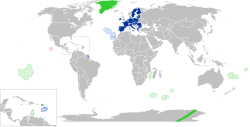
European Union
show
European Union | |
|---|---|
 Flag | |
Motto: "In Varietate Concordia" (Latin) "United in Diversity" | |
Anthem: "Anthem of Europe" (instrumental) | |
 | |
| Institutional seats | Brussels
Frankfurt
Luxembourg City
Strasbourg
|
| Largest metropolis | Paris |
| Official languages | |
| Official scripts |
|
| Religion (2015)[3] |
|
| Demonym(s) | European |
| Type | Supranational union |
| Member states | show
27 states |
| Government | Intergovernmental |
• President of the Commission | Ursula von der Leyen |
| David Sassoli | |
• President of the European Council | Charles Michel |
• Presidency of the Council of the EU | |
| Formation[4] | |
• Treaty of Rome | 1 January 1958 |
• Single European Act | 1 July 1987 |
• Treaty of Maastricht | 1 November 1993 |
• Treaty of Lisbon | 1 December 2009 |
• Last polity admitted | 1 July 2013 (Croatia) |
• Last polity withdrawn | 31 January 2020 (United Kingdom) |
| Area | |
• Total | 4,233,262 km2 (1,634,472 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 3.08 |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | |
• Density | 106/km2 (274.5/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2021 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | $46,888 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2021 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | $38,256 |
| Gini (2019) | medium |
| HDI (2019) | very high · 14th |
| Currency | Euro (EUR; €; in eurozone) and show
9 others |
| Time zone | UTC to UTC+2 (WET, CET, EET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+1 to UTC+3 (WEST, CEST, EEST) |
| (see also Summer Time in Europe)[b] | |
| Internet TLD | .eu[c] |
Website europa | |
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe.[9] The union has a total area of 4,233,255.3 km2 (1,634,469.0 sq mi) and an estimated total population of about 447 million. An internal single market has been established through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states have agreed to act as one. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market;[10] enact legislation in justice and home affairs; and maintain common policies on trade,[11] agriculture,[12] fisheries and regional development.[13] Passport controls have been abolished for travel within the Schengen Area.[14] A monetary union was established in 1999, coming into full force in 2002, and is composed of 19 member states which use the euro currency. The EU has often been described as a sui generis political entity (without precedent or comparison) with the characteristics of either a federation or confederation.[15][16]
The union and EU citizenship were established when the Maastricht Treaty came into force in 1993.[17] The EU traces its origins to the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) and the European Economic Community (EEC), established, respectively, by the 1951 Treaty of Paris and 1957 Treaty of Rome. The original member states of what came to be known as the European Communities were the Inner Six: Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany. The communities and their successors have grown in size by the accession of new member states and in power by the addition of policy areas to their remit. The United Kingdom became the first member state to leave the EU[18] on 31 January 2020. Before this, three territories of member states had left the EU or its forerunners. The latest major amendment to the constitutional basis of the EU, the Treaty of Lisbon, came into force in 2009.
Containing some 5.8 per cent of the world population in 2020,[d] the EU had generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around US$17.1 trillion in 2021,[6] constituting approximately 18 per cent of global nominal GDP.[20][better source needed] Additionally, all EU countries have a very high Human Development Index according to the United Nations Development Programme. In 2012, the EU was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize.[21] Through the Common Foreign and Security Policy, the union has developed a role in external relations and defence. It maintains permanent diplomatic missions throughout the world and represents itself at the United Nations, the World Trade Organization, the G7 and the G20. Due to its global influence, the European Union has been described by some scholars as an emerging superpower.[22][23][24]
History
Since the end of World War II, sovereign European countries have entered into treaties and thereby co-operated and harmonised policies (or pooled sovereignty) in an increasing number of areas, in the so-called European integration project or the construction of Europe (French: la construction européenne). The following timeline outlines the legal inception of the European Union (EU)—the principal framework for this unification. The EU inherited many of its present responsibilities from the European Communities (EC), which were founded in the 1950s in the spirit of the Schuman Declaration.
| Legend: S: signing F: entry into force T: termination E: expiry de facto supersession Rel. w/ EC/EU framework: de facto inside outside |
[Cont.] | |||||||||||||||
| (Pillar I) | ||||||||||||||||
| European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom) | [Cont.] | |||||||||||||||
| European Economic Community (EEC) | ||||||||||||||||
| Schengen Rules | European Community (EC) | |||||||||||||||
| 'TREVI' | Justice and Home Affairs (JHA, pillar II) | |||||||||||||||
| [Cont.] | Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters (PJCC, pillar II) | |||||||||||||||
Anglo-French alliance |
[Defence arm handed to NATO] | European Political Co-operation (EPC) | Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP, pillar III) | |||||||||||||
| [Tasks defined following the WEU's 1984 reactivation handed to the EU] | ||||||||||||||||
| [Social, cultural tasks handed to CoE] | [Cont.] | |||||||||||||||
Background


During the centuries that followed the fall of Rome in 476, several European states viewed themselves as translatio imperii ("transfer of rule") of the defunct Roman Empire: the Frankish Empire (481–843) and the Holy Roman Empire (962–1806) were thereby attempts to resurrect Rome in the West.[e] This political philosophy of a supra-national rule over the continent, similar to the example of the ancient Roman Empire, resulted in the early Middle Ages in the concept of a renovatio imperii ("restoration of the empire"),[27] either in the forms of the Reichsidee ("imperial idea")[28] or the religiously inspired Imperium Christianum ("christian empire").[29][30] Medieval Christendom and the political power of the Papacy have been cited as conducive to European integration and unity.[31][32][33][34][relevant?]
In the oriental parts of the continent, the Russian Tsardom, and ultimately the Empire (1547–1917), declared Moscow to be Third Rome and inheritor of the Eastern tradition after the fall of Constantinople in 1453.[35] The gap between Greek East and Latin West had already been widened by the political scission of the Roman Empire in the 4th century and the Great Schism of 1054,[36][37][38] and would be eventually widened again by the Iron Curtain (1945–1991) before the enlargement of the European Union towards Eastern Europe since 2004 onward.[39][40][relevant?]
Pan-European political thought truly emerged during the 19th century, inspired by the liberal ideas of the French and American Revolutions after the demise of Napoléon's Empire (1804–1815). In the decades following the outcomes of the Congress of Vienna,[41] ideals of European unity flourished across the continent, especially in the writings of Wojciech Jastrzębowski (1799–1882)[42] or Giuseppe Mazzini (1805–1872).[43] The term United States of Europe (French: États-Unis d'Europe) was used at that time by Victor Hugo (1802–1885) during a speech at the International Peace Congress held in Paris in 1849:
A day will come when all nations on our continent will form a European brotherhood ... A day will come when we shall see ... the United States of America and the United States of Europe face to face, reaching out for each other across the seas.[44]
During the interwar period, the consciousness that national markets in Europe were interdependent though confrontational, along with the observation of a larger and growing US market on the other side of the ocean, nourished the urge for the economic integration of the continent.[45] In 1920, advocating the creation of a European economic union, British economist John Maynard Keynes wrote that "a Free Trade Union should be established ... to impose no protectionist tariffs whatever against the produce of other members of the Union."[46] During the same decade, Richard von Coudenhove-Kalergi, one of the first to imagine of a modern political union of Europe, founded the Pan-Europa Movement.[47] His ideas influenced his contemporaries, among whom was then-Prime Minister of France Aristide Briand. In 1929, the latter gave a speech in favour of a European Union before the assembly of the League of Nations, precursor of the United Nations.[48] In a radio address in March 1943, with war still raging, Britain's leader Sir Winston Churchill spoke warmly of "restoring the true greatness of Europe" once victory had been achieved, and mused on the post-war creation of a "Council of Europe" which would bring the European nations together to build peace.[49][50]
Preliminary (1945–1957)

After World War II, European integration was seen as an antidote to the extreme nationalism which had devastated parts of the continent.[51] In a speech delivered on 19 September 1946 at the University of Zürich, Switzerland, Winston Churchill went further and advocated the emergence of a United States of Europe.[52] The 1948 Hague Congress was a pivotal moment in European federal history, as it led to the creation of the European Movement International and of the College of Europe, where Europe's future leaders would live and study together.[53]
It also led directly to the founding of the Council of Europe in 1949, the first great effort to bring the nations of Europe together, initially ten of them. The council focused primarily on values—human rights and democracy—rather than on economic or trade issues, and was always envisaged as a forum where sovereign governments could choose to work together, with no supra-national authority. It raised great hopes of further European integration, and there were fevered debates in the two years that followed as to how this could be achieved.
But in 1952, disappointed at what they saw as the lack of progress within the Council of Europe, six nations decided to go further and created the European Coal and Steel Community, which was declared to be "a first step in the federation of Europe".[54] This community helped to economically integrate and coordinate the large number of Marshall Plan funds from the United States.[55] European leaders Alcide De Gasperi from Italy, Jean Monnet and Robert Schuman from France, and Paul-Henri Spaak from Belgium understood that coal and steel were the two industries essential for waging war, and believed that by tying their national industries together, future war between their nations became much less likely.[56] These men and others are officially credited as the founding fathers of the European Union.
Treaty of Rome (1957–1992)

In 1957, Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany signed the Treaty of Rome, which created the European Economic Community (EEC) and established a customs union. They also signed another pact creating the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom) for co-operation in developing nuclear energy. Both treaties came into force in 1958.[56]
The EEC and Euratom were created separately from the ECSC and they shared the same courts and the Common Assembly. The EEC was headed by Walter Hallstein (Hallstein Commission) and Euratom was headed by Louis Armand (Armand Commission) and then Étienne Hirsch. Euratom was to integrate sectors in nuclear energy while the EEC would develop a customs union among members.[57][58]
During the 1960s, tensions began to show, with France seeking to limit supranational power. Nevertheless, in 1965 an agreement was reached and on 1 July 1967 the Merger Treaty created a single set of institutions for the three communities, which were collectively referred to as the European Communities.[59][60] Jean Rey presided over the first merged commission (Rey Commission).[61]
In 1973, the communities were enlarged to include Denmark (including Greenland, which later left the Communities in 1985, following a dispute over fishing rights), Ireland, and the United Kingdom.[62] Norway had negotiated to join at the same time, but Norwegian voters rejected membership in a referendum. In 1979, the first direct elections to the European Parliament were held.[63]
Greece joined in 1981, Portugal and Spain following in 1986.[64] In 1985, the Schengen Agreement paved the way for the creation of open borders without passport controls between most member states and some non-member states.[65] In 1986, the European flag began to be used by the EEC[66] and the Single European Act was signed.
In 1990, after the fall of the Eastern Bloc, the former East Germany became part of the communities as part of a reunified Germany.[67]
Maastricht Treaty (1992–2007)
The European Union was formally established when the Maastricht Treaty—whose main architects were Helmut Kohl and François Mitterrand—came into force on 1 November 1993.[17][68] The treaty also gave the name European Community to the EEC, even if it was referred as such before the treaty. With further enlargement planned to include the former communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, as well as Cyprus and Malta, the Copenhagen criteria for candidate members to join the EU were agreed upon in June 1993. The expansion of the EU introduced a new level of complexity and discord.[69] In 1995, Austria, Finland, and Sweden joined the EU.

In 2002, euro banknotes and coins replaced national currencies in 12 of the member states. Since then, the eurozone has increased to encompass 19 countries. The euro currency became the second largest reserve currency in the world. In 2004, the EU saw its biggest enlargement to date when Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia, and Slovenia joined the union.[70]
Lisbon Treaty (2007–present)
In 2007, Bulgaria and Romania became EU members. Later that year, Slovenia adopted the euro,[70] followed by Cyprus and Malta in 2008, Slovakia in 2009, Estonia in 2011, Latvia in 2014, and Lithuania in 2015.

