Directed-energy weapon

A directed-energy weapon (DEW) is a ranged weapon that damages its target with highly focused energy, including lasers, microwaves, particle beams, and sound beams. Potential applications of this technology include weapons that target personnel, missiles, vehicles, and optical devices.[1][2] In the United States, the Pentagon, DARPA, the Air Force Research Laboratory, United States Army Armament Research Development and Engineering Center, and the Naval Research Laboratory are researching directed-energy weapons and railguns to counter ballistic missiles, hypersonic cruise missiles, and hypersonic glide vehicles. These systems of missile defense are expected to come online no sooner than the mid to late-2020s.[3] The Electro-Magnetic Laboratory Rail Gun has been in testing since 2012.
Russia,[4][5][6] China,[7][8][9][10] India[11][12][13] and the United Kingdom[14][15] are also developing military grade directed-energy weapons while Iran[16][17][18][19] and Turkey claim to have them in active service.[20][21][22] The first usage of directed-energy weapons in combat between military forces was claimed to have occurred in Libya in August 2019 by Turkey, which claimed to use the ALKA directed-energy weapon.[23][24] After decades of research and development, most directed-energy weapons are still at the experimental stage and it remains to be seen if or when they will be deployed as practical, high-performance military weapons.[25][26]
Operational advantages[]
Directed energy weapons could have several main advantages over conventional weaponry:
- Directed-energy weapons can be used discreetly; radiation does not generate sound and is invisible if outside the visible spectrum.[27][28]
- Light is, for practical purposes, unaffected by gravity, windage and Coriolis force, giving it an almost perfectly flat trajectory. This makes aim much more precise and extends the range to line-of-sight, limited only by beam diffraction and spread (which dilute the power and weaken the effect), and absorption or scattering by intervening atmospheric contents.
- Lasers travel at light-speed and have long range, making them suitable for use in space warfare.
- Laser weapons potentially eliminate many logistical problems in terms of ammunition supply, as long as there is enough energy to power them.
- Depending on several operational factors, directed-energy weapons may be cheaper to operate than conventional weapons in certain contexts.[29]
Types[]
Microwave[]
Although some devices are labeled as microwave weapons, the microwave range is commonly defined as being between 300 MHz and 300 GHz, which is within the RF range[30]—these frequencies having wavelengths of 1 meter to 1 millimeter. Some examples of weapons which have been publicized by the military are as follows:
Active Denial System[]
Active Denial System is a millimeter wave source that heats the water in a human target's skin and thus causes incapacitating pain. It was developed by the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory and Raytheon for riot-control duty. Though intended to cause severe pain while leaving no lasting damage, concern has been voiced as to whether the system could cause irreversible damage to the eyes. There has yet to be testing for long-term side effects of exposure to the microwave beam. It can also destroy unshielded electronics.[31] The device comes in various sizes, including attached to a Humvee.
Vigilant Eagle[]
Vigilant Eagle is a proposed airport defense system that directs high-frequency microwaves towards any projectile that is fired at an aircraft.[32] The system consists of a missile-detecting and tracking subsystem (MDT), a command and control system, and a scanning array. The MDT is a fixed grid of passive infrared (IR) cameras. The command and control system determines the missile launch point. The scanning array projects microwaves that disrupt the surface-to-air missile's guidance system, deflecting it from the aircraft.[33]
Bofors HPM Blackout[]
Bofors HPM Blackout is a high-powered microwave weapon that is said to be able to destroy at short distance a wide variety of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) electronic equipment and is purportedly non-lethal.[34][35][36]
EL/M-2080 Green Pine|EL/M-2080 Green P[]
The effective radiated power (ERP) of the EL/M-2080 Green Pine radar makes it a hypothetical candidate for conversion into a directed-energy weapon, by focusing pulses of radar energy on target missiles.[37] The energy spikes are tailored to enter missiles through antennas or sensor apertures where they can fool guidance systems, scramble computer memories or even burn out sensitive electronic components.[37]
Active electronically scanned array[]
AESA radars mounted on fighter aircraft have been slated as directed energy weapons against missiles, however, a senior US Air Force officer noted: "they aren't particularly suited to create weapons effects on missiles because of limited antenna size, power and field of view".[38] Potentially lethal effects are produced only inside 100 meters range, and disruptive effects at distances on the order of one kilometer. Moreover, cheap countermeasures can be applied to existing missiles.[39]
Counter-electronics High Power Microwave Advanced Missile Project[]
Counter-electronics High Power Microwave Advanced Missile Project
Laser[]
A laser weapon is a directed-energy weapon based on lasers.[40]
Particle-beam[]
Particle-beam weapons can use charged or neutral particles, and can be either endoatmospheric or exoatmospheric. Particle beams as beam weapons are theoretically possible, but practical weapons have not been demonstrated yet. Certain types of particle beams have the advantage of being self-focusing in the atmosphere.
