Etchmiadzin Cathedral
| Etchmiadzin Cathedral | |
|---|---|
 View of the cathedral from the south-east, 2010 | |
| Religion | |
| Affiliation | Armenian Apostolic Church |
| Rite | Armenian |
| Leadership | Catholicos of All Armenians |
| Status | Active, under renovation |
| Location | |
| Location | Vagharshapat, Armavir Province, Armenia |
| Geographic coordinates | 40°09′42″N 44°17′28″E / 40.161769°N 44.291164°ECoordinates: 40°09′42″N 44°17′28″E / 40.161769°N 44.291164°E |
| Architecture | |
| Type | Cathedral |
| Style | Armenian |
| Founder | Gregory the Illuminator (original) |
| Groundbreaking | 301 (original building; traditional date)[1] |
| Completed | 303 (original building; traditional date)[1] |
| Specifications | |
| Length | 33 metres (108 ft)[2] |
| Width | 30 metres (98 ft)[2] |
| Height (max) | not available; over 27 metres (89 ft)[B] |
UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
| Official name: Cathedral and Churches of Echmiatsin and the Archaeological Site of Zvartnots | |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | (ii) (iii) |
| Designated | 2000 (24th session) |
| Reference no. | 1011-001 |
| Region | Western Asia |
Etchmiadzin Cathedral[C] (Armenian: Էջմիածնի մայր տաճար, Ēǰmiatsni mayr tačar) is the mother church of the Armenian Apostolic Church, located in the city of Vagharshapat (Etchmiadzin), Armenia.[D] According to most scholars it was the first cathedral built in ancient Armenia,[E] and is often considered the oldest cathedral in the world.[F]
The original church was built in the early fourth century[32]—between 301 and 303 according to tradition—by Armenia's patron saint Gregory the Illuminator, following the adoption of Christianity as a state religion by King Tiridates III. It was built over a pagan temple, symbolizing the conversion from paganism to Christianity. The core of the current building was built in 483/4 by Vahan Mamikonian after the cathedral was severely damaged in a Persian invasion. From its foundation until the second half of the fifth century, Etchmiadzin was the seat of the Catholicos, the supreme head of the Armenian Church.
Although never losing its significance, the cathedral subsequently suffered centuries of virtual neglect. In 1441 it was restored as catholicosate and remains as such to this day.[33] Since then the Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin has been the administrative headquarters of the Armenian Church. Etchmiadzin was plundered by Shah Abbas I of Persia in 1604, when relics and stones were taken out of the cathedral to New Julfa in an effort to undermine Armenians' attachment to their land. Since then the cathedral has undergone a number of renovations. Belfries were added in the latter half of the seventeenth century and in 1868 a sacristy was constructed at the cathedral's east end.[2] Today, it incorporates styles of different periods of Armenian architecture. Diminished during the early Soviet period, Etchmiadzin revived again in the second half of the twentieth century, and under independent Armenia.[2]
As the main shrine of Armenian Christians worldwide, Etchmiadzin has been an important location in Armenia not only religiously, but also politically and culturally.[34] A major pilgrimage site, it is one of the most visited places in the country.[35] Along with several important early medieval churches located nearby, the cathedral was listed as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 2000.
History[]

Foundation and etymology[]
According to Armenian church tradition, the cathedral was built between 301 and 303,[4][G] near the royal palace in what was then the Armenian royal capital of Vagharshapat,[1] on the location of a pagan temple.[H] In the early fourth century the Kingdom of Armenia, under Tiridates III, had became the first country in the world to adopt Christianity as a state religion.[I] Agathangelos narrates in his History of the Armenians the legend of the foundation of the cathedral. Armenia's patron saint Gregory the Illuminator had a vision of Jesus Christ descending from heaven and striking the earth with a golden hammer to show where the cathedral should be built. Hence, the patriarch gave the church the name of Etchmiadzin (էջ ēĵ "descent" + մի mi "only" + -ա- -a- (linking element) + ծին tsin "begotten"),[47] which translates to "the Descent of the Only-Begotten [Son of God]."[2][19] However, the name Etchmiadzin did not come into use until the 15th century,[4] while earlier sources call it "Cathedral of Vagharshapat."[J] The Feast of the Cathedral of Holy Etchmiadzin (Տոն Կաթողիկե Սբ. Էջմիածնի) is celebrated by the Armenian Church 64 days after Easter, during which "a special hymn is sung, written by the 8th century Catholicos Sahak III of Dzorapor, telling of St. Gregory's vision and the Cathedral's construction."[50]
as proposed by Alexander Sahinian (1966)[51] | |
 |
 
|
During archaeological excavations at the cathedral in 1955–56 and 1959, led by architectural historian Alexander Sahinian, remains of the original fourth-century building were discovered—including two levels of pillar bases below the current ones and a narrower altar apse under the present one.[1][37] Based on these findings, Sahinian asserted that the original church had been a three-naved[52] vaulted basilica,[1] similar to the basilicas of Tekor, Ashtarak and Aparan (Kasakh).[53] However, other scholars, have rejected Sahinian's view.[54] Among them, Suren Yeremian and Armen Khatchatrian held that the original church had been in the form of a rectangle with a dome supported by four pillars.[52] Stepan Mnatsakanian suggested that the original building had been a "canopy erected on a cross [plan]," while architecture researcher Vahagn Grigoryan suggests what Mnatsakanian describes as an "extreme view,"[55] according to which the cathedral has been essentially in the same form as it is today.[52]
Reconstruction and decline[]

According to Faustus of Byzantium, the cathedral and the city of Vagharshapat were almost completely destroyed during the invasion of Persian King Shapur II in the 360s[56] (circa 363).[2][57] Due to Armenia's unfavorable economic conditions, the cathedral was renovated only partially by Catholicoi Nerses the Great (r. 353–373) and Sahak Parthev (r. 387–439).[32]
In 387, Armenia was partitioned between the Roman Empire and the Sasanian Empire. The eastern part of Armenia where Etchmiadzin was located remained under the rule of Armenian vassal kings subject to Persia until 428, when the Armenian Kingdom was dissolved.[58]
In 450, in an attempt to impose Zoroastrianism on Armenians, Sasanian King Yazdegerd II built a fire temple inside the cathedral.[5] The pyre of the fire temple was unearthed under the altar of the east apse during the excavations in the 1950s.[37][K]
By the last quarter of the fifth century the cathedral was dilapidated.[59] According to Ghazar Parpetsi, it was rebuilt from the foundations by marzban (governor) of Persian Armenia Vahan Mamikonian in 483/4,[60] when the country was relatively stable,[61] following the struggle for religious freedom against Persia.[60] Most[59] researchers have concluded that, thus, the church was converted into cruciform church and mostly took its current form.[L] The new church was very different from the original one and "consisted of quadric-apsidal hall built of dull, grey stone containing four free-standing cross-shaped pillars disdained to support a stone cupola." The new cathedral was "in the form of a square enclosing a Greek cross and contains two chapels, one on either side of the east apse."[2] According to Robert H. Hewsen, the design of the new church was a mixture of the design of a Zoroastrian fire temple and a mausoleum of classical antiquity.[2]
Although the seat of the Catholicos was transferred to Dvin sometime in the 460s–470s[62] or 484,[63][64] the cathedral never lost its significance and remained "one of the greatest shrines of the Armenian Church."[65] The last known renovations until the 15th century were made by Catholicos Komitas in 618 (according to Sebeos) and Catholicos Nerses III (r. 640–661).[2][37] In 982 the cross of the cathedral was reportedly removed by an Arab emir.[7]
During these centuries of neglect, the cathedral's "condition deteriorated so badly"[66] that it prompted the prominent archbishop Stepanos Orbelian to write one of his most notable poems, "Lament on Behalf of the Cathedral" ("Ողբ ի դիմաց Կաթողիկէին" Voğb i dimats Katoğikein) in 1300.[M] In the poem, which tells about the consequences of the Mongol and Mamluk invasions of Armenia and Cilicia, Orbelian portrays Etchmiadzin Cathedral "as a woman in mourning, contemplating her former splendor and exhorting her children to return to their homeland [...] and restore its glory."[69]
From revival to plunder[]
Following the fall of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia in 1375, the See of Sis experienced decline and disarray. The Catholicosate of Aghtamar and the locally influential Syunik bishops enhanced the importance of the region around Etchmiadzin. In 1441 a general council of several hundred religious figures met in Etchmiadzin and voted to reestablish a catholicosate there.[70] The cathedral was restored by Catholicos Kirakos (Cyriacus) between 1441 and 1443.[2] At that time Etchmiadzin was under the control of the Turkic Kara Koyunlu, but in 1502, Safavid Iran gained control of parts of Armenia, including Etchmiadzin, and granted the Armenian Church some privileges.[71]