On 1 December 2009, the Lisbon Treaty entered into force and reformed many aspects of the EU. In particular, it changed the legal structure of the European Union, merging the EU three pillars system into a single legal entity provisioned with a legal personality, created a permanent president of the European Council, the first of which was Herman Van Rompuy, and strengthened the position of the high representative of the union for foreign affairs and security policy.[71][72]
In 2012, the EU received the Nobel Peace Prize for having "contributed to the advancement of peace and reconciliation, democracy, and human rights in Europe."[73][74] In 2013, Croatia became the 28th EU member.[75]
From the beginning of the 2010s, the cohesion of the European Union has been tested by several issues, including a debt crisis in some of the Eurozone countries, increasing migration from Africa and Asia, and the United Kingdom's withdrawal from the EU.[76] A referendum in the UK on its membership of the European Union was held in 2016, with 51.9 per cent of participants voting to leave.[77] The UK formally notified the European Council of its decision to leave on 29 March 2017, initiating the formal withdrawal procedure for leaving the EU; following extensions to the process, the UK left the European Union on 31 January 2020, though most areas of EU law continued to apply to the UK for a transition period which lasted until 23:00 GMT on 31 December 2020.[78]
Demographics
Population
As of 1 February 2020, the population of the European Union was about 447 million people (5.8 per cent of the world population).[79][80] In 2015, 5.1 million children were born in the EU-28 corresponding to a birth rate of 10 per 1,000, which is 8 births below the world average.[81] For comparison, the EU-28 birth rate had stood at 10.6 in 2000, 12.8 in 1985 and 16.3 in 1970.[82] Its population growth rate was positive at an estimated 0.23 per cent in 2016.[83]
In 2010, 47.3 million people who lived in the EU were born outside their resident country. This corresponds to 9.4 per cent of the total EU population. Of these, 31.4 million (6.3 per cent) were born outside the EU and 16.0 million (3.2 per cent) were born in another EU member state. The largest absolute numbers of people born outside the EU were in Germany (6.4 million), France (5.1 million), the United Kingdom (4.7 million), Spain (4.1 million), Italy (3.2 million), and the Netherlands (1.4 million).[84] In 2017, approximately 825,000 people acquired citizenship of a member state of the European Union. The largest groups were nationals of Morocco, Albania, India, Turkey and Pakistan.[85] 2.4 million immigrants from non-EU countries entered the EU in 2017.[86][87]
Urbanisation
The EU contains about 40 urban areas with populations of over 1 million. With a population of over 13 million,[88] Paris is the largest metropolitan area and the only megacity in the EU.[89] Paris is followed by Madrid, Barcelona, Berlin, the Ruhr, Rome, and Milan, all with a metropolitan population of over 4 million.[90]
The EU also has numerous polycentric urbanised regions like Rhine-Ruhr (Cologne, Dortmund, Düsseldorf et al.), Randstad (Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, Utrecht et al.), Frankfurt Rhine-Main (Frankfurt, Wiesbaden, Mainz et al.), the Flemish Diamond (Antwerp, Brussels, Leuven, Ghent et al.) and Upper Silesian area (Katowice, Ostrava et al.).[89]
| Largest population centres of the European Union metropolitan regions, Eurostat 2019[91] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | City name | State | Pop. | Rank | City name | State | Pop. | ||
| 1 | Paris | France | 12,244,807 | 11 | Marseille | France | 3,100,329 | ||
| 2 | Madrid | Spain | 6,641,649 | 12 | Naples | Italy | 3,084,890 | ||
| 3 | Barcelona | Spain | 5,575,204 | 13 | Warsaw | Poland | 3,053,104 | ||
| 4 | Berlin | Germany | 5,303,846 | 14 | Budapest | Hungary | 3,031,160 | ||
| 5 | Ruhr | Germany | 5,111,530 | 15 | Munich | Germany | 2,908,664 | ||
| 6 | Milan | Italy | 4,354,448 | 16 | Vienna | Austria | 2,853,903 | ||
| 7 | Rome | Italy | 4,342,212 | 17 | Lisbon | Portugal | 2,846,332 | ||
| 8 | Athens | Greece | 3,561,750 | 18 | Stuttgart | Germany | 2,787,724 | ||
| 9 | Hamburg | Germany | 3,327,940 | 19 | Frankfurt | Germany | 2,710,127 | ||
| 10 | Amsterdam | Netherlands | 3,242,852 | 20 | Katowice | Poland | 2,695,108 | ||
Languages
| Language | Native speakers[f][94] | Total[g][95] |
|---|---|---|
| German | 18% | 32% |
| French | 13% | 26% |
| Italian | 12% | 16% |
| Spanish | 8% | 15% |
| Polish | 8% | 9% |
| Romanian | 5% | 5% |
| Dutch | 4% | 5% |
| Greek | 3% | 4% |
| Hungarian | 3% | 3% |
| Portuguese | 2% | 3% |
| Czech | 2% | 3% |
| Swedish | 2% | 3% |
| Bulgarian | 2% | 2% |
| English | 1% | 51% |
| Slovak | 1% | 2% |
| Danish | 1% | 1% |
| Finnish | 1% | 1% |
| Lithuanian | 1% | 1% |
| Croatian | 1% | 1% |
| Slovene | <1% | <1% |
| Estonian | <1% | <1% |
| Irish | <1% | <1% |
| Latvian | <1% | <1% |
| Maltese | <1% | <1% |
The European Union has 24 official languages: Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hungarian, Italian, Irish, Latvian, Lithuanian, Maltese, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Slovak, Slovene, Spanish, and Swedish. Important documents, such as legislation, are translated into every official language and the European Parliament provides translation for documents and plenary sessions.[96][97]
Due to the high number of official languages, most of the institutions use only a handful of working languages. The European Commission conducts its internal business in three procedural languages: English, French, and German.[1] Similarly, the Court of Justice of the European Union uses French as the working language,[98] while the European Central Bank conducts its business primarily in English.[99][100]
Even though language policy is the responsibility of member states, EU institutions promote multilingualism among its citizens.[h][101] In 2012, English was the most widely spoken language in the EU, being understood by 51 per cent of the EU population when counting both native and non-native speakers. However, following the UK's exit from the block in early 2020 the percentage of the EU population who spoke English as their native language fell from 13 per cent to 1 per cent.[102] German is the most widely spoken mother tongue (18 per cent of the EU population), and the second most widely understood foreign language, followed by French (13 per cent of the EU population). In addition, both are official languages of several EU member states. More than half (56 per cent) of EU citizens are able to engage in a conversation in a language other than their mother tongue.[103]
A total of twenty official languages of the EU belong to the Indo-European language family, represented by the Balto-Slavic,[i] the Italic,[j] the Germanic,[k] the Hellenic,[l] and the Celtic[m] branches. Only four languages, namely Hungarian, Finnish, Estonian (all three Uralic), and Maltese (Semitic), are not Indo-European languages.[104] The three official alphabets of the European Union (Cyrillic, Latin, and modern Greek) all derive from the Archaic Greek scripts.[2][105]
Luxembourgish (in Luxembourg) and Turkish (in Cyprus) are the only two national languages that are not official languages of the EU. On 26 February 2016 it was made public that Cyprus has asked to make Turkish an official EU language, in a "gesture" that could help solve the division of the country.[106] Already in 2004, it was planned that Turkish would become an official language when Cyprus reunites.[107]
Besides the 24 official languages, there are about 150 regional and minority languages, spoken by up to 50 million people.[104] Catalan, Galician and Basque are not recognised official languages of the European Union but have official status in one member state (Spain): therefore, official translations of the treaties are made into them and citizens have the right to correspond with the institutions in these languages.[108][109] The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages ratified by most EU states provides general guidelines that states can follow to protect their linguistic heritage. The European Day of Languages is held annually on 26 September and is aimed at encouraging language learning across Europe.[110]
Religion
| Affiliation | per cent of EU population | |
|---|---|---|
| Christian | 71.6 | |
| Catholic | 45.3 | |
| Protestant | 11.1 | |
| Eastern Orthodox | 9.6 | |
| Other Christian | 5.6 | |
| Muslim | 1.8 | |
| Other faiths | 2.6 | |
| Irreligious | 24.0 | |
| Non-believer/Agnostic | 13.6 | |
| Atheist | 10.4 | |
The EU has no formal connection to any religion. Article 17 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union[111] recognises the "status under national law of churches and religious associations" as well as that of "philosophical and non-confessional organisations".[112]
The preamble to the Treaty on European Union mentions the "cultural, religious and humanist inheritance of Europe".[112] Discussion over the draft texts of the European Constitution and later the Treaty of Lisbon included proposals to mention Christianity or a god, or both, in the preamble of the text, but the idea faced opposition and was dropped.[113]
Christians in the European Union are divided among members of Catholicism (both Roman and Eastern Rite), numerous Protestant denominations (Anglicans, Lutherans, and Reformed forming the bulk of this category), and the Eastern Orthodox Church. In 2009, the EU had an estimated Muslim population of 13 million,[114] and an estimated Jewish population of over a million.[115] The other world religions of Buddhism, Hinduism, and Sikhism are also represented in the EU population.
According to new polls about religiosity in the European Union in 2015 by Eurobarometer, Christianity is the largest religion in the European Union, accounting for 71.6 per cent of the EU population. Catholics are the largest Christian group, accounting for 45.3 per cent of the EU population, while Protestants make up 11.1 per cent, Eastern Orthodox make up 9.6 per cent, and other Christians make up 5.6 per cent.[3]
Eurostat's Eurobarometer opinion polls showed in 2005 that 52 per cent of EU citizens believed in a god, 27 per cent in "some sort of spirit or life force", and 18 per cent had no form of belief.[116] Many countries have experienced falling church attendance and membership in recent years.[117] The countries where the fewest people reported a religious belief were Estonia (16 per cent) and the Czech Republic (19 per cent).[116] The most religious countries were Malta (95 per cent, predominantly Catholic) as well as Cyprus and Romania (both predominantly Orthodox) each with about 90 per cent of citizens professing a belief in their respective god. Across the EU, belief was higher among women, older people, those with religious upbringing, those who left school at 15 or 16, and those "positioning themselves on the right of the political scale".[116]
Member states

Through successive enlargements, the European Union has grown from the six founding states (Belgium, France, West Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands) to 27 members. Countries accede to the union by becoming party to the founding treaties, thereby subjecting themselves to the privileges and obligations of EU membership. This entails a partial delegation of sovereignty to the institutions in return for representation within those institutions, a practice often referred to as "pooling of sovereignty".[118][119]
To become a member, a country must meet the Copenhagen criteria, defined at the 1993 meeting of the European Council in Copenhagen. These require a stable democracy that respects human rights and the rule of law; a functioning market economy; and the acceptance of the obligations of membership, including EU law. Evaluation of a country's fulfilment of the criteria is the responsibility of the European Council.[120] Article 50 of the Lisbon Treaty provides the basis for a member to leave the EU. Two territories have left the union: Greenland (an autonomous province of Denmark) withdrew in 1985;[121] the United Kingdom formally invoked Article 50 of the Consolidated Treaty on European Union in 2017, and became the only sovereign state to leave when it withdrew from the EU in 2020.
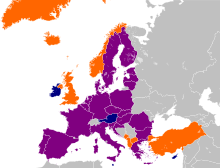
There are six countries that are recognised as candidates for membership: Albania, Iceland, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Turkey,[122] though Iceland suspended negotiations in 2013.[123] Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kosovo are officially recognised as potential candidates,[122] with Bosnia and Herzegovina having submitted a membership application. Georgia and Ukraine are preparing to formally apply for EU membership in 2024, in order to join the European Union in the 2030s.[124][125][126]
The four countries forming the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) are not EU members, but have partly committed to the EU's economy and regulations: Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway, which are a part of the single market through the European Economic Area, and Switzerland, which has similar ties through bilateral treaties.[127][128] The relationships of the European microstates, Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City include the use of the euro and other areas of co-operation.[129]
| State | Capital | Accession | Population (2019)[79] | Area | Population density | MEPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vienna | 1 January 1995 | 8,858,775 | 83,855 km2 (32,377 sq mi) |
106/km2 (270/sq mi) |
19 | |
| Brussels | Founder | 11,467,923 | 30,528 km2 (11,787 sq mi) |
376/km2 (970/sq mi) |
21 | |
| Sofia | 1 January 2007 | 7,000,039 | 110,994 km2 (42,855 sq mi) |
63/km2 (160/sq mi) |
17 | |
| Zagreb | 1 July 2013 | 4,076,246 | 56,594 km2 (21,851 sq mi) |
72/km2 (190/sq mi) |
12 | |
| Nicosia | 1 May 2004 | 875,898 | 9,251 km2 (3,572 sq mi) |
95/km2 (250/sq mi) |
6 | |
| Prague | 1 May 2004 | 10,649,800 | 78,866 km2 (30,450 sq mi) |
135/km2 (350/sq mi) |
21 | |
| Copenhagen | 1 January 1973 | 5,806,081 | 43,075 km2 (16,631 sq mi) |
135/km2 (350/sq mi) |
14 | |
| Tallinn | 1 May 2004 | 1,324,820 | 45,227 km2 (17,462 sq mi) |
29/km2 (75/sq mi) |
7 | |
| Helsinki | 1 January 1995 | 5,517,919 | 338,424 km2 (130,666 sq mi) |
16/km2 (41/sq mi) |
14 | |
| Paris | Founder | 67,028,048 | 640,679 km2 (247,368 sq mi) |
105/km2 (270/sq mi) |
79 | |
| Berlin | Founder[n] | 83,019,214 | 357,021 km2 (137,847 sq mi) |
233/km2 (600/sq mi) |
96 | |
| Athens | 1 January 1981 | 10,722,287 | 131,990 km2 (50,960 sq mi) |
81/km2 (210/sq mi) |
21 | |
| Budapest | 1 May 2004 | 9,797,561 | 93,030 km2 (35,920 sq mi) |
105/km2 (270/sq mi) |
21 | |
| Dublin | 1 January 1973 | 4,904,226 | 70,273 km2 (27,133 sq mi) |
70/km2 (180/sq mi) |
13 | |
| Rome | Founder | 60,359,546 | 301,338 km2 (116,347 sq mi) |
200/km2 (520/sq mi) |
76 | |
| Riga | 1 May 2004 | 1,919,968 | 64,589 km2 (24,938 sq mi) |
30/km2 (78/sq mi) |
8 | |
| Vilnius | 1 May 2004 | 2,794,184 | 65,200 km2 (25,200 sq mi) |
43/km2 (110/sq mi) |
11 | |
| Luxembourg City | Founder | 613,894 | 2,586 km2 (998 sq mi) |
237/km2 (610/sq mi) |
6 | |
| Valletta | 1 May 2004 | 493,559 | 316 km2 (122 sq mi) |
1,562/km2 (4,050/sq mi) |
6 | |
| Amsterdam | Founder | 17,282,163 | 41,543 km2 (16,040 sq mi) |
416/km2 (1,080/sq mi) |
29 | |
| Warsaw | 1 May 2004 | 37,972,812 | 312,685 km2 (120,728 sq mi) |
121/km2 (310/sq mi) |
52 | |
| Lisbon | 1 January 1986 | 10,276,617 | 92,390 km2 (35,670 sq mi) |
111/km2 (290/sq mi) |
21 | |
| Bucharest | 1 January 2007 | 19,401,658 | 238,391 km2 (92,043 sq mi) |
81/km2 (210/sq mi) |
33 | |
| Bratislava | 1 May 2004 | 5,450,421 | 49,035 km2 (18,933 sq mi) |
111/km2 (290/sq mi) |
14 | |
| Ljubljana | 1 May 2004 | 2,080,908 | 20,273 km2 (7,827 sq mi) |
103/km2 (270/sq mi) |
8 | |
| Madrid | 1 January 1986 | 46,934,632 | 504,030 km2 (194,610 sq mi) |
93/km2 (240/sq mi) |
59 | |
| Stockholm | 1 January 1995 | 10,230,185 | 449,964 km2 (173,732 sq mi) |
23/km2 (60/sq mi) |
21 | |
| 27 total | 446,834,579 | 4,233,262 km2 (1,634,472 sq mi) |
106/km2 (270/sq mi) |
705 | ||
Geography

The European Union's member states cover an area of 4,233,262 square kilometres (1,634,472 sq mi).[o] The EU's highest peak is Mont Blanc in the Graian Alps, 4,810.45 metres (15,782 ft) above sea level.[130] The lowest points in the EU are Lammefjorden, Denmark and Zuidplaspolder, Netherlands, at 7 m (23 ft) below sea level.[131] The landscape, climate, and economy of the EU are influenced by its coastline, which is 65,993 kilometres (41,006 mi) long.
Including the overseas territories of France which are located outside the continent of Europe, but which are members of the union, the EU experiences most types of climate from Arctic (north-east Europe) to tropical (French Guiana), rendering meteorological averages for the EU as a whole meaningless. The majority of the population lives in areas with a temperate maritime climate (North-Western Europe and Central Europe), a Mediterranean climate (Southern Europe), or a warm summer continental or hemiboreal climate (Northern Balkans and Central Europe).[132]
The EU's population is highly urbanised, with some 75 per cent of inhabitants living in urban areas as of 2006. Cities are largely spread out across the EU with a large grouping in and around the Benelux.[133]
Several overseas territories and dependencies of various member states are also formally part of the EU.[134]
Politics

The European Union operates through a hybrid system of supranational and intergovernmental decision-making,[135][136] and according to the principles of conferral (which says that it should act only within the limits of the competences conferred on it by the treaties) and of subsidiarity (which says that it should act only where an objective cannot be sufficiently achieved by the member states acting alone). Laws made by the EU institutions are passed in a variety of forms.[137] Generally speaking, they can be classified into two groups: those which come into force without the necessity for national implementation measures (regulations) and those which specifically require national implementation measures (directives).[138]
Constitutionally, the EU bears some resemblance to both a confederation and a federation,[139][140] but has not formally defined itself as either. (It does not have a formal constitution: its status is defined by the Treaty of European Union and the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union). It is more integrated than a traditional confederation of states because the general level of government widely employs qualified majority voting in some decision-making among the member states, rather than relying exclusively on unanimity.[141][142] It is less integrated than a federal state because it is not a state in its own right: sovereignty continues to flow 'from the bottom up', from the several peoples of the separate member states, rather than from a single undifferentiated whole. This is reflected in the fact that the member states remain the 'masters of the Treaties', retaining control over the allocation of competences to the union through constitutional change (thus retaining so-called Kompetenz-kompetenz); in that they retain control of the use of armed force; they retain control of taxation; and in that they retain a right of unilateral withdrawal under Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union. In addition, the principle of subsidiarity requires that only those matters that need to be determined collectively are so determined.
The European Union has seven principal decision-making bodies, its institutions: the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council of the European Union, the European Commission, the Court of Justice of the European Union, the European Central Bank and the European Court of Auditors. Competence in scrutinising and amending legislation is shared between the Council of the European Union and the European Parliament, while executive tasks are performed by the European Commission and in a limited capacity by the European Council (not to be confused with the aforementioned Council of the European Union). The monetary policy of the eurozone is determined by the European Central Bank. The interpretation and the application of EU law and the treaties are ensured by the Court of Justice of the European Union. The EU budget is scrutinised by the European Court of Auditors. There are also a number of ancillary bodies which advise the EU or operate in a specific area.
EU policy is in general promulgated by EU directives, which are then implemented in the domestic legislation of its member states, and EU regulations, which are immediately enforceable in all member states. Lobbying at EU level by special interest groups is regulated to try to balance the aspirations of private initiatives with public interest decision-making process.[143]


Institutions
| European Council | Council of the European Union | European Parliament | European Commission |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provides impetus and direction | Legislative | Legislative | Executive |
| Based in Brussels, |
Based in Brussels, |
Meets in Strasbourg, |
Based in Brussels, |
| Sets the general political directions and priorities of the Union by gathering together its member states' heads of state/government (elected chief executives). The conclusions of its summits (held at least quarterly) are adopted by consensus. | Brings together ministers of member states governments' departments. It serves to represent the various governments directly and its approval is required for any proposal to enter into law. | Consists of 705 directly elected representatives. It shares with the Council of the EU equal legislative powers to amend, approve or reject Commission proposals for most areas of EU legislation. Its powers are limited in areas where member states' view sovereignty to be of primary concern (i.e. defence). It elects the commission's president, must approve the College of Commissioners, and may vote to remove them collectively from office. | The only institution empowered to propose legislation, serves as the "Guardian of the Treaties". It consists of an executive cabinet of public officials, led by an indirectly elected President. This College of Commissioners manages and directs the commission's permanent civil service. It turns the consensus objectives of the European Council into legislative proposals. |
European Council

