English Americans
 English Americans and Canadians as percent of population by state and province. | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 23,593,434 (2019)[1] 50,000,000+ | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Throughout the entire United States | |
| California | 4,946,554[4] |
| Texas | 3,083,323[4] |
| Ohio | 2,371,236[4] |
| New York | 2,320,503[4] |
| Florida | 2,232,514[4] |
| Michigan | 2,036,021[4] |
| Illinois | 1,808,333[4] |
| North Carolina | 1,778,008[4] |
| Georgia | 1,584,303[4] |
| Tennessee | 1,435,147[4] |
| Pennsylvania | 1,058,737[5] |
| Languages | |
| English (American and British English dialects) | |
| Religion | |
| |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Other English diaspora, American ancestry, Old Stock Americans, other British Americans | |
| Part of a series on |
| English people |
|---|
| Culture |
| Music |
| Language |
| Cuisine |
| Dance |
| Religion |
| People |
| Diaspora |
|
English Americans, or Anglo-Americans are Americans whose ancestry originates wholly or partly in England. In the 2019 American Community Survey, 23.59 million self-identified as being of English origin.[6]
The term is distinct from British Americans, which includes not only English Americans but also Scottish, Scotch-Irish ( descended from Ulster-Scots from Ulster), Welsh, Cornish and Manx Americans from the whole of the United Kingdom. Demographers regard the reported number of English Americans as a serious undercount, as the index of inconsistency is high and many if not most Americans from English stock have a tendency to identify simply as "Americans"[7][8][9][10] or if of mixed European ancestry, identify with a more recent and differentiated ethnic group.[11] In the 1980 Census, over 49 million (49,598,035) Americans claimed English ancestry. At 26.34%, this was the largest group amongst the 188 million people who reported at least one ancestry. The population was 226 million which would have made the English ancestry group 22% of the total.[12] Scotch-Irish Americans are for the most part descendants of Lowland Scots and Northern English (specifically - County Durham, Cumberland, Northumberland and Yorkshire) settlers who colonized Ireland during the Plantation of Ulster in the 17th century.
In 1982, an opinion poll showed respondents a card listing a number of ethnic groups and asked, "Thinking both of what they have contributed to this country and have gotten from this country, for each one tell me whether you think, on balance, they've been a good or a bad thing for this country." The English were the top ethnic group, with 66% saying they were a good thing for the United States, followed by the Irish at 62%. Ben J. Wattenberg argues that this poll demonstrates a general American bias against Latino and other recent immigrant populations.[13]
The majority of the Founding Fathers of the United States were of English ancestry. English immigrants in the 19th century, as with other groups, sought economic prosperity. They began migrating in large numbers, without state support, in the 1840s and continued into the 1890s.[14]
Sense of identity[]

Americans of English heritage are often seen, and identify, as simply "American" due to the many historic cultural ties between England and the U.S. and their influence on the country's population. Relative to ethnic groups of other European origins, this may be due to the early establishment of English settlements; as well as to non-English groups having emigrated in order to establish significant communities.[15]
Since 1776, English Americans have been less likely to proclaim their heritage, unlike Latino Americans, African Americans, Italian Americans, Irish Americans, Native Americans or other ethnic groups. A leading specialist, Charlotte Erickson, found them to be ethnically "invisible," dismissing the occasional St. George Societies as ephemeral elite clubs that were not in touch with a larger ethnic community.[16] In Canada, by contrast, the English organized far more ethnic activism, as the English competed sharply with the well-organized French and Irish elements.[17] In the United States the Scottish immigrants were much better organized than the English in the 19th century, as were their descendants in the late 20th century.[18]
Number of English Americans[]
| Results per U.S. census | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Population | Percent | ||
| 1980[19][20] | 49,598,035 | 26.34 | ||
| 1990[21] | 32,651,788 | 13.1 | ||
| 2000[22] | 24,515,138 | 8.7 | ||
| 2018[23] | 22,807,283 | N/D | ||
The original 17th century settlers were overwhelmingly English. From the time of the first permanent English presence in the New World until 1900, these immigrants and their descendants outnumbered all others firmly establishing the English cultural pattern as predominant for the American version.[24]
Colonial period[]
According to studies and estimates, the ethnic populations in the British American Colonies of 1700, 1755 and 1775 were:
| Ethnic composition of the American Colonies | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1700 / % | 1755 / % | 1775 / % | |||
| English / Welsh | 80.0 | English / Welsh | 52.0 | English | 48.7 |
| African | 11.0 | African | 20.0 | African | 20.0 |
| Dutch | 4.0 | German | 7.0 | Scots-Irish | 7.8 |
| Scottish | 3.0 | Scots-Irish | 7.0 | German | 6.9 |
| Other European | 2.0 | Irish | 5.0 | Scottish | 6.6 |
| - | - | Scottish | 4.0 | Dutch | 2.7 |
| - | - | Dutch | 3.0 | French | 1.4 |
| - | - | Other European | 2.0 | Swedish | 0.6 |
| - | - | - | - | Other | 5.3 |
| 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||
| Source:[25][26][27] (*Province of Georgia not included) | |||||
| Colonial English ancestry 1776[28] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colonies | Percent of approx population | |||
| New England | 70.5 | |||
| Middle | 40.6 | |||
| Southern | 37.4 | |||
Data[]
National origins: 1790-1900[]
The ancestries of the population in 1790 (the first national population census) has been estimated by various sources, first in 1909, then again in 1932, 1980 and 1984 by sampling distinctive surnames in the census and assigning them a country of origin. There is debate over the accuracy between the studies with individual scholars and the Federal Government using different techniques and conclusion for the ethnic composition.[29][30] A study published in 1909 titled A Century of Population Growth. From the First to the Twelfth census of the United States: 1790-1900 by the Government Census Bureau estimated the English were 83.5%, 6.7% Scottish, 1.6% Irish, 2.0% Dutch, 0.5% French, 5.6% German and 0.1% all others of the white population.[31] Hebrews were less than one-tenth of 1 per cent. When the Scotch and Irish are added, British origins would be more than 90% of the European stock.[32][33][34] The same 1909 data for each state (of the total European population only) of English stock were Connecticut 96.2%, Rhode Island 96.0%, Vermont 95.4%, Massachusetts 95.0%, New Hampshire 94.1%, Maine 93.1%, Virginia 85.0%, Maryland 84.0%, North Carolina 83.1%, South Carolina 82.4%, New York 78.2% and Pennsylvania 59.0%.[35]