Blooming is also a problem in particle-beam weapons. Energy that would otherwise be focused on the target spreads out and the beam becomes less effective:
- Thermal blooming occurs in both charged and neutral particle beams, and occurs when particles bump into one another under the effects of thermal vibration, or bump into air molecules.
- Electrical blooming occurs only in charged particle beams, as ions of like charge repel one another.
Plasma[]
Plasma weapons fire a beam, bolt, or stream of plasma, which is an excited state of matter consisting of atomic electrons & nuclei and free electrons if ionized, or other particles if pinched.
The MARAUDER (Magnetically Accelerated Ring to Achieve Ultra-high Directed-Energy and Radiation) used the Shiva Star project (a high energy capacitor bank which provided the means to test weapons and other devices requiring brief and extremely large amounts of energy) to accelerate a toroid of plasma at a significant percentage of the speed of light.[41]
The Russian Federation is developing plasma weapons.[42]
Sonic[]
Long Range Acoustic Device (LRAD)[]

The Long Range Acoustic Device (LRAD) is an acoustic hailing device developed by LRAD Corporation to send messages and warning tones over longer distances or at higher volume than normal loudspeakers, and as a non-lethal directed-energy weapon. LRAD systems are used for long-range communications in a variety of applications[43] and as a means of non-lethal, non-kinetic crowd control. They are also used on ships as an anti-piracy measure.
According to the manufacturer's specifications, the systems weigh from 15 to 320 pounds (6.8 to 145.1 kg) and can emit sound in a 30°- 60° beam at 2.5 kHz.[44] They range in size from small, portable handheld units which can also be strapped to a person's chest, to larger models which require a mount to stabilise them.[45] The power of LRADs means that the sound beam which they produce can penetrate vehicles and buildings whilst retaining a high degree of fidelity, meaning verbal messages can be conveyed more clearly in some situations.[46] Their weapons capability has been controversially used in the USA to disrupt numerous protests.
History[]
Ancient[]
Mirrors of Archimedes[]
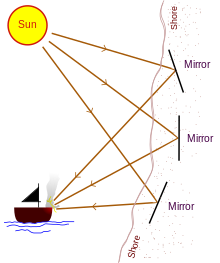
According to a legend, Archimedes created a mirror with an adjustable focal length (or more likely, a series of mirrors focused on a common point) to focus sunlight on ships of the Roman fleet as they invaded Syracuse, setting them on fire.[47] Historians point out that the earliest accounts of the battle did not mention a "burning mirror", but merely stated that Archimedes's ingenuity combined with a way to hurl fire were relevant to the victory. Some attempts to replicate this feat have had some success; in particular, an experiment by students at MIT showed that a mirror-based weapon was at least possible, if not necessarily practical.[48] The hosts of MythBusters tackled the Mirrors of Archimedes three times (in episodes 19, 57 and 172) and were never able to make the target ship catch fire, declaring the myth busted three separate times.
