Diocese of Thrace
| Diocese of Thrace Dioecesis Thraciae Διοίκησις Θρᾴκης | |
|---|---|
| Diocese of the Roman Empire | |
| 314–535 | |
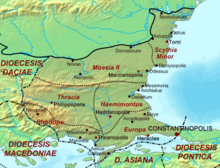 The Diocese of Thrace c. 400. | |
| Capital | Philippopolis |
| History | |
| Historical era | Late Antiquity |
• Established | 314 |
• Diocese abolished by emperor Justinian I | 535 |
| Today part of | |
The Diocese of Thrace (Latin: Dioecesis Thraciae, Greek: Διοίκησις Θρᾴκης) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of the eastern Balkan Peninsula (comprising territories in modern south-eastern Romania, central and eastern Bulgaria, and Greek and Turkish Thrace). Philippopolis (modern Plovdiv, in Bulgaria) was the capital.
The diocese was established as part of the reforms of Diocletian and Constantine the Great, and was headed by a vicarius subordinate to the praetorian prefecture of the East. As outlined in the Notitia Dignitatum of c. 400, the diocese included the provinces of Europa, Thracia, Haemimontus, Rhodope, and Scythia Minor.
In May 535, with Novel 26, Justinian I abolished the Diocese of Thrace. Its vicarius retained his rank of vir spectabilis and received the new title of praetor Justinianus, uniting in his hand both civil and military authority over the provinces of the former diocese, in a crucial departure from the strict separation of authority from the Diocletianian system. A year later, in May 536, the two Danubian provinces, Moesia Inferior and Scythia, where detached to form, along with other provinces, the quaestura exercitus.[1]
List of known Vicarii Thraciarum[]
- Aelius Claudius Dulcitius (?–361)
- Capitolinus (361–363)
- Andronicus (c. 366)
- Philoxenus (c. 392)
- Solomon (?–582)
References[]
Sources[]
- Bury, John Bagnell (1923). History of the Later Roman Empire: From the Death of Theodosius I to the Death of Justinian. London: MacMillan & Co. ISBN 0-486-20399-9.
- States and territories established in the 310s
- States and territories disestablished in the 530s
- Civil dioceses of the Roman Empire
- Roman Thrace
- Greece in the Roman era
- Civil dioceses of the Byzantine Empire
- Medieval Thrace
- Geography of ancient Thrace
- Ancient history of Romania
- Bulgaria in the Roman era
- History of Dobruja
- Praetorian prefecture of the East
- 314 establishments
- 535 disestablishments
- Ancient Rome stubs
- Byzantine Empire geography stubs