Another source by Thomas L. Purvis in 1984[36] estimated that people of English ancestry made up about 47.5% of the total population or 60.9% of the European American or white population (his figures can also be found, and as divided by region, in Colin Bonwick, The American Revolution, 1991 p. 2540-839-1346-2).[36][37] The study which gives similar results can be found in The American Revolution, Colin Bonwick in percentages for 1790: 47.9 English, 3.5 Welsh, 8.5 Scotch Irish (Ulster), 4.3 Scottish, 4.7 Irish (South), 7.2 German, 2.7 Dutch, 1.7 French, 0.2 Swedish, 19.3 Black. The difference between the two estimates are found by comparing the ratios of the groups (adding and subtracting) to accommodate and adding the Welsh.[38] The category 'Irish' in the Bonwick study represents immigrants from Ireland outside the Province of Ulster, the overwhelming majority of whom were Protestant and not ethnically Irish, though from Ireland. They were not Irish Catholics. By the time the American War for Independence started in 1776, Catholics were 1.6%, or 40,000 persons of the 2.5 million population of the 13 colonies.[39][40] Some 80.7% of the total United States population was of European origin.[41]
Using the first model above, in 1900, an estimated 28,375,000 or 37.8% of the population of the United States was wholly or partly of English ancestry from colonial stock. The estimate was based on the Census Bureaus Estimate that approximately thirty five million white Americans were descended from colonial forebears[42]
Census: 1980-2000[]
In 1980, 23,748,772 Americans claimed only English ancestry and another 25,849,263 claimed English along with another ethnic ancestry.[43] 13.3 million or 5.9% of the total U.S. population chose to identify as "American" (counted under "not specified") as also seen in censuses that followed.[44] Below shows the persons who reported at least one specific ancestry are as follows.[45][46]
| Response | Number | Percent | Northeast | North Central |
South | West | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single ancestry | 23,748,772 | 47.9 | 2,984,931 | 4,438,223 | 12,382,681 | 3,942,937 | |
| Multiple ancestry | 25,849,263 | 52.1 | 5,190,045 | 7,099,961 | 7,235,689 | 6,323,568 | |
| Totals | 49,598,035 | 8,174,976 | 11,538,184 | 19,618,370 | 10,266,505 | ||
In 1990, the national level response rate for the question was high with 90.4% of the total United States population choosing at least one specific ancestry and 9.6% ignored the question completely. Of those who chose English, 66.9% of people chose it as their first response. Totals for the English showed a considerable decrease from the previous census.[47] Responses for "American" slightly decreased both numerically and as a percentage from 5.9% to 5.2% in 1990 with most being from the South.[48]
| Response | Number | Percent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| First ancestry | 21,834,160 | 66.9% | |
| Second ancestry | 10,817,628 | 33.1% | |
| Totals | 32,651,788 | ||
In the 2000 census, 24.5 million or 8.7% of Americans reported English ancestry, a decline of some eight million people. At the national level, the response rate for the ancestry question fell to 80.1% of the total U.S. population, while 19.9% were unclassified or ignored the question completely. It was the fourth largest ancestral group.[49] Some Cornish Americans may not identify as English American, even though Cornwall had been part of England since long before their ancestors arrived in North America. Responses were:[50]
| Response | Number | change, 1990-2000 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| First ancestry | 16,623,938 | -24.9% | |
| Second ancestry | 7,885,754 | ||
| Totals | 24,509,692 | ||
Geographical distribution[]

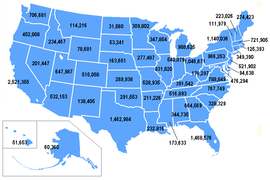

States[]

English Americans are found in large numbers throughout the United States, particularly in the Northeast, South and West. According to the 2000 US census, the 10 states with the largest populations of self-reported English Americans are:
| No. | State | Number | No. | State | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | California | (3,521,355 - 7.4% of state population) | 1 | Utah | 29.0 |
| 2 | Florida | (1,468,576 - 9.2%) | 2 | Maine | 21.5 |
| 3 | Texas | (1,462,984 - 7%) | 3 | Vermont | 18.4 |
| 4 | New York | (1,140,036 - 6%) | 4 | Idaho | 18.1 |
| 5 | Ohio | (1,046,671 - 9.2%) | 5 | New Hampshire | 18.0 |
| 6 | Pennsylvania | (966,253 - 7.9%) | 6 | Wyoming | 15.9 |
| 7 | Michigan | (988,625 - 9.9%) | 7 | Oregon | 13.2 |
| 8 | Illinois | (831,820 - 6.7%) | 8 | Montana | 12.7 |
| 9 | Virginia | (788,849 - 11.1%) | 9 | Delaware | 12.1 |
| 10 | North Carolina | (767,749 - 9.5%) | 10 | Colorado, Rhode Island, Washington | 12.0 each |
English was the highest reported European ancestry in the states of Maine, Vermont and Utah; joint highest along with German in the Carolinas.
Cities[]
Following are the top 20 highest percentages of people of English ancestry, in U.S. communities with 500 or more total inhabitants (for the total list of the 101 communities, see the reference):[51]
| Rank | City | State | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hildale | Utah | 66.9 |
| 2 | Colorado City | Arizona | 52.7 |
| 3 | Milbridge | Maine | 41.1 |
| 4 | Panguitch | Utah | 40 |
| 5 | Beaver | Utah | 39.8 |
| 6 | Enterprise | Utah | 39.4 |
| 7 | East Machias | Maine | 39.1 |
| 8 | Marriott-Slaterville | Utah | 38.2 |
| 9 | Wellsvile | Utah | 37.9 |
| 10 | Morgan | Utah | 37.2 |
| 11 | Harrington | Maine | 36.9 |
| 12 | Farmington | Utah | 36.9 |
| 13 | Highland | Utah | 36.7 |
| 14 | Nephi | Utah | 36.4 |
| 15 | Fruit Heights | Utah | 35.9 |
| 16 | Addison | Maine | 35.6 |
| 17 | Farr West | Utah | 35.4 |
| 18 | Hooper | Utah | 35.0 |
| 19 | Lewiston | Utah | 35.0 |
| 20 | Plain City | Utah | 34.7 |
On the top right, a map showing percentages by county of Americans who declared English ancestry in the 2000 Census. Dark blue and purple colours indicate a higher percentage: highest in the east and west (see also Maps of American ancestries). Center, a map showing the population of English Americans by state. On the right, a map showing the percentages of English Americans by state.
History[]

Early settlement and colonization[]
English settlement in America began with Jamestown in the Virginia Colony in 1607. With the permission of James I, three ships (the Susan Constant, The Discovery, and The God Speed) sailed from England and landed at Cape Henry in April, under the captainship of Christopher Newport,[14] who had been hired by the London Company to lead expeditions to what is now America.[52]

The second successful colony was Plymouth Colony, founded in 1620 by people who later became known as the Pilgrims. Fleeing religious persecution in the East Midlands in England, they first went to Holland, but feared losing their English identity.[53] Because of this, they chose to relocate to the New World, with their voyage being financed by English investors. In September 1620, 102 passengers set sail aboard the Mayflower, eventually settling at Plymouth Colony in November.[54] Of the passengers on the Mayflower, 41 men signed the "Mayflower Compact" aboard ship on November 11, 1620, while anchored in Provincetown Harbor. Signers included Carver, Alden, Standish, Howland, Bradford, Allerton, and Fuller.[55][56] This story has become a central theme in the United States cultural identity.
A number of English colonies were established under a system of proprietary governors, who were appointed under mercantile charters to English joint stock companies to found and run settlements.
England also took over the Dutch colony of New Netherland (including the New Amsterdam settlement), renaming it the Province of New York in 1664.[57] With New Netherland, the English came to control the former New Sweden (in what is now Delaware), which the Dutch had conquered from Sweden earlier.[58] This became part of Pennsylvania.
