Disorders of sex development
hideThis article has multiple issues. Please help or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
| Disorders of sex development | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Disorders of sex differentiation, differences of sex development[1] |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Intersex topics |
|---|
 |
Disorders of sex development (DSDs), also known as differences in sex development, diverse sex development and variations in sex characteristics (VSC),[2] are congenital conditions affecting the reproductive system, in which development of chromosomal, gonadal, or anatomical sex is atypical.[3]
DSDs are subdivided into groups in which the labels generally emphasize the karyotype's role in diagnosis: 46,XX, 46,XY, sex chromosome, XX, sex reversal, ovotesticular disorder, XY, sex reversal.
The term disorders of sex development has been generally been accepted by the medical community, as well as being a popular term in literature.[4] However, the term is not universal among patients or support groups.[5] One study stated that it can affect individuals covered by the description in a negative way, and that the terminology might impact choice and utilization of health care providers.[6] Another study found that most affected individuals didn’t find the term offensive.[7] The World Health Organization and some medical journals still[when?] reference DSDs as intersex traits or conditions.[8] The Council of Europe[9] and Inter-American Commission on Human Rights[10] have called for a review of medical classifications that unnecessarily medicalize intersex traits.[9][10][11]
Overview[]
DSDs are medical conditions encompassing any problem noted at birth where the genitalia are atypical in relation to the chromosomes or gonads.[12] There are several types of DSDs and their effect on the external and internal reproductive organs varies greatly.
A frequently-used social and medical adjective for people with DSDs is "intersex".[13] Urologists were concerned that terms like intersex, hermaphrodite, and pseudohermaphrodite were confusing and pejorative. This led to the Chicago Consensus, recommending a new terminology based on the umbrella term disorders of sex differentiation.[14]
DSDs are divided into following categories, emphasizing the karyotype's role in diagnosis:[15] [16]
- 46, XX DSD: mainly virilized females as a result of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) and girls with aberrant ovarian development.
- 46, XY DSD: patients with abnormal testicular differentiation, defects in testosterone biosynthesis, and impaired testosterone action.
- Sex chromosome DSD: patients with sex chromosome aneuploidy or mosaic sex karyotypes. This includes patients with Turner Syndrome and Klinefelter Syndrome even though they do not generally present with atypical genitals.
- XX, Sex Reversal: consist of two groups of patients with male phenotypes, the first with translocated SRY and the second with no SRY gene.
- Ovotesticular disorder: patients having both ovarian and testicular tissue. In some cases the ovarian tissue is functional.
- : patients with female phenotypes where duplication in the Xp21.2 region of the X chromosome that contains the DAX1 gene is associated with XY sex reversal.
Genital anatomy[]
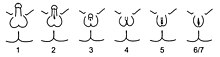
The penis (males) and clitoris (females) have a mutual origin, both arising from an embryonic structure called the primordial phallus. In typical males, the urethra is located at the tip of the penis, while in typical females the urethra is located below the base of the clitoris. It is also possible to have a urethral opening located along the shaft; this condition is known as hypospadias.
Management of DSDs[]
It is widely accepted that children with DSDs should be managed by a experienced multidisciplinary team.[17] Health care providers generally agree that children with DSDs should be notified early.[18]
Open-minded parenting, appropriate and conservative medical intervention, and age-appropriate child involvement in the treatment plan contribute greatly to successful outcomes for the entire range of DSDs.[19][pages needed]
Prevalence estimates[]
Estimates of prevalence vary depending on what conditions count as DSDs. A 2019 review states that DSDs occur in 1 in 4,500 to 1 in 5,000 births,[20] while a 2012 review estimated that DSDs occur in 1 in 5,500 births.[21]
The most common DSD is CAH.[22] CAH is estimated to make up 95% of all 46,XX DSD and 50% of all cases of ambiguous genitalia.[23]
Androgen insensitivity syndrome is estimated to make up about 15 to 20% of all DSDs and affects 1 in 20,000 to 1 in 64,000 males.[24]
Ovotesticular disorder makes up 10% of DSDs.[25]
Conditions[]
- 5α-reductase deficiency (also known as 5-ARD) - An autosomal recessive condition caused by a mutation of the 5-alpha reductase type 2 gene. It only affects people with Y chromosomes, namely genetic males. People with this condition are fertile, with the ability to father children, but may be raised as females due to ambiguous or feminized genitalia.[citation needed]
- 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency – A condition characterized by impaired androgen and estrogen synthesis in males and females, respectively. Results in pseudohermaphroditism/undervirilization in males and in excessive virilization of adult females.
