Derrubone
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
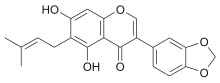
| IUPAC name
5,7-Dihydroxy-6-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-3′,4′-[methylenebis(oxy)]isoflavone
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-5,7-dihydroxy-6-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
5,7-Dihydroxy-3',4'-methylenedioxy-6-prenylisoflavone
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H18O6 | |
| Molar mass | 366.369 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Derrubone is a prenylated isoflavone, a type of flavonoid. It was originally isolated from the Indian tree Derris robusta.[1] Recent research indicates that it acts as an inhibitor of Hsp90 to its function as a chaperone protein.[2]
References[]
- ^ East AJ, Ollis WD, Wheeler RE (1969). "Natural occurrence of 3-aryl-4-hydroxycoumarins. Part I. Phytochemical examination of Derris robusta(roxb.) benth". J. Chem. Soc. C. 3 (3): 365–74. doi:10.1039/J39690000365.
- ^ Hadden MK, Galam L, Gestwicki JE, Matts RL, Blagg BS (December 2007). "Derrubone, an inhibitor of the Hsp90 protein folding machinery". J. Nat. Prod. 70 (12): 2014–8. doi:10.1021/np070190s. PMID 18020309.
Categories:
- Isoflavones
- Prenylflavonoids
- Benzodioxoles
- Resorcinols
- Aromatic compound stubs