English immigration after 1776[]
Cultural similarities and a common language allowed English immigrants to integrate rapidly and gave rise to a unique Anglo-American culture. An estimated 3.5 million English immigrated to the U.S. after 1776.[59] English settlers provided a steady and substantial influx throughout the 19th century.
| English immigration to the United States | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Period | Arrivals | Period | Arrivals |
| 1820-1830 | 15,837 | 1901-1910 | 388,017 |
| 1831-1840 | 7,611 | 1911-1920 | 249,944 |
| 1841-1850 | 32,092 | 1921-1930 | 157,420 |
| 1851-1860 | 247,125 | 1931-1940 | 21,756 |
| 1861-1870 | 222,277 | 1941-1950 | 112,252 |
| 1871-1880 | 437,706 | 1951-1960 | 156,171 |
| 1881-1890 | 644,680 | 1961-1970 | 174,452 |
| 1891-1900 | 216,726 | 1971-1980 | - |
| Total (1820-1970): 3,084,066[60][61][62] | |||
The first wave of growing English immigration began in the late 1820s and was sustained by unrest in the United Kingdom until it peaked in 1842 and declined slightly for nearly a decade. Most of these were small farmers and tenant farmers from depressed areas in rural counties in southern and western England and urban laborers who fled from the depressions and from the social and industrial changes of the late 1820s-1840s. While some English immigrants were drawn by dreams of creating model utopian societies in America, most others were attracted by the lure of new lands, textile factories, railroads, and the expansion of mining.
A number of English settlers moved to the United States from Australia in the 1850s (then a British political territory), when the California Gold Rush boomed; these included the so-called "Sydney Ducks" (see Australian Americans).
During the last years of the 1860s, annual English immigration grew to over 60,000 and continued to rise to over 75,000 per year in 1872, before experiencing a decline. The final and most sustained wave of immigration began in 1879 and lasted until the depression of 1893. During this period English annual immigration averaged more than 82,000, with peaks in 1882 and 1888 and did not drop significantly until the financial panic of 1893.[63] The building of America's transcontinental railroads, the settlement of the great plains, and industrialization attracted skilled and professional emigrants from England.
| English-born in the United States | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Population | % of foreign-born | |
| 1850 | 278,675 | 12.4 | |
| 1860 | 431,692 | - | |
| 1870 | 550,924 | 10.0 | |
| 1880 | 662,676 | - | |
| 1890 | 908,141 | 9.8 | |
| 1900 | 840,513 | - | |
| 1910 | 877,719 | 6.5 | |
| 1920 | 813,853 | - | |
| 1930 | 809,563 | 5.7 | |
| 1940 | - | - | |
| 1950 | - | - | |
| 1960 | 528,205 | 5.4 | |
| 1970 | 458,114 | 4.8 | |
| 1980 | 442,499 | - | |
| 1990 | 405,588 | - | |
| 2000 | 423,609 | - | |
| 2010 | 356,489 | 0.9 | |
| Source:[63][64][65] | |||
Also, cheaper steamship fares enabled unskilled urban workers to come to America, and unskilled and semiskilled laborers, miners, and building trades workers made up the majority of these new English immigrants. While most settled in America, a number of skilled craftsmen remained itinerant, returning to England after a season or two of work. Groups of English immigrants came to America as missionaries for the Salvation Army and to work with the activities of the Evangelical and LDS Churches.
The depression of 1893 sharply decreased English emigration to the United States, and it stayed low for much of the twentieth century. This decline reversed itself in the decade of World War II when over 100,000 English (18 percent of all European immigrants) came from England. In this group was a large contingent of war brides who came between 1945 and 1948. In these years four women emigrated from England for every man.[63] In the 1950s, English immigration increased to over 150,000.and rose to 170,000 in the 1960s.[66] While differences developed, it is not surprising that English immigrants had little difficulty in assimilating to American life. The American resentment against the policies of the British government[67] was rarely transferred to English settlers who came to America in the first decades of the nineteenth century.
Political influence[]
As the earliest colonists of the United States, settlers from England and their descendants often held positions of power and made and enforced laws,[68] often because many had been involved in government back in England.[69] In the original 13 colonies, most laws contained elements found in the English common law system.[70]

The majority of the Founding Fathers of the United States were of English extraction. A minority were of high social status and can be classified as White Anglo-Saxon Protestant (WASP). Many of the prewar WASP elite were Loyalists who left the new nation.[71]
While WASPs (White Anglo-Saxon Protestants usually of English origins) have been major players in every major American political party, an exceptionally strong association has existed between WASPs and the Republican Party, before the 1980s. A few top Democrats qualified, such as Franklin D. Roosevelt. Northeastern Republican leaders such as Leverett Saltonstall of Massachusetts, Prescott Bush of Connecticut and especially Nelson Rockefeller of New York exemplified the pro-business liberal Republicanism of their social stratum, espousing internationalist views on foreign policy, supporting social programs, and holding liberal views on issues like racial integration. A famous confrontation was the 1952 Senate election in Massachusetts where John F. Kennedy, a Catholic of Irish descent, defeated WASP Henry Cabot Lodge, Jr.. However the challenge by Barry Goldwater in 1964 to the Eastern Republican establishment helped undermine the WASP dominance.[72] Goldwater himself had solid WASP credentials through his mother, of a prominent old Yankee family, but was instead mistakenly seen as part of the Jewish community (which he had never associated with). By the 1980s, the liberal Rockefeller Republican wing of the party was marginalized, overwhelmed by the dominance of the Southern and Western conservative Republicans.[73]
Asking "Is the WASP leader a dying breed?" journalist Nina Strochlic in 2012 pointed to eleven WASP top politicians—typically scions of upper class English families. She ended with Republicans G.H.W. Bush elected in 1988, his son George W. Bush elected in 2000 and 2004, and John McCain, who was nominated but defeated in 2008.[74]
Language[]

English is the most commonly spoken language in the U.S, where it is estimated that two thirds of all native speakers of English live.[75] The American English dialect developed from English colonization. It serves as the de facto official language, the language in which government business is carried out. According to the 1990 census, 94% of the U.S. population speak only English.[76] Adding those who speak English "well" or "very well" brings this figure to 96%.[76] Only 0.8% speak no English at all as compared with 3.6% in 1890. American English differs from British English in a number of ways, the most striking being in terms of pronunciation (for example, American English retains the pronunciation of the letter "R" after vowels, unlike standard British English, though it still can be heard in several regional dialects in England) and spelling (one example is the "u" in words such as color, favor (US) vs colour, favour (UK)). Less obvious differences are present in grammar and vocabulary. The differences are rarely a barrier to effective communication between American English and British English speakers, but there are certainly enough differences to cause occasional misunderstandings, usually surrounding slang or dialect differences.
Some states, like California, have amended their constitutions to make English the only official language, but in practice, this only means that official government documents must at least be in English, and does not mean that they should be exclusively available only in English. For example, the standard California Class C driver's license examination is available in 32 different languages.
Expression[]
"In for a penny, in for a pound" is an expression to mean, ("if you're going to take a risk at all, you might as well make it a big risk"), is used in the United States which dates back to the colonial period, when cash in the colonies was denominated in Pounds, shillings and Pence.[77] Today, the one-cent coin is commonly known as a penny. A modern alternative expression is "In for a dime, in for a dollar".