- Androgen insensitivity syndrome (also known as AIS) – A condition which affects a genetic male's virilization. A person with androgen insensitivity syndrome produces androgens and testosterone but their body does not recognize it, either partially or completely. Mild androgen insensitivity syndrome generally causes no developmental issues and people with this form are raised as males. Partial androgen insensitivity syndrome results in ambiguous genitalia and there is no consensus regarding whether to raise a child with this form as male or female. Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome causes a genetic male to have a vagina (often incompletely developed, nearly always blind-ending), breasts, and a clitoris and people with this form are raised as females.
- Aphallia – A rare condition where a XY male is born without a penis. As of 2017 only 100 cases have been reported in literature.[26]
- Aromatase deficiency – A disorder which, in females, is characterized by androgen excess and estrogen deficiency, and can result in inappropriate virilization, though without pseudohermaphroditism (i.e., genitals are phenotypically appropriate) (with the exception of the possible incidence of clitoromegaly). Aromatase deficiency can also be caused by mutations in P450 oxidoreductase gene.[27]
- Aromatase excess syndrome (also known as familial hyperestrogenism) - A condition that causes excessive estrogen production, resulting in feminization without pseudohermaphroditism (i.e., male genitalia at birth and female secondary sexual characteristics at puberty) in males and hyperfeminization in females.
- Campomelic dysplasia – a condition caused by de novo autosomal dominant mutations in the SOX9 gene, causing bowing of the limbs, sex reversal in around two thirds of 46,XY males (but not in 46,XX females), and respiratory insufficiency. While in roughly 95% of cases, death occurs in the neonatal period due to respiratory distress, those that live past infancy typically survive to become adults.[citation needed]
- Clitoromegaly – A clitoris that is considered larger than average. While clitoromegaly may be a symptom of an intersex condition, it may also be considered a normal variation in clitoris size. Clitoromegaly causes no health issues. Surgical reduction of the clitoris or its complete removal may be performed to normalize the appearance of the genitalia. While female genital mutilation is outlawed in many countries, reduction or the removal of the clitoris in cases of clitoromegaly are generally exempt, despite the fact that it is a nontherapeutic and sexually damaging surgery. Clitoromegaly may also be caused by females using testosterone or anabolic steroids for purposes related to female to male gender transition or bodybuilding.
- Combined 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency – A condition in which presents as a combination of the symptoms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia and isolated 17,20-lyase deficiency. See those two conditions for more information.
- Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome (also known as CAIS) – A condition which completely affects a genetic male's ability to recognize androgens. It is considered a form of androgen insensitivity syndrome and is the most severe form. People with complete androgen insensitivity are raised as females and usually do not discover they are genetic males until they experience amenorrhoea in their late teens or they need medical intervention due to a hernia caused by their undescended testes. Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome results in a genetic male having a vagina, clitoris, and breasts which are capable of breastfeeding. However, they will not have ovaries or a uterus. Because they do not have ovaries or sufficiently developed testicles, people with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome are infertile.
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (also known as CAH) – A condition that causes excessive androgen production, which causes excessive virilization. It is most problematic in genetic females, where severe virilization can result in her having vaginal agenesis (absence of vagina) and a functional penis which is capable of penetrative intercourse. Females with this condition are usually fertile, with the ability to become pregnant and give birth. The salt-wasting variety of this condition is fatal in infants if left untreated.
- Denys–Drash syndrome and the related Frasier syndrome - similar rare conditions arising from de novo autosomal dominant mutations in the WT1 gene, causing symptoms ranging from undervirilization to complete sex reversal with persistent Müllerian ducts in affected 46,XY males (but not in 46,XX females). The disorders are invariably fatal before the age of 15, causing kidney failure due to nephrotic syndrome.
- Estrogen insensitivity syndrome (EIS) – The estrogen counterpart to androgen insensitivity syndrome. Extremely rare, with only one verified case having been reported; a biological male presented with tall stature, a heightened risk of osteoporosis, and sterility.
- Gonadal Dysgenesis – is any congenital developmental disorder of the reproductive system characterized by a progressive loss of primordial germ cells on the developing gonads of an embryo.
- Isolated 17,20-lyase deficiency – A condition that is characterized by either partial or complete inability to produce androgens and estrogens.[28] Results in partial or complete feminization and undervirilization in males and in a delayed, reduced, or absent puberty in both sexes, in turn causing sexual infantilism and infertility, among other symptoms.