20th Century[]
Robert Watson-Watt[]
In 1935, the British Air Ministry asked Robert Watson-Watt of the Radio Research Station whether a "death ray" was possible.[49][50] He and colleague Arnold Wilkins quickly concluded that it was not feasible, but as a consequence suggested using radio for the detection of aircraft and this started the development of radar in Britain.[51][52]
The fictional "engine-stopping ray"[]
Stories in the 1930s and World War Two gave rise to the idea of an "engine-stopping ray". They seemed to have arisen from the testing of the television transmitter in Feldberg, Germany. Because electrical noise from car engines would interfere with field strength measurements, sentries would stop all traffic in the vicinity for the twenty minutes or so needed for a test. Reversing the order of events in retelling the story created a "tale" where tourists car engine stopped first and then were approached by a German soldier who told them that they had to wait. The soldier returned a short time later to say that the engine would now work and the tourists drove off. Such stories were circulating in Britain around 1938 and during the war British Intelligence relaunched the myth as a "British engine-stopping ray," trying to spoof the Germans into researching what the British had supposedly invented in an attempt to tie up German scientific resources.[53]
German World War II experimental weapons[]
During the early 1940s Axis engineers developed a sonic cannon that could cause fatal vibrations in its target body. A methane gas combustion chamber leading to two parabolic dishes pulse-detonated at roughly 44 Hz. This sound, magnified by the dish reflectors, caused vertigo and nausea at 200–400 meters (220–440 yd) by vibrating the middle ear bones and shaking the cochlear fluid within the inner ear. At distances of 50–200 meters (160–660 ft), the sound waves could act on organ tissues and fluids by repeatedly compressing and releasing compressive resistant organs such as the kidneys, spleen, and liver. (It had little detectable effect on malleable organs such as the heart, stomach and intestines.) Lung tissue was affected at only the closest ranges as atmospheric air is highly compressible and only the blood rich alveoli resist compression. In practice, the weapon was highly vulnerable to enemy fire. Rifle, bazooka and mortar rounds easily deformed the parabolic reflectors, rendering the wave amplification ineffective.[54]
In the later phases of World War II, Nazi Germany increasingly put its hopes on research into technologically revolutionary secret weapons, the Wunderwaffe.
Among the directed-energy weapons the Nazis investigated were X-ray beam weapons developed under Heinz Schmellenmeier, Richard Gans and Fritz Houtermans. They built an electron accelerator called Rheotron (invented by Max Steenbeck at Siemens-Schuckert in the 1930s, these were later called Betatrons by the Americans) to generate hard X-ray synchrotron beams for the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM). The intent was to pre-ionize ignition in aircraft engines and hence serve as anti-aircraft DEW and bring planes down into the reach of the flak. The Rheotron was captured by the Americans in Burggrub on April 14, 1945.[citation needed]
Another approach was Ernst Schiebolds 'Röntgenkanone' developed from 1943 in Großostheim near Aschaffenburg. Richert Seifert & Co from Hamburg delivered parts.[55]
Reported use in Sino-Soviet conflicts[]
The Central Intelligence Agency informed Secretary Henry Kissinger that it had twelve reports of Soviet forces using laser-based weapons against Chinese forces during the 1969 Sino-Soviet border clashes, though William Colby doubted that they had actually been employed.[56]
Northern Ireland "squawk box" field trials[]
In 1973, New Scientist magazine reported that a sonic weapon known as a 'squawk box' underwent successful field trials in Northern Ireland, using soldiers as guinea pigs. The device combined two slightly different frequencies which when heard would be heard as the sum of the two frequencies (ultrasonic) and the difference between the two frequencies (infrasonic) e.g. two directional speakers emitting 16,000 Hz and 16,002 Hz frequencies would produce in the ear two frequencies of 32,002 Hz and 2 Hz. The article states: 'The squawk box is highly directional which gives it its appeal. Its effective beam width is so small that it can be directed at individuals in a riot. Other members of a crowd are unaffected, except by panic when they see people fainting, being sick, or running from the scene with their hands over their ears. The virtual inaudibility of the equipment is said to produce a "spooky" psychological effect.'[57] The British Ministry of Defence denied the existence of such a device. It stated that it did have, however, an 'ultra-loud public address system which [...] could be "used for verbal communication over two miles, or put out a sustained or modulated sound blanket to make conversation, and thus crowd organisation, impossible."'[58][59]