Cultural contributions[]

Much of American culture shows influences from English culture.
Cuisine[]
- Apple pie - New England was the first region to experience large-scale English colonization in the early 17th century, beginning in 1620, and it was dominated by East Anglian Calvinists, better known as the Puritans. Baking was a particular favorite of the New Englanders and was the origin of dishes seen today as quintessentially "American", such as apple pie and the oven-roasted Thanksgiving turkey.[78] "As American as apple pie" is a well-known phrase used to suggest that something is all-American.
- Roast Beef - In the middle of the 17th century a second wave of English immigrants began arriving in North America, settling mainly in the Chesapeake Bay region of Virginia and Maryland, expanding upon the Jamestown settlement. Their roast beef was often served with Yorkshire puddings and horseradish sauce.
Celebrations[]

- Thanksgiving was celebrated by English settlers to give thanks to God for helping the Pilgrims of Plymouth Colony survive the brutal winter. This feast lasted three days —as accounted by attendee Edward Winslow.[79][80][81]
Law[]
The American legal system also has its roots in English law.[82] For example, elements of the Magna Carta were incorporated into the United States constitution.[83] English law prior to the revolution is still part of the law of the United States, and provides the basis for many American legal traditions and policies. After the revolution, English law was again adopted by the now independent American States.[84]
Education[]
The first American schools in the thirteen original colonies opened in the 17th century. Boston Latin School was founded in 1635 and is both the first public school and oldest existing school in the United States.[85] The first free taxpayer-supported public school in North America, the Mather School, was opened in Dorchester, Massachusetts, in 1639.[86][87]
New England had a long emphasis on literacy in order that individuals could read the Bible. Harvard College was founded by the colonial legislature in 1636, and named after an early benefactor. Most of the funding came from the colony, but the college began to build an endowment from its early years.[88] Harvard at first focused on training young men for the ministry, but many alumni went into law, medicine, government or business. The college was a leader in bringing Newtonian science to the colonies.[89]
A school of higher education for both Native American young men and the sons of the colonists was one of the earliest goals of the leaders of the Colony of Virginia. The College of William & Mary was founded founded on February 8, 1693, under a royal charter (legally, letters patent) to "make, found and establish a certain Place of Universal Study, a perpetual College of Divinity, Philosophy, Languages, and other good arts and sciences...to be supported and maintained, in all time coming."[90] Named in honor of the reigning monarchs King William III and Queen Mary II, the college is the second oldest college in the United States. It hired the first law professor and trained many of the lawyers, politicians, and leading planters.[91] Students headed for the ministry were given free tuition.
Yale College was founded by Puritans in 1701, and in 1716 was relocated to New Haven, Connecticut. The conservative Puritan ministers of Connecticut had grown dissatisfied with the more liberal theology of Harvard, and wanted their own school to train orthodox ministers. However president Thomas Clap (1740–1766) strengthened the curriculum in the natural sciences and made Yale a stronghold of revivalist New Light theology.[92]
The Colonial Colleges are nine institutions of higher education chartered in the Thirteen Colonies before the United States of America became a sovereign nation after the American Revolution.[93] These nine have long been considered together, notably since the survey of their origins in the 1907 The Cambridge History of English and American Literature.[94] Seven of the nine colonial colleges became seven of the eight Ivy League universities: Harvard, Columbia, Princeton, Yale, University of Pennsylvania, Dartmouth, and Brown.
Music[]
- National anthem - The Star-Spangled Banner takes its melody from the 18th-century English song "To Anacreon in Heaven" written by John Stafford Smith for the Anacreontic Society, a men's social club in London. The lyrics were written by Francis Scott Key of English descent. This became a well-known and recognized patriotic song throughout the United States, which was officially designated as the U.S. national anthem in 1931.[95][96][97]
- Hail to the Chief - is the song to announce the arrival or presence of the President of the United States. English songwriter James Sanderson (c. 1769 – c. 1841), composed the music and was first performed in 1812 in New York.[98]
Before 1931, other songs served as the hymns of American officialdom.
- The Liberty Song - written by John Dickinson of English descent in 1768 to the music of Englishman William Boyce's "Heart of Oak", is perhaps the first patriotic song written in America. The song contains the line "by uniting we stand, by dividing we fall", the first recorded use of the sentiment.
- America (My Country, 'Tis of Thee) - whose melody was indirectly derived from the British national anthem,[99] also served as a de facto anthem before the adoption of "The Star-Spangled Banner."[100]
- Amazing Grace - written by English poet and clergyman John Newton became such an icon in American culture that it has been used for a variety of secular purposes and marketing campaigns, placing it in danger of becoming a cliché.[101]
- Yankee Doodle - is written and accredited to Englishman Dr. Richard Shuckburgh an army doctor. The tune comes from the English nursery rhyme Lucy Locket.[102]
English ballads, jigs, and hornpipes had a large influence on American folk music, eventually contributing to the formation of such genres as old time, country, bluegrass, and to a lesser extent, blues as well.
Sports[]

- Baseball was invented in England.[104] English lawyer William Bray recorded a game of baseball on Easter Monday 1755 in Guildford, Surrey; Bray's diary was verified as authentic in September 2008.[105][106] This early form of the game was apparently brought to North America by British immigrants. The first appearance of the term that exists in print was in "A Little Pretty Pocket-Book" in 1744, where it is called Base-Ball.[107]
- American football traces its roots to early versions of rugby football, played in England and first developed in American universities in the mid-19th century.[108]
English family names[]
In 2010, the top ten family names in the United States, seven have English origins or having possible mixed British Isles heritage, the other three being of Spanish origin.[109] Many African Americans have their origins in slavery (i.e. slave name) and ancestrally came to bear the surnames of their former owners. Many freed slaves either created family names themselves or adopted the name of their former master. Due to anti-German xenophobia during the first and second world wars, some German families anglicised their names.[110] For example changing "Schmidt" to "Smith," causing an increase of English names.
| Name | No. | Number | Country of Origin | England (2001)[111][112] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smith | 1 | 2,442,977 | England,[113] Scotland,[114] Ireland[115] (Common however also among German Americans who are likely originally held the surname "Schmidt") | Smith |
| Johnson | 2 | 1,932,812 | England, Scotland (Can also be an anglicization of the Dutch Jansen or Scandinavian Johansen, Johansson, Jonsson, etc.)[116][117] | |
| Williams | 3 | 1,625,252 | England, Wales[118] | Taylor |
| Brown | 4 | 1,437,026 | England, Ireland, Scotland[119] | Brown |
| Jones | 5 | 1,425,470 | England, Wales[120] | Williams |
| García | 6 | 1,166,120 | Spain,[121] Mexico and other Hispanic nations | Wilson |
| Miller | 7 | 1,161,437 | England, Ireland, or Scotland (Miller can be the anglicized version of Mueller/Müller - a surname from Germany)[122] | Johnson |
| Davis | 8 | 1,116,357 | England, Wales[123] | Davies |
| Rodríguez | 9 | 1,094,924 | Spain[124] | Robinson, Roderick |
| Martinez | 10 | 1,060,159 | Spain, Mexico and other Hispanic nations | Wright |
English place names in the United States[]


This is a partial list of places in the United States named after places in England as a result of the many English settlers and explorers; in addition, some places were named after the English royal family. These include the region of New England and some of the following:
Alabama[]
- Birmingham after Birmingham, England
- Brighton after Brighton, England
California[]
- Westminster after Westminster in London, England
- Exeter after Exeter, England
- Windsor after Windsor, Berkshire, in England
Delaware[]
- Dover after Dover, England
- Wilmington named by Proprietor Thomas Penn after his friend Spencer Compton, Earl of Wilmington, who was prime minister in the reign of George II of Great Britain.