- Klinefelter syndrome (also known as 47, XXY and XXY syndrome) – A condition that describes a male born with at least one extra X chromosome. Though the most common variation is 47, XXY, a man may also be 48, XXXY or 49, XXXXY. It is a common occurrence, affecting 1 in 500 to 1,000 men.[29] While some men may have no issues related to the syndrome, some may experience gynecomastia, micropenis, cognitive difficulties, hypogonadism, reduced fertility/infertility, and/or little or no facial hair. Testosterone therapy may be pursued by men who desire a more masculine appearance and those with gynecomastia may opt to undergo a reduction mammoplasty. Men who wish to father children may be able to do so with the help of IVF.[30][3][31]
- Leydig cell hypoplasia - A condition solely affecting biological males which is characterized by partial or complete inactivation of the luteinizing hormone receptor, resulting in stymied androgen production. Patients may present at birth with a fully female phenotype, ambiguous genitalia, or only mild genital defects such as micropenis and hypospadias. Upon puberty, sexual development is either impaired or fully absent.
- Lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia – An endocrine disorder that arises from defects in the earliest stages of steroid hormone synthesis: the transport of cholesterol into the mitochondria and the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone—the first step in the synthesis of all steroid hormones.
- Mild androgen insensitivity syndrome (also known as MAIS) – A condition which mildly affects a genetic male's ability to recognize androgens. It is considered a form of androgen insensitivity syndrome and is considered the least severe form. While men generally do not need any specialized medical care related to this form, mild androgen insensitivity syndrome may result in gynecomastia and hypospadias. Neither gynecomastia nor hypospadias require surgical intervention or adversely affect a man's health though some men may opt to undergo surgery to remove their breasts and/or repair their hypospadias. Men with mild androgen insensitivity syndrome may have reduced fertility.
- Mixed gonadal dysgenesis – is a condition of unusual and asymmetrical gonadal development leading to an unassigned sex differentiation. A number of differences have been reported in the karyotype, most commonly a mosaicism 45,X/ 46, XY.
- Ovotesticular disorder (also called true hermaphroditism) is rare a condition where an individual has both ovarian and testicular tissue.[25] It is the rarest DSD with at least 500 cases being reported in literature.[32]
- Partial androgen insensitivity syndrome (also known as PAIS) – A condition which partially affects a genetic male's ability to recognize androgens. It is considered a form of androgen insensitivity syndrome and while it is not as severe as complete androgen insensitivity syndrome, it is more severe than mild androgen insensitivity syndrome. Partial androgen insensitivity syndrome causes major problems with gender assignment because it causes ambiguous genitalia such as a micropenis or clitoromegaly in addition to breast development. People with partial androgen insensitivity syndrome who are assigned as males may undergo testosterone therapy to virilize their body while those who are assigned as females may undergo a surgical reduction of the clitoris and/ or estrogen therapy.
- Penoscrotal transposition
- Persistent Müllerian duct syndrome A condition where Fallopian tubes, uterus, or the upper part of the vagina are present in an otherwise normal male.
- Pseudovaginal perineoscrotal hypospadias (also known as PPSH) – A form of ambiguous genitalia which results in a phallic structure that is smaller than a penis but larger than a clitoris, a chordee, hypospadias, and a shallow vagina.
- Swyer Syndrome (Also known as Pure Gonadal Dysgenesis or XY gonadal dysgenesis) is a type of hypogonadism in a person whose karyotype is 46,XY. The person is externally female with streak gonads, and left untreated, will not experience puberty. Such gonads are typically surgically removed (as they have a significant risk of developing tumors) and a typical medical treatment would include hormone replacement therapy with female hormones.
- Turner syndrome (also known as Ullrich-Turner syndrome and gonadal dysgenesis) – A condition that describes a female born with only one X chromosome or with an abnormal X chromosome, making her karotype 45, XO. It occurs in 1 in 2,000 to 5,000 females. Turner syndrome causes numerous health and development problems, including but not limited to short stature, lymphedema, infertility, webbed neck, coarctation of the aorta, ADHD, amenorrhoea, and obesity.
- Müllerian agenesis (also known as Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser Syndrome or Vaginal Agenesis) – A condition that causes the uterus and other reproductive organs in a 46,XX female to be small or absent, as well as the vaginal canal itself. It affects 1 out of 4,500 to 5,000 females and can also come with skeletal or endocrine system issues at conception.