During the 16th and 17th centuries, Armenia suffered from its location between Persia and Ottoman Turkey, and the conflicts between those two empires. Concurrently with the deportation of up to 350,000 Armenians into Persia by Shah Abbas I as part of the scorched earth policy during the war with the Ottoman Empire,[72][73] Etchmiadzin was plundered in 1604.[71] The Shah wanted to "dispel Armenian hopes of returning to their homeland"[74] by moving the religious center of the Armenians to Iran[75] in order to provide Persia with a strong Armenian presence.[76] He wanted to destroy the cathedral and have its remains brought to Isfahan.[75] In the event, only some important stones—the altar, the stone where Jesus Christ descended according to tradition, and Armenian Church's holiest relic,[77] the Right Arm of Gregory the Illuminator—were moved to New Julfa, Isfahan in central Iran.[61] They were incorporated in the local Armenian St. Georg Church when it was built in 1611.[74][78] Shah Abbas reportedly offered the cathedral to the Pope.[79]

17th–18th centuries[]
Since 1627, the cathedral underwent major renovation under Catholicos Movses (Moses), when the dome, ceiling, roof, foundations and paving were repaired.[61] At this time, cells for monks, a guesthouse and other structures were built around the cathedral.[37] Additionally, a wall was built around the cathedral, making it a fort-like complex.[61] Eli Smith wrote in 1833: "The whole of the premises are surrounded by a high wall flanked with circular towers, and have externally the appearance of a fortress. Within, is a city in miniature."[81] Douglas Freshfield wrote in 1869 that "convent and cathedral are within a large fortified enclosure" and claimed that it "has in its time resisted many attacks from the infidels."[82]
The renovation works were interrupted by the Ottoman-Safavid War of 1635–36, during which the cathedral remained intact.[37] The renovations resumed under Catholicos Pilippos (1632–55), who built new cells for monks and renovated the roof.[37] During this century, belfries were added to many Armenian churches.[7] In 1653–54, he started the construction of the belfry in the western wing of Etchmiadzin Cathedral. It was completed in 1658 by Catholicos Hakob IV Jugayetsi.[61] According to Hewsen the bell is of Tibetian origin with a Buddhist inscription, "probably the long-forgotten gift of some Mongol or Ilkhanid khan."[2] Decades later, in 1682, Catholicos Yeghiazar constructed smaller bell towers with red tufa turrets on the southern, eastern, and northern wings.[2][37]
The renovations of Etchmiadzin continued during the 18th century. In 1720, Catholicos Astvatsatur and then, in 1777–83 Simeon I of Yerevan took actions in preserving the cathedral.[37] In 1770, Simeon I established a publishing house near Etchmiadzin, the first in Armenia.[83][2] During Simeon's reign, the monastery was completely walled and separated from the city of Vagharshapat.[4] Catholicos Ghukas (Lucas) continued the renovations in 1784–86.[37]


Russian takeover[]
The Russian Empire gradually penetrated Transcaucasia by the early 19th century. Persia's Erivan Khanate, in which Etchmiadzin was located, became an important target for the Russians. In June 1804, during the Russo-Persian War (1804–13), the Russian troops led by General Pavel Tsitsianov tried to take Etchmiadzin, but failed.[84][85] A few days after the attempt, the Russians returned to Etchmiadzin, where they caught a different Persian force by surprise and routed them.[85][84] Tsitsianov's forces entered Etchmiadzin, which, according to Auguste Bontems-Lefort, a contemporary French military envoy to Persia, they looted, seriously damaging the Armenian religious buildings.[85] Shortly after, the Russians were forced to withdraw from the area as a result of the successful Persian defense of Erivan.[85][86][87] According to Bontems-Lefort, the Russian behaviour at Etchmiadzin contrasted with that of the Persian king, who treated the local Christian population with respect.[85]
On 13 April 1827, during the Russo-Persian War (1826–28), Etchmiadzin was captured by the Russian General Ivan Paskevich's troops without fight and was formally annexed by Russia, with the Persian-controlled parts of Armenia, roughly corresponding to the territory of the modern Republic of Armenia (also known as Eastern Armenia), according to the 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay.[88]
The cathedral prospered under Russian rule, despite the suspicions that the Imperial Russian government had about Etchmiadzin becoming a "possible center of the Armenian nationalist sentiment."[2] Formally, Etchmiadzin became the religious center of the Armenians living within the Russian Empire by the 1836 statute or constitution (polozhenie).[89]
In 1868, Catholicos Gevorg (George) IV made the last major alteration to the cathedral by adding a sacristy to its east end.[2] In 1874, he established the Gevorgian Seminary, a theological school-college located on the cathedral's premises.[90][2] Catholicos Markar I undertook the restoration of the interior of the cathedral in 1888.[7]
20th century and on[]

In 1903, the Russian government issued an edict to confiscate the properties of the Armenian Church, including the treasures of Etchmiadzin.[2] Russian policemen and soldiers entered and occupied the cathedral.[91][92] Due to popular resistance and the personal defiance of Catholicos Mkrtich Khrimian, the edict was canceled in 1905.[89]
During the Armenian genocide, the cathedral of Etchmiadzin and its surrounding became a major center for Turkish Armenian refugees. At the end of 1918, there were about 70,000 refugees in the Etchmiadzin district.[93] A hospital and an orphanage within the cathedral's grounds were established and maintained by the U.S.-based Armenian Near East Relief by 1919.[2]
In the spring of 1918 the cathedral was in danger of an attack by the Turks.[94] Prior to the May 1918 Battle of Sardarabad, which took place just miles away from the cathedral, the civilian and military leadership of Armenia suggested Catholicos Gevorg (George) V to leave for Byurakan for security purposes, but he refused.[95][96] The Armenian forces eventually repelled the Turkish offensive and set the foundations of the First Republic of Armenia.
Soviet period[]
Suppression[]
After two years of independence, Armenia was Sovietized in December 1920. During the 1921 February Uprising Etchmiadzin was briefly (until April) taken over by the nationalist Armenian Revolutionary Federation, which had dominated the pre-Soviet Armenian government between 1918 and 1920.[97]
In December 1923, the southern apse of the cathedral collapsed. It was restored under Toros Toramanian's supervision in what was the first case of restoration of an architectural monument in Soviet Armenia.[98]