Georgia[]
- Georgia was named after King George II.[126]
Maryland[]
- Maryland named so for Queen Henrietta Maria (Queen Mary).[127]
Massachusetts[]
- Boston after Boston, England[128]
- Braintree after Braintree, England
- Gloucester after Gloucester, England
- Northampton after Northampton, England
- Southampton after Southampton, England[129]
- Springfield after Springfield, Essex, England
New Hampshire[]
New Jersey[]
- Burlington County and Burlington after the English east-coast town of Bridlington.[132]
- Camden named by local Jacob Cooper after Charles Pratt, 1st Earl Camden.[133]
- Gloucester County and Gloucester City after the city of Gloucester / county of Gloucestershire in England.[134]
- Newark after the town of Newark-on-Trent, England[135]
New York[]
- Cornwall (originally "New Cornwall") after the county of Cornwall in southwest England
- Liverpool Village after Liverpool England.
- New York City (after the Duke of York[136])
- New York (State) (also after the Duke of York)
- Suffolk County after Suffolk, England
Pennsylvania[]
- Bedford and Bedford County after Bedford, England
- Berks County after Berkshire (pronounced "Barkshire"), England
- Bristol and Bristol Township after Bristol, England[137]
- Bucks County after Buckinghamshire, England
- Chester County and Chester after Chester, England
- Darby derived from Derby (pronounced "Darby"), the county town of Derbyshire (pronounced "Darbyshire")[138]
- Horsham after Horsham (pronounced "Hor-sham"), England
- Lancaster County and Lancaster after the city of Lancaster in the county of Lancashire in England, the native home of John Wright, one of the early settlers.[139]y
- New Castle after Newcastle upon Tyne, England
- Northampton County after Northamptonshire, England
- Reading, Berks County after Reading (pronounced "Redding"), Berkshire (pronounced "Barkshire"), England
- Trafford after Trafford Borough in Greater Manchester, England
- Warminster after the small town of Warminster in the county of Wiltshire, at the western extremity of Salisbury Plain, England.[140]
- Warrington after Warrington, England[141]
- Warwick after Warwick, England[142]
The Carolinas[]
- The province, named Carolina (The Carolinas-North and South) to honor King Charles I of England, was divided into SC and NC in 1729, although the actual date is the subject of debate.[143]
Virginia[]
- The name Virginia was first applied by Queen Elizabeth I (the "Virgin Queen") and Sir Walter Raleigh in 1584.[144]
- Norfolk after the county of Norfolk, England
- Portsmouth after Portsmouth, England[145]
- Richmond named by William Byrd II after Richmond, London where he spent part of his childhood.
- Suffolk after the county of Suffolk, England
Notable people[]
Presidents of English descent[]
 George Washington |  John Adams |  Thomas Jefferson |
 Abraham Lincoln |  Gerald Ford |  George W. Bush |
Most of the presidents of the United States have had English ancestry.[146] The extent of English heritage varies. Earlier presidents were predominantly of colonial English Yankee stock. Later presidents' ancestry can often be traced to ancestors from multiple nations in Europe, including England. The presidents who have lacked recent English ancestry are Martin Van Buren, James Buchanan, Woodrow Wilson, John F. Kennedy, and Donald Trump.[147]
18th century[]
George Washington,[148][149] John Adams[150]
19th century[]
Thomas Jefferson, James Madison[151] John Quincy Adams,[150] Andrew Jackson,[152][153] William Henry Harrison,[154] John Tyler,[155] Zachary Taylor, Millard Fillmore,[156] Franklin Pierce,[157] Abraham Lincoln,[158][159] Andrew Johnson,[160] Ulysses S. Grant, Rutherford B. Hayes,[161] James A. Garfield,[162] Chester A. Arthur, Grover Cleveland, Benjamin Harrison, William McKinley.
20th century[]
Theodore Roosevelt, William Howard Taft,[163][164] Warren G. Harding,[165] Calvin Coolidge,[166] Herbert Hoover, Franklin D. Roosevelt, Harry S. Truman,[167][168] Dwight D. Eisenhower, Lyndon B. Johnson, Richard Nixon, Gerald Ford, Jimmy Carter,[169] Ronald Reagan,[170] George H. W. Bush,[171][172] Bill Clinton.
21st century[]
George W. Bush,[173] Barack Obama,[174][175] Joe Biden[176]
See also[]
- American ethnicity
- Americans or American people
- Anglo America
- Anglo-Celtic Australian
- Boston Brahmin
- British American
- Demographic history of the United States
- English (ethnic group)
- English colonial empire
- English diaspora
- European American
- Immigration to the United States
- Maps of American ancestries
- Old Stock Americans
- Scotch-Irish American
- Scottish American
- Anglo-American relations
- Welsh American
- White Anglo-Saxon Protestant
- White Southerners
- Yankee
- Romanichal
References[]
- ^ "U.S. Census Bureau, 2019 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates". data.census.gov. Retrieved February 25, 2021.
- ^ "1980 United States census" (PDF). census.gov. Retrieved April 3, 2020.Archived 23 December 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ In the 1980 census, 49,598,035 Americans identified as being of English ancestry, although in later censuses most of these same people identified as being of "American" ancestry, when that was added as an option.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j "Rank of States for Selected Ancestry Groups with 100,000 or More Persons: 1980" (PDF). Census.gov. Retrieved 21 August 2017.Archived 29 July 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bureau, U.S. Census. "American FactFinder - Results". factfinder.census.gov. Archived from the original on 3 February 2012. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "U.S. Census Bureau, 2019 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates". data.census.gov. Retrieved February 25, 2021.
- ^ Pulera, Dominic (20 October 2004). Sharing the Dream: White Males in Multicultural America. A&C Black. ISBN 9780826416438. Retrieved 21 August 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ Reynolds Farley, 'The New Census Question about Ancestry: What Did It Tell Us?', Demography, Vol. 28, No. 3 (August 1991), pp. 414, 421.
- ^ Stanley Lieberson and Lawrence Santi, 'The Use of Nativity Data to Estimate Ethnic Characteristics and Patterns', Social Science Research, Vol. 14, No. 1 (1985), pp. 44-46.
- ^ Stanley Lieberson and Mary C. Waters, "Ethnic Groups in Flux: The Changing Ethnic Responses of American Whites", Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, Vol. 487, No. 79 (September 1986), pp. 82-86.
- ^ Mary C. Waters, Ethnic Options: Choosing Identities in America (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1990), p. 36.