- XX Testicular DSD is a condition where an individual with an XX karyotype has a male appearance. Genitalia can range from normal to ambiguous genitalia.[33] It is estimated to occur in 1 in 20,000 males.[citation needed]
Management[]
This section needs expansion. You can help by . (August 2021) |
It is widely accepted that children with DSDs should be managed by a experienced multidisciplinary team.[34]
Open-minded parenting, appropriate and conservative medical intervention, and age-appropriate child involvement in the treatment plan contribute greatly to successful outcomes for the entire range of DSDs.[19]
Organizations[]
Clinical networks and organizations[]
DSD-TRN[]
The Differences of Sex Development-Translational Research Network (DSD-TRN) is based in the United States and aims to improve DSD care across the United States.[35]
In 2015, key patient organizations and individuals left the Network, citing a "pattern of misrepresentation",[36] and network function that served "not to change medicine but to absolve clinicians of their responsibility.[37][38]
I-DSD[]
The International-Differences of Sex Development (I-DSD) is a research organization in Europe. This organization connects medical and research centers internationally in an effort to improve clinical practice, research, and general understanding of differences of sex development.[39] I-DSD regularly hosts a symposium in order to provides updates on current care in DSD internationally, facilitate networking for those in DSD Care, and promote high quality DSD research.[40]
Patient support and advocacy organizations[]
Notable patient support and advocacy organizations include:
Africa[]
- Intersex South Africa
- SIPD Uganda
Asia[]
- Intersex Asia
- Oii-Chinese
- OII Russia
- Srishti Madurai (India)
Europe[]
- Collectif intersexes et allié.e.s (CIA-OII France)
- InterAction Suisse (Switzerland)
- Internationalen Vereinigung Intergeschlechtlicher Menschen (OII Germany)
- Intersex Russia
- Intersex UK
- OII Europe
- Organisation Internationale des Intersexes - Francophonie (OII French-speaking)
- OII UK
- Zwischengeschlecht (Switzerland/Germany)
Latin America[]
- Brújula Intersexual (Intersex Compass) (Mexico and Latin America)
North America[]
- Accord Alliance (USA)
- Brújula Intersexual (Intersex Compass)
- interACT, formerly known as Advocates for Informed Choice (USA)
- Intersex Campaign for Equality (IC4E), formerly OII-USA
- Intersex Society of North America (ISNA) (defunct)
- Organisation Internationale des Intersexes - Francophonie (Canada)
Oceania[]
- Intersex Human Rights Australia, formerly OII Australia
- Intersex Peer Support Australia (also known as AISSGA, Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome Support Group Australia)
- Intersex Trust Aotearoa New Zealand, also known as Intersex Awareness New Zealand
International[]
- GATE
- International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association (ILGA)
- Organisation Intersex International (OII)
Controversy[]
This article relies excessively on partisan sources. (April 2021) |
This article relies extensively on quotations that were previously collated by an advocacy or lobbying group. (April 2021) |
Human rights and community concerns[]
The term DSD (and particularly its association with medical disorders) has been controversial. The argument over terminology reflects a deeper disagreement over the extent to which intersex conditions require medical intervention, the appropriateness of certain interventions, and whether physicians and parents should make irreversible treatment decisions on behalf of young children if the condition is not life-threatening.
- Use of the term disorder of sex development (DSD) is controversial among many activists and community organizations due to the label "disorders".[41][42][43][44] Many governments and international institutions use the term 'intersex' in preference to 'DSD', or have called for the review of medical classifications.[9][10] In May 2019, more than 50 intersex-led organizations signed a multilingual joint statement condemning the introduction of "disorders of sex development" language into the International Classification of Diseases, stating that this causes "harm" and facilitates human rights violations, calling on the World Health Organization to publish clear policy to ensure that intersex medical interventions are "fully compatible with human rights norms".[45][46][47][48][49]
- Lee et al. in a 2006 Consensus statement on management of intersex disorders proposed a system of nomenclature based on "disorders of sex development" for clinical use, suggesting that "terms such as intersex, pseudohermaphroditism, hermaphroditism, sex reversal, and gender based diagnostic labels are particularly controversial," may be perceived as pejorative, and are confusing to practitioners and parents alike.[3] However, research by the Lurie Children's Hospital, Chicago, and the AIS-DSD Support Group published in 2017 found that affected persons, and care givers, object to the term, and that this may impact choice, access, and utilization of health care providers.[6] Australian sociological research on people born with atypical sex characteristics, published in 2016, found that 3% of respondents choose the term "disorders of sex development" or "DSD" to define their sex characteristics, while 21% use the term when accessing medical services. In contrast, 60% used the term "intersex" in some form to self-describe their sex characteristics.[50]
- A committee of the Senate of Australia found that labelling intersex as "pejorative" appeared to be a post-hoc rationalisation in the 2006 Consensus statement. It recommended a review of clinical use of the term.[51]
- Alternative terms have been offered: Milton Diamond has suggested the use of "variation"[52][53] or of "difference",[1] Elizabeth Reis has suggested "divergence";[54] Liao and Simmonds suggest "diverse sex development".[55] The latter suggestions would retain the initial D in DSD.