East German "decomposition" methods[]

In East Germany in the 1960's, many people were arrested and interrogated for holding politically incorrect views or for performing actions deemed hostile by the ruling socialist state. Such arrests, which could also involve direct physical torture, were condemned internationally. In an effort to avoid such condemnation the state security service, the Stasi, attempted alternative methods of repression which could paralyse people without keeping them in a physical prison. They could therefore avoid there being any evidence of repression or at least limit it. One such alternative method was called decomposition (transl. Zersetzung). In the 1970's and 80's it became the primary method of repressing domestic 'hostile-negative'[63] forces. It was a psychological warfare method which could involve the group based and systematic gaslighting of targets, among other things.[64] Some of the victims of this method suffered from suspicious cases of cancer and have claimed that they had also been targeted with directed X-rays. In addition, when the East German state collapsed powerful X-ray equipment was found in prisons without there being any apparent reason to justify its presence. In 1999, the modern German state was investigating the possibility that this X-ray equipment was being used as weaponry and that it was a deliberate policy of the Stasi to attempt to give prisoners radiation poisoning, and thereby cancer, through the use of directed X-rays.[61] The negative effects of the radiation poisoning and cancer would extend past the period of incarceration. In this manner someone could be debilitated even though they were no longer imprisoned. The historian Mary Fulbrook states, ‘The subsequent serious illnesses and premature deaths of dissidents such as the novelist Jürgen Fuchs, and the author of the critical analysis of ‘The Alternative in Eastern Europe’, Rudolf Bahro, have been linked by some to the suspicion of exposure to extraordinarily high and sustained levels of X-rays while waiting for interrogations, and being strapped to unpleasant chairs in small prison cells in front of mysterious closed boxes- boxes that, along with their mysterious apparatus, curiously disappeared after the collapse of the SED (Socialist Unity Party of Germany) system.’[65]
Strategic Defense Initiative[]
In the 1980s, U.S. President Ronald Reagan proposed the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) program, which was nicknamed Star Wars. It suggested that lasers, perhaps space-based X-ray lasers, could destroy ICBMs in flight. Panel discussions on the role of high-power lasers in SDI took place at various laser conferences, during the 1980s, with the participation of noted physicists including Edward Teller.[66][67]
Though the strategic missile defense concept has continued to the present under the Missile Defense Agency, most of the directed-energy weapon concepts were shelved. However, Boeing has been somewhat successful with the Boeing YAL-1 and Boeing NC-135, the first of which destroyed two missiles in February 2010. Funding has been cut to both of the programs.
Iraq War[]
During the Iraq War, electromagnetic weapons, including high power microwaves, were used by the U.S. military to disrupt and destroy Iraqi electronic systems and may have been used for crowd control. Types and magnitudes of exposure to electromagnetic fields are unknown.[68]
Alleged tracking of Space Shuttle Challenger[]
The Soviet Union invested some effort in the development of ruby and carbon dioxide lasers as anti-ballistic missile systems, and later as a tracking and anti-satellite system. There are reports that the Terra-3 complex at Sary Shagan was used on several occasions to temporarily "blind" US spy satellites in the IR range.