- ^ "1980 United States Census" (PDF). Docs.google.com. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Ben J. Wattenberg (1985). "Chapter 14. The First Universal Nation". The Good News Is the Bad News Is Wrong. American Enterprise Institute. p. 77. ISBN 978-0-671-60641-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "English Emigration". Spartacus.schoolnet.co.uk. Archived from the original on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Lieberson, Stanley; Waters, Mary C. (1988). From Many Strands: Ethnic and Racial Groups in Contemporary America. Russell Sage Foundation. ISBN 9780871545435.
- ^ Charlotte Erickson, Invisible immigrants: the adaptation of English and Scottish immigrants in nineteenth-century America (1990)
- ^ Tanja Bueltmann, and Don MacRaild, "Globalizing St George: English associations in the Anglo-world to the 1930s" Journal of Global History (2012) 7#1 pp. 79-105
- ^ Rowland Berthoff, "Under the Kilt: Variations on the Scottish-American Ground" Journal of American Ethnic History (1982) 1#2 pp. 5-34 online
- ^ "Census.gov Persons Who Reported at Least One Specific Ancestry Group for the United States: 1980" (PDF). Census.gov. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "Rank of States for Selected Ancestry Groups with 100,00 or more persons: 1980" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 30 November 2012.
- ^ "1990 Census of Population Detailed Ancestry Groups for States" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. 18 September 1992. Retrieved 30 November 2012.
- ^ "Ancestry: 2000". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 12 February 2020. Retrieved 30 November 2012.
- ^ "U.S. Census Bureau, 2018 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates". data.census.gov. Retrieved April 3, 2020.
- ^ Powell, John (2009). Encyclopedia of North American Immigration. ISBN 9781438110127. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Boyer, Paul S.; Clark, Clifford E.; Halttunen, Karen; Kett, Joseph F.; Salisbury, Neal (1 January 2010). The Enduring Vision: A History of the American People. Cengage Learning. ISBN 9781111786090. Retrieved 21 August 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Scots to Colonial North Carolina Before 1775". Dalhousielodge.org. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "U.S. Federal Census :: United States Federal Census :: US Federal Census". 1930census.com. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Parrillo, Vincent N. (30 November 2015). Diversity in America. Routledge. ISBN 9781317261063. Retrieved 21 August 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ "People of Western European origin" (PDF). CSun.edu. Retrieved April 4, 2020.
- ^ Lieberson, Stanley; Waters, Mary C. (20 September 1988). From Many Strands: Ethnic and Racial Groups in Contemporary America. Russell Sage Foundation. ISBN 9780871545435. Retrieved 21 August 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ "A Century of Population Growth. From the First to the Twelfth census of the United States: 1790-1900" (PDF). census.gov. 1909. Retrieved April 4, 2020.
- ^ "A Century of Population Growth. From the First to the Twelfth census of the United States: 1790-1900" (PDF). census.gov. 1909. Retrieved April 4, 2020.
- ^ Rossiter, W. S. (1909). "A Century of Population Growth. From the First to the Twelfth census of the United States: 1790-1900" (PDF). Retrieved April 4, 2020.
- ^ Council, American Rearned (1969). Surnames in the United States Census of 1790: An Analysis of National Origins of the Population. ISBN 9780806300047. Retrieved April 4, 2020.
- ^ "A Century of Population Growth. From the First to the Twelfth census of the United States: 1790-1900 (P. 111-117)" (PDF). census.gov. 1909. Retrieved April 4, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Purvis, Thomas L. (1984). "The European Ancestry of the United States Population, 1790: A Symposium". The William and Mary Quarterly. 41 (1): 85–101. doi:10.2307/1919209. JSTOR 1919209.
- ^ Szucs, Loretto Dennis; Luebking, Sandra Hargreaves (2006). The Source. Ancestry Publishing. p. 361. ISBN 9781593312770. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
English US census 1790.
- ^ 1991, ISBN 0-8139-1346-2
- ^ Richard Middleton, Colonial America (2003), 95–100, 145, 158, 159, 349n
- ^ Maynard, 126-126
- ^ "Table 1. United States - Race and Hispanic Origin: 1790 to 1990" (PDF). Webcitation.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-02-25. Retrieved 2017-08-21.
- ^ Orth, Samuel Peter (21 August 2017). Our Foreigners: A Chronicle of Americans in the Making. Library of Alexandria. ISBN 9781465601483. Retrieved 21 August 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Census.gov Persons Who Reported at Least One Specific Ancestry Group for the United States: 1980" (PDF). Census.gov. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Ancestry of the Population by State: 1980 (Supplementary Report PC80-S1-10) Issued: April 1983
- ^ Single ancestry response by Region, Division and State - 1980 census
- ^ Multiple ancestry response by Region, Division and State - 1980 census
- ^ "1990 Census of Population Detailed Ancestry Groups for States" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. 18 September 1992. Retrieved 30 November 2012.
- ^ "1990 Census of Population Detailed Ancestry Groups for States" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. 18 September 1992. Retrieved 30 November 2012.
- ^ Ancestry: 2000 - Census 2000 Brief
- ^ First, Second, and Total Responses to the Ancestry Question - by Detailed Ancestry Code: 2000
- ^ "Top 101 cities with the most residents of English ancestry (population 500+)". Archived from the original on 2007-10-11. Retrieved 2007-08-02.
- ^ "Newport, Christopher". Infoplease.com. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "Bassetlaw Museum". Bassetlawmuseum.org.uk. Archived from the original on 13 October 2007. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "Pilgrims - Learn English". Learnenglish.org.uk. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Bradford, William (1898). "Book 2, Anno 1620" (PDF). In Hildebrandt, Ted (ed.). Bradford's History "Of Plimoth Plantation". Boston: Wright & Potter. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2006-06-01.
- ^ William Bradford, Edward Winslow (printer G. Mourt [George Morton], Relation or Iournall of the beginning and proceedings of the English Plantation setled at Plimoth in New England, Early English Books Online, p.4
- ^ "Digital History". Digitalhistory.uh.edu. Archived from the original on 18 April 2012. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "New Sweden". U-s-history.com. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "Synonyms Thesaurus with Antonyms & Definitions - Synonym.com". Trivia-library.com. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "Statistical Abstract of the United States". U.S. Government Printing Office. 21 August 2017. Retrieved 21 August 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Statistical Abstract of the United States". U.S. Government Printing Office. 21 August 2017. Retrieved 21 August 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Statistical Abstract of the United States". U.S. Government Printing Office. 21 August 1968. Retrieved 21 August 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Ward, David (1980). "Immigration: Settlement Patterns and Spatial Distribution". In Thernstrom, Stephan; Orlov, Ann; Handlin, Oscar (eds.). Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups. Harvard University Press. pp. 496–508. ISBN 0674375122. OCLC 1038430174.
- ^ "1850-2000" (PDF). Census.gov. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Patten, Eileen (21 February 2012). "Statistical Portrait of the Foreign-Born Population in the United States, 2010". Pewhispanic.org. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "English Americans - History, Contemporary england, Immigration, settlement, and employment, Acculturation and Assimilation". Everyculture.com. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Billington, Ray Allen (14 April 2016). The Historian's Contribution to Anglo-American Misunderstanding: Report of a Committee on National Bias in Anglo-American History Text Books. Routledge. ISBN 9781317271772 – via Google Books.