- The 2006 Consensus statement on management of intersex disorders stated that evidence for early surgery for cosmetic reasons is lacking, outcomes include "decreased sexual sensitivity" and long term outcome data is absent.[3] A 2016 Global Disorders of Sex Development Update since 2006 states that there is "still no consensual attitude regarding indications, timing, procedure and evaluation of outcome of DSD surgery" and "no evidence regarding the impact of surgically treated or non-treated DSDs during childhood for the individual, the parents, society or the risk of stigmatization".[31]
- In 2013, Juan E. Méndez, the United Nations Special Rapporteur on torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment, condemned "irreversible sex assignment, involuntary sterilization, involuntary genital normalizing surgery, performed without their informed consent, or that of their parents, 'in an attempt to fix their sex'" stating that "members of sexual minorities are disproportionately subjected to torture and other forms of ill-treatment because they fail to conform to socially constructed gender expectations".[56]
- In May 2014, the World Health Organization issued a joint statement on Eliminating forced, coercive and otherwise involuntary sterilization, An interagency statement with the OHCHR, UN Women, UNAIDS, UNDP, UNFPA and UNICEF. Referencing the involuntary surgical "sex-normalising or other procedures" on "intersex persons", the report recommends a range of guiding principles for medical treatment, including ensuring patient autonomy in decision-making, ensuring non-discrimination, accountability and access to remedies.[57]
- During 2015, the Council of Europe[9] and Inter-American Commission on Human Rights[10] called for a review of medical classifications that may unnecessarily medicalize intersex traits,[9][10][11] an end to medical interventions without consent, and improved disclosure. The Council of Europe's Human Rights Commissioner recommended:
National and international medical classifications which pathologise variations in sex characteristics should be reviewed with a view to eliminating obstacles to the effective enjoyment, by intersex persons, of human rights, including the right to the highest attainable standard of health.[9]
- The European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights[11] and UN Treaty Bodies have called for informed consent by individuals subjected to medical treatment, improved disclosure, and access to redress.[58][59]
Clinical disagreements about the term[]
While the 2006 clinical consensus statement that introduced the term,[3] its 2016 update,[31] included some sex chromosome anomalies within the term DSD, the inclusion of those conditions is opposed by some clinicians.[citation needed] Medical historian David Griffiths has identified continued controversy about the relationship between sex chromosome variations and intersex/DSD classifications.[60]
Similarly, some clinicians have proposed that congenital adrenal hyperplasia be excluded.[61] Human rights advocate Morgan Carpenter has remarked that this proposal appears motivated by support for contentious medical interventions.[62]
A member of the legal committee for the World Professional Association for Transgender Health and co-founder of the Australian and New Zealand Professional Association for Transgender Health has described "transsexualism" as "an intersex condition and a disorder of sexual development therapeutically medically treated by hormonal therapy and Genital Reassignment Surgery".[63] Such views are contested.[64]
Attitudes towards the term[]
Sociological research in Australia on 272 "people born with atypical sex characteristics," published in 2016, found that 3% of respondents used the term "disorders of sex development" or "DSD" to define their sex characteristics, while 21% use the term when accessing medical services. In contrast, 60% used the term "intersex" in some form to self-describe their sex characteristics.[50] U.S. research by the Lurie Children's Hospital, Chicago, and the AIS-DSD Support Group (now InterConnect Support Group) published in 2017 found that "disorders of sex development" terminology may negatively affect care, give offense, and result in lower attendance at medical clinics.[65][66]
A "dsd-LIFE" study in 2020 found that around 69% of 10,40 participants didn’t think the term disorders of sex development was offensive.[7]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Diamond M, Beh HG (January 2008). "Changes in the management of children with intersex conditions". Nature Clinical Practice. Endocrinology & Metabolism. 4 (1): 4–5. doi:10.1038/ncpendmet0694. hdl:10125/66380. PMID 17984980. S2CID 13382948.
- ^ "Differences in sex development". U.K. National Health Service (NHS). 2017-10-18. Retrieved 2020-04-10.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Lee PA, Houk CP, Ahmed SF, Hughes IA (August 2006). "Consensus statement on management of intersex disorders. International Consensus Conference on Intersex". Pediatrics. 118 (2): e488-500. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-0738. PMC 2082839. PMID 16882788.
- ^ Al-Salem AH (2020-01-02). Atlas of Pediatric Surgery: Principles and Treatment. Springer Nature. p. 863. ISBN 978-3-030-29211-9.