It has been claimed (and proven false) that the USSR made use of the lasers at the Terra-3 site to target the Space Shuttle Challenger in 1984.[69][70] At the time, the Soviet Union were concerned that the shuttle was being used as a reconnaissance platform. On 10 October 1984 (STS-41-G), the Terra-3 tracking laser was allegedly aimed at Challenger as it passed over the facility. Early reports claimed that this was responsible for causing "malfunctions on the space shuttle and distress to the crew", and that the United States filed a diplomatic protest about the incident.[69][70] However, this story is comprehensively denied by the crew members of STS-41-G and knowledgeable members of the US intelligence community.[71] After the end of the Cold War, the Terra-3 facility was found to be a low-power laser testing site with limited satellite tracking capabilities, which is now abandoned and partially disassembled.
Modern 21st Century use[]
Havana Syndrome[]
Havana syndrome is a set of medical symptoms reported by US personnel in Havana, Cuba and other locations, suspected by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to be caused by microwave energy.[72]
Anti-piracy measures[]
LRADs are often fitted on commercial and military ships. They have been used on several occasions to repel pirate attacks by sending warnings and by producing intolerable levels of sound. For example, in 2011 the cruise liner The Spirit of Adventure defended itself from Somali pirates in the Indian ocean by using its LRAD to force them to retreat.[73][74]
Non-lethal weapon capability[]
The TECOM Technology Symposium in 1997 concluded on non-lethal weapons, "determining the target effects on personnel is the greatest challenge to the testing community", primarily because "the potential of injury and death severely limits human tests".[75]
Also, "directed-energy weapons that target the central nervous system and cause neurophysiological disorders may violate the Certain Conventional Weapons Convention of 1980. Weapons that go beyond non-lethal intentions and cause 'superfluous injury or unnecessary suffering' may also violate the Protocol I to the Geneva Conventions of 1977."[76]
Some common bio-effects of non-lethal electromagnetic weapons include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Disorientation
- Nausea
- Pain
- Vertigo
- Other systemic discomfort
Interference with breathing poses the most significant, potentially lethal results.
Light and repetitive visual signals can induce epileptic seizures. Vection and motion sickness can also occur.
Cruise ships are known to use sonic weapons (such as LRAD) to drive off pirates.[77]
Russia has been reportedly using blinding laser weapons during its military intervention in Donbass.[78]
See also[]
- Electronic warfare
- Electromagnetic pulse
- Ivan's hammer
- L3Harris Technologies
- Laser applications
- MEDUSA (weapon)
Notes[]
- ^ "Daily Telegraph, 12th September 2013", Golden Eye-style energy beam is developed by Nato scientists, Oct. 08, 2013
- ^ "Milsat Magazine, Satnews Daily, June 24th 2009", U.S. Navy Laser Versus UAVs... Laser Wins..., Oct. 08, 2013
- ^ Thaad-ER In Search Of A Mission – Aviationweek.com, 20 January 2015
- ^ Egorov, Boris (July 12, 2017). "A farewell to traditional arms: Russia develops weapons for the future". rbth.com.
- ^ "Russia's new MiG-35 fighter jet to use laser weapons". PravdaReport. January 27, 2017.
- ^ Sudakov, Dmitry (August 3, 2016). "Russia's combat laser weapons declassified". PravdaReport.
- ^ General·Asia·December 19, Ryan; Read, 2016·1 Min (December 20, 2016). "The Chinese Military Now Has Laser Weapons". NextShark.
- ^ "Drones, lasers, and tanks: China shows off its latest weapons". Popular Science. 18 March 2019.
- ^ Mizokami, Kyle (January 30, 2017). "New Chinese Microwave Weapon Can Short Out IEDs and Tanks". Popular Mechanics.
- ^ "How China Is Weaponizing Outer Space". thediplomat.com.
- ^ DelhiSeptember 21, India Today Web Desk New; September 24, 2015UPDATED; Ist, 2015 15:13. "KALI: India's weapon to destroy any uninvited missiles and aircrafts [sic]". India Today.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- ^ "Future technologies must be propelled by power of today's youth: DRDO chairman". OnManorama. Retrieved 2020-09-15.