The European Council gives political direction to the EU. It convenes at least four times a year and comprises the president of the European Council (presently Charles Michel), the president of the European Commission and one representative per member state (either its head of state or head of government). The high representative of the union for foreign affairs and security policy (presently Josep Borrell) also takes part in its meetings. It has been described by some as the union's "supreme political authority".[144] It is actively involved in the negotiation of treaty changes and defines the EU's policy agenda and strategies.
The European Council uses its leadership role to sort out disputes between member states and the institutions, and to resolve political crises and disagreements over controversial issues and policies. It acts externally as a "collective head of state" and ratifies important documents (for example, international agreements and treaties).[145]
Tasks for the president of the European Council are ensuring the external representation of the EU,[146] driving consensus and resolving divergences among member states, both during meetings of the European Council and over the periods between them.
The European Council should not be mistaken for the Council of Europe, an international organisation independent of the EU based in Strasbourg.
European Commission

The European Commission acts both as the EU's executive arm, responsible for the day-to-day running of the EU, and also the legislative initiator, with the sole power to propose laws for debate.[147][148][149] The commission is 'guardian of the Treaties' and is responsible for their efficient operation and policing.[150] It operates de facto as a cabinet government,[citation needed] with 27 European commissioners for different areas of policy, one from each member state, though commissioners are bound to represent the interests of the EU as a whole rather than their home state.
One of the 27 is the president of the European Commission (presently Ursula von der Leyen for 2019–2024), appointed by the European Council, subject to the Parliament's approval. After the President, the most prominent commissioner is the high representative of the union for foreign affairs and security policy, who is ex-officio a vice-president of the European Commission and is also chosen by the European Council.[151] The other 26 commissioners are subsequently appointed by the Council of the European Union in agreement with the nominated president. The 27 commissioners as a single body are subject to approval (or otherwise) by vote of the European Parliament.
Council of the European Union
The Council of the European Union (also called the Council[152] and the "Council of Ministers", its former title)[153] forms one half of the EU's legislature. It consists of a representative from each member state's government and meets in different compositions depending on the policy area being addressed. Notwithstanding its different configurations, it is considered to be one single body. In addition to the legislative functions, members of the council also have executive responsibilities, such as the development of a Common Foreign and Security Policy and the coordination of broad economic policies within the Union.[154] The Presidency of the council rotates between member states, with each holding it for six months. Beginning on 1 July 2021, the position is held by Slovenia.[155]
In some policies, there are several member states that ally with strategic partners within the union. Examples of such alliances include the Visegrad Group, Benelux, the Baltic Assembly, the New Hanseatic League, the Weimar Triangle, the Lublin Triangle, EU Med Group, the Craiova Group and Bucharest Nine.
European Parliament

The European Parliament is one of three legislative institutions of the EU, which together with the Council of the European Union is tasked with amending and approving the European Commission's proposals. 705 members of the European Parliament (MEPs) are directly elected by EU citizens every five years on the basis of proportional representation. MEPs are elected on a national basis and they sit according to political groups rather than their nationality. Each country has a set number of seats and is divided into sub-national constituencies where this does not affect the proportional nature of the voting system.[156]
In the ordinary legislative procedure, the European Commission proposes legislation, which requires the joint approval of the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union to pass. This process applies to nearly all areas, including the EU budget. The parliament is the final body to approve or reject the proposed membership of the commission, and can attempt motions of censure on the commission by appeal to the Court of Justice. The president of the European Parliament (presently David Sassoli) carries out the role of speaker in Parliament and represents it externally. The president and vice-presidents are elected by MEPs every two and a half years.[157]
Budget

The European Union had an agreed budget of €120.7 billion for the year 2007 and €864.3 billion for the period 2007–2013,[159] representing 1.10 per cent and 1.05 per cent of the EU-27's GNI forecast for the respective periods. In 1960, the budget of the then European Economic Community was 0.03 per cent of GDP.[160]
In the 2010 budget of €141.5 billion, the largest single expenditure item is "cohesion & competitiveness" with around 45 per cent of the total budget.[161] Next comes "agriculture" with approximately 31 per cent of the total.[161] "Rural development, environment and fisheries" takes up around 11 per cent.[161] "Administration" accounts for around 6 per cent.[161] The "EU as a global partner" and "citizenship, freedom, security and justice" bring up the rear with approximately 6 per cent and 1 per cent respectively.[161]
The Court of Auditors is legally obliged to provide the parliament and the council (specifically, the Economic and Financial Affairs Council) with "a statement of assurance as to the reliability of the accounts and the legality and regularity of the underlying transactions".[162] The Court also gives opinions and proposals on financial legislation and anti-fraud actions.[163] The parliament uses this to decide whether to approve the commission's handling of the budget.
The European Court of Auditors has signed off the European Union accounts every year since 2007 and, while making it clear that the European Commission has more work to do, has highlighted that most of the errors take place at national level.[164][165] In their report on 2009 the auditors found that five areas of Union expenditure, agriculture and the cohesion fund, were materially affected by error.[166] The European Commission estimated in 2009 that the financial effect of irregularities was €1,863 million.[167]
In November 2020, members of the union, Hungary and Poland, blocked approval to the EU's budget at a meeting in the Committee of Permanent Representatives (Coreper), citing a proposal that linked funding with adherence to the rule of law. The budget included a COVID-19 recovery fund of €750 billion. The budget may still be approved if Hungary and Poland withdraw their vetos after further negotiations in the council and the European Council.[168][169]
Competences
Member states retain all powers not explicitly handed to the European Union. In some areas the EU enjoys exclusive competence. These are areas in which member states have renounced any capacity to enact legislation. In other areas the EU and its member states share the competence to legislate. While both can legislate, member states can only legislate to the extent to which the EU has not. In other policy areas the EU can only co-ordinate, support and supplement member state action but cannot enact legislation with the aim of harmonising national laws.[170]
That a particular policy area falls into a certain category of competence is not necessarily indicative of what legislative procedure is used for enacting legislation within that policy area. Different legislative procedures are used within the same category of competence, and even with the same policy area.
The distribution of competences in various policy areas between member states and the union is divided in the following three categories:
|
|
| |||||||||||
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
Legal system and justice
The European Union is based on a series of treaties. These first established the European Community and the EU, and then made amendments to those founding treaties.[172] These are power-giving treaties which set broad policy goals and establish institutions with the necessary legal powers to implement those goals. These legal powers include the ability to enact legislation[p] which can directly affect all member states and their inhabitants.[q] The EU has legal personality, with the right to sign agreements and international treaties.[173]
Under the principle of supremacy, national courts are required to enforce the treaties that their member states have ratified, and thus the laws enacted under them, even if doing so requires them to ignore conflicting national law, and (within limits) even constitutional provisions.[r]
The direct effect and supremacy doctrines were not explicitly set out in the European Treaties but were developed by the Court of Justice itself over the 1960s, apparently under the influence of its then most influential judge, Frenchman Robert Lecourt[174]
Court of Justice of the European Union

The judicial branch of the European Union is formally called the Court of Justice of the European Union and consists of two courts: the Court of Justice and the General Court.[175] The Court of Justice primarily deals with cases taken by member states, the institutions, and cases referred to it by the courts of member states.[176] Because of the doctrines of direct effect and supremacy, many judgments of the Court of Justice are automatically applicable within the internal legal orders of the member states.
The General Court mainly deals with cases taken by individuals and companies directly before the EU's courts,[177] and the European Union Civil Service Tribunal adjudicates in disputes between the European Union and its civil service.[178] Decisions from the General Court can be appealed to the Court of Justice but only on a point of law.[179]
Fundamental rights
The treaties declare that the European Union itself is "founded on the values of respect for human dignity, freedom, democracy, equality, the rule of law and respect for human rights, including the rights of persons belonging to minorities ... in a society in which pluralism, non-discrimination, tolerance, justice, solidarity and equality between women and men prevail."[180]
In 2009, the Lisbon Treaty gave legal effect to the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union. The charter is a codified catalogue of fundamental rights against which the EU's legal acts can be judged. It consolidates many rights which were previously recognised by the Court of Justice and derived from the "constitutional traditions common to the member states."[181] The Court of Justice has long recognised fundamental rights and has, on occasion, invalidated EU legislation based on its failure to adhere to those fundamental rights.[182]

Signing the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR) is a condition for EU membership.[s] Previously, the EU itself could not accede to the convention as it is neither a state[t] nor had the competence to accede.[u] The Lisbon Treaty and Protocol 14 to the ECHR have changed this: the former binds the EU to accede to the convention while the latter formally permits it.
The EU is independent from the Council of Europe, although they share purpose and ideas, especially on the rule of law, human rights and democracy. Furthermore, the European Convention on Human Rights and European Social Charter, as well as the source of law for the Charter of Fundamental Rights are created by the Council of Europe. The EU has also promoted human rights issues in the wider world. The EU opposes the death penalty and has proposed its worldwide abolition. Abolition of the death penalty is a condition for EU membership.[183]
On 19 October 2020, the European Union revealed new plans to create a legal structure to act against human rights violations worldwide. The new plan was expected to provide the European Union with greater flexibility to target and sanction those responsible for serious human rights violations and abuses around the world.[184]
Acts
The main legal acts of the European Union come in three forms: regulations, directives, and decisions. Regulations become law in all member states the moment they come into force, without the requirement for any implementing measures,[v] and automatically override conflicting domestic provisions.[p] Directives require member states to achieve a certain result while leaving them discretion as to how to achieve the result. The details of how they are to be implemented are left to member states.[w] When the time limit for implementing directives passes, they may, under certain conditions, have direct effect in national law against member states.
Decisions offer an alternative to the two above modes of legislation. They are legal acts which only apply to specified individuals, companies or a particular member state. They are most often used in competition law, or on rulings on State Aid, but are also frequently used for procedural or administrative matters within the institutions. Regulations, directives, and decisions are of equal legal value and apply without any formal hierarchy.[185]
European Ombudsman
The European Ombudsman was established by the Maastricht Treaty. The ombudsman is elected by the European Parliament for the length of the parliament's term, and the position is renewable.[186] Any EU citizen or entity may appeal to the ombudsman to investigate an EU institution on the grounds of maladministration (administrative irregularities, unfairness, discrimination, abuse of power, failure to reply, refusal of information or unnecessary delay).[187] Emily O'Reilly has been the ombudsman since 2013.[188]
Home affairs and migration
Since the creation of the European Union in 1993, it has developed its competencies in the area of justice and home affairs; initially at an intergovernmental level and later by supranationalism. Accordingly, the union has legislated in areas such as extradition,[189] family law,[190] asylum law,[191] and criminal justice.[192] Prohibitions against sexual and nationality discrimination have a long standing in the treaties.[x] In more recent years, these have been supplemented by powers to legislate against discrimination based on race, religion, disability, age, and sexual orientation.[y] By virtue of these powers, the EU has enacted legislation on sexual discrimination in the work-place, age discrimination, and racial discrimination.[z]
The EU has also established agencies to co-ordinate police, prosecutorial and immigrations controls across the member states: Europol for co-operation of police forces,[193] Eurojust for co-operation between prosecutors,[194] and Frontex for co-operation between border control authorities.[195] The EU also operates the Schengen Information System[14] which provides a common database for police and immigration authorities. This co-operation had to particularly be developed with the advent of open borders through the Schengen Agreement and the associated cross border crime.

The borders inside the Schengen Area between Germany and Austria

Europol Headquarters in The Hague, Netherlands

Eurojust Headquarters in The Hague, Netherlands

Seat of Frontex in Warsaw, Poland
Foreign relations


Foreign policy co-operation between member states dates from the establishment of the community in 1957, when member states negotiated as a bloc in international trade negotiations under the EU's common commercial policy.[196] Steps for a more wide-ranging co-ordination in foreign relations began in 1970 with the establishment of European Political Cooperation which created an informal consultation process between member states with the aim of forming common foreign policies. In 1987 the European Political Cooperation was introduced on a formal basis by the Single European Act. EPC was renamed as the Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) by the Maastricht Treaty.[197]
The aims of the CFSP are to promote both the EU's own interests and those of the international community as a whole, including the furtherance of international co-operation, respect for human rights, democracy, and the rule of law.[198] The CFSP requires unanimity among the member states on the appropriate policy to follow on any particular issue. The unanimity and difficult issues treated under the CFSP sometimes lead to disagreements, such as those which occurred over the war in Iraq.[199]

The coordinator and representative of the CFSP within the EU is the high representative of the union for foreign affairs and security policy who speaks on behalf of the EU in foreign policy and defence matters, and has the task of articulating the positions expressed by the member states on these fields of policy into a common alignment. The high representative heads up the European External Action Service (EEAS), a unique EU department[200] that has been officially implemented and operational since 1 December 2010 on the occasion of the first anniversary of the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon.[201] The EEAS will serve as a foreign ministry and diplomatic corps for the European Union.[202]
Besides the emerging international policy of the European Union, the international influence of the EU is also felt through enlargement. The perceived benefits of becoming a member of the EU act as an incentive for both political and economic reform in states wishing to fulfil the EU's accession criteria, and are considered an important factor contributing to the reform of European formerly Communist countries.[203]:762 This influence on the internal affairs of other countries is generally referred to as "soft power", as opposed to military "hard power".[204]
Switzerland was called to vote on whether to end the agreement with European Union on the free movement of people, in September 2020.[205] The demand of Swiss People's Party (SPP) was, however, turned down, as the voters rejected SPP's demand for taking back immigration control.[206]
Security and defence
The predecessors of the European Union were not devised as a military alliance because NATO was largely seen as appropriate and sufficient for defence purposes.[207] 21 EU members are members of NATO[208] while the remaining member states follow policies of neutrality.[209] The Western European Union, a military alliance with a mutual defence clause, was disbanded in 2010 as its role had been transferred to the EU.[210]
Since the withdrawal of the United Kingdom, France is the only member officially recognised as a nuclear weapon state and the sole holder of a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council. Possessing the EU's largest armed forces and the largest national defence budget of the bloc,[211] France is also the only EU country that has power projection capabilities outside of Europe.[212]
Most EU member states opposed the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty.[213]
Following the Kosovo War in 1999, the European Council agreed that "the Union must have the capacity for autonomous action, backed by credible military forces, the means to decide to use them, and the readiness to do so, in order to respond to international crises without prejudice to actions by NATO". To that end, a number of efforts were made to increase the EU's military capability, notably the Helsinki Headline Goal process. After much discussion, the most concrete result was the EU Battlegroups initiative, each of which is planned to be able to deploy quickly about 1500 personnel.[214]
EU forces have been deployed on peacekeeping missions from middle and northern Africa to the western Balkans and western Asia.[215] EU military operations are supported by a number of bodies, including the European Defence Agency, European Union Satellite Centre and the European Union Military Staff.[216] Frontex is an agency of the EU established to manage the cooperation between national border guards securing its external borders. It aims to detect and stop illegal immigration, human trafficking and terrorist infiltration. In 2015 the European Commission presented its proposal for a new European Border and Coast Guard Agency having a stronger role and mandate along with national authorities for border management. In an EU consisting of 27 members, substantial security and defence co-operation is increasingly relying on collaboration among all member states.[217]
Humanitarian aid
The European Commission's Humanitarian Aid and Civil Protection department, or "ECHO", provides humanitarian aid from the EU to developing countries. In 2012, its budget amounted to €874 million, 51 per cent of the budget went to Africa and 20 per cent to Asia, Latin America, the Caribbean and Pacific, and 20 per cent to the Middle East and Mediterranean.[218]
Humanitarian aid is financed directly by the budget (70 per cent) as part of the financial instruments for external action and also by the European Development Fund (30 per cent).[219] The EU's external action financing is divided into 'geographic' instruments and 'thematic' instruments.[219] The 'geographic' instruments provide aid through the Development Cooperation Instrument (DCI, €16.9 billion, 2007–2013), which must spend 95 per cent of its budget on official development assistance (ODA), and from the European Neighbourhood and Partnership Instrument (ENPI), which contains some relevant programmes.[219] The European Development Fund (EDF, €22.7 billion for the period 2008–2013 and €30.5 billion for the period 2014–2020) is made up of voluntary contributions by member states, but there is pressure to merge the EDF into the budget-financed instruments to encourage increased contributions to match the 0.7 per cent target and allow the European Parliament greater oversight.[219][220]
In 2016, the average among EU countries was 0.4 per cent and five had met or exceeded the 0.7 per cent target: Denmark, Germany, Luxembourg, Sweden and the United Kingdom.[221] If considered collectively, EU member states are the largest contributor of foreign aid in the world.[222][223]
International cooperation and development partnerships

The European Union uses foreign relations instruments like the European Neighbourhood Policy which seeks to tie those countries to the east and south of the European territory of the EU to the union. These countries, primarily developing countries, include some who seek to one day become either a member state of the European Union, or more closely integrated with the European Union. The EU offers financial assistance to countries within the European Neighbourhood, so long as they meet the strict conditions of government reform, economic reform and other issues surrounding positive transformation. This process is normally underpinned by an Action Plan, as agreed by both Brussels and the target country.