During the Great Purge and the radical state atheist policies in the late 1930s, the cathedral was a "besieged institution as the campaign was underway to eradicate religion."[99] The repressions climaxed when Catholicos Khoren I was murdered in April 1938 by the NKVD.[100] In August of that year, the Armenian Communist Party decided to close down the cathedral, but the central Soviet government seemingly did not approve of such a measure. Isolated from the outside world, the cathedral barely continued to function and its administrators were reduced to some twenty people.[2][101] It was reportedly the only church in Soviet Armenia not to have been seized by the Communist government.[102] The dissident anti-Soviet Armenian diocese in the US wrote that "the great cathedral became a hollow monument."[103]
Revival[]
Etchmiadzin slowly recovered its religious importance during World War II. The Holy See's official magazine resumed publication in 1944, while the seminary was reopened in September 1945.[104] In 1945 Catholicos Gevorg VI was elected after the seven-year vacancy of the position. The number of baptisms conducted at Etchmiadzin rose greatly: from 200 in 1949 to around 1,700 in 1951.[105] Nevertheless, the cathedral's role was downplayed by the Communist official circles. "For them the ecclesiastical Echmiadzin belongs irrevocably to the past, and even if the monastery and the cathedral are occasionally the scene of impressive ceremonies including the election of a new catholicos, this has little importance from the communist point of view," wrote Walter Kolarz in 1961.[106]
Etchmiadzin revived under Catholicos Vazgen I since the Khrushchev Thaw in the mid-1950s, following Stalin's death. Archaeological excavations were held in 1955–56 and in 1959; the cathedral underwent a major renovation during this period.[7][37] Wealthy diaspora benefactors, such as Calouste Gulbenkian and Alex Manoogian, financially assisted the renovation of the cathedral.[7] Gulbenkian alone provided $400,000.[107]
Independent Armenia[]

In 2000[108] Etchmiadzin underwent a renovation prior to the celebrations of the 1700th anniversary of the Christianization of Armenia in 2001.[7] In 2003 the 1700th anniversary of the consecration of the cathedral was celebrated by the Armenian Church.[109] Catholicos Karekin II declared 2003 the Year of Holy Etchmiadzin.[110] In September of that year an academic conference on the cathedral was held at the Pontifical Residence.[111]
The latest renovation of the cathedral began in 2012,[108] with a focus on strengthening and restoring the dome and the roof.[112]
Architecture[]
Today, Etchmiadzin "has a cruciform plan with a central cupola, four free-standing piers, and four projecting apses which are semicircular on the interior and polygonal on the exterior. The central piers, cruciform in section, divide the interior space into nine equal square compartments."[37]

General view of the cathedral

A close up view

Side view

The cathedral as seen from the surrounding gardens

The dome
Exterior design[]
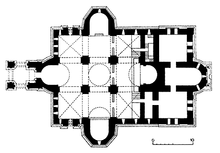
Alexander Sahinian declared that Etchmiadzin holds a unique position in Armenian (and non-Armenian) architecture history because it reproduces features of different periods of Armenian architecture.[113] According to Mack Chahin the cathedral's building is of "immense architectural interest, especially because of the many alterations and additions that have been made to it since its foundation. Thus, at the present day, the cathedral building incorporates more than one styles of architecture."[114] Despite the fact that the cathedral was renovated many times through the centuries and some alterations were made in the 17th and 19th centuries, it retains the form of the building constructed in 483/4.[2][37][115] The fifth-century building is the core of the cathedral, while the stone cupola, turrets, belfry, and rear extension are all later additions.[2] Engraved on the exterior of the edifice are decorative geometric and floral patterns as well as blind arcades and medallions depicting saints.[37] Portions of the northern and eastern walls of the original building have survived.[56]
The cathedral's external appearance has been described as ascetic,[116] unostentatious,[117] "an extreme austere and commanding work of man",[118] and as a "massive cube surmounted by a faceted cone on a simple cylinder."[119] Robert H. Hewsen writes that it is "neither the largest nor the most beautiful of Armenian churches", nevertheless, "the overall impression presented by the ensemble is inspiring, and Armenians hold the building in great reverence."[2] James Bryce wrote that the cathedral is "small, that is to say, compared with its fame or importance".[120] Paul Bloomfield, writing for The Times, expressed a similar view: "[the] cathedral, though diminutive by European standards, is immensely important."[121] Herbert Lottman wrote in a 1976 New York Times article: "Like all ancient Armenian churches, the cathedral is characterized by a disarmingly naive, coneshaped steeple. With a minimum of ornament, the building [...] is a solid stone construction, its arches sober romanesque curves."[122]
 
|
 
|
Reliefs[]
- Greek reliefs
The northern wall of the cathedral contains two reliefs which depict Paul the Apostle and Saint Thecla[123] and a cross with all arms of equal length with Greek inscriptions.[37] Paul and Thecla are represented in conversation, Paul is shown seated on cross-legged stool.[124] These reliefs have been dated by various authors between the first and sixth centuries.[125] Shahkhatunian[126] and Ghevont Alishan suggested that these reliefs were created before the invention of the Armenian alphabet in 405.[127] Art historian Sirarpie Der Nersessian believed that they are from the fifth or sixth century.[124] In his 2012 analysis, Grigoryan wrote that "we can insist that the three reliefs of the Echmiadzin Cathedral were created from the very beginning, in 302–325."[125] According to Hasratyan they are the earliest reliefs on the cathedral's walls[60] and among the earliest items of Christian Armenian sculpture art.[56]
- reliefs and ornaments on the western (main) belfry

Relief of a winged creature

Ornaments

A relief depicting the Christ

Ornaments
A cross sculpture
Interior design[]
The early frescoes inside the cathedral were restored in the 18th century. Stepanos Lehatsi (Stephen of Poland) illustrated the belfry in 1664. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Armenian painters created frescoes of scenes from the old testament and Armenian saints.[2] Naghash Hovnatan painted parts of the interior between 1712 and 1721. His paintings on the dome and the painting of the Mother of God under the altar have survived to this day. Other members of the prominent Hovnatanian family (Hakob, Harutyun and Hovnatan) created paintings throughout the 18th century. Their work was continued by the succeeding generations of the same family (Mkrtum and Hakob) in the 19th century.[128]
The wooden doors of the cathedral were carved in Tiflis in 1889.[2] The paintings were moved out of the cathedral by the order of Catholicos Mkrtich Khrimian in 1891 and are now kept in various museums in Armenia, including the National Gallery of Armenia.[37] The frescoes inside the cathedral were restored by Lydia Durnovo in 1956[129] and in 1981–82 under the directorship of Vardges Baghdasaryan.[130]
In the 1950s, the stone floor was replaced with one of marble.[2]

The cupola

Frescoes on the dome

Close up view of the frescoes on the dome

The interior
The altar

The main entrance
Influence[]