- ^ P, Rajat; Sep 14, it / TNN / Updated; 2020; Ist, 13:41. "DRDO plans Star Wars-style weapons for battles of future | India News - Times of India". The Times of India. Retrieved 2020-09-15.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- ^ "Dragonfire laser turret unveiled at DSEI 2017 – MBDA". MBDA. Retrieved 2017-10-21.
- ^ "Dragonfire, a guide to the new British laser weapon". UK Defence Journal. 2017-09-18. Retrieved 2017-10-21.
- ^ "Iran starts producing laser weapons for air defense". news.am.
- ^ "Iran achieves Laser Weapon System's deflection technology". worldbulletin.net/.
- ^ "Iran is Producing Laser Air Defense System". Islam Times. November 16, 2019.
- ^ "IRGC Navy develops anti-laser weapon". Tehran Times. March 3, 2019.
- ^ "Turkey's laser weapon ARMOL passes acceptance tests". DailySabah. 30 September 2019. Retrieved 2020-02-08.
- ^ "Janes | Latest defence and security news". Janes.com.
- ^ "Turkey's laser gun passes acceptance tests". aa.com.tr. Retrieved 2020-02-08.
- ^ "Army Recognition". armyrecognition.com. Retrieved 2020-02-08.
- ^ "Is Turkey the first country to shoot down a drone with a laser?". Ahval. 3 September 2019. Retrieved 2020-02-08.
- ^ "Navy's new laser weapon: Hype or reality?". May 18, 2015.
- ^ "Full Page Reload". IEEE Spectrum: Technology, Engineering, and Science News. 27 September 2017.
- ^ "Defence IQ talks to Dr Palíšek about Directed Energy Weapon systems", Defence iQ', Nov. 20, 2012
- ^ Spectrum Tutorial Archived 2013-05-31 at the Wayback Machine, University of Wisconsin Electromagnetic Spectrum Tutorial, accessed 22/06/2013
- ^ "US Navy Laser Weapon Fires At $1 Per Shot". Defenseworld.net. Retrieved 12 July 2019.
- ^ RF vs Microwave Freq range, microwaves and radio waves
- ^ "The Pentagon's Ray Gun". CBS News. 2008-06-01. Retrieved 2009-03-30.
- ^ "Raytheon focuses on non-lethal weapons", Andrew Johnson, The Arizona Republic, 09-17-2009.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ "Home". BAE Systems | International. Archived from the original on August 25, 2010.
- ^ Magnus Karlsson (2009). "Bofors HPM Blackout". Artilleri-Tidskrift (2–2009): s. s 12–15. Retrieved 2010-01-04.
- ^ "Google". google.com.
- ^ a b Fulghum, David A. (2005-12-17). "Israel tests improved Arrow interceptor". Aviation Week & Space Technology. Retrieved 2009-08-19.
- ^ David A. Fulghum & Douglas Barrie (2005-09-06). "Radar Becomes A Weapon". Aviation Week & Space Technology. Retrieved 2014-05-16.
- ^ Colonel of Aviation Grigoriy "Grisha" Medved (retd) (2008-04-13). "Grisha's Radar fry-off". Air Power Australia. Retrieved 2014-05-16.
- ^ "Directed Energy".
- ^ Degnan, J. H.; Peterkin, Jr; Baca, G. P.; Beason, J. D.; Bell, D. E.; Dearborn, M. E.; Dietz, D.; Douglas, M. R.; Englert, S. E.; Englert, T. J.; Hackett, K. E.; Holmes, J. H.; Hussey, T. W.; Kiuttu, G. F.; Lehr, F. M.; Marklin, G. J.; Mullins, B. W.; Price, D. W.; Roderick, N. F.; Ruden, E. L.; Sovinec, C. R.; Turchi, P. J.; Bird, G.; Coffey, S. K.; Seiler, S. W.; Chen, Y. G.; Gale, D.; Graham, J. D.; Scott, M.; Sommars, W. (August 1993). "Compact toroid formation, compression, and acceleration". Physics of Fluids B. 5:8 (8): 2938–2958. Bibcode:1993PhFlB...5.2938D. doi:10.1063/1.860681. OSTI 7369133.