International recognition of sustainable development as a key element is growing steadily. Its role was recognized in three major UN summits on sustainable development: the 1992 UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD) in Johannesburg, South Africa; and the 2012 UN Conference on Sustainable Development (UNCSD) in Rio de Janeiro. Other key global agreements are the Paris Agreement and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (United Nations, 2015). The SDGs recognize that all countries must stimulate action in the following key areas – people, planet, prosperity, peace and partnership – in order to tackle the global challenges that are crucial for the survival of humanity.
EU development action is based on the European Consensus on Development, which was endorsed on 20 December 2005 by EU Member States, the council, the European Parliament and the commission.[224] It is applied from the principles of Capability approach and Rights-based approach to development.
Partnership and cooperation agreements are bilateral agreements with non-member nations.[225]
| Non-EU Member state | PCA Name | Date Signed | Agreement Supersedes (if any) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Armenia | EU-Armenia Comprehensive and Enhanced Partnership Agreement[226] | 2018 | EU-Armenia Partnership and Cooperation Agreement,[227] 1999 |
| Kyrgyz Republic | EU and Kyrgyz Republic Enhanced Partnership and Cooperation Agreement[228] | 2019 | – |
Trade
The European Union is the largest exporter in the world[229] and as of 2008 the largest importer of goods and services.[230][231] Internal trade between the member states is aided by the removal of barriers to trade such as tariffs and border controls. In the eurozone, trade is helped by not having any currency differences to deal with amongst most members.[232]
The European Union Association Agreement does something similar for a much larger range of countries, partly as a so-called soft approach ('a carrot instead of a stick') to influence the politics in those countries. The European Union represents all its members at the World Trade Organization (WTO), and acts on behalf of member states in any disputes. When the EU negotiates trade related agreement outside the WTO framework, the subsequent agreement must be approved by each individual EU member state government.[232]
The European Union has concluded free trade agreements (FTAs)[233] and other agreements with a trade component with many countries worldwide and is negotiating with many others.[234]
The European Union's services trade surplus rose from $16 billion in 2000 to more than $250 billion in 2018. [235]
In 2020, in part due to the COVID-19 pandemic, China became the EU's largest trading partner, displacing the United States.[236]
Economy
As a political entity the European Union is represented in the World Trade Organization (WTO). EU member states own the estimated second largest after the United States (US$105 trillion) net wealth in the world, equal to around 20 per cent (~€60 trillion) of the US$36 trillion (~€300 trillion)[237] global wealth.[238]
19 member states have joined a monetary union known as the eurozone, which uses the euro as a single currency. The currency union represents 342 million EU citizens.[239] The euro is the second largest reserve currency as well as the second most traded currency in the world after the United States dollar.[240][241][242]
Of the top 500 largest corporations in the world measured by revenue in 2010, 161 had their headquarters in the EU.[243] In 2016, unemployment in the EU stood at 8.9 per cent[244] while inflation was at 2.2 per cent, and the account balance at −0.9 per cent of GDP. The average annual net earnings in the European Union was around €24,000 (US$30,000)[245] in 2015.
There is a significant variation in nominal GDP per capita within individual EU states. The difference between the richest and poorest regions (281 NUTS-2 regions of the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics) ranged, in 2017, from 31 per cent (Severozapaden, Bulgaria) of the EU28 average (€30,000) to 253 per cent (Luxembourg), or from €4,600 to €92,600.[246]
Internal market
Two of the original core objectives of the European Economic Community were the development of a common market, subsequently becoming a single market, and a customs union between its member states. The single market involves the free circulation of goods, capital, people, and services within the EU,[239] and the customs union involves the application of a common external tariff on all goods entering the market. Once goods have been admitted into the market they cannot be subjected to customs duties, discriminatory taxes or import quotas, as they travel internally. The non-EU member states of Iceland, Norway, Liechtenstein and Switzerland participate in the single market but not in the customs union.[127] Half the trade in the EU is covered by legislation harmonised by the EU.[247]
Free movement of capital is intended to permit movement of investments such as property purchases and buying of shares between countries.[248] Until the drive towards economic and monetary union the development of the capital provisions had been slow. Post-Maastricht there has been a rapidly developing corpus of ECJ judgements regarding this initially neglected freedom. The free movement of capital is unique insofar as it is granted equally to non-member states.
The free movement of persons means that EU citizens can move freely between member states to live, work, study or retire in another country. This required the lowering of administrative formalities and recognition of professional qualifications of other states.[249]
The free movement of services and of establishment allows self-employed persons to move between member states to provide services on a temporary or permanent basis. While services account for 60 per cent to 70 per cent of GDP, legislation in the area is not as developed as in other areas. This lacuna has been addressed by the Services in the Internal Market Directive 2006 which aims to liberalise the cross border provision of services.[250] According to the treaty the provision of services is a residual freedom that only applies if no other freedom is being exercised.

A national identity card (German version pictured)

A European driving licence card (Croatian version pictured)
A European passport, displaying the name of the member state, the national arms and the words "European Union" given in their official language(s). (Irish version pictured)

A European vehicle registration plate, consisting of a blue strip on the left side with the EU flag symbol, along with the country code of the member state in which the vehicle is registered. (Slovak version pictured)
Monetary union and financial services
The creation of a European single currency became an official objective of the European Economic Community in 1969. In 1992, having negotiated the structure and procedures of a currency union, the member states signed the Maastricht Treaty and were legally bound to fulfil the agreed-on rules including the convergence criteria if they wanted to join the monetary union. The states wanting to participate had first to join the European Exchange Rate Mechanism.
In 1999, the currency union started, first as an accounting currency with eleven member states joining. In 2002, the currency was fully put into place, when euro notes and coins were issued and national currencies began to phase out in the eurozone, which by then consisted of 12 member states. The eurozone (constituted by the EU member states which have adopted the euro) has since grown to 19 countries.[251][aa]

The euro, and the monetary policies of those who have adopted it in agreement with the EU, are under the control of the European Central Bank (ECB).[252] The ECB is the central bank for the eurozone, and thus controls monetary policy in that area with an agenda to maintain price stability. It is at the centre of the European System of Central Banks, which comprehends all EU national central banks and is controlled by its General Council, consisting of the President of the ECB, who is appointed by the European Council, the Vice-President of the ECB, and the governors of the national central banks of all 27 EU member states.[253]
The European System of Financial Supervision is an institutional architecture of the EU's framework of financial supervision composed by three authorities: the European Banking Authority, the European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority and the European Securities and Markets Authority. To complement this framework, there is also a European Systemic Risk Board under the responsibility of the central bank. The aim of this financial control system is to ensure the economic stability of the EU.[254]
To prevent the joining states from getting into financial trouble or crisis after entering the monetary union, they were obliged in the Maastricht treaty to fulfil important financial obligations and procedures, especially to show budgetary discipline and a high degree of sustainable economic convergence, as well as to avoid excessive government deficits and limit the government debt to a sustainable level.
Industry and digital economy
The European Commission working sectors are: aeronautics, automotive, biotechnology, chemicals, construction, cosmetics, defense, electronics, firearms, food and drink, gambling, healthcare, maritime, mechanics, medical, postal, raw materials, space, textile, tourism, toys and social economy (Societas cooperativa Europaea).
Energy

In 2006, the EU-27 had a gross inland energy consumption of 1,825 million tonnes of oil equivalent (toe).[256] Around 46 per cent of the energy consumed was produced within the member states while 54 per cent was imported.[256] In these statistics, nuclear energy is treated as primary energy produced in the EU, regardless of the source of the uranium, of which less than 3 per cent is produced in the EU.[257]
The EU has had legislative power in the area of energy policy for most of its existence; this has its roots in the original European Coal and Steel Community. The introduction of a mandatory and comprehensive European energy policy was approved at the meeting of the European Council in October 2005, and the first draft policy was published in January 2007.[258]
The EU has five key points in its energy policy: increase competition in the internal market, encourage investment and boost interconnections between electricity grids; diversify energy resources with better systems to respond to a crisis; establish a new treaty framework for energy co-operation with Russia while improving relations with energy-rich states in Central Asia[259] and North Africa; use existing energy supplies more efficiently while increasing renewable energy commercialisation; and finally increase funding for new energy technologies.[258]
In 2007, EU countries as a whole imported 82 per cent of their oil, 57 per cent of their natural gas[260] and 97.48 per cent of their uranium[257] demands. The three largest suppliers of natural gas to the European Union are Russia, Norway and Algeria, that amounted for about three quarters of the imports in 2019.[261] There is a strong dependence on Russian energy that the EU has been attempting to reduce.[262]
Infrastructure

The European Union is working to improve cross-border infrastructure, for example through the Trans-European Networks (TEN). Projects under TEN include the Channel Tunnel, LGV Est, the Fréjus Rail Tunnel, the Öresund Bridge, the Brenner Base Tunnel and the Strait of Messina Bridge. In 2010 the estimated network covers: 75,200 kilometres (46,700 mi) of roads; 78,000 kilometres (48,000 mi) of railways; 330 airports; 270 maritime harbours; and 210 internal harbours.[263][264]
Rail transport in Europe is being synchronised with the European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS), an initiative to greatly enhance safety, increase efficiency of trains and enhance cross-border interoperability of rail transport in Europe by replacing signalling equipment with digitised mostly wireless versions and by creating a single Europe-wide standard for train control and command systems.
The developing European transport policies will increase the pressure on the environment in many regions by the increased transport network. In the pre-2004 EU members, the major problem in transport deals with congestion and pollution. After the recent enlargement, the new states that joined since 2004 added the problem of solving accessibility to the transport agenda.[265] The Polish road network was upgraded such as the A4 autostrada.[266]
Telecommunications and space

The Galileo positioning system is another EU infrastructure project. Galileo is a proposed Satellite navigation system, to be built by the EU and launched by the European Space Agency (ESA). The Galileo project was launched partly to reduce the EU's dependency on the US-operated Global Positioning System, but also to give more complete global coverage and allow for greater accuracy, given the aged nature of the GPS system.[267]
Agriculture and fisheries

The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) is one of the long lasting policies of the European Community.[268] The policy has the objectives of increasing agricultural production, providing certainty in food supplies, ensuring a high quality of life for farmers, stabilising markets, and ensuring reasonable prices for consumers.[ac] It was, until recently, operated by a system of subsidies and market intervention. Until the 1990s, the policy accounted for over 60 per cent of the then European Community's annual budget, and as of 2013 accounts for around 34 per cent.[269]
The policy's price controls and market interventions led to considerable overproduction. These were intervention stores of products bought up by the community to maintain minimum price levels. To dispose of surplus stores, they were often sold on the world market at prices considerably below Community guaranteed prices, or farmers were offered subsidies (amounting to the difference between the community and world prices) to export their products outside the community. This system has been criticised for under-cutting farmers outside Europe, especially those in the developing world.[270] Supporters of CAP argue that the economic support which it gives to farmers provides them with a reasonable standard of living.[270]
Since the beginning of the 1990s, the CAP has been subject to a series of reforms. Initially, these reforms included the introduction of set-aside in 1988, where a proportion of farm land was deliberately withdrawn from production, milk quotas and, more recently, the 'de-coupling' (or disassociation) of the money farmers receive from the EU and the amount they produce (by the Fischler reforms in 2004). Agriculture expenditure will move away from subsidy payments linked to specific produce, toward direct payments based on farm size. This is intended to allow the market to dictate production levels.[268] One of these reforms entailed the modification of the EU's sugar regime, which previously divided the sugar market between member states and certain African-Caribbean nations with a privileged relationship with the EU.[271]
Competition
The EU operates a competition policy intended to ensure undistorted competition within the single market.[ad]
The European commissioner for competition (presently Margrethe Vestager) is one of the most powerful positions in the commission, notable for the ability to affect the commercial interests of trans-national corporations.[citation needed] For example, in 2001 the commission for the first time prevented a merger between two companies based in the United States (General Electric and Honeywell) which had already been approved by their national authority.[272] Another high-profile case against Microsoft, resulted in the commission fining Microsoft over €777 million following nine years of legal action.[273]
Labour market
The EU seasonally adjusted unemployment rate was 6.7 per cent in September 2018.[274] The euro area unemployment rate was 8.1 per cent.[274] Among the member states, the lowest unemployment rates were recorded in the Czech Republic (2.3 per cent), Germany and Poland (both 3.4 per cent), and the highest in Spain (14.9 per cent) and Greece (19.0 in July 2018).[274]
Social policy and equality
| Nation | Social expenditure ( per cent of GDP) |
|---|---|
| 31.0 | |
| 29.1 | |
| 28.9 | |
| 28.3 | |
| 28.2 | |
| 26.9 | |
| 25.9 | |
| 25.5 | |
| 24.7 | |
| 24.0 | |
| 22.6 | |
| 21.6 | |
| 21.3 | |
| 21.1 | |
| 19.2 | |
| 18.1 | |
| 17.7 | |
| 17.7 | |
| 16.7 | |
| 16.4 | |
| 16.1 | |
| 13.4 |
The European Union has long sought to mitigate the effects of free markets by protecting workers rights and preventing social and environmental dumping. To this end it has adopted laws establishing minimum employment and environmental standards. These included the Working Time Directive and the Environmental Impact Assessment Directive.
The EU has also sought to coordinate the social security and health systems of member states to facilitate individuals exercising free movement rights and to ensure they maintain their ability to access social security and health services in other member states. Social security main legislation is found in the Equal Treatment in Occupational Social Security Directive 86/378, the Equal Treatment in Social Security Directive 79/7/EEC, the Social Security Regulation 1408/71/EC and 883/2004/EC and the Directive 2005/36/EC
The European Social Charter is the main body that recognizes the social rights of European citizens.
A European unemployment insurance has been proposed among others by the commissioner of Jobs Nicolas Schmit.[276] A European Directive about Minimum Wage has also been discussed[277]
Since 2019 there has been a European commissioner for equality and the European Institute for Gender Equality has existed since 2007.
In 2020, the first ever European Union Strategy on LGBTIQ equality was approved under Helena Dalli mandate.[278]
Housing, youth, childhood, Functional diversity or elderly care are supportive competencies of the European Union and can be financed by the European Social Fund.
Regional and local policy
Structural Funds and Cohesion Funds are supporting the development of underdeveloped regions of the EU. Such regions are primarily located in the states of central and southern Europe.[279][280] Several funds provide emergency aid, support for candidate members to transform their country to conform to the EU's standard (Phare, ISPA, and SAPARD), and support to the Commonwealth of Independent States (TACIS). TACIS has now become part of the worldwide EuropeAid programme.
Demographic transition to a society of aging population, low fertility-rates and depopulation of non-metropolitan regions is tackled within this policies.
Environment and climate