- ^ Lee PA, Nordenström A, Houk CP, Ahmed SF, Auchus R, Baratz A, et al. (2016). "Global Disorders of Sex Development Update since 2006: Perceptions, Approach and Care". Hormone Research in Paediatrics. 85 (3): 158–80. doi:10.1159/000442975. PMID 26820577.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Johnson EK, Rosoklija I, Finlayson C, Chen D, Yerkes EB, Madonna MB, et al. (December 2017). "Attitudes towards "disorders of sex development" nomenclature among affected individuals". Journal of Pediatric Urology. 13 (6): 608.e1-608.e8. doi:10.1016/j.jpurol.2017.03.035. PMID 28545802.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bennecke E, Köhler B, Röhle R, Thyen U, Gehrmann K, Lee P, et al. (May 2021). "Disorders or Differences of Sex Development? Views of Affected Individuals on DSD Terminology". Journal of Sex Research. 58 (4): 522–531. doi:10.1080/00224499.2019.1703130. PMID 31985272. S2CID 210923829. Archived from the original on 29 August 2020. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- ^ Jordan-Young RM, Sönksen PH, Karkazis K (April 2014). "Sex, health, and athletes". BMJ. 348: g2926. doi:10.1136/bmj.g2926. PMID 24776640. S2CID 2198650.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Council of Europe; Commissioner for Human Rights (April 2015), Human rights and intersex people, Issue Paper
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Comisión Interamericana de Derechos Humanos (November 12, 2015), Violencia contra Personas Lesbianas, Gays, Bisexuales, Trans e Intersex en América (PDF) (in Spanish)
- ^ Jump up to: a b c European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights (April 2015), The fundamental rights situation of intersex people (PDF)
- ^ Hughes, Ieuan A. (February 2008). "Disorders of sex development: a new definition and classification". Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 22 (1): 119–134. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2007.11.001.
In its place, a consensus statement recommends the term ‘disorder of sex development’ (DSD), a generic definition encompassing any problem noted at birth where the genitalia are atypical in relation to the chromosomes or gonads.
- ^ UN Committee against Torture; UN Committee on the Rights of the Child; UN Committee on the Rights of People with Disabilities; UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment; Juan Méndez, Special Rapporteur on torture and other cruel inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment; Dainius Pῡras Special Rapporteur on the right of everyone to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health; Dubravka Šimonoviæ, Special Rapporteur on violence against women its causes and consequences; Marta Santos Pais, Special Representative of the UN Secretary-General on Violence against Children; African Commission on Human and Peoples' Rights; Council of Europe Commissioner for Human Rights; Inter-American Commission on Human Rights (October 24, 2016), "Intersex Awareness Day – Wednesday 26 October. End violence and harmful medical practices on intersex children and adults, UN and regional experts urge", Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights
- ^ Kim KS, Kim J (January 2012). "Disorders of sex development". Korean Journal of Urology. 53 (1): 1–8. doi:10.4111/kju.2012.53.1.1. PMC 3272549. PMID 22323966.
- ^ Witchel SF (April 2018). "Disorders of sex development". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology. 48: 90–102. doi:10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2017.11.005. PMC 5866176. PMID 29503125.
- ^ Hughes, Ieuan A. (February 2008). "Disorders of sex development: a new definition and classification". Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 22 (1): 119–134. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2007.11.001.
Adding some diagnostic specificity to the generic DSD definition utilizes knowledge of the karyotype. This is based on recognizing the central role of karyotype analysis in the investigation of most cases of DSD, and knowledge in general about sex chromosomes.
- ^ O'Connell MA, Hutson GM, Grover SR (2020-06-10). "Medical management of DSD". In Hutson JM, Grover SR, O'Connell MA, Bouty A, Hanna C (eds.). Disorders|Differences of Sex Development: An Integrated Approach to Management. Springer Nature. p. 204. ISBN 978-981-13-7864-5.
- ^ Cools M, Nordenström A, Robeva R, Hall J, Westerveld P, Flück C, et al. (July 2018). "Caring for individuals with a difference of sex development (DSD): a Consensus Statement". Nature Reviews. Endocrinology. 14 (7): 415–429. doi:10.1038/s41574-018-0010-8. PMC 7136158. PMID 29769693.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Zderic SA, Canning DA, Carr MC, Snyder III HM, eds. (2002). Pediatric gender assignment: a critical reappraisal; [proceedings from a conference ... in Dallas in the spring of 1999. New York, NY: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers. ISBN 978-0-306-46759-2.[page needed]
- ^ García-Acero M, Moreno O, Suárez F, Rojas A (January 2020). "Disorders of Sexual Development: Current Status and Progress in the Diagnostic Approach". Current Urology. 13 (4): 169–178. doi:10.1159/000499274. PMC 6976999. PMID 31998049.
- ^ Kim KS, Kim J (January 2012). "Disorders of sex development". Korean Journal of Urology. 53 (1): 1–8. doi:10.4111/kju.2012.53.1.1. PMC 3272549. PMID 22323966.
- ^ "Disorders of Sex Differentiation". Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved 2021-08-04.
- ^ Legato MJ (2017-05-15). Principles of Gender-Specific Medicine: Gender in the Genomic Era. Academic Press. p. 31. ISBN 978-0-12-803542-9.
