154742986.Since David Marquand coined his famous phrase 'democratic deficit' to describe the functioning of the European Community, the debate has raged about the extent and content of this deficit.
- ^ Commission of Latin American Parliament joins call for UN Parliamentary Assembly | Campaign for a UN Parliament
- ^ Jerzak, Connor T. (1 September 2014). "The EU's Democratic Deficit and Repeated Referendums in Ireland". International Journal of Politics, Culture, and Society. 27 (3): 367–388. doi:10.1007/s10767-014-9185-8. S2CID 144466639.
- ^ Reif, K. and Schmitt, H. (1980) ‘Nine Second-Order National Elections: A Conceptual Framework for the Analysis of European Election Results’. European Journal of Political Research, Vol. 8, No. 1, pp. 3–45.
- ^ David Ward (2002) The European Union Democratic Deficit and the Public Sphere: An Evaluation of EU Media Policy. IOS Press.
- ^ "Interest Representation: Can Lobbying Regulation Help EU Overcome Democratic Deficit?".
- ^ Karr, Karolina (2007). Democracy and lobbying in the European Union. Campus Verlag. p. 10. ISBN 9783593384122.
- ^ "The Democratic Deficit in the States Jeffrey R. Lax Columbia University Justin H. Phillips Columbia University" (PDF).
- ^ "Voter Turnout By Income, 2008 US Presidential Election - Demos". www.demos.org.
- ^ "The Democratic Deficit in Americ, Sanford Levinson".
- ^ Sanford Levinson (LA Times article available on website) (16 October 2006). "Our Broken Constitution". University of Texas School of Law -- News & Events. Archived from the original on 5 October 2009. Retrieved 10 October 2009.
- 1977 neologisms
- Democracy
- United Nations reform