In 1957, when the European Economic Community was founded, it had no environmental policy.[281] Over the past 50 years, an increasingly dense network of legislation has been created, extending to all areas of environmental protection, including air pollution, water quality, waste management, nature conservation, and the control of chemicals, industrial hazards, and biotechnology.[281] According to the Institute for European Environmental Policy, environmental law comprises over 500 Directives, Regulations and Decisions, making environmental policy a core area of European politics.[282]
European policy-makers originally increased the EU's capacity to act on environmental issues by defining it as a trade problem.[281] Trade barriers and competitive distortions in the Common Market could emerge due to the different environmental standards in each member state.[283] In subsequent years, the environment became a formal policy area, with its own policy actors, principles and procedures. The legal basis for EU environmental policy was established with the introduction of the Single European Act in 1987.[282]
Initially, EU environmental policy focused on Europe. More recently, the EU has demonstrated leadership in global environmental governance, e.g. the role of the EU in securing the ratification and coming into force of the Kyoto Protocol despite opposition from the United States. This international dimension is reflected in the EU's Sixth Environmental Action Programme,[284] which recognises that its objectives can only be achieved if key international agreements are actively supported and properly implemented both at EU level and worldwide. The Lisbon Treaty further strengthened the leadership ambitions.[281] EU law has played a significant role in improving habitat and species protection in Europe, as well as contributing to improvements in air and water quality and waste management.[282]
Mitigating climate change is one of the top priorities of EU environmental policy. In 2007, member states agreed that, in the future, 20 per cent of the energy used across the EU must be renewable, and carbon dioxide emissions have to be lower in 2020 by at least 20 per cent compared to 1990 levels.[285] The EU has adopted an emissions trading system to incorporate carbon emissions into the economy.[286] The European Green Capital is an annual award given to cities that focuses on the environment, energy efficiency, and quality of life in urban areas to create smart city.
In the 2019 elections to the European Parliament, the green parties increased their power, possibly because of the rise of post materialist values.[287]
Proposals to reach a zero carbon economy in the European Union by 2050 were suggested in 2018 – 2019. Almost all member states supported that goal at an EU summit in June 2019. The Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, and Poland disagreed.[288]
In 2017, the EU emitted 9.1 per cent of global greenhouse-gas emissions.[289] The EU has a target of zero GHG emission by 2050.[290]
Education and research

Basic education is an area where the EU's role is limited to supporting national governments. In higher education, the policy was developed in the 1980s in programmes supporting exchanges and mobility. The most visible of these has been the Erasmus Programme, a university exchange programme which began in 1987. In its first 20 years, it supported international exchange opportunities for well over 1.5 million university and college students and became a symbol of European student life.[291]
There are similar programmes for school pupils and teachers, for trainees in vocational education and training, and for adult learners in the Lifelong Learning Programme 2007–2013. These programmes are designed to encourage a wider knowledge of other countries and to spread good practices in the education and training fields across the EU.[292][293] Through its support of the Bologna Process, the EU is supporting comparable standards and compatible degrees across Europe.
Scientific development is facilitated through the EU's Framework Programmes, the first of which started in 1984. The aims of EU policy in this area are to co-ordinate and stimulate research. The independent European Research Council allocates EU funds to European or national research projects.[294] EU research and technological framework programmes deal in a number of areas, for example energy where the aim is to develop a diverse mix of renewable energy to help the environment and to reduce dependence on imported fuels.[295]
Health care and food safety

The EU has no major competences in the field of health care and Article 35 of the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union affirms that "A high level of human health protection shall be ensured in the definition and implementation of all Union policies and activities". The European Commission's Directorate-General for Health and Consumers seeks to align national laws on the protection of people's health, on the consumers' rights, on the safety of food and other products.[296][297][298]
All EU and many other European countries offer their citizens a free European Health Insurance Card which, on a reciprocal basis, provides insurance for emergency medical treatment insurance when visiting other participating European countries.[299] A directive on cross-border healthcare aims at promoting co-operation on health care between member states and facilitating access to safe and high-quality cross-border healthcare for European patients.[300][301][302]
The EU has some of the highest levels of life expectancy in the world, with Spain, Italy, Sweden, France, Malta, Ireland, Netherlands, Luxembourg, and Greece all among the world's top 20 countries with the highest life expectancy.[303] In general, life expectancy is lower in Eastern Europe than in Western Europe.[304] In 2018, the EU region with the highest life expectancy was Madrid, Spain at 85.2 years, followed by the Spanish regions of La Rioja and Castilla y León both at 84.3 years, Trentino in Italy at 84.3 years and Île-de-France in France at 84.2 years. The overall life expectancy in the EU in 2018 was 81.0 years, higher than the World average of 72.6 years.[305]
Culture
Cultural co-operation between member states has been an interest of the European Union since its inclusion as a community competency in the Maastricht Treaty.[306] Actions taken in the cultural area by the EU include the Culture 2000 seven-year programme,[306] the European Cultural Month event,[307] and orchestras such as the European Union Youth Orchestra.[308] The European Capital of Culture programme selects one or more cities in every year to assist the cultural development of that city.[309]
Sport
Association football is by far the most popular sport in the European Union by the number of registered players. The other sports with the most participants in clubs are tennis, basketball, swimming, athletics, golf, gymnastics, equestrian sports, handball, volleyball and sailing.[310]
Sport is mainly the responsibility of the member states or other international organisations, rather than of the EU. There are some EU policies that have affected sport, such as the free movement of workers, which was at the core of the Bosman ruling that prohibited national football leagues from imposing quotas on foreign players with European citizenship.[311]
The Treaty of Lisbon requires any application of economic rules to take into account the specific nature of sport and its structures based on voluntary activity.[312] This followed lobbying by governing organisations such as the International Olympic Committee and FIFA, due to objections over the application of free market principles to sport, which led to an increasing gap between rich and poor clubs.[313] The EU does fund a programme for Israeli, Jordanian, Irish, and British football coaches, as part of the Football 4 Peace project.[314]
Symbols
The flag of Europe consists of a circle of 12 golden stars on a blue background. Originally designed in 1955 for the Council of Europe, the flag was adopted by the European Communities, the predecessors of the present European Union, in 1986. The Council of Europe gave the flag a symbolic description in the following terms,[315] though the official symbolic description adopted by the EU omits the reference to the "Western world":[316]
Against the blue sky of the Western world, the stars symbolise the peoples of Europe in a form of a circle, the sign of union. The number of stars is invariably twelve, the figure twelve being the symbol of perfection and entirety.
— Council of Europe. Paris, 7–9 December 1955.

United in Diversity was adopted as the motto of the union in 2000, having been selected from proposals submitted by school pupils.[317] Since 1985, the flag day of the union has been Europe Day, on 9 May (the date of the 1950 Schuman declaration). The anthem of the EU is an instrumental version of the prelude to the Ode to Joy, the 4th movement of Ludwig van Beethoven's ninth symphony. The anthem was adopted by European Community leaders in 1985 and has since been played on official occasions.[318] Besides naming the continent, the Greek mythological figure of Europa has frequently been employed as a personification of Europe. Known from the myth in which Zeus seduces her in the guise of a white bull, Europa has also been referred to in relation to the present union. Statues of Europa and the bull decorate several of the EU's institutions and a portrait of her is seen on the 2013 series of euro banknotes. The bull is, for its part, depicted on all residence permit cards.[319]
Charles the Great, also known as Charlemagne (Latin: Carolus Magnus) and later recognised as Pater Europae ("Father of Europe"),[320][321][322] has a symbolic relevance to Europe. The commission has named one of its central buildings in Brussels after Charlemagne and the city of Aachen has since 1949 awarded the Charlemagne Prize to champions of European unification.[323] Since 2008, the organisers of this prize, in conjunction with the European Parliament, have awarded the Charlemagne Youth Prize in recognition of similar efforts led by young people.[324]
Media

Media freedom is a fundamental right that applies to all member states of the European Union and its citizens, as defined in the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights as well as the European Convention on Human Rights.[325]:1 Within the EU enlargement process, guaranteeing media freedom is named a "key indicator of a country's readiness to become part of the EU".[326]
The majority of media in the European Union are national-oriented, although some EU-wide media focusing on European affairs have emerged since the early 1990s, such as Euronews, Eurosport, EUobserver, EURACTIV or Politico Europe.[327][328] ARTE is a public Franco-German TV network that promotes programming in the areas of culture and the arts. 80 per cent of its programming are provided in equal proportion by the two member companies, while the remainder is being provided by the European Economic Interest Grouping ARTE GEIE and the channel's European partners.[329]
The MEDIA Programme of the European Union has supported the European popular film and audiovisual industries since 1991. It provides support for the development, promotion and distribution of European works within Europe and beyond.[330]
Impact