On Armenian architecture[]
The design of Etchmiadzin Cathedral—classified as "a four-apsed square with ciborium,"[131] and called Ejmiatsnatip "Etchmiadzin-type" in Armenian architectural historiography[61]—was not common in Armenia in the early medieval period. The now-destroyed St. Theodore Church of Bagaran, dating from 624 to 631,[132] was the only known church with a significantly similar plan and structure from that period.[133][134]
In the 19th century, during an architectural revival that looked back to Armenia's past, the plan of Etchmiadzin Cathedral began to be directly copied in new Armenian churches.[135] Some notable examples from this period include the narthex of the St. Thaddeus Monastery in northern Iran, dating from 1811 or 1819 through 1830,[135][136] and the Ghazanchetsots Cathedral in Shusha, dating from 1868.[137][138] Its plan was also replicated in the Armenian diaspora. One example is the Armenian Church of Bucharest, Romania, designed by Dimitrie Maimarolu and built in 1911–12.[139][140]
On European architecture[]
Art historian Josef Strzygowski, who was the first European to thoroughly study Armenian architecture[141] and place Armenia in the center of European architecture,[142] suggested that several churches and chapels in Western Europe have been influenced by the cathedrals of Etchmiadzin and Bagaran due to similarities found within their plans.[37][143] According to Strzygowski, some examples of churches influenced by Etchmiadzin and Bagaran are the 9th-century church of Germigny-des-Prés in France (built by Odo of Metz, probably an Armenian) and San Satiro of Milan, Italy.[N] This view was later supported by Alexander Sahinian and Varazdat Harutyunyan.[37] Sahinian suggested that Armenian church architecture was spread in Western Europe in the 8th–9th centuries by the Paulicians, who migrated from Armenia en mase after being suppressed by the Byzantines during the Iconoclasm period. Sahinian added many other medieval churches in Europe, such as the Palatine Chapel of Aachen in Germany, to the list of churches to have been influenced by the cathedrals of Etchmiadzin and Bagaran and by Byzantine decorative arts.[61] According to Murad Hasratyan, Etchmiadzin's design was spread to Europe via the Eastern Roman Empire and served as a model—besides Germigny-des-Prés and San Satiro—for the Nea Ekklesia church in Constantinople and the churches of Mount Athos in Greece.[145]
Heritage designation[]
In 2000 UNESCO added Etchmiadzin Cathedral, the churches of St. Hripsime, St. Gayane, Shoghakat and the ruined Zvartnots Cathedral to the list of World Heritage Sites.[146] In 2002, the cathedral complex with over 50 monuments, including many khachkars (cross-stones) and graves located around the cathedral, was listed by the Government of Armenia in the list of historical and cultural monuments of the Armavir Province.[147]

Relics[]
The museum of the cathedral has numerous items on display, including manuscripts and religious objects. Among its notable exhibits are the Holy Lance (Spear), relics belonging to Apostles of Jesus and John the Baptist, and a fragment of Noah's Ark.[122][148]
Significance[]

The locus of Etchmiadzin is "a sanctified soil" similar to Temple Mount and the Golden Temple, for Jews and Sikhs, respectively.[149] Catholicos Vazgen I described the cathedral as "our Solomon's Temple."[150] The cathedral complex has been called "Armenian Vatican" or "Armenian Mecca" as it is a major pilgrimage site for Armenians worldwide.[151][152] Since the cathedral has been so important to the development of Armenians' sense of identity, a pilgrimage to Etchmiadzin is "as much as ethnic as a religious experience."[153] Italian diplomat Luigi Villari wrote in 1906: "A visit to Etchmiadzin enables us to understand the tenacity of this people and their devotion to their faith better than a whole library of books."[154]
For many centuries, Etchmiadzin was the national and political center of the stateless Armenian people, with one journalist describing it as "the focal point of Armenians everywhere."[155] Before the foundation of the First Republic of Armenia and the official designation of Yerevan as its capital in 1918, Western sources emphasized Etchmiadzin's political significance. A 1920 book prepared by the Historical Section of the British Foreign Office acknowledged that Etchmiadzin "was regarded as the national capital of the Armenians."[156] "Deprived of a political head and even a political capital the [Armenian] people have, for at least five hundred years, looked to Etchmiadzin as the home of their people, the centre to which they looked for guidance, unfailing sympathy, and practical aid," wrote W. Llewelyn Williams in his 1916 book about Armenia.[157]
Notable visitors[]
- Travelers
Early European visitors to Etchmiadzin who gave descriptions of the cathedral included Jean-Baptiste Tavernier (before 1668),[158] Jean Chardin (1673),[159] Joseph Pitton de Tournefort (c. 1700),[160] James Morier (1810–16),[161] Robert Ker Porter (1817–20),[162] Friedrich Parrot (1829),[163] August von Haxthausen (1843),[164] Moritz Wagner (1843),[165] James Bryce (1876),[166] H. F. B. Lynch (1893).[167]
- Artists & humanitarians
Many prominent individuals have visited Etchmiadzin, including Russian diplomat and playwright Alexander Griboedov (1828),[168] Russian poets Valery Bryusov[169] and Andrei Bely,[170] Fridtjof Nansen (1925),[171] Armenian American writer William Saroyan (1976),[172] English composer Benjamin Britten,[173] Russian singer-songwriter Vladimir Vysotsky,[174] Russian-American poet and essayist Joseph Brodsky,[175] Andrei Sakharov,[176] Cher,[177] Kim Kardashian[178] and many others.
- Religious leaders
Religious leaders like Patriarch Cyril of Bulgaria (1967),[179] Archbishops of Canterbury Donald Coggan (1977)[180] and George Carey (1993),[181] Patriarch Ilia II of Georgia (1997, 2003),[182][183] Pope John Paul II (2001),[184] Bartholomew I of Constantinople (2001),[185] Ignatius Zakka I Iwas (2002),[186][187] Patriarch Kirill of Moscow (2010),[188] Pope Francis (2016) have visited Etchmiadzin. Pope Francis gave a prayer at the cathedral on 24 June. He called the cathedral "a witness to the history of your people and the centre from which its spirituality radiates."[189]
- State leaders
Leaders of several countries, such as Russia (Vladimir Putin in 2005),[190] France (Jacques Chirac in 2006[191] and Nicolas Sarkozy in 2011),[192][193] Georgia (Mikheil Saakashvili in 2004,[194] Giorgi Margvelashvili in 2014),[195] Romania (Emil Constantinescu in 1998),[196] Lebanon (Michel Aoun, 2018),[197] Germany (Angela Merkel, 2018),[198][199] and royalty, such as Nicholas I of Russia (1837),[200] King Mahendra of Nepal (1958),[201] Prince Charles (2013)[202] have visited the cathedral as part of their state or private visits to Armenia.
Cultural depictions[]

The Etchmiadzin monthly, the official periodical of the Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin founded in 1944, features the cathedral on its cover page as the logo.[203]
In the 1991 film Mayrig, directed by French-Armenian director Henri Verneuil, actual footage of the cathedral is shown when Azad Zakarian, the main character and a son of Armenian genocide survivors, is being questioned about his faith in a Catholic school.[204]
The Soviet Union and Armenia issued postage stamps depicting the cathedral in 1978 and 2009, respectively. The cathedral is depicted on the obverse side of the 50,000 dram banknote (2001).[205]
Artistic depictions[]

