Eskimo Nebula
| Emission nebula | |
|---|---|
| Planetary nebula | |
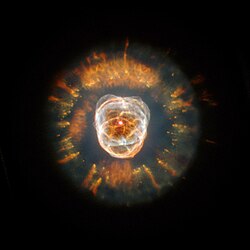 NGC 2392, the Eskimo Nebula by HST in 1999. Credit: NASA/ESA/STScI | |
| Observation data: J2000 epoch | |
| Right ascension | 07h 29m 10.7669s[1] |
| Declination | +20° 54′ 42.488″[1] |
| Distance | 6520±560[2] ly |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 10.1[1] |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 48″; × 48″;[3] |
| Constellation | Gemini |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Radius | ≥0.34 ly[a] ly |
| Absolute magnitude (V) | ≤0.4 [b] |
| Notable features | – |
| Designations | NGC 2392,[1] Caldwell 39, PN G197.8+17.3 Central Star: HIP 36369, HD 59088, TYC 1372-1287-1 |
The Eskimo Nebula (NGC 2392), also known as the Clown-faced Nebula, Lion Nebula,[4] or Caldwell 39, is a bipolar[5] double-shell[6] planetary nebula (PN). It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1787. The formation resembles a person's head surrounded by a parka hood. It is surrounded by gas that composed the outer layers of a Sun-like star. The visible inner filaments are ejected by a strong wind of particles from the central star. The outer disk contains unusual, light-year-long filaments.
NGC 2392 lies about 6500 light-years away, and is visible with a small telescope in the constellation of Gemini.
Historic data[]

The nebula was discovered by William Herschel on January 17, 1787, in Slough, England. He described it as "A star 9th magnitude with a pretty bright middle, nebulosity equally dispersed all around. A very remarkable phenomenon."[7] NGC 2392 WH IV-45 is included in the Astronomical League's Herschel 400 observing program.
Location[]

- NGC 2392 is located just east of δ Geminorum, just south the ecliptic.
Naming controversy[]
On 11 August 2020, the IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN),[citation needed] NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED),[citation needed] and SIMBAD Astronomical Database (CDS) discontinued use of three nicknames that were perceived as offensive - "Eskimo Nebula", "Clown Face Nebula", and "Clownface Nebula" - and strongly recommended the nebula be referred to by its NGC designation in further publications.[8][1]
See also[]
- List of planetary nebulae
- New General Catalogue
Notes[]
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "NGC 2392". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2006-12-22.
- ^ Gaia Collaboration et al. (2018b): Summary of the contents and survey properties
- ^ O'Dell, C. R.; Balick, B.; Hajian, A. R.; Henney, W. J.; et al. (2002). "Knots in Nearby Planetary Nebulae". The Astronomical Journal. 123 (6): 3329–3347. Bibcode:2002AJ....123.3329O. doi:10.1086/340726.
- ^ Deep-Sky Companions: The Caldwell Objects, 2nd Edition, Stephen James O'Meara, 2016, p.181
- ^ O'dell, C. R.; Balick, B.; Hajian, A. R.; Henney, W. J.; et al. (2003). "Knots in Planetary Nebulae". In S. J. Arthur & W. J. Henney (ed.). Revista Mexicana de Astronomía y Astrofísica (Serie de Conferencias). Winds, Bubbles, and Explosions: a conference to honor John Dyson, Pátzcuaro, Michoacán, México, September 9–13, 2002. 15. pp. 29–33. Bibcode:2003RMxAC..15...29O.
- ^ Guerrero, M. A.; Chu, Y.-H.; Gruendl, R. A.; Meixner, M. (2005). "XMM-Newton detection of hot gas in the Eskimo Nebula: Shocked stellar wind or collimated outflows?". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 430 (3): L69–L72. arXiv:astro-ph/0412540. Bibcode:2005A&A...430L..69G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200400131.
- ^ The Scientific Papers of Sir William Herschel by J. L. E. Dreyer, Royal Society, London 1912
- ^ Talbert, Tricia (11 August 2020). "NASA to Reexamine Nicknames for Cosmic Objects". NASA. Retrieved 11 August 2020.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to NGC 2392. |
- NGC 2392 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
- APOD (2003-12-07) – NGC 2392
- Eskimo Nebula Lowell Observatory
- The Structure & Evolution of the Eskimo Planetary Nebula University of Maryland Astronomy Department
- A Kinematic Determination of the Structure of the Double Ring Planetary Nebula NGC 2392, the Eskimo Astrophysical Journal v.362, p.226 October 1990
- A Cat's Eye view of the Eskimo from Saturn Maria-Teresa Garc ́ıa-D ́ıaz, Jose-Alberto L ́opez, Wofgang Steffen,Michael G. Richer and Hortensia Riesgo, 2011
Coordinates: ![]() 07h 29m 10.7669s, +20° 54′ 42.488″
07h 29m 10.7669s, +20° 54′ 42.488″
- Planetary nebulae
- Gemini (constellation)
- NGC objects
- Astronomical objects discovered in 1787
- Caldwell objects