- ^ "Russia is developing laser, electromagnetic and plasma weapons". The Independent. January 22, 2017.
- ^ "Applications – LRAD Corporation website".
- ^ Corbett, Peter (2009). A Modern Plague of Pirates. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-9562107-0-8.
- ^ Peskoe-Yang, Lynne (17 June 2020). "How to Dodge the Sonic Weapon Used by Police". Popular Mechanics. Retrieved 18 September 2021.
- ^ "LRAD 100X" (PDF). darley.com. Retrieved 18 September 2021.
- ^ Bill Sweetman. "Directed-Energy Weapons: No Longer Science Fiction Aviation Week & Space Technology, 2015. Archive
- ^ "2.009 Archimedes Death Ray". web.mit.edu.
- ^ Sim, Philip (2014-05-15). "The pioneer who went under the radar". Retrieved 2019-11-22.
- ^ "Robert Watson-Watt: Biography on Undiscovered Scotland". undiscoveredscotland.co.uk. Retrieved 2019-11-22.
- ^ Harford, Tim (2017-10-09). "How the search for a 'death ray' led to radar". Retrieved 2019-11-22.
- ^ "Robert Watson-Watt biography - Science Hall of Fame - National Library of Scotland". digital.nls.uk. Retrieved 2019-11-22.
- ^ Jones, R.V. (1978). Most Secret War: British Scientific Intelligence 1939–1945. Coronet. pp. 84, 124. ISBN 0-340-24169-1.
- ^ Martin O'Collins, director (21 February 2006). "Weird Weapons: The Axis". Modern Marvels. Season 12. Episode 8. The History Channel.
- ^ "Forschungsstätte für Hitlers "Todesstrahlen"". Main-netz.de. 2009-08-19. Retrieved 2012-06-12.
- ^ Colby, William E. (October 29, 1974). "REPORTS OF USE OF LASER WEAPONS BY THE SOVIETS AGAINST THE CHINESE" (PDF). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved September 20, 2017.
- ^ "Army tests new riot weapon". New Scientist: 684. 20 September 1973. Retrieved 18 September 2021.
- ^ Rodwell, Robert (27 September 1973). "How dangerous is the Army's squawk box?". New Scientist: 730. Retrieved 18 September 2021.
- ^ Altmann, Jurgen (2001). "Acoustic Weapons - A Prospective Assessment" (PDF). Science & Global Security. 9 (3): 170. Bibcode:2001S&GS....9..165A. doi:10.1080/08929880108426495. S2CID 31795453.
- ^ Tierney, Dominic (13 September 2020). "How Putin Got Into America's Mind". The Atlantic. Retrieved 27 September 2021.
- ^ a b Stiastny, Terry. "World: Europe Dissidents say Stasi gave them cancer". BBC. Retrieved 27 September 2021.
- ^ Wensierski, Peter (16 May 1999). "In Kopfhöhe ausgerichtet". Der Spiegel. Retrieved 27 September 2021.
- ^ Dennis, Mike (2003). "Tackling the enemy- quiet repression and preventive decomposition". The Stasi: Myth and Reality. Pearson Education Limited. p. 112. ISBN 0582414229.
- ^ Dennis, Mike (2003). "Tackling the enemy- quiet repression and preventive decomposition". The Stasi: Myth and Reality. Pearson Education Limited. pp. 112–113. ISBN 0582414229.
- ^ Fulbrook, Mary (2008). The People's State: East German Society from Hitler to Honecker. New Haven: Yale University Press. p. 245. ISBN 9780300144246.