"View of Ararat and the Monastery of Echmiadzin", from the 1846 English translation of Friedrich Parrot's Journey to Ararat

by Grigory Gagarin, 1847

from John Mason Neale's A History of the Holy Eastern Church (1850)

by August von Haxthausen, 1854

by Robert Sears, 1855

by Floriant Gille, 1859

by Panos Terlemezian, 1903

A relief of Etchmiadzin Cathedral on the headquarters of the Eastern Diocese of the Armenian Church of America next to the St Vartan Cathedral, New York City

A silver plate depicting the cathedral displayed at the American Museum of Natural History[206]
References[]
- Notes
- ^ "Այժմյան գմբեթը հետագա (հավանաբար XVII դար) վերակառուցման արգասիք է:"[5]
- ^ Grigoryan wrote in 1986 that even the main dimensions of the cathedral are unknown.[6] The belfry, which is shorter than the dome, is reportedly 27 metres (89 ft) high.[7]
- ^ Less commonly referred to as the Cathedral of Holy Etchmiadzin,[8][9] Holy Etchmiadzin (Սուրբ Էջմիածին, Surb Ejmiatsin) or simply Etchmiadzin. Alternatively spelled Echmiadzin, Ejmiatsin,[10] and Edjmiadsin.[11]
- ^ The city has been called Vagharshapat for the most of its history. It was officially called Etchmiadzin between 1945 and 1995. Nowadays, both names are interchangeably used.[12]
- ^ Architecture historian Vahagn Grigoryan,[13] author and priest Torkom Postajian,[14] historians Tadevos Hakobyan,[15] Z. Harutiunian,[16] and Hasmik Hmayakyan[17] state that Etchmiadzin is Armenia's first cathedral. Etchmiadzin is sometimes called Armenia's first church building.[18][19] However, this claim has found little support among scholars. Robert W. Thomson,[20] Mnatsakanian,[21] Vrej Nersessian,[22] and Grigoryan[23] have all rejected this claim and stated that Armenia's first church was in Ashtishat, in the Taron region of Western Armenia. Thomson writes that Etchmiadzin was neither the first church, nor the first cathedral in Armenia.[20]
- ^ According to Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Africa and the Middle East, it is "generally regarded" as the oldest cathedral in the world,[24] while historian Steven Gertz wrote in Christianity Today that Etchmiadzin is regarded as such "according to some scholars."[25] Among those who support this view are architect Édouard Utudjian,[26] historians Sarkis Papajian,[27] Elisabeth Bauer-Manndorff,[28] professor of liturgical studies Michael Daniel Findikyan,[29] and others.[30][31]
- ^ Malachia Ormanian suggested that the cathedral was built within seven months, from February to August 303 because "the construction material was ready and the building was not huge and probably, partially made of wood and the people's desire and effort [to build the cathedral] was great." He added, "It's not impossible to think that the base of the preexisting temple could have been used."[36] Architectural researcher Vahagn Grigoryan dismisses these dates as "impossible" and states that at least several years were needed to build the cathedral. He cites Agathangelos, who does not mention the cathedral in an episode that took place in 306 and suggests the usage of the span of 302 to 325—the reign of Gregory the Illuminator as Catholicos as the dates of the cathedral's construction.[36]
- ^ Alexander Sahinian dated the temple to the Urartian period.[32] (An Urartian stele was uncovered during archaeological excavations in the 1950s).[37] The temple was dedicated to either goddess Anahit[38][39] or archangel Sandaramet,[4][17][40] both figures in Armenian mythology.
- ^ 301 AD is the traditional date,[41] first calculated by historian Mikayel Chamchian.[42] A growing number of authors argue that the correct date is 314 by citing the Edict of Milan.[43][44] Elizabeth Redgate writes that "the scholarly consensus is to prefer c. 314."[45][46]
- ^ Վաղարշապատի Կաթողիկե եկեղեցի Vağaršapati Kat'oğike ekeghetsi)[48][49] or simply Kat'oghike (Կաթողիկե, literally "Cathedral".[37] Malachia Ormanian defined "katoghike" as "cathedral" and wrote that the word was used particularly for Etchmiadzin Cathedral. In modern Armenian, "katoghike" is also used to refer to the Catholic Church. It is derived from the Ancient Greek word καθολικός katholikos, which means "universal". The cathedral has been so called as a description of the "universality" of the Church.[50]
- ^ The remains of the 4th century apse, the fire temple and other architectural details are now kept at a special structure built relatively recently under the east apse.[5]
- ^ "In 483/484 ... the basic core of the current structure was created..."[2] "483–484 Reconstructed by Vahan Mamikonyan. Etchmiadzin develops the design we see today."[7]
- ^ The complete title is "Allegorical prosopopoeia on the Holy Cathedral at Vagharshapat"[67] ("Բան բարառնական ոդեալ դիմառնաբար ի դիմաց Վաղարշապատու ս. Կաթուղիկէին" Ban barařnakan vodeal dimařnabar i dimats Vagharshapatu s. Katoğikein). It was first printed in Nor Nakhichevan in 1790, later in Kolkata in 1846 and in Tiflis in 1885.[68]
- ^ "...at Germigny-des-Prés (on the Loire, near Orleans) is an exact reproduction of the Armenian apse-buttressed square with free central pillars, dating from the ninth century. The latter type occurs also at Milan (San Satiro). In both cases the plan closely resembles that of Bagaran in Armenia."[144]
- Citations
- ^ a b c d e Sahinian, Zarian & Ghazarian 1978, p. 71.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad Hewsen, Robert H. (2001). "The Monastery of Ējmiatsin". Armenia: A Historical Atlas. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 259. ISBN 0-226-33228-4.
- ^ Hasratyan 2003, p. 271.
- ^ a b c d e Melik-Bakhshyan, Stepan (2009). Հայոց պաշտամունքային վայրեր [Armenian places of worship] (in Armenian). Yerevan State University Publishing. pp. 145–146. ISBN 978-5-8084-1068-8.
- ^ a b c Arakelian et al. 1984, p. 572.
- ^ Grigoryan 1986, p. 77: "...չկան նույնիսկ նրա հիմնական չափագրությունները...
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin: Mother Cathedral: History". Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin. Archived from the original on 4 April 2014.
- ^ Azadian, Edmond Y. (1999). History on the Move: Views, Interviews and Essays on Armenian Issues. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. p. 211. ISBN 978-0-8143-2916-0.
- ^ Melton, J. Gordon; Baumann, Martin, eds. (2010). Religions of the World: A Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Beliefs and Practices (2nd ed.). Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 186. ISBN 978-1-59884-204-3.
- ^ "Ejmiatsin". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 4 April 2014.
- ^ Adalian 2010, p. 297.
- ^ "Պատմաաշխարհագրական ակնարկ [Historical-geographic overview]" (in Armenian). Armavir Province: Armenian Ministry of Territorial Administration. Archived from the original on 28 February 2014. Retrieved 15 April 2014.