The European Union has had a significant positive economic impact on most member states.[331] According to a 2019 study of the member states who joined from 1973 to 2004, "without European integration, per capita incomes would have been, on average, approximately 10 per cent lower in the first ten years after joining the EU."[331] Greece was the exception reported by the study, which analysed up to 2008, "to avoid confounding effects from the global financial crisis".[331]
The European Union has contributed to peace in Europe, in particular by pacifying border disputes,[332][333] and to the spread of democracy, especially by encouraging democratic reforms in aspiring Eastern European member states after the collapse of the USSR.[334][335] Scholar Thomas Risse wrote in 2009, "there is a consensus in the literature on Eastern Europe that the EU membership perspective had a huge anchoring effects for the new democracies."[335] However, R. Daniel Kelemen argues that the EU has proved beneficial to leaders who are overseeing democratic backsliding, as the EU is reluctant to intervene in domestic politics, gives authoritarian governments funds which they can use to strengthen their regimes, and because freedom of movement within the EU allows dissenting citizens to leave their backsliding countries. At the same time, the union provides an external constraint that prevents soft authoritarian regimes from progressing into hard dictatorships.[336]
See also
- Outline of the European Union
- Special member state territories and the European Union
- List of country groupings
- List of multilateral free-trade agreements
- Euroscepticism
- Pan-European nationalism
- Brexit withdrawal agreement
- European Union–United Kingdom free trade agreement
Notes
- ^ The 24 languages are equally official and accepted as working languages. Three of them – English, French and German – have the higher status of procedural languages and are used in the day-to-day workings of the European institutions.[1]
- ^ With the exception of the Canary Islands and Madeira, the outermost regions observe different time zones not shown: Martinique, Guadeloupe, Saint Martin (UTC−4); French Guiana (UTC−3); Azores (UTC−1 / UTC); Mayotte (UTC+3); and La Réunion (UTC+4); which, other than the Azores, do not observe DST.
- ^ .eu is representative of the whole of the EU; member states also have their own TLDs.
- ^ This figure is from February 2020, and takes account of the United Kingdom leaving the European Union. The population of the UK is roughly 0.9% of the world's population.[19]
- ^ The Frankish Empire has had a symbolic relevance for the building of Europe since the 20th century: Charlemagne is often regarded as the "Father of Europe" and a similarity between the borders of Charlemagne's Empire and that of the European Economic Community was made explicit during the 1965 Aachen exhibition sponsored by the Council of Europe.[25] Kikuchi Yoshio (菊池良生) of Meiji University suggested that the notion of Holy Roman Empire as a federal political entity influenced the later structural ideas of the European Union.[26]
- ^ Native language
- ^ EU citizens able to hold a conversation in this language
- ^ See Articles 165 and 166 (ex Articles 149 and 150) of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, on eur-lex.europa.eu
- ^ Slavic: Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Polish, Slovak and Slovene. Baltic: Latvian and Lithuanian.
- ^ French, Italian, Portuguese, Romanian and Spanish.
- ^ Danish, Dutch, English, German and Swedish.
- ^ Greek
- ^ Irish
- ^ On 3 October 1990, the constituent states of the former German Democratic Republic acceded to the Federal Republic of Germany, automatically becoming part of the EU.
- ^ This figure includes the extra-European territories of member states which are part of the European Union, and excludes the European territories of member states which are not part of the Union. For more information see Special member state territories and the European Union.
- ^ Jump up to: a b See Article 288 (ex Article 249 TEC) of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, on eur-lex.europa.eu
- ^ According to the principle of Direct Effect first invoked in the Court of Justice's decision in Van Gend en Loos v Nederlandse Administratie der Belastingen, Eur-Lex (European Court of Justice 1963). See: Craig and de Búrca, ch. 5.
- ^ According to the principle of Supremacy as established by the ECJ in Case 6/64, Falminio Costa v. ENEL [1964] ECR 585. See Craig and de Búrca, ch. 7. See also: Factortame litigation: Factortame Ltd. v. Secretary of State for Transport (No. 2) [1991] 1 AC 603, Solange II (Re Wuensche Handelsgesellschaft, BVerfG decision of 22 October 1986 [1987] 3 CMLR 225,265) and Frontini v. Ministero delle Finanze [1974] 2 CMLR 372; Raoul George Nicolo [1990] 1 CMLR 173.
- ^ and is effectively treated as one of the Copenhagen criteria.Assembly.coe.int. This is a political and not a legal requirement for membership. Archived 26 June 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The European Convention on Human Rights was previously only open to members of the Council of Europe (Article 59.1 of the Convention), and even now only states may become member of the Council of Europe (Article 4 of the Statute of the Council of Europe).
- ^ Opinion (2/92) of the European Court of Justice on "Accession by the Community to the European Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms" 1996 E.C.R. I-1759 (in French), ruled that the European Community did not have the competence to accede to the ECHR.
- ^ See: Case 34/73, Variola v. Amministrazione delle Finanze [1973] ECR 981.
- ^ To do otherwise would require the drafting of legislation which would have to cope with the frequently divergent legal systems and administrative systems of all of the now 28 member states. See Craig and de Búrca, p. 115
- ^ See Articles 157 (ex Article 141) of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, on eur-lex.europa.eu
- ^ See Article 2(7) of the Amsterdam Treaty on eur-lex.europa.eu Archived 17 February 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Council Directive 2000/43/EC of 29 June 2000 implementing the principle of equal treatment between persons irrespective of racial or ethnic origin (OJ L 180, 19 July 2000, pp. 22–26); Council Directive 2000/78/EC of 27 November 2000 establishing a general framework for equal treatment in employment and occupation (OJ L 303, 2 December 2000, pp. 16–22).
- ^ "ERM II". Danish Finance Ministry. 20 March 2009. Archived from the original on 3 May 2011. Retrieved 26 December 2009.
- ^ Almost all uranium is imported and nuclear power is considered primary energy produced in the EU.
- ^ Article 39 (ex Article 33) of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, on eur-lex.europa.eu
- ^ Article 3(1)(g) of the Treaty of Rome
References
Citations
- ^ Jump up to: a b "European Commission – Frequently asked questions on languages in Europe". europa.eu.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Leonard Orban (24 May 2007). "Cyrillic, the third official alphabet of the EU, was created by a truly multilingual European" (PDF). europe.eu. Retrieved 3 August 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "DISCRIMINATION IN THE EU IN 2015". Special Eurobarometer. 437. European Union: European Commission. 2015. Retrieved 15 October 2017 – via GESIS.
- ^ Current Article 1 of the Treaty on European Union reads: "The Union shall be founded on the present Treaty and on the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union. Those two Treaties shall have the same legal value. The Union shall replace and succeed the European Community".
- ^ [1]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2021 (EU countries)". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income – EU-SILC survey". ec.europa.eu. Eurostat. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ "Inequalities in Human Development in the 21st Century" (PDF). Human Development Report. p. 5.
- ^ "The EU in brief". European Union. 16 June 2016.
- ^ European Commission. "The EU Single Market: Fewer barriers, more opportunities". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 1 October 2007. Retrieved 27 September 2007.
"Activities of the European Union: Internal Market". Europa web portal. Retrieved 29 June 2007. - ^ "Common commercial policy". Europa Glossary. Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 16 January 2009. Retrieved 6 September 2008.
- ^ "Agriculture and Fisheries Council". The Council of the European Union. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ "Regional Policy Inforegio". Europa web portal. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Schengen area". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 10 August 2011. Retrieved 8 September 2010.
- ^ Phelan, William (2012). "What Is Sui Generis About the European Union? Costly International Cooperation in a Self-Contained Regime". International Studies Review. 14 (3): 367–385. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2486.2012.01136.x.
- ^ Hlavac, Marek (2010). "Less than a State, More than an International Organization: The Sui Generis Nature of the European Union" (PDF). Central European Labour Studies Institute. Rochester, N.Y. doi:10.2139/ssrn.1719308. S2CID 153480456.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Craig & De Burca 2011, p. 15.
- ^ Rawlinson, Kevin; Topping, Alexandra; Murphy, Simon; Henley, Jon; Murray, Jessica; Freedland, Jonathan; Rawlinson, Kevin (1 February 2020). "Brexit day: end of an era as United Kingdom leaves EU – as it happened-GB". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- ^ "European Union reaches 500 Million through Combination of Accessions, Migration and Natural Growth". Vienna Institute of Demography. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2021". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ "EU collects Nobel Peace Prize in Oslo". BBC News. 10 December 2012. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ McCormick 2007.
- ^ Rifkin, Jeremy (2004). The European Dream. Polity Press. ISBN 1-58542-345-9.
- ^ Moravcsik, Andrew (2009). "Europe: The quiet superpower". French Politics. 7 (3–4): 403–422. doi:10.1057/fp.2009.29. ISSN 1476-3419. S2CID 143049416.
- ^ Story, Joanna (2005). Charlemagne: Empire and Society. Manchester University Press. pp. 2–3. ISBN 978-0-7190-7089-1.
- ^ Kikuchi (菊池), Yoshio (良生) (2003). 神聖ローマ帝国. p. 264. ISBN 978-4-06-149673-6.
- ^ Corbet, Patrick (2002). "Renovatio imperii romanorum". In Vauchez, André (ed.). Oxford Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages. James Clarke & Co. ISBN 978-0-227-67931-9.
- ^ Schramm, Percy E. (1957). Kaiser, Rom und Renovatio; Studien zur Geschichte des römischen Erneuerungsgedankens vom Ende des karolingischen Reiches bis zum Investiturstreit (in German). Darmstadt: Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft. p. 143. OCLC 15021725.
- ^ Folz, Robert (1969). The concept of empire in Western Europe from the fifth to the fourteenth century. London: Edward Arnold. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-7131-5451-1. OCLC 59622.
- ^ Gorp, Bouke Van; Renes, Hans (2007). "A European Cultural Identity? Heritage and shared histories in the European Union" (PDF). Tijdschrift voor Economische en Sociale Geografie. 98 (3): 411. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9663.2007.00406.x. ISSN 1467-9663.
For the last two thousand years, the Christian church has attempted to unify Europe in cultural terms. Christianity did not originate in Europe but, building upon the organisation of the Roman Empire, has tried throughout the Middle Ages to become a Europe-wide organisation.
- ^ Pagden & Hamilton 2002, p. 89.
- ^ Mather 2006, pp. 16–18.
- ^ Nelsen, Brent F.; Guth, James L. (2015). Religion and the Struggle for European Union: Confessional Culture and the Limits of Integration. Georgetown University Press. pp. 48–49. ISBN 978-1-62616-070-5.
- ^ Perkins, Mary Anne (2004). Christendom and European Identity: The Legacy of a Grand Narrative Since 1789. Walter de Gruyter. p. 341. ISBN 978-3-11-018244-6.
- ^ Skolimowska, Anna (2018). Perceptions of the European Union's Identity in International Relations. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-351-00560-9.
- ^ Pagden & Hamilton 2002, pp. 60, 75.
- ^ Nelsen, Brent F.; Guth, James L. (2015). Religion and the Struggle for European Union: Confessional Culture and the Limits of Integration. Georgetown University Press. pp. 9–10. ISBN 978-1-62616-070-5.
- ^ Semenenko, Irina (2013). "The Quest for Identity. Russian Public Opinion on Europe and the European Union and the National Identity Agenda". Perspectives on European Politics and Society. 14 (1): 102–122. doi:10.1080/15705854.2012.732396. ISSN 1570-5854. S2CID 143894553.
- ^ Anderson & Bort 2001, pp. 1–2.
- ^ O'Brennan 2006, pp. 1–2.
- ^ Ghervas, Stella (2014). "Antidotes to Empire: From the Congress System to the European Union". In Boyer, John W.; Molden, Berthold (eds.). EUtROPEs. The Paradox of European Empire. University of Chicago Center in Paris. pp. 49–81. ISBN 978-2-9525962-6-8.
- ^ Pinterič, Uroš; Prijon, Lea (2013). European Union in 21st Century. University of SS. Cyril and Methodius, Faculty of Social Sciences. ISBN 978-80-8105-510-2.
- ^ Smith, Denis Mack (2008). Mazzini. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-17712-1.
- ^ Metzidakis, Angelo (1994). "Victor Hugo and the Idea of the United States of Europe". Nineteenth-Century French Studies. 23 (1/2): 72–84. JSTOR 23537320.
- ^ Kaiser & Varsori 2010, p. 140.
- ^ John Maynard Keynes, Economic Consequences of the Peace, New York: Harcourt, Brace & Howe, 1920, pp. 265–66.
- ^ Rosamond 2000, pp. 21–22.
- ^ Weigall & Stirk 1992, pp. 11–15.
- ^ Klos, Felix (2017). Churchill's Last Stand: The Struggle to Unite Europe. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 51. ISBN 978-1-78673-292-7.
- ^ Churchill, Winston (21 March 1943). "National Address". The International Churchill Society.
- ^ "The political consequences". CVCE. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ "Ein britischer Patriot für Europa: Winston Churchills Europa-Rede, Universität Zürich, 19. September 1946" [A British Patriot for Europe: Winston Churchill's Speech on Europe University of Zurich, 19 September 1946]. Zeit Online. Retrieved 13 January 2010.
- ^ Dieter Mahncke; Léonce Bekemans; Robert Picht, eds. (1999). The College of Europe. Fifty Years of Service to Europe. Bruges: College of Europe. ISBN 978-90-804983-1-0. Archived from the original on 28 December 2016.
- ^ "Declaration of 9 May 1950". European Commission. Retrieved 5 September 2007.
- ^ "Europe: How The Marshall Plan Took Western Europe From Ruins To Union". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "A peaceful Europe – the beginnings of cooperation". European Commission. Retrieved 12 December 2011.
- ^ "A European Atomic Energy Community". Cvce.eu. 13 October 1997. Retrieved 13 October 2013.
- ^ "A European Customs Union". cvce.eu. 2016.
- ^ "Merging the executives". CVCE – Centre Virtuel de la Connaissance sur l'Europe. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ "Merging the executives" CVCE.eu
- ^ "Discover the former Presidents: The Rey Commission", Europa (web portal). Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ "The first enlargement". CVCE. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ "The new European Parliament". CVCE. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ "Negotiations for enlargement". CVCE. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ "Schengen agreement". BBC News. 30 April 2001. Retrieved 18 September 2009.
- ^ "History of the flag". Europa web portal. Retrieved 13 March 2009.
- ^ "1980–1989 The changing face of Europe – the fall of the Berlin Wall". Europa web portal. Retrieved 25 June 2007.
- ^ "Treaty of Maastricht on European Union". Activities of the European Union. Europa web portal. Retrieved 20 October 2007.
- ^ Hunt, Michael H. (2014). The World Transformed, 1945 to the Present. New York: Oxford University press. pp. 516–517. ISBN 978-0-19-937103-7.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "A decade of further expansion". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 11 February 2007. Retrieved 25 June 2007.
- ^ Piris 2010, p. 448.
- ^ "European Parliament announces new President and Foreign Affairs Minister". Archived from the original on 15 May 2016. Retrieved 1 December 2009.
- ^ "The Nobel Peace Prize 2012". Nobelprize.org. 12 October 2012. Retrieved 12 October 2012.
- ^ "Nobel Committee Awards Peace Prize to E.U". New York Times. 12 October 2012. Retrieved 12 October 2012.
- ^ "Croatia: From isolation to EU membership". BBC News. BBC. 26 April 2013. Retrieved 14 May 2013.
- ^ "EU Referendum Result". BBC. Retrieved 26 June 2016.
- ^ Erlanger, Steven (23 June 2016). "Britain Votes to Leave E.U., Stunning the World". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 24 June 2016.
- ^ Landler, Mark; Castle, Stephen-US; Mueller, Benjamin (31 January 2020). "At the Stroke of Brexit, Britain Steps, Guardedly, Into a New Dawn". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Population on 1st January by age, sex and type of projection". Eurostat. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ^ "Share of world population, 1960, 2015 and 2060 (%)". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
- ^ "The World Factbook – Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Archived from the original on 11 December 2007. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
- ^ "Fertility statistics". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
- ^ "The World Factbook – Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 23 November 2017.
- ^ "6.5% of the EU population are foreigners and 9.4% are born abroad" Archived 12 August 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Eurostat, Katya VASILEVA, 34/2011.
- ^ "Acquisition of citizenship statistics". www.ec.europa.eu. Eurostat. March 2019. Retrieved 4 May 2019.
- ^ "Migration and migrant population statistics". Eurostat. March 2019.
- ^ "Migration and migrant population statistics" (PDF). Eurostat. March 2019.
- ^ "Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Paris (001)". INSEE. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Eurostat – Data Explorer". Eurostat. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ https://appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/nui/submitViewTableAction.do
- ^ "Population on 1 January by broad age group, sex and metropolitan regions - Eurostat". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- ^ Keating, Dave. "Despite Brexit, English Remains The EU's Most Spoken Language By Far". Forbes. Retrieved 7 February 2020.
- ^ "Europeans and Their Languages, 2012 Report" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 January 2016. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ European Commission (2012). "Europeans and their Languages" (PDF). Special Eurobarometer 386. europa.eu. pp. 54–59. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ^ European Commission (2012). "Europeans and their Languages" (PDF). Special Eurobarometer 386. europa.eu. pp. 78–83. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ^ EUR-Lex (12 December 2006). "Council Regulation (EC) No 1791/2006 of 20 November 2006". Official Journal of the European Union. Europa web portal. Retrieved 2 February 2007.
- ^ "Languages in Europe – Official EU Languages". EUROPA web portal. Archived from the original on 2 February 2009. Retrieved 12 October 2009.
- ^ Sharpston, Eleanor V.E. (29 March 2011). "Appendix 5: Written Evidence of Advocate General Sharpston". The Workload of the Court of Justice of the European Union. House of Lords European Union Committee. Retrieved 27 August 2013.
- ^ Buell, Todd (29 October 2014). "Translation Adds Complexity to European Central Bank's Supervisory Role: ECB Wants Communication in English, But EU Rules Allow Use of Any Official Language". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 11 October 2015.
- ^ Athanassiou, Phoebus (February 2006). "The Application of multilingualism in the European Union Context" (PDF). ECB. p. 26. Retrieved 11 October 2015.
- ^ European Parliament (2004). "European Parliament Fact Sheets: 4.16.3. Language policy". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 19 February 2007. Retrieved 3 February 2007.
- ^ Keating, Dave (6 February 2020). "Despite Brexit, English Remains The EU's Most Spoken Language By Far". Forbes. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ^ European Commission (2006). "Special Eurobarometer 243: Europeans and their Languages (Executive Summary)" (PDF). Europa web portal. p. 3. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