- ^ "GI Roundtable Series". Historians.org. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ History of Colonial America. Archived from the original on 2009-10-31.
- ^ "The Colonial Period". Law.jrank.org. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Richard D. Brown, "The Founding Fathers of 1776 and 1787: A collective view." William and Mary Quarterly (1976) 33#3: 465-480, especially pp 466, 478-79. online
- ^ Gregory L. Schneider, ed. (2003). Conservatism in America Since 1930: A Reader. NYU Press. pp. 289–. ISBN 9780814797990.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- ^ Nicol C. Rae, The Decline and Fall of the Liberal Republicans: From 1952 to the Present (1989)
- ^ Nina Strochlic, "George Washington to George W. Bush: 11 WASPs Who Have Led America," Daily Beast Aug. 16, 2012
- ^ "National Virtual Translation Center". Nvtc.gov. Retrieved 2017-08-21.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Summary Tables on Language Use and English Ability: 2000 (PHC-T-20). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2010-06-11. Retrieved 2010-04-18.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ Fischer, pp. 74, 114, 134–39.
- ^ Winslow, Edward (1622), Mourt's Relation (PDF), p. 133, archived from the original (PDF) on November 25, 2015, retrieved November 20, 2013,
many of the Indians coming amongst us, and amongst the rest their greatest king Massasoyt, with some ninetie men, whom for three dayes we entertained and feasted
- ^ "Primary Sources for 'The First Thanksgiving' at Plymouth" (PDF). Pilgrim Hall Museum. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 24, 2012. Retrieved November 26, 2009.
The 53 Pilgrims at the First Thanksgiving
- ^ William Bradford, Of Plymouth Plantation 1620–1647, 85.
- ^ "Features - Sources of United States of America Legal Information in Languages Other than English - LLRX.com". Llrx.com. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "Magna Charta - Magna Charta". Law.jrank.org. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "COMMON LAW V. CIVIL LAW SYSTEMS". Usinfo.state.gov. Archived from the original on 14 November 2008. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "History of Boston Latin School—oldest public school in America". BLS Web Site. Archived from the original on 2007-05-02. Retrieved 2007-06-01.
- ^ "History". Mather Elementary School. Retrieved 2017-02-14.
- ^ "The Mather School is marking 375 years of public education; NYPD's Bratton, an alumnus, to speak at assembly | Dorchester Reporter". www.dotnews.com. Retrieved 2017-02-14.
- ^ Report of the president of Harvard College and reports of departments. Harvard University. 1902. pp. 2–.
- ^ Frederick E. Brasch, "The Newtonian Epoch in the American Colonies." Proceedings of the American Antiquarian Society Vol. 49. (1939).
- ^ "Earl Gregg Swem Library Special Collections". Swem.wm.edu. Archived from the original on September 19, 2008. Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ^ Craig Evan Klafter, "St. George Tucker: The First Modern American Law Professor." Journal of The Historical Society 6.1 (2006): 133-150.
- ^ Louis Leonard Tucker, Puritan Protagonist President Thomas Clap of Yale College (1962).
- ^ Stoeckel, Althea (1976). "Presidents, professors, and politics: the colonial colleges and the American revolution". Conspectus of History. 1 (3): 45.
- ^ "XXIII. Education. § 13. Colonial Colleges.". The Cambridge History of English and American Literature.
- ^ "John Stafford Smith: Composer of the Star Spangled Banner". Archived from the original on 2007-07-11.
- ^ "Fort McHenry - National Anthem". 21 July 2007. Archived from the original on 21 July 2007. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Lesley Nelson. "Star Spangled Banner". Contemplator.com. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Heintze, James R. (9 January 2007). The Fourth of July Encyclopedia. McFarland. ISBN 9780786477166. Retrieved 21 August 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ "My country 'tis of thee [Song Collection]". The Library of Congress. Retrieved 2009-01-20.
- ^ Snyder, Lois Leo (1990). Encyclopedia of Nationalism. Paragon House. p. 13. ISBN 1-55778-167-2.
- ^ "Amazing Grace". NPR.org. 29 December 2002. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Lomax, John A.; Lomax, Alan (January 1994). American Ballads and Folk Songs. p. 521. ISBN 9780486282763.
- ^ "The Englishman dubbed the father of baseball". BBC News. July 6, 2015. Retrieved February 11, 2020.
- ^ "Why isn't baseball more popular in the UK?". BBC News. 26 July 2013. Retrieved July 26, 2013.
- ^ "BBC NEWS - UK - England - Baseball 'origin' uncovered". news.bbc.co.uk. 17 September 2008. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "BBC - South Today - Features - Baseball history". Bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Telegraph staff and agencies (11 September 2008). "Major League Baseball told: Your sport is British, not American". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Pope, S. W.; Pope, Steven W. (1997). The New American Sport History. ISBN 9780252065675. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "Frequently Occurring Surnames from the 2010 Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- ^ Hawgood, John (1970). The Tragedy of German-America. New York: Arno Press.
- ^ "Ucl.ac.uk/paediatric-epidemiology Most common surnames in Britain" (PDF). Ucl.ac.uk. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Kimberly Powell. "English Surnames: Meanings and Origins". About.com Parenting. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Kimberly Powell. "Smith - Surname Meaning, Origin and Genealogy". About.com Parenting. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "Scottish Surnames". Fife.50megs.com. Archived from the original on 21 March 2015. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "A History of Irish Surnames: Is Yours Here?" An example of this was the common Irish surname Mac Gabhann, which meant "son of a smith". Some Mac Gabhanns, living in County Cavan, had their name translated to Smith and it remained that way.
Smith is the fifth most common surname in Ireland.
- ^ Kimberly Powell. "Johnson (Surname) - Origin and Genealogy". About.com Parenting. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "Is Your Last Name Johnson? Learn What it Means and Where it Came From!". Thoughtco.com. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- ^ Kimberly Powell. "Williams - Meaning and Origin of This Surname". About.com Parenting. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Kimberly Powell. "BROWN - Surname Meaning, Origin and Genealogy". About.com Parenting. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Kimberly Powell. "JONES - Surname Meaning - Origin for the Surname Jones Genealogy". About.com Parenting. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Kimberly Powell. "Origin for the Surname Garcia - Genealogy". About.com Parenting. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "The Geography of European Surnames". Geocurrents.info. Archived from the original on 28 March 2014. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Kimberly Powell. "Origin for the Surname "Davis" - Genealogy". About.com Parenting. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Kimberly Powell. "Rodriguez Name Meaning and Origin". About.com Parenting. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ Homberger, Eric (2005). The Historical Atlas of New York City: A Visual Celebration of 400 Years of New York City's History. Owl Books. p. 34. ISBN 0-8050-7842-8.
- ^ "The State of Maryland". Netstate.com. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "The State of Maryland". netstate.com.
- ^ "A Tale of Two Bostons - iBoston". Iboston.org. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "ePodunk". Epodunk.com. Archived from the original on 7 November 2017. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ http://www.n-state.com, NSTATE, LLC. "The State of New Hampshire - An Introduction to the Granite State from NETSTATE.COM". Netstate.com. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "New Hampshire". boulter.com. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Hutchinson, Viola L. The Origin of New Jersey Place Names, New Jersey Public Library Commission, May 1945. Accessed August 28, 2015.