- ^ Wang, C. P. (Ed.), Proceedings of the International Conference on Lasers '85 (STS, McLean, Va, 1986).
- ^ Duarte, F. J. (Ed.), Proceedings of the International Conference on Lasers '87 (STS, McLean, Va, 1988).
- ^ U.S. Senate – Committee on Veterans Affairs: Hearings – Gulf War Illnesses; Testimony to the Senate Veterans Affairs Committee; Meryl Nass, MD, Director of Pulmonary Rehabilitation, Mount Desert Island Hospital Bar Harbor, Maine; September 25, 2007 [2]
- ^ a b Kononenko, Boris. "Silent Space Is Being Monitored". Archived from the original on 10 December 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- ^ a b Zaloga, Steven. "RED STAR WARS". Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- ^ "STS-41-G". Astronautix.com. Archived from the original on 2012-06-20. Retrieved 2012-06-12.
- ^ "Long before Havana Syndrome, the U.S. reported microwaves beamed at an embassy". NPR.org. Retrieved 2021-10-27.
- ^ Casley-Maslen, Stuart (2014). Weapons under International Human Rights Law. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 154. ISBN 978-1107027879.
- ^ Giannangeli Marco, Jeory Ted (16 January 2011). "Pirate raid on cruise ship foiled by 'blast'". The Daily Express. Retrieved 18 September 2021.
- ^ Human Effects Advisory Panel Program; presented to: NDIANon-Lethal Defense IV [3]
- ^ Non-Lethal Weaponry: From Tactical to Strategic Applications; Colonel Dennis B. Herbert, USMC (Ret.), program developer, Institute for Non-Lethal Defense Technologies at Pennsylvania State University; pg. 4 [4]
- ^ Smith, David (November 22, 2006). "Pirates shoot at Britons' cruise liner". The Guardian. London.
- ^ "Another blinding laser attack on Ukrainian soldier reported in Donbas war zone | KyivPost". KyivPost. 2018-10-02. Retrieved 2018-10-04.
References[]
- The E-Bomb: How America's New Directed Energy Weapons Will Change the Way Future Wars Will Be Fought. Doug Beason (2005). ISBN 0-306-81402-1
- US claims that China has used high-energy lasers to interfere with US satellites: Jane's Defence
- China jamming test sparks U.S. satellite concerns: USA Today
- Beijing secretly fires lasers to disable US satellites: The Telegraph
- China Attempted To Blind U.S. Satellites With Laser: Defense News
- China Has Not Attacked US Satellites Says DoD: United Press International
- SpaceWar
- Gertz, Bill (July 21, 2011). "Report: China building electromagnetic pulse weapons for use against U.S. carriers". The Washington Times. Retrieved April 29, 2012.
- Hambling, David (October 10, 2008). "Army Orders Pain Ray Trucks; New Report Shows 'Potential for Death'". Wired Magazine. Retrieved April 29, 2012.
- Beckhusen, Robert (April 1, 2013). "Air Force Wants New Energy Weapons to Cause Non-Lethal 'Bioeffects'". Wired Magazine. Retrieved April 1, 2013.
External links[]
![]() Media related to Directed-energy weapons at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Directed-energy weapons at Wikimedia Commons
- Airpower Australia
- Applied Energetics – Photonic and high-voltage energetics (formerly Ionatron)
- Wired News (AP) article on weapons deployment in Iraq, Active Denial System and Stunstrike, July 10, 2005
- Boeing Tests Laser-Mounted Humvee as IED Hunter, November 13, 2007
- WSTIAC Quarterly, Vol. 7, No. 1 – Directed Energy Weapons
- Ogonek Report on '21st Century Weapons'
- How 'Revolutionary' Is CHAMP, New Air Force Microwave Weapon?, November 28, 2012 By David Axe
- Directed-energy weapons
- Electromagnetic radiation
- Emerging technologies
- Non-lethal weapons