56% of citizens in the EU Member States are able to hold a conversation in one language apart from their mother tongue.
- ^ Jump up to: a b European Commission (2004). "Many tongues, one family. Languages in the European Union" (PDF). Europa web portal. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 March 2007. Retrieved 3 February 2007.
- ^ Coulmas, Florian (1996). The Blackwell Encyclopedia of Writing Systems. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers Ltd. ISBN 978-0-631-21481-6.
- ^ Rettman, Andrew (26 February 2016). "Cyprus asks to make Turkish an EU language". EU Observer. Retrieved 23 September 2020.
- ^ See article 8 in Proposal for an ACT OF ADAPTATION OF THE TERMS OF ACCESSION OF THE UNITED CYPRUS REPUBLIC TO THE EUROPEAN UNION
- ^ Klimczak-Pawlak, Agata (2014). Towards the Pragmatic Core of English for European Communication: The Speech Act of Apologising in Selected Euro-Englishes. Springer Science & Business. ISBN 978-3-319-03557-4.
- ^ "MEPs push for EU recognition of Catalan, Welsh languages". EURACTIV.com-GB. 8 March 2010. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
- ^ "Committee of Ministers – European Year of Languages Parliamentary Assembly Recommendation 1539". Wcd.coe.int. 2001. Retrieved 26 September 2012.
- ^ "Consolidated version of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union" – via Wikisource.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Consolidated version of the Treaty on European Union".
- ^ Castle, Stephen (21 March 2007). "EU celebrates 50th birthday-with a row about religion". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 5 April 2008. Retrieved 4 March 2008.
- ^ "Muslim Population" (PDF). europa web portal. Retrieved 1 November 2010.
- ^ Jewish population figures may be unreliable. Sergio DellaPergola. "World Jewish Population (2002)". American Jewish Year Book. The Jewish Agency for Israel. Archived from the original on 22 December 2004. Retrieved 3 May 2007.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Eurostat (2005). "Social values, Science and Technology" (PDF). Special Eurobarometer 225. Europa, web portal: 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 May 2006. Retrieved 11 June 2009.
- ^ Ford, Peter (22 February 2005). "What place for God in Europe". USA Today. Retrieved 24 July 2009.
- ^ "Answers – The Most Trusted Place for Answering Life's Questions". Answers.com. Archived from the original on 20 January 2016. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- ^ "EU institutions and other bodies". Europa. Archived from the original on 1 June 2009. Retrieved 4 September 2009.
- ^ "Accession criteria (Copenhagen criteria)". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 5 July 2007. Retrieved 26 June 2007.
- ^ "The Greenland Treaty of 1985". The European Union and Greenland. Greenland Home Rule Government. Archived from the original on 3 May 2011. Retrieved 10 November 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "European Commission – Enlargement – Candidate and Potential Candidate Countries". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 8 April 2012. Retrieved 13 March 2012.
- ^ Fox, Benjamin (16 June 2013). "Iceland's EU bid is over, commission told". Reuters. Retrieved 16 June 2013.
- ^ "У 2024 році Україна подасть заявку на вступ до ЄС". www.ukrinform.ua.
- ^ Makszimov, Vlagyiszlav (22 January 2021). "Georgian president visits Brussels in push for 2024 EU membership application". www.euractiv.com. Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- ^ "Georgia-EU Relations Within Georgia's 2024 Objective to Apply for the EU Membership". GeorgianJournal (in Georgian). Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b European Commission. "The European Economic Area (EEA)". Europa web portal. Retrieved 10 February 2010.
- ^ "The EU's relations with Switzerland". Europa web portal. Retrieved 3 November 2010.
- ^ European Commission. "Use of the euro in the world". The euro outside the euro area. Europa web portal. Retrieved 27 February 2008.
- ^ "Mont Blanc shrinks by 45 cm (17.72 in) in two years". Sydney Morning Herald. 6 November 2009. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ "The World Factbook". cia.gov. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- ^ "Humid Continental Climate". The physical environment. University of Wisconsin–Stevens Point. 2007. Archived from the original on 30 May 2007. Retrieved 29 June 2007.
- ^ "Urban sprawl in Europe: The ignored challenge, European Environmental Agency" (PDF). 2006. Retrieved 13 October 2013.
- ^ "Europe's overseas territories: What you need to know". Deutsche Welle. 3 November 2018.
- ^ "European Union". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 3 July 2013.
international organisation comprising 28 European countries and governing common economic, social, and security policies ...
- ^ "European Union". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- ^ According to P.C. Schmitter, Comparative Politics: Its Past, Present and Future (2016), 1 Chinese Political Science Review, 397, at 410, "European Union is the most complex polity in the world".
- ^ These legislative instruments are dealt with in more detail below.
- ^ Kiljunen, Kimmo (2004). The European Constitution in the Making. Centre for European Policy Studies. pp. 21–26. ISBN 978-92-9079-493-6.
- ^ Burgess, Michael (2000). Federalism and European union: The building of Europe, 1950–2000. Routledge. p. 49. ISBN 0-415-22647-3. "Our theoretical analysis suggests that the EC/EU is neither a federation nor a confederation in the classical sense. But it does claim that the European political and economic elites have shaped and moulded the EC/EU into a new form of international organization, namely, a species of "new" confederation."
- ^ "Qualified majority – Consilium". www.consilium.europa.eu. Retrieved 10 April 2019.
- ^ "Practical Law UK Signon". signon.thomsonreuters.com. Retrieved 10 April 2019.
- ^ "EU Library Briefing:Lobbying the EU institutions" (PDF). Europarl. Retrieved 3 March 2018.
- ^ "How does the EU work". Europa (web portal). Retrieved 12 July 2007.
- ^ With US or against US?: European trends in American perspective Parsons, Jabko. European Union Studies Association, p.146:
Fourth, the European Council acts a "collective head of state" for the EU. - ^ "President of the European Council" (PDF). General Secretariat of the Council of the EU. 24 November 2009. Retrieved 24 November 2009.
- ^ "Legislative powers". European Parliament. Retrieved 13 February 2019.
- ^ "Parliament's legislative initiative" (PDF). Library of the European Parliament. 24 October 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2019.
- ^ "Planning and proposing law". European Commission. 20 April 2019.
- ^ "Guardian of the Treaties". CVCE Education Unit. University of Luxembourg. Retrieved 8 June 2019.
- ^ Treaty on European Union: Article 17:7
- ^ The Latin word consilium is occasionally used when a single identifier is required, as on the Council Web site.
- ^ "Institutional affairs: Council of the European Union". Europa. European Commission. 6 January 2010.
It is commonly called the Council of Ministers
. - ^ "Institutions: The Council of the European Union". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 3 July 2007. Retrieved 25 June 2007.
- ^ "Presidency of the Council of the European Union". Slovenian Presidency of the Council of the European Union. Retrieved 6 July 2021.
- ^ Wellfire Interactive. "MEPs must be elected on the basis of proportional representation, the threshold must not exceed 5%, and the electoral area may be subdivided in constituencies if this will not generally affect the proportional nature of the voting system". Fairvote.org. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ "Institutions: The European Parliament". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 24 June 2007. Retrieved 25 June 2007.
- ^ "EU funding programmes 2014–2020". European Commission. Retrieved 2 January 2020.
- ^ "European Commission – PRESS RELEASES – Press release – Q&A on Interinstitutional Agreement on Budgetary Discipline and Sound Financial Management 2007–2013". europa.eu.
- ^ David Smith., David (1999). Will Europe work?. London: Profile Books. ISBN 978-1-86197-102-9.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e European Commission. "EU Budget in detail 2010". Europa web portal. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 August 2010. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- ^ Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, Section 7, Article 287."Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union". European Commission.
- ^ "Institutions: Court of Auditors". Europa (web portal). Archived from the original on 22 December 2009. Retrieved 8 February 2010.
- ^ "2012 annual report". Europa (web portal). Retrieved 13 November 2015.>
- ^ "European auditors point to errors but sign off EU's accounts – some UK media decline to listen to what the auditors say". Europa (web portal). Retrieved 13 November 2015.>
- ^ "Annual Report of the Court of Auditors on the implementation of the budget concerning the financial year 2009, together with the institutions' replies" (PDF). p. 12. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 February 2011. Retrieved 18 December 2010.
- ^ "Protection of the European Union's financial interests – Fight against fraud – Annual Report 2009 (vid. pp. 6, 15)" (PDF). Europa. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 July 2010.
- ^ "Hungary and Poland block EU coronavirus recovery package". Politico. 16 November 2020. Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- ^ "EU budget blocked by Hungary and Poland over rule of law issue". BBC News. 16 November 2020. Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- ^ "Competences and consumers". Retrieved 25 November 2010.
- ^ As outlined in Title I of Part I of the consolidated Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union
- ^ "Sources of EU law". European Commission. Archived from the original on 28 February 2008. Retrieved 5 September 2007.
- ^ de Schoutheete, Philippe; Andoura, Sami (2007). "The Legal Personality of the European Union" (PDF). Studia Diplomatica. LX (1). Retrieved 15 November 2010. Its examples are the ratifications of United Nations Convention against Corruption and Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities by EU. And Article 47 of the Consolidated Treaty on European Union.
- ^ William Phelan, Great Judgments of the European Court of Justice: Rethinking the Landmark Decisions of the Foundational Period (Cambridge, 2019).
- ^ "Article 19 of the Treaty on European Union". eur-lex.europa.eu. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- ^ "Court of Justice: presentation". Europa web portal. Retrieved 26 December 2009.
- ^ "General Court: presentation". Europa web portal. Retrieved 26 December 2009.
- ^ "Civil Service Tribunal: presentation". Europa web portal. Retrieved 26 December 2009.
- ^ Article 256(1) (ex article 225(1)) of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, on eur-lex.europa.eu
- ^ Article 2, Treaty on European Union (consolidated 1 December 2009)
- ^ Case 11/70, Internationale Handelsgesellschaft v. Einfuhr und Vorratstelle für Getreide und Futtermittel; Article 6(2) of the Maastricht Treaty (as amended).
- ^ "Respect for fundamental rights in the EU – general development". European Parliament Fact Sheets. The European Parliament. Retrieved 6 September 2008.
- ^ "EU Policy on Death Penalty". Europa. European Union External Action Service. Retrieved 4 June 2013.
- ^ "Europe Unveils New Sanctions Plan for Human Rights Violations". Bloomberg Tax. Retrieved 19 October 2020.
- ^ "How EU takes decisions". Archived from the original on 2 January 2011. Retrieved 1 November 2010.
- ^ "Emily O'Reilly re-elected European Ombudsman | News | European Parliament". www.europarl.europa.eu. 18 December 2019.
- ^ "European Ombudsman". www.ombudsman.europa.eu.
- ^ "European Ombudsman". www.ombudsman.europa.eu.
- ^ "European arrest warrant replaces extradition between EU Member States". Europa web portal. Retrieved 4 September 2007.
- ^ "Jurisdiction and the recognition and enforcement of judgments in matrimonial matters and in matters of parental responsibility (Brussels II)". Europa web portal. Retrieved 5 September 2008.
- ^ "Minimum standards on the reception of applicants for asylum in Member States". Europa web portal. Retrieved 5 September 2008.
- ^ "Specific Programme: 'Criminal Justice'". Europa web portal. Retrieved 5 September 2008.
- ^ "European police office now in full swing". Europa web portal. Retrieved 4 September 2007.
- ^ "Eurojust coordinating cross-border prosecutions at EU level". Europa web portal. Retrieved 4 September 2007.
- ^ Frontex. "What is Frontex?". Europa web portal. Retrieved 4 September 2007.
- ^ "Qualified-Majority Voting: Common commercial policy". Europa web portal. Retrieved 3 September 2007.
- ^ The European commission. "European political co-operation (EPC)". Europa Glossary. Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 8 July 2007. Retrieved 3 September 2007.
- ^ Article 21 of the Treaty on European Union (as inserted by the Treaty of Lisbon), on eur-lex.europa.eu
- ^ "Divided EU agrees Iraq statement". BBC News. BBC. 27 January 2003. Retrieved 13 March 2009.
- ^ Rettman, Andrew (23 October 2009) EU states envisage new foreign policy giant, EU Observer
- ^ "European External Action Service gives Europe voice on world stage". German Foreign Ministry. 1 December 2010. Retrieved 4 June 2013.
- ^ "European External Action Service". Europa web portal. 2010. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- ^ Peterson, John (August 2008). "Enlargement, reform and the European Commission. Weathering a perfect storm?". Journal of European Public Policy. 15 (5): 761–780. doi:10.1080/13501760802133328. S2CID 154664296.
- ^ Bildt, Carl (2005). "Europe must keep its 'soft power'". Financial Times on Centre for European Reform. Archived from the original on 9 June 2007. Retrieved 26 June 2007.
- ^ "Swiss to vote on whether to end free movement deal with EU". The Guardian. 25 September 2020. Retrieved 25 September 2020.
- ^ Chazan, David (27 September 2020). "Large majority of Swiss reject bid to rein in immigration from EU, says exit poll". The Telegraph. Retrieved 27 September 2020.
- ^ Wilkinson 2007, p. 100.
- ^ "NATO Member Countries". Retrieved 25 August 2009.
- ^ Laursen, Finn (1 June 1997). "The EU 'neutrals,' the CFSP and defence policy". Biennial Conference of the European Union Studies Association. Seattle, WA: University of Pittsburgh. p. 27. Retrieved 24 July 2009.
- ^ "Statement of the Presidency of the Permanent Council of the WEU" – on behalf of the High Contracting Parties to the Modified Brussels Treaty – Belgium, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain and the United Kingdom – Western European Union 31 March 2010.
- ^ The French Defence budget is higher than that of Germany, Italy, or the UK (which left the EU in early 2020), see Military spending saw biggest increase in a decade in 2019, Euractiv, 27 April 2020
- ^ Post-Brexit EU Defence Policy: Is Germany Leading towards a European Army?, e-International Relations, 5 July 2020
- ^ "Treaty on the prohibition of nuclear weapons ─ the 'Ban Treaty'". European Parliament. 17 January 2018.
- ^ Council of the European Union (July 2009). "EU battlegroups" (PDF). Europa web portal. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ Council of the European Union (April 2003). "Overview of the missions and operations of the European Union". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 2 December 2011. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ Council of the European Union. "CSDP structures and instruments". Europa web portal. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ "The Russo-Georgian War and Beyond: towards a European Great Power Concert, Danish Institute of International Studies". Diis.dk. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- ^ "ECHO's finances". ec.europa.eu. Humanitarian Aid and Civil Protection, European Commission. Archived from the original on 18 July 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Mikaela Gavas 2010. Financing European development cooperation: the Financial Perspectives 2014–2020. Archived 16 March 2011 at the Wayback Machine London: Overseas Development Institute
- ^ "[2]." ec.europa.eu. Retrieved on 9 December 2018. "ACP – Main funding programmes."
- ^ "Development aid rises again in 2016" (PDF). OECD. 11 April 2017. Retrieved 23 December 2017.
- ^ GHA (22 February 2015). "GHA report 2014". globalhumanitarianassistance.org.
- ^ OECD (4 August 2013). "Aid to developing countries (2013)". OECD.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 27 August 2011.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Partnership and cooperation agreement (PCA) – EU monitor". www.eumonitor.eu.
- ^ "EUR-Lex – 22018A0126(01) – EN – EUR-Lex". eur-lex.europa.eu.
- ^ "EU-Armenia Partnership and Cooperation Agreement" (PDF). EU External Services. European Commission.
- ^ "EU and Kyrgyz Republic initial Enhanced Partnership and Cooperation Agreement". European Commission.
- ^ "Central Intelligence Agency". Cia.gov. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "World trade report 2009" (PDF). WTO information website.
- ^ "EU position in world trade". European Commission. Retrieved 24 May 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Se-jeong, Kim (19 July 2009). "EU-Korea FTA Will Be a Long Process: Greek Ambassador". The Korea Times. Retrieved 15 August 2009.
- ^ "Free trade agreements". European Commission. 15 April 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2018.
- ^ "Agreements". European Commission. Retrieved 17 March 2016.
- ^ "The European Union and its trade partners | Fact Sheets on the European Union | European Parliament". www.europarl.europa.eu. Retrieved 7 June 2021.
- ^ Wong, Audrye (May 2021). "How Not to Win Allies and Influence Geopolitics China's Self-Defeating Economic Statecraft". Foreign Affairs. 100 (3).
- ^ "3.17E+14 USD to EUR | Convert US Dollars to Euros | XE". www.xe.com.
- ^ "Global Wealth Report 2019" (PDF). Credit Suisse. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 October 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The Single Market". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 1 October 2007. Retrieved 27 June 2007.
- ^ "Triennial Central Bank Survey 2007" (PDF). BIS. 19 December 2007. Retrieved 25 July 2009.
- ^ Aristovnik, Aleksander; Čeč, Tanja (30 March 2010). "Compositional Analysis of Foreign Currency Reserves in the 1999–2007 Period. The Euro vs. The Dollar As Leading Reserve Currency" (PDF). Munich Personal RePEc Archive, Paper No. 14350. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ Boesler, Matthew (11 November 2013). "There Are Only Two Real Threats To The US Dollar's Status As The International Reserve Currency". Business Insider. Retrieved 8 December 2013.
- ^ "Global 500 2010: Countries – Australia". Fortune. Retrieved 8 July 2010. Number of companies data taken from the "Pick a country" box.
- ^ "Euro area unemployment rate at 10.3%, EU28 at 8.9%" (PDF). Europa web portal. 1 March 2016. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- ^ "Database – Eurostat". ec.europa.eu.
- ^ "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 31% to 626% of the EU average in 2017". ec.europa.eu.
- ^ European Commission. "A Single Market for goods". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 21 June 2007. Retrieved 27 June 2007.
- ^ European Commission. "A Single Market for Capital". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 18 May 2007. Retrieved 27 June 2007.
- ^ European Commission. "Living and working in the Single Market". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 27 June 2007.
- ^ European Commission. "A Single Market for Services". Europa. Archived from the original on 10 June 2007. Retrieved 27 June 2007.
- ^ Kuchler, Teresa (25 October 2006). "Almunia says 'undesirable' to act on Sweden's euro refusal". EUobserver.com. Retrieved 26 December 2006.
- ^ "ECB, ESCB and the Eurosystem". European Central Bank. Retrieved 15 September 2007.
- ^ "ECB, ESCB and the Eurosystem". European Central Bank. Retrieved 7 July 2011.
- ^ "Europe seals deal on financial supervision". euobserver.com.
- ^ "The European Power Sector in 2020 / Up-to-Date Analysis on the Electricity Transition" (PDF). ember-climate.org. Ember and Agora Energiewende. 25 January 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 January 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Energy consumption and production: EU27 energy dependence rate at 54% in 2006: Energy consumption stable" (PDF) (Press release). Eurostat. 10 July 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 September 2008. Retrieved 12 September 2008.