- ^ Nistal M, González-Peramato P, Serrano A (2017-03-07). Clues in the Diagnosis of Non-tumoral Testicular Pathology. Springer. p. 41. ISBN 978-3-319-49364-0.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Nistal M, González-Peramato P, Serrano Á (2017-03-07). Clues in the Diagnosis of Non-tumoral Testicular Pathology. Springer. p. 33. ISBN 978-3-319-49364-0.
- ^ Legato MJ (2017-05-15). Principles of Gender-Specific Medicine: Gender in the Genomic Era. Academic Press. p. 38. ISBN 978-0-12-803542-9.
- ^ Parween S, Fernández-Cancio M, Benito-Sanz S, Camats N, Rojas Velazquez MN, López-Siguero JP, et al. (April 2020). "Molecular Basis of CYP19A1 Deficiency in a 46,XX Patient With R550W Mutation in POR: Expanding the PORD Phenotype". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 105 (4): e1272–e1290. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa076. PMID 32060549.
- ^ Miller WL (January 2012). "The syndrome of 17,20 lyase deficiency". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 97 (1): 59–67. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-2161. PMC 3251937. PMID 22072737.
- ^ "X & Y Variations". The Focus Foundation. Archived from the original on 13 January 2013.
- ^ Fullerton G, Hamilton M, Maheshwari A (March 2010). "Should non-mosaic Klinefelter syndrome men be labelled as infertile in 2009?". Human Reproduction. 25 (3): 588–97. doi:10.1093/humrep/dep431. PMID 20085911.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Lee PA, Nordenström A, Houk CP, Ahmed SF, Auchus R, Baratz A, et al. (January 28, 2016). "Global Disorders of Sex Development Update since 2006: Perceptions, Approach and Care". Hormone Research in Paediatrics. 85 (3): 158–80. doi:10.1159/000442975. PMID 26820577.
- ^ "Ovotesticular Disorder of Sex Development". Rare Disease Database. National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD). Retrieved 2021-08-01.
- ^ "46,XX testicular disorder of sex development". Rare Disease Database. National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD). Retrieved 2021-08-04.
- ^ Hutson JM, Grover SR, O'Connell MA, Bouty A, Hanna CA (2020-06-10). Disorders|Differences of Sex Development: An Integrated Approach to Management. Springer Nature. p. 204. ISBN 978-981-13-7864-5.
- ^ "Disorders/Differences of Sex Development (DSD) - Translational Research Network". NIH RePORTER. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Retrieved 2021-01-18.
- ^ Baratz AB, Devore T, Jones A, Lake J, Moran L, Robertson M, Walsh K, Zieselman K, et al. (Advocacy Advisory Network (AAN)) (November 24, 2015). "NIH Translational Research Network and NIH Research Coordinating Committee For Sexual and Gender Minorities" (PDF).
- ^ Dreger AD (2015-11-21), Rejecting the Tranquilizing Drug of Gradualism in Intersex Care
- ^ Devore T (2015-11-21), Tiger Devore's Statement
- ^ "I-DSD/I-CAH/I-TS Registries". home.i-dsd.org. Retrieved 2021-01-18.
- ^ "7th I-DSD Symposium 2019". I-CAH. 2018-08-29. Retrieved 2021-01-18.
- ^ "An Interview with Dr. Tiger Howard Devore PhD". We Who Feel Differently. February 7, 2011.
- ^ interACT (May 2016). "interACT Statement on Intersex Terminology". Interact Advocates for Intersex Youth. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ Briffa T (8 May 2014). "Disorders of Sex Development". Organisation Intersex International Australia.
- ^ "Why Not "Disorders of Sex Development"?". UK Intersex Association. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ Intersex Human Rights Australia (2019-05-23). "Joint statement on the International Classification of Diseases 11".
- ^ Crittenton A (2019-05-24). "World Health Organization condemned for classifying intersex as 'disorder'". Gay Star News. Retrieved 2019-06-02.
- ^ Leighton-Dore S (2019-05-28). "World Health Organisation drops transgender from list of mental health disorders". SBS. Retrieved 2019-06-02.
- ^ Barr S (2019-05-28). "Transgender no longer classified as 'mental disorder' by WHO". The Independent. Retrieved 2019-06-02.
- ^ Wills E (2019-05-29). "Campaigners hail changes to WHO classification of trans health issues". Evening Standard. Retrieved 2019-06-02.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Jones T, Hart B, Carpenter M, Ansara G, Leonard W, Lucke J (2016). Intersex: Stories and Statistics from Australia (PDF). Cambridge, UK: Open Book Publishers. ISBN 978-1-78374-208-0. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 September 2016. Retrieved 2 February 2016.