...Վաղարշապատ (1945–1995թթ. կոչվել է Էջմիածին) քաղաքը...
- ^ Grigoryan 2012a, p. 30: "Ուրեմն, Հայաստանի առաջին Կաթողիկե հաստատությունն ու շինությունը Վաղարշապատի Մայր տաճարն է:"
- ^ Postajian, Torkom (2005). The Armenian Church and the Others. Glendale, California. OCLC 216938598.
...the first Armenian Christian cathedral, which was called "Echmiadzin" (the Only-Begotten Son of God Descended).
- ^ Hakobian, Tadevos (1987). "Մայրաքաղաքը և քաղաքները. Էջմիածին [The capital and the cities: Etchmiadzin]". Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia (in Armenian). 13. Yerevan: Armenian Encyclopedia Publishing. p. 623.
301—303-ին այստեղ հիմնվեց Կաթողիկե եկեղեցին՝ Հայաստանի քրիստ․ առաջին Մայր տաճարը։
- ^ Harutiunian 1978, p. 66: "...հիմնում (301–303) Կաթողիկե եկեղեցի՝ Հայաստանի քրիստոնեական անդրանիկ Մայր տաճար Ս. Էջմիածինը..."
- ^ a b Hmayakyan, Hasmik (2005). "Հոգևոր ավանդույթների ժառանգությունը (Պտղաբերության պաշտամունքից մինչև քրիստոնեություն) [Heritage of spiritual heritage (From fertility cult to Christianity)]" (PDF). 21st Century (in Armenian). Yerevan: Noravank Foundation. 2 (8): 169. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 August 2014. Retrieved 3 August 2014.
Հետագայում Կաթողիկե եկեղեցին (Էջմիածինը՝ Հայաստանի քրիստոնեական առաջին տաճարը) ըստ Ագաթանգեղոսի վկայության, կառուցվում է Տրդատ թագավորի, Գրիգոր Լուսավորչի և ժողովրդի կողմից ավերված Սանդարամետի մեհյանի տեղում:
- ^ "Մայր աթոռ Սուրբ Էջմիածին [Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin]". Դպրոցական Մեծ Հանրագիտարան, Գիրք II [Great School Encyclopedia Book II] (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Encyclopedia. 2010. Archived from the original on 5 November 2021. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
Սբ Էջմիածնի գլխավոր շինությունը Մայր տաճարն է. այն հայկական առաջին եկեղեցին է...
- ^ a b Wainwright, Geoffrey; Westerfield Tucker, Karen B., eds. (2005). The Oxford History of Christian Worship. Oxford University Press. p. 147. ISBN 978-0-19-513886-3.
In a vision, Gregory was shown to build the first church in the country, in Etchmiadzin...
- ^ a b Piccolotto, Moreno; Shahinian, Sarkis, eds. (1996). Armenien: Tagebuch einer Reise in das Land des Ararat. Zürich: Institut für Hochbautechnik ETH Zurich. p. 110. ISBN 978-3-7281-2292-6.
The cathedral of Edjmiadzin is according to Thomson neither the first cathedral nor the first church built by Krikor. It was preceded by the church the latter had built at Ashtishat, in Western Armenia...
- ^ Mnatsakanian 1987, p. 150: "Таким образом, первое церковное здание в стране было возведено именно в Аштишате, а не в Вагаршапате, как это иногда отмечается в литературе."
- ^ Nersessian, Vrej (2001). Treasures from the Ark: 1700 Years of Armenian Christian Art. Los Angeles: J. Paul Getty Museum. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-89236-639-2.
...Ashtishat, 'where the first church had been built...
- ^ Grigoryan 2012a, p. 26: "Ուրեմն, Հայաստանի առաջին եկեղեցի հաստատությունը Աշտիշատի սուրբ Երրորդություն եկեղեցին է:"
- ^ Stokes, Jamie, ed. (2008). Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Africa and the Middle East. New York: Infobase Publishing. p. 65. ISBN 978-1-4381-2676-0.
Etchmiatzin is located in the west of modern Armenia, close to the border with Turkey, and its fourth-century cathedral is generally regarded as the oldest in the world.
- ^ Gertz, Steven (1 January 2005). "How Armenia "Invented" Christendom". Christianity Today. Carol Stream, Illinois: Christianity Today International (85). ISSN 0009-5753. Archived from the original on 5 November 2021. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- ^ Utudjian, Édouard (1968). Armenian Architecture: 4th to 17th Century. Paris: Editions A. Morancé. p. 7. OCLC 464421.
...the oldest cathedral in Christendom, that of Etchmiadzin, founded in the 4th century.
- ^ Papajian, Sarkis (1974). A Brief History of Armenia. Fresno, California: Armenian Evangelical Union of North America.
...he built the Cathedral of Etchmiadzin (The descent of the Only Begotten). It is the oldest Christian Cathedral in existence.
- ^ Bauer-Manndorff, Elisabeth (1981). Armenia: Past and Present. Lucerne: Reich Verlag. OCLC 8063377.
Etchmiadzin, with the world's oldest cathedral and the seat of the Catholicos, draws tourists from all over the world.
- ^ Findikyan, Michael Daniel. "Eastern Liturgy in the West: The Case of Armenian Church" (PDF). Yale University. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
...the spot on which the first cathedral of Christendom would be built.
- ^ Woodsworth, Judith; Delisle, Jean, eds. (2012). "Mesrop Mashtots and the flowering of Armenian culture". Translators through History (rev. ed.). Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company. p. 6. ISBN 978-90-272-7381-9.
...Echmiadzin Cathedral, the first cathedral in Christendom.
- ^ "Holy Etchmiadzin". New York: Diocese of the Armenian Church of America (Eastern). Archived from the original on 13 June 2014.
The cathedral dates back to the 4th century, and is reckoned the oldest Christian cathedral in world.
- ^ a b c Arakelian et al. 1984, p. 571.
- ^ Adalian 2010, p. 128.
- ^ Jaloyan, Vardan. "Էջմիածնի կաթողիկոսության հիմնադրման քաղաքական և աստվածաբանական հանգամանքները [Theological and political circumstances of the foundation of the Etchmiadzin Catholicosate]" (in Armenian). Religions in Armenia. Archived from the original on 11 April 2014. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ^ "The number of foreign tourists visiting Armenia expected to surge to one million". ARKA News Agency. 30 June 2014. Archived from the original on 13 January 2015. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
Foreign tourists usually visit the pagan temple of Garni, Geghard Monastery, Holy Etchmiadzin and Lake Sevan.
- ^ a b Grigoryan 2012a, pp. 28–29.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s "Etchmiadzin". Armenian Studies Program California State University, Fresno. Archived from the original on 23 June 2014.
- ^ Payaslian 2007, p. 37: "Churches replaced old pagan shrines in Ani and Vagharshapat; in the latter, the temple of Anahit was replaced by the Cathedral of Holy Echmiadzin...
- ^ Bournoutian, George A. (1993). A History of the Armenian People: Pre-history to 1500 A.D. Costa Mesa, California: Mazda Publishers. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-939214-96-9.
Following Gregory's vision, the great temple of Anahit in Vagharshapat was replaced by the cathedral of Edjmiadsin.
- ^ Avetisyan, Kamsar (1979). Հայրենագիտական էտյուդներ [Armenian studies sketches] (in Armenian). Yerevan: Sovetakan Grogh. p. 200.
....Էջմիածնի Մայր տաճարը ... որտեղ գտնվում էր Սանդարամետի գետնափոր մեհյանը։