- ^ Hutchinson, Viola L. The Origin of New Jersey Place Names, New Jersey Public Library Commission, May 1945. Accessed December 1, 2017.
- ^ Kane, Joseph Nathan; and Aiken, Charles Curry. The American Counties: Origins of County Names, Dates of Creation, and Population Data, 1950-2000, p. 112. Scarecrow Press, 2005. ISBN 0810850362. Accessed January 21, 2013.
- ^ Hutchinson, Viola L. The Origin of New Jersey Place Names, New Jersey Public Library Commission, May 1945. Accessed December 1, 2017.
- ^ "New York State Information - Symbols, Capital, Constitution, Flags, Maps, Songs". 50states.com. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Espenshade, A. Howry (1925). Pennsylvania Place Names. Harrisburg, PA: The Evangelical Press. p. 37.
- ^ Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Govt. Print. Off. pp. 100.
- ^ "PHMC Doc Heritage: Lancaster County Petition". 7 August 2006. Archived from the original on 7 August 2006. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "WARMINSTER TOWNSHIP HISTORY". Township of Warminster. 5 March 2013. Retrieved 2015-07-31.
- ^ "WARRINGTON TOWNSHIP HISTORY". Township of Warrington. Retrieved 2017-12-01.
- ^ "WARWICK TOWNSHIP HISTORY". Township of Warwick. Retrieved 2017-12-01.
- ^ "The Split - One Colony Becomes Two". Carolana.com. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ In 1584 Sir Walter Raleigh sent Philip Amadas and Arthur Barlowe to lead an exploration of what is now the North Carolina coast, and they returned with word of a regional "king" named "Wingina." This was modified later that year by Raleigh and the Queen to "Virginia", perhaps in part noting her status as the "Virgin Queen." Stewart, George (1945). Names on the Land: A Historical Account of Place-Naming in the United States. New York: Random House. p. 22.
- ^ "City of Portsmouth History". City of Portmouth. Retrieved 2017-12-01.
- ^ "Genealogy and Ancestry of Barack Obama and the Other U.S. Presidents".
- ^ Powell, Kimberly. "Ancestry of Donald Trump". Genealogy.about.com. Retrieved 2017-08-21.
- ^ "AmericanHeritage.com / The Presidents: George Washington". 10 July 2010. Archived from the original on 10 July 2010. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Irvin Haas (1992). Historic Homes of the American Presidents. Courier Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-26751-2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Henry Adams born 1583 Barton St David, Somerset, England Archived March 24, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "The Fourth President • 1809-1817: James Madison". Archived from the original on January 2, 2010. Retrieved February 14, 2010.
- ^ "The Presidents, Andrew Jackson". American Heritage.com. Archived from the original on 10 February 2006. Retrieved 19 November 2009.
- ^ Jackson, Elmer Martin (1985). Keeping the lamp of remembrance lighted: a genealogical narrative with pictures and charts about the Jacksons and their allied families. Maryland: Hagerstown Bookbinding and Printing Co. p. 9.
- ^ "The Ninth President • 1841-1841: illiam Henry Harrison". Archived from the original on January 2, 2010. Retrieved February 14, 2010.
- ^ "AmericanHeritage.com / The Presidents: John Tyler". 2 January 2010. Archived from the original on 2 January 2010. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "AmericanHeritage.com / The Presidents: Millard Fillmore". 11 May 2010. Archived from the original on 11 May 2010. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "The Fourteenth President • 1853-1857: Franklin Pierce". Archived from the original on February 6, 2010. Retrieved February 14, 2010.
- ^ Lea, James Henry; Hutchinson, John Robert (1909). The Ancestry of Abraham Lincoln. Houghton Mifflin. p. 160. Retrieved 21 August 2017 – via Internet Archive.
swanton morley lincoln norfolk.
- ^ "Ancestors of Abraham Lincoln". Genbox.com. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "AmericanHeritage.com / The Presidents: Andrew Johnson". 11 May 2010. Archived from the original on 11 May 2010. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ "The Nineteenth President • 1877-1881: Rutherford Birchard Hayes". Archived from the original on January 2, 2010. Retrieved February 14, 2010.
- ^ "The Twentieth President • 1881-1881: James Abram Garfield". Archived from the original on January 2, 2010. Retrieved February 14, 2010.
- ^ Marck, John T. "William H. Taft". aboutfamouspeople.com. Retrieved 2008-04-14.
- ^ "The Presidents, William Taft". American Heritage.com. Archived from the original on 10 February 2006. Retrieved 19 November 2009.
- ^ "Warren Gamaliel Harding". thinkquest.com. Retrieved 2008-04-16.
- ^ "The Thirtieth President • 1923-1929: Calvin Coolidge". Archived from the original on January 2, 2010. Retrieved February 14, 2010.
- ^ Marck, John T. "Harry S. Truman". aboutfamouspeople.com. Retrieved 2008-04-16.
- ^ "The Presidents, Harry S Truman". American Heritage.com. Archived from the original on 10 February 2006. Retrieved 19 November 2009.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter Library". Jimmycarterlibrary.org. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "The Presidents, Ronald Reagan". American Heritage.com. Archived from the original on 10 February 2006. Retrieved 19 November 2009.
- ^ Chrisafis, Angelique (2005-01-27). "Scion of traitors and warlords: why Bush is coy about his Irish links". London: Guardian. Retrieved 13 July 2010.
- ^ "American Presidents with Irish Ancestors". Directory of Irish Genealogy. Retrieved 15 April 2008.
- ^ "BBC News - UK POLITICS - George W Bush, Essex boy". News.bbc.co.uk. 7 November 2000. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ "The Forty-Fourth President • 2009-present: Barack Hussein Obama". Archived from the original on July 10, 2010. Retrieved September 9, 2010.
- ^ "Ancestry of Barack Obama". William Addams Reitwiesner. Retrieved 2009-12-02.
- ^ "'Joe Biden will be the first US president to have Sussex ancestry'". Retrieved 15 January 2021.
Further reading[]
- Berthoff, Rowland. British Immigrants in Industrial America, 1790-1950 (1953).
- Bridenbaugh, Carl. Vexed and Troubled Englishmen, 1590-1642 (1976).
- Erickson, Charlotte. Invisible Immigrants: The Adaptation of English and Scottish Immigrants in Nineteenth-Century America (1972_.
- Furer, Howard B., ed. ;;The British in America: 1578-1970 (1972).
- Hanft, Sheldon. "English Americans." in Gale Encyclopedia of Multicultural America, edited by Thomas Riggs, (3rd ed., vol. 2, Gale, 2014), pp. 73-86. Online
- Tennenhouse, Leonard. The Importance of Feeling English: American Literature and the British Diaspora, 1750-1850 (2007{.
- Van Vugt, William E. "British (English, Scottish, Scots Irish, and Welsh) and British Americans, 1870–1940’." in Elliott Barkan, ed., Immigrants in American History: Arrival, Adaptation, and Integration (2013): 4:237+.
- Van Vugt, William E. British Buckeyes: The English, Scots, and Welsh in Ohio, 1700-1900 (2006).
- American people of English descent
- English American
- English-American history
- European-American society