In the EU27, gross inland energy consumption was 1 825 million tonnes of oil equivalent (toe) in 2006, stable compared with 2005, while energy production decreased by 2.3% to 871 mn toe ...
Gross inland consumption is defined as primary production plus imports, recovered products and stock change, less exports and fuel supply to maritime bunkers (for seagoing ships of all flags) ...
A tonne of oil equivalent (toe) is a standardised unit defined on the basis of one tonne of oil having a net calorific value of 41.868 Gigajoules. - ^ Jump up to: a b "EU supply and demand for nuclear fuels" (PDF). Euratom Supply Agency – Annual Report 2007. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities. 2008. p. 22. ISBN 978-92-79-09437-8. Retrieved 1 March 2009.
European uranium mining supplied just below 3% of the total EU needs, coming from the Czech Republic and Romania (a total of 526 tU).
Nuclear energy and renewable energy are treated differently from oil, gas, and coal in this respect. - ^ Jump up to: a b "Q&A: EU energy plans". BBC. 9 March 2007. Retrieved 13 July 2007.
- ^ Shamil Midkhatovich Yenikeyeff (November 2008). "Kazakhstan's Gas: Export Markets and Export Routes" (PDF). Oxford Institute for Energy Studies. Retrieved 17 November 2011.
- ^ "'Low-carbon economy' proposed for Europe". NBC News. 10 January 2007. Retrieved 24 January 2007.
- ^ Abnett, Kate; Nasralla, Shadia (17 July 2020). "EU's greenhouse gas strategy fails to plug methane hole". Reuters.
- ^ European Parliament. "Ukraine-Russia gas dispute – call for stronger EU energy policy". Europa web portal. Retrieved 27 February 2008.
- ^ "The trans-European transport network: new guidelines and financial rules" (PDF). Europa web portal. European Commission. 1 October 2003. Retrieved 15 August 2007.
- ^ Mirea, Silvia. "The trans-European transport network: new guidelines and financial rules". The Railway Journal. Archived from the original on 23 April 2007. Retrieved 15 August 2007.
- ^ "White Paper on Transport". Euractiv. 22 September 2004. Retrieved 15 August 2007.
- ^ "EUR 650 million for the Polish Road Network". Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2010.
- ^ Barrot, Jacques. "Jacques Barrot Home Page, Commission vice president for transport". Europa web portal. Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Stead, David (22 June 2007). Robert Whaples (ed.). "Common Agricultural Policy". EH.Net Encyclopedia. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
- ^ "Agriculture: Meeting the needs of farmers and consumers". Europa: Gateway to the European Union. European Commission. 26 August 2011. Archived from the original on 29 November 2011. Retrieved 4 November 2011.
the common agricultural policy is the most integrated of all EU policies and consequently takes a large share of the EU budget. Nevertheless, its portion of the EU budget has dropped from a peak of nearly 70% in the 1970s to 34% over the 2007–2013 period.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Jeffery, Simon (26 June 2003). "The EU common agricultural policy". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
- ^ "Sugar: Commission proposes more market-, consumer- and trade-friendly regime". Europa. 14 April 2007. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
- ^ "The Commission prohibits GE's acquisition of Honeywell". Europa web portal. 3 July 2001. Retrieved 12 November 2007.
- ^ Gow, David (22 October 2007). "Microsoft caves in to European Commission". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 12 November 2007.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Eurostat – Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". ec.europa.eu.
- ^ "Social spending data". OECD.
- ^ "Así es el seguro europeo contra el paro que propone el futuro comisario de Empleo de la UE – elEconomista.es". www.eleconomista.es.
- ^ Johnston, Raymond (3 December 2020). "Proposed EU directive on minimum wage brews controversy from all sides". Expats.cz.
- ^ "Union of Equality: The Commission presents its first-ever strategy on LGBTIQ equality in the EU". European Commission. 12 November 2020.
- ^ Select Committee on European Union (2008). "Chapter 2: The European Union Structural and Cohesion Funds". Nineteenth Report. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ "EU Structural and Cohesion funds". Archived from the original on 29 May 2010. Retrieved 1 November 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Jordan & Adelle 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Institute for European Environmental Policy (2012) Manual of European Environmental Policy, Earthscan, London.
- ^ Johnson, S.P. and Corcelle, G. (1989) The Environmental Policy of the European Communities, Graham & Trotman, London
- ^ "EUR-Lex – l28027 – EN – EUR-Lex". eur-lex.europa.eu.
- ^ Aldred, Jessica (23 January 2008). "EU sets 20% target for carbon cuts". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 29 February 2008.
- ^ "EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS)". Climate Action – European Commission. 23 November 2016.
- ^ Berman, Sheri (3 June 2019). "Populists, greens and the new map of European politics". Social Europe. Retrieved 21 June 2019.
- ^ "EU summit deadlock over top jobs and climate discord". 21 June 2019.
- ^ "Global Emissions". Center for Climate and Energy Solutions. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ "2050 long-term strategy". European Commission website. European Union. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ European Commission. "The Erasmus programme celebrates its 20th anniversary". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 3 July 2007. Retrieved 21 July 2007.; Jean-Sébastien, Lefebvre (22 January 2007). "Erasmus turns 20 – time to grow up?". Café Babel. Archived from the original on 12 September 2010. Retrieved 10 August 2007.
- ^ EACEA. "About the Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 29 April 2015. Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ European Commission. "Lifelong Learning Programme". Europa web portal. Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ European Research Council. "What is the ERC?". Europa web portal. Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ European Commission. "Energy". Europa web portal. Retrieved 12 November 2007.
- ^ "Europa web portal". Europa (web portal). Archived from the original on 12 November 2010. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ "Europa web portal". Europa (web portal). Archived from the original on 11 November 2010. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ "Europa web portal". Europa (web portal). 18 November 2010. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ "info about health care and EHIC". Nhs.uk. 29 April 2010. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ "Consilium.europa.eu" (PDF). Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ "Eur-lex.europa.eu". Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ "NHSconfed.org". NHSconfed.org. 17 May 2011. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ "2019 Human Development Index Ranking | Human Development Reports". hdr.undp.org. Archived from the original on 30 April 2020. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- ^ "In Europe, life expectancy is lower in the east". The Economist.
- ^ "Life expectancy: Are you in one of the top 5 regions?". ec.europa.eu.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bozoki, Andras. "Cultural Policy and Politics in the European Union" (PDF). Cultural Policy and Politics in the European Union.pdf. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 February 2013. Retrieved 4 June 2013.
- ^ European Commission. "European Culture Month". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 2 February 2008. Retrieved 27 February 2008.
- ^ "An Overture to the European Union Youth Orchestra". The European Youth Orchestra. Archived from the original on 11 June 2007. Retrieved 12 August 2007.
- ^ European Commission. "European Capitals of Culture". Europa web portal. Archived from the original on 3 August 2010.
- ^ M. van Bottenburg; B. Rijnen; J.C. van Sterkenburg (2005). "Sports participation in the European Union : Trends and differences". WJH Mulier Instituut. dspace.library.uu.nl: 33 (table 2.5). hdl:1874/305728.
- ^ Fordyce, Tom (11 July 2007). "10 years since Bosman". BBC News. Retrieved 13 July 2007.
- ^ Cases C-403/08 and C-429/08, Opinion of Advocate General Kokott, para 207
- ^ "IOC, FIFA presidents welcomes new EU treaty, call it breakthrough to give sports more power". International Herald Tribune. 19 October 2007. Archived from the original on 1 December 2008. Retrieved 21 October 2007.
- ^ "Sports coaches from Israel travel to UK for training". Eeas.europa.eu. 29 March 2011. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ "Thirty-sixth meeting of the ministers' deputies: resolution (55) 32" (PDF). Council of Europe. 9 December 1955. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 May 2009. Retrieved 2 February 2008.
- ^ (in French) Guide graphique relatif à l'emblème européen (1996), p. 3: Description symbolique: Sur le fond bleu du ciel, les étoiles figurant les peuples d'Europe forment un cercle en signe d'union. Elles sont au nombre invariable de douze, symbole de la perfection et de la plénitude...Description héraldique: Sur fond azur, un cercle composé de douze étoiles d'or à cinq rais, dont les pointes ne se touchent pas. c.f. "Graphical specifications for the European Emblem". European Commission. Archived from the original on 22 June 2006. Retrieved 4 August 2004.
- ^ Simons 2002, p. 110.
- ^ "Council of Europe". www.coe.int. Archived from the original on 19 December 2009.
- ^ Demey 2007, p. 387.
- ^ Riché, Preface xviii, Pierre Riché reflects: "[H]e enjoyed an exceptional destiny, and by the length of his reign, by his conquests, legislation and legendary stature, he also profoundly marked the history of Western Europe."
- ^ "Der Karlspreisträger Seine Heiligkeit Papst Johannes Paul II. außerordentlicher Karlspreis 2004". Karlspreis.de. Archived from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 1 January 2012.
- ^ Chamberlin, Russell (2004). The Emperor Charlemagne. Stroud, Gloucestershire: The History Press. ISBN 978-0-7509-3482-4.
- ^ "Laureates". karlspreis.de. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- ^ "Winners 2015". charlemagneyouthprize.eu. Archived from the original on 12 December 2015. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- ^ Maria Poptcheva, Press freedom in the EU Legal framework and challenges, EPRS | European Parliamentary Research Service, Briefing April 2015
- ^ "European Neighbourhood Policy and Enlargement Negotiations". European Commission. Archived from the original on 24 January 2016. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
- ^ Mollin, Sandra (2006). Euro-English : assessing variety status. Tübingen: Gunter Narr Verlag. p. 56. ISBN 978-3-8233-6250-0. OCLC 804963256.
- ^ "2018 EU Media Survey" (PDF). ComRes/Burson-Marsteller. 2018.
- ^ "How is ARTE funded?". ARTE Entreprise. Retrieved 26 June 2016.
- ^ "Media Programme". Europa. European Commission. Archived from the original on 21 June 2013. Retrieved 13 June 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Campos, Nauro F.; Coricelli, Fabrizio; Moretti, Luigi (1 May 2019). "Institutional integration and economic growth in Europe". Journal of Monetary Economics. 103: 88–104. doi:10.1016/j.jmoneco.2018.08.001. ISSN 0304-3932.
- ^ Diez, Thomas; Stetter, Stephan; Albert, Mathias (July 2006). "The European Union and Border Conflicts: The Transformative Power of Integration". International Organization. 60 (3): 563–593. doi:10.1017/S0020818306060218. ISSN 1531-5088. S2CID 102491575.
- ^ Diez, Thomas; Albert, Mathias; Stetter, Stephan, eds. (2008). The European Union and Border Conflicts: The Power of Integration and Association. Cambridge Core. doi:10.1017/cbo9780511491337. ISBN 978-0-511-49133-7. Retrieved 19 December 2019.
- ^ Poast, Paul; Chinchilla, Alexandra (2020). "Good for democracy? Evidence from the 2004 NATO expansion". International Politics. 57 (3): 471–490. doi:10.1057/s41311-020-00236-6. ISSN 1740-3898. S2CID 219012478.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Risse, Thomas (2009). "Conclusions: Towards Transatlantic Democracy Promotion?". In Magen, Amichai; Risse, Thomas; McFaul, Michael A. (eds.). Promoting Democracy and the Rule of Law. Promoting Democracy and the Rule of Law: American and European Strategies. Governance and Limited Statehood Series. Palgrave Macmillan UK. pp. 244–271. doi:10.1057/9780230244528_9. ISBN 978-0-230-24452-8.
- ^ Kelemen, R. Daniel (3 March 2020). "The European Union's authoritarian equilibrium". Journal of European Public Policy. 27 (3): 481–499. doi:10.1080/13501763.2020.1712455. ISSN 1350-1763.
Bibliography
- Anderson, M.; Bort, E. (2001). Frontiers of the European Union. Springer. ISBN 978-0-230-50797-5.
- Barnard, Catherine (2010). The Substantive Law of the EU: The four freedoms (3rd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-956224-4.
- Bomberg, Elizabeth; Peterson, John; Corbett, Richard, eds. (2012). The European Union: How Does it Work? (New European Union) (3rd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-957080-5.
- Bretherton, Charlotte; Vogler, John (2005). The European Union as a Global Actor. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-45882-0.
- Cini, Michelle; Borragán, Nieves Pérez-Solórzano (2019). European Union Politics. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-880653-0.
- Craig, Paul; De Burca, Grainne (2011). EU Law: Text, Cases and Materials (5th ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-957699-9.
- Demey, Thierry (2007). Brussels, capital of Europe. S. Strange (trans.). Brussels: Badeaux. ISBN 978-2-9600414-6-0.
- Jones, Erik; Anand, Menon; Weatherill, Stephen (2012). The Oxford Handbook of the European Union. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-954628-2.
- Jordan, A.J.; Adelle, Camilla, eds. (2012). Environmental Policy in the European Union: Contexts, Actors and Policy Dynamics (3rd ed.). Abingdon-on-Thames: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-84971-469-3.
- Kaiser, Wolfram; Varsori, A. (2010). European Union History: Themes and Debates. Springer. ISBN 978-0-230-28150-9.
- Mather, J. (2006). Legitimating the European Union: Aspirations, Inputs and Performance. Springer. ISBN 978-0-230-62562-4.
- McCormick, John (2007). The European superpower. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4039-9845-3. OCLC 71266552.
- McCormick, John (2014). Understanding the European Union: A Concise Introduction. Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-137-36234-6.
- McCormick, John (2013). The European Union: Politics and Policies (5th ed.). Boulder, CO: Westview Press. ISBN 978-0-8133-4202-3.
- McLaren, L. (2005). Identity, Interests and Attitudes to European Integration. Springer. ISBN 978-0-230-50424-0.
- Murray, Fiona (2012). The European Union and Member State Territories: A New Legal Framework Under the EU Treaties. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-90-6704-825-5.
- Nugent, Neill (2006). The Government and Politics of the European Union. Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0-8223-3870-3.
- O'Brennan, John (2006). The Eastern Enlargement of the European Union. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-23440-0.
- Pagden, Anthony; Hamilton, Lee H. (2002). The Idea of Europe: From Antiquity to the European Union. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-79552-4.
- Pinder, John; Usherwood, Simon (2013). The European Union: A Very Short Introduction (3rd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-968169-3.
- Piris, Jean-Claude (2010). The Lisbon Treaty: A Legal and Political Analysis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-19792-2.
- Rosamond, Ben (2000). Theories of European Integration. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-312-23120-0.
- Scheuer, Angelika (2005). How Europeans See Europe: Structure and Dynamics of European Legitimacy Beliefs. Amsterdam University Press. ISBN 978-90-5629-408-3.
- Simons, George F., ed. (2002). EuroDiversity. Abingdon-on-Thames: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-87719-381-4.
- Smith, Hazel Knowles (2002). European Union Foreign Policy: What it is and What it Does. Pluto Press. ISBN 978-0-7453-1870-7.
- Smith, Karen E. (2008). European Union Foreign Policy in a Changing World. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-7456-4018-1.
- Urwin, Derek W. (2014). The Community of Europe: A History of European Integration Since 1945. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-89252-6.
- Weigall, David; Stirk, Peter M.R. (1992). The Origins and development of the European Community. Leicester University Press. ISBN 978-0-7185-1428-0.
- Wilkinson, Paul (2007). International Relations: A Very Short Introduction (1st ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-280157-9.
Further reading
- Berend, Ivan T. (2017). The Contemporary Crisis of the European Union: Prospects for the Future. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-138-24419-1.
- Corbett, Richard; Jacobs, Francis; Shackleton, Michael (2011). The European Parliament (8th ed.). London: John Harper Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9564508-5-2.
- Federiga, Bindi, ed. (2010). The Foreign Policy of the European Union: Assessing Europe's Role in the World (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: Brookings Institution Press. ISBN 978-0-8157-2252-6.
- Gareis, Sven; Hauser, Gunther; Kernic, Franz, eds. (2013). The European Union – A Global Actor?. Leverkusen, Germany: Barbara Budrich Publishers. ISBN 978-3-8474-0040-0.
- Grinin, L.; Korotayev, A.; Tausch, A. (2016). Economic Cycles, Crises, and the Global Periphery. Heidelberg, New York, Dordrecht, London: Springer International Publishing. ISBN 978-3-319-17780-9.
- Kaiser, Wolfram (2009). Christian Democracy and the Origins of European Union. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-511-49705-6.
- Le Gales, Patrick; King, Desmond (2017). Reconfiguring European States in Crisis. Corby: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-879337-3.
- McAuley, James (15 August 2019). "A More Perfect Union?". New York Review of Books. ISSN 0028-7504.
- Mount, Ferdinand (6 June 2019). "Why we go to war". London Review of Books. 41 (11). ISSN 0260-9592. Retrieved 11 October 2020.
- Rifkin, Jeremy (2005). The European Dream: How Europe's Vision of the Future Is Quietly Eclipsing the American Dream. City of Westminster, London: TarcherPerigee. ISBN 978-1-58542-435-1.
- Smith, Charles (2007). International Trade and Globalisation (3rd ed.). Stocksfield: Anforme Ltd. ISBN 978-1-905504-10-7.
- Staab, Andreas (2011). The European Union Explained: Institutions, Actors, Global Impact. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0-253-22303-6. excerpt and text search
- Steiner, Josephine; Woods, Lorna; Twigg-Flesner, Christian (2006). EU Law (9th ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-927959-3.
- Tausch, Arno (2012). Globalization, the Human Condition, and Sustainable Development in the Twenty-first Century: Cross-national Perspectives and European Implications. With Almas Heshmati and a Foreword by Ulrich Brand (1st ed.). Anthem Press, London. ISBN 978-0-85728-410-5.
- Yesilada, Birol A.; Wood, David M. (2009). The Emerging European Union (5th ed.). Abingdon-on-Thames: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-205-72380-5.
External links
- EUROPA – official web portal
- Historical Archives of the European Union
- Eurostat – European Union Statistics Explained
- CIA World Factbook: European Union. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- The European Union: Questions and Answers Congressional Research Service
- Works by European Union at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about European Union at Internet Archive
- European Union on Nobelprize.org

- European Union
- 1993 establishments in the Netherlands
- Confederations
- G20 nations
- G7 nations
- Group of Eight nations
- International organizations based in Europe
- International political organizations
- Organisations based in Brussels
- Organizations awarded Nobel Peace Prizes
- Organizations established in 1993
- Political organizations based in Europe
- Political systems
- Supranational unions
- Trade blocs
- United Nations General Assembly observers