- ^ Balakian, Peter (2009). The Burning Tigris. New York: HarperCollins. p. 29. ISBN 978-0-06-186017-1.
- ^ Panossian 2006, p. 106.
- ^ Panossian 2006, p. 42.
- ^ Hastings, Adrian; Mason, Alistair; Pyper, Hugh, eds. (2000). The Oxford Companion to Christian Thought. Oxford University Press. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-19-860024-4.
- ^ Redgate, A. E. (2000). The Armenians. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. p. 314. ISBN 978-0-631-22037-4.
- ^ Guroian, Vigen (2000). "Armenian tradition". In Hastings, Adrian; Mason, Alistair; Pyper, Hugh (eds.). The Oxford Companion to Christian Thought. Oxford University Press. p. [https://books.google.com/books?id=ognCKztR8a4C&pg=PA39 39]. ISBN 978-0-19-860024-4.
Most scholars now place that event in 314 [...] but 301 remains the date of tradition.
- ^ "Feast of the Cathedral of Holy Etchmiadzin". Araratian Patriarchal Diocese of the Armenian Holy Apostolic Church. Archived from the original on 29 March 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2013.
- ^ Arakelian et al. 1984, p. 205.
- ^ Grigoryan 2012a, p. 27.
- ^ a b "Տոն Կաթողիկե Սբ. Էջմիածնի [Feast of the Cathedral of Holy Etchmiadzin]" (in Armenian). Araratian Patriarchal Diocese. Archived from the original on 29 March 2014.
- ^ Sahinian 1966, pp. 91–92.
- ^ a b c Hasratyan 2003, p. 266.
- ^ Sahinian 1966, p. 84.
- ^ Edwards, Robert W., "Ēĵmiacin" (2016). The Eerdmans Encyclopedia of Early Christian Art and Archaeology, ed., Paul Corby Finney. Grand Rapids, Michigan: William B. Eerdmans Publishing. pp. 455–456. ISBN 978-0-8028-9016-0.
- ^ Mnatsakanian 1987, p. 149: "...крайняя точка зрения..."
- ^ a b c Hasratyan 2003, p. 267.
- ^ Sahinian 1966, p. 72.
- ^ Hacikyan, Agop Jack; Basmajian, Gabriel; Franchuk, Edward S.; Ouzounian, Nourhan (2000). The Heritage of Armenian Literature: From the Oral Tradition to the Golden Age. 1. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. p. 168. ISBN 978-0-8143-2815-6.
- ^ a b Hasratyan 2003, p. 269.
- ^ a b c Hasratyan 2003, p. 268.
- ^ a b c d e f g Sahinian, Zarian & Ghazarian 1978, p. 72.
- ^ Harutyunyan, Arsen (2013). "Հայրապետական աթոռի' Վաղարշապատից Դվին տեղափոխման հարցի շուրջ [About Transfer of the Patriarchal Throne to Dvin from Vagharshapat]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences (3): 171. ISSN 0135-0536. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
- ^ Ferguson, Everett; McHugh, Michael P.; Norris, Frederick W. (1999). Encyclopedia of Early Christianity. 1 (2nd ed.). New York: Routledge. p. 227. ISBN 978-0-8153-3319-7.
- ^ Casiday, Augustine, ed. (2012). The Orthodox Christian World. Oxon: Routledge. p. 47. ISBN 978-1-136-31484-1.
- ^ Mnatsakanian 1987, p. 154: "Со дня своего основания, независимо от того, был ли храм кафедральной церковью католнкосата Армении или же католикосы находились в других местах, этот памятник вплоть до XX века являлся одной из величайших святынь армянской церкви..."
- ^ Adalian 2010, p. 299.
- ^ Hacikyan et al. 2005, p. 536.
- ^ Grigorian, G. M. (1976). "Ստեփանոս Օրբելյան [Stepanos Orbelian]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences (4): 162. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 24 November 2013.
- ^ Hacikyan et al. 2005, pp. 535–536.
- ^ Kurkjian, Vahan (1958). A History of Armenia. New York: Armenian General Benevolent Union. p. 355.
- ^ a b Adalian 2010, p. 300.
- ^ Hacikyan et al. 2005, pp. 4–5.
- ^ Gervers, Michael; Bikhazi, Ramzi Jibran (1990). Conversion and Continuity: Indigenous Christian Communities in Islamic Lands Eighth to Eighteenth Centuries. Toronto: Pontifical Institute of Mediaeval Studies. p. 230. ISBN 978-0-88844-809-5.
- ^ a b Sanjian, Avedis Krikor (1999). Medieval Armenian Manuscripts at the University of California, Los Angeles. Berkeley: University of California Press. p. 40. ISBN 978-0-520-09792-6.
- ^ a b Babaie, Sussan (2004). Slaves of the Shah: New Elites of Safavid Iran. London: I. B. Tauris. p. 56. ISBN 978-1-86064-721-5.
- ^ Cowe, S. Peter (9 December 2011). "Ejmiatsin". Encyclopædia Iranica. Archived from the original on 28 December 2014. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- ^ Hovannisian, Richard, ed. (2000). Armenian Van/Vaspurakan. Costa Mesa, California: Mazda Publishers. ISBN 978-1-56859-130-8.
...the holiest relic of the Armenian Church, the right arm of Saint Gregory the Illuminator...
- ^ Vivier-Muresan, Anne Sophie (2007). "Autour de l'Eglise Saint-Georges d'Esfahan". Archives de Sciences Sociales des Religions (in French). School for Advanced Studies in the Social Sciences (138): 49–68. doi:10.4000/assr.4542.
- ^ Matthee, Rudi (2012). Persia in Crisis: Safavid Decline and the Fall of Isfahan. New York: I. B. Tauris. p. 179. ISBN 978-1-84511-745-0.
He [Shah Abbas] thus offered the famous Armenian cathedral of Echmiadzin near Yerevan to the pope...
- ^ Sears, Robert (1855). An Illustrated Description of the Russian Empire. New York: Robert Sears. p. 295.
- ^ Smith, Eli; Dwight, H. G. O (1833). Researches of the rev. E. Smith and rev. H.G.O. Dwight in Armenia, Volume 2. Boston: Crocker & Brewster. p. 94.
- ^ Freshfield, Douglas W. (1869). Travels in the Central Caucasus and Bashan. London: Longmans, Green, and Co. p. 166.
- ^ Adalian 2010, p. 543.
- ^ a b Atkin 1980, p. 120.
- ^ a b c d e Behrooz 2013, p. 56.
- ^ Bournoutian 1992, p. 14.
- ^ Atkin 1980, pp. 120–121.
- ^ Nercissian, M. G. (1972). "Արևելյան Հայաստանի միացումը Ռուսաստանին [Eastern Armenia Joining Russia]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian) (1): 12. Archived from the original on 13 October 2020. Retrieved 16 July 2014.
- ^ a b Adalian 2010, p. 130.
- ^ Adalian 2010, p. 301.
- ^ Barrett, David B.; Kurian, George Thomas; Johnson, Todd M. (2001). World Christian encyclopedia: a comparative survey of churches and religions in the modern world, Volume 1 (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 78. ISBN 978-0-19-510318-2.
In 1903, in the part of Armenia controlled by Russia, Armenian Orthodox churches and schools were forcibly closed and church property confiscated. The clergy resisted, and Russian police occupied Holy Echmiadzin.
- ^ Rev. Samuel G. Wilson (November 1905). Pierson, Arthur Tappan (ed.). "Riots and the gospel in Transcaucasia". The Missionary Review of the World. New York: Missionary Review Publishing Company. 28 (11): 817.
This measure was forcibly carried out, and churches, monasteries, and even the cathedral and treasure-house at Etchmiadzin, were entered by soldiers, and the properties listed or seized.
- ^ Hovannisian, Richard (1971). The Republic of Armenia: The First Years, 1918–1919. Los Angeles: University of California Press. p. 127. ISBN 0-520-01805-2.
- ^ Asatryan, Hayk (2004). Հատընտիր [Selection] (PDF) (in Armenian). Yerevan: Republican Party of Armenia. p. 332. ISBN 99930-1-057-X. OCLC 61254330. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 August 2014. Retrieved 18 August 2014.