- ^ "Involuntary or coerced sterilisation of intersex people in Australia". Senate Community Affairs Committee. October 2013.
- ^ Beh H, Diamond M (2006). "Variations of Sex Development Instead of Disorders of Sex Development". Archives of Disease in Childhood (26 July 2006).
- ^ Tamar-Mattis A, Diamond M (April 2007). "Managing variation in sex development". Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism. 20 (4): 552–3. PMID 17550222.
- ^ Reis E (2007). "Divergence or disorder?: the politics of naming intersex". Perspectives in Biology and Medicine. 50 (4): 535–43. doi:10.1353/pbm.2007.0054. PMID 17951887. S2CID 17398380.
- ^ Liao LM, Simmonds M (2013). "A values-driven and evidence-based health care psychology for diverse sex development" (PDF). Psychology & Sexuality. 5 (1): 83–101. doi:10.1080/19419899.2013.831217. ISSN 1941-9899. S2CID 36307047.
- ^ Méndez J (February 2013). Report of the Special Rapporteur on torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment, A.HRC.22.53 (PDF).
- ^ "Eliminating forced, coercive and otherwise involuntary sterilization, An interagency statement". World Health Organization. May 2014.
- ^ United Nations; Committee on the Rights of Persons with Diabilities (April 17, 2015), Concluding observations on the initial report of Germany (advance unedited version), Geneva: United Nations
- ^ United Nations; Committee on the Rights of Child (February 26, 2015), Concluding observations on the combined second to fourth periodic reports of Switzerland, Geneva: United Nations
- ^ Griffiths DA (February 2018). "Shifting syndromes: Sex chromosome variations and intersex classifications". Social Studies of Science. 48 (1): 125–148. doi:10.1177/0306312718757081. PMC 5808814. PMID 29424285.
- ^ González R, Ludwikowski BM (2016). "Should CAH in Females Be Classified as DSD?". Frontiers in Pediatrics. 4: 48. doi:10.3389/fped.2016.00048. PMID 27242977. S2CID 16478320.
- ^ Carpenter M (April 2021). "Intersex human rights, sexual orientation, gender identity, sex characteristics and the Yogyakarta Principles plus 10". Culture, Health & Sexuality. 23 (4): 516–532. doi:10.1080/13691058.2020.1781262. PMID 32679003. S2CID 220631036.
- ^ Wallbank R (2015). "The Legal Status of People who Experience Difference in Sexual Formation and Gender Expression in Australia". The legal status of transsexual and transgender persons. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Intersentia. pp. 457–526. doi:10.1017/9781780685588.022. ISBN 978-1-78068-196-2.
- ^ Costello CG (2016). "Intersex and Trans* Communities: Commonalities and Tensions". Transgender and Intersex: Theoretical, Practical, and Artistic Perspectives. New York: Palgrave Macmillan US. pp. 83–113. doi:10.1057/978-1-349-71325-7_4. ISBN 978-1-137-54352-3.
- ^ Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago (11 May 2017). "Term "Disorders of Sex Development" May Have Negative Impact". Newswise. Archived from the original on 15 May 2017. Retrieved 11 May 2017.
- ^ Johnson EK, Rosoklija I, Finlayson C, Chen D, Yerkes EB, Madonna MB, et al. (December 2017). "Attitudes towards "disorders of sex development" nomenclature among affected individuals". Journal of Pediatric Urology. 13 (6): 608.e1-608.e8. doi:10.1016/j.jpurol.2017.03.035. PMID 28545802.
Further reading[]
- Lee PA, Houk CP, Ahmed SF, Hughes IA (August 2006). "Consensus statement on management of intersex disorders. International Consensus Conference on Intersex". Pediatrics. 118 (2): e488-500. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-0738. PMC 2082839. PMID 16882788.
- Lee PA, Nordenström A, Houk CP, Ahmed SF, Auchus R, Baratz A, et al. (January 28, 2016). "Global Disorders of Sex Development Update since 2006: Perceptions, Approach and Care". Hormone Research in Paediatrics. 85 (3): 158–80. doi:10.1159/000442975. PMID 26820577.
External links[]
| Classification |
|
|---|
- "Disorders of Sex Development Research". – Provides information regarding the causes, frequency and implications of DSD.
- "Accord Alliance". – Approaches to care for people that are affected by differences of sex development (DSD).
- "Disorders of Sex Development (DSD) Resources". YourChild. University of Michigan Health System.
- "Sex Development". Toronto: The Hospital for Sick Children. An Overview Animation of prenatal genital development
- "Handbook for Parents". Consortium on the Management of Disorders of Sex Development.
- "Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Disorders of Sex Development in Childhood". Consortium on the Management of Disorders of Sex Development.
- Intersex
- Congenital disorders of genital organs
- Intersex and medicine