- ^ Ayvazian, Arthur A. (1985). Armenian victories at Khznavous and Sardarabad on May 23, 1918: and program for re-establishment of independent and neutral state of Armenia. New York: St. Vartan Press. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-934728-15-7.
- ^ Kayaloff, Jacques (1973). The Battle of Sardarabad. The Hague: Mouton. p. 29.
- ^ Sukiasyan, H. (2014). "Եկեղեցու սեփականության բռնագրավումը Խորհրդային Հայաստանում (1920 թ. դեկտեմբեր – 1921 թ. փետրվար) [Expropriation of church in Soviet Armenia (December 1920 – February 1921)]". Lraber Hasarakakan Gitutyunneri (in Armenian). Armenian Academy of Sciences (1): 95–102. ISSN 0320-8117. Archived from the original on 12 July 2020. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- ^ Harutyunyan 1984, p. 56.
- ^ Burchard, Christopher (1993). Armenia and the Bible: papers presented to the international symposium held at Heidelberg, July 16-19, 1990. Atlanta: Scholars Press. ISBN 978-1-55540-597-7.
- ^ Corley 1996, p. 9.
- ^ Corley, Felix (2010). "The Armenian Apostolic Church". In Leustean, Lucian N. (ed.). Eastern Christianity and the Cold War, 1945–91. Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. p. 190. ISBN 978-1-135-23382-2.
- ^ According to
Charles J. Kersten (R-WI), the chairman of the Select Committee on Communist Aggression. Investigation of Communist takeover and occupation of the non-Russian nations of the U. S. S. R. Washington, D.C.: United States Government Printing Office. 1954. p. 312.
The Communists seized all churches in Armenia with the exception of one. That is the mother church of Armenia called Etchmiadzin. That alone was not seized. However, it is also under the control of the Communists. The other churches were seized.
- ^ Central Diocesan Board (1958). Crisis in the Armenian church: text of a memorandum to the National Council of the Churches of Christ in the United States of America on the dissident Armenian Church in America. Boston: Armenian National Apostolic Church of America. pp. 22–23.
- ^ Corley 1996, p. 18.
- ^ Corley 1996, p. 21.
- ^ Kolarz, Walter (1961). Religion in the Soviet Union. London: Macmillan. p. 153.
- ^ Corley 1996, p. 25.
- ^ a b "Renovation of the Mother Cathedral". Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin. 10 June 2014. Archived from the original on 4 July 2014.
- ^ "Celebrating 1,700th Anniversary of the Consecration of the Mother Cathedral of Holy Etchmiadzin". Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin, Information Services. 30 January 2003. Archived from the original on 6 September 2014.
- ^ "His Holiness Karekin II Declares 2003 as the Year of Holy Etchmiadzin". Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin, Information Services. 3 February 2003. Archived from the original on 6 September 2014.
- ^ Danielyan, Gayane (12 September 2003). "Գիտաժողով՝ նվիրված Սուրբ Էջմիածնի Մայր Տաճարի օծման 1700-ամյակին [Academic conference on the 1700th anniversary of the consecration of Etchmiadzin Cathedral]" (in Armenian). RFE/RL Armenian Service. Archived from the original on 6 September 2014.
- ^ "Խորհրդակցություն Մայր տաճարի վերականգնման հարցերի շուրջ [Consultation on the Mother Cathedral's restoration issue]". Hetq (in Armenian). 22 February 2013. Archived from the original on 4 July 2014. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
...Մայր Տաճարի գմբեթների եւ տանիքների ամրակայման եւ վերանորոգման...
- ^ Sahinian 1966, p. 71: "Նրա կառուցվածքը ակնհայտորեն վերարտադրում է հայկական ճարտարապետության կազմավորման հանգուցային մի քանի կարևորագույն շրջանները, որով և բացառիկ տեղ է գրավում Հայաստանի (և ոչ միայն Հայաստանի) ճարտարապետական-կառուցողական արվեստի պատմության մեջ:"
- ^ Chahin, Mack (2001). The Kingdom of Armenia: A History (2nd revised ed.). Richmond: Curzon Press. p. Z-72. ISBN 978-0-7007-1452-0.
The building is of immense architectural interest, especially because of the many alterations and additions that have been made to it since its foundation. Thus, at the present day, the cathedral building incorporates more than one styles of architecture.
- ^ Adalian 2010, p. 298.
- ^ Zorkin, Anton (2013). "Путешествие по весенней Армении: день первый [Journey through spring in Armenia: day first]" (in Russian). National Geographic Russia. Archived from the original on 23 June 2014. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
Эчмиадзинский монастырь [...] впечатляет своим аскетизмом...
- ^ Telfer, John Buchan (29 May 1891). "Armenia and Its People". Journal of the Society of Arts. London: Royal Society of Arts. XXXIX (2, 010): 575.
- ^ Jordan, Robert Paul (June 1978). "The Proud Armenians" (PDF). The National Geographic Magazine. 153 (6): 873. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 July 2013.
- ^ Mikhailov, Nicholas; Pokshishevsky, Vadim (1948). Soviet Russia: the Land and Its People Volume 25. George H. Hanna (translator). New York: Sheridan House. p. 125.
- ^ Bryce 1878, p. 300.
- ^ Bloomfield, Paul (16 May 2015). "Armenia: mountains, monasteries and a glimpse of the land of Noah". The Times. Archived from the original on 23 November 2015. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
Our first port of call was Ejmiatsin, a suburb of Yerevan and seat of the Katholikos, head of the Armenian Apostolic Church. Its cathedral, though diminutive by European standards, is immensely important.
- ^ a b Lottman, Herbert R. (29 February 1976). "Despite Ages of Captivity, The Armenians Persevere". The New York Times. p. 287. Archived from the original on 23 June 2018. Retrieved 7 February 2017.
- ^ Arakelian et al. 1984, p. 594: "...Թեկղի և Պողոս (Էջմիածնի Մայր տաճարի հյուսիսային պատի վրա դրսից արված քանդակները)..."
- ^ a b Der Nersessian 1945, p. 95.
- ^ a b Grigoryan 2012b, p. 20.
- ^ Shahkhatunian 1842.
- ^ Grigoryan 2012b, p. 9.
- ^ Sahinian, Zarian & Ghazarian 1978, pp. 72–73.
- ^ Sahinian, Zarian & Ghazarian 1978, p. 73.
- ^ Մայր Տաճար > Պատմություն. armenianchurch.org (in Armenian). Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin. Archived from the original on 28 December 2014. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- ^ Thierry & Donabedian 1989, p. 599.
- ^ Hewsen, Robert H. (15 December 1988). "Bagaran". Encyclopædia Iranica. Archived from the original on 17 May 2014. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
Bagaran was noted for the fine church of St. Theodore (erected 624-31), now totally destroyed.
- ^ Mnatsakanian 1987, p. 157: "Можно отметить лишь одно сооружение—храм в Багаране, который в значительной степени повторяет общую структуру Эчмиадзинского храма, хотя здесь резко изменена вся пропорциональная система."
- ^ Thierry & Donabedian 1989, p. 66.
- ^ a b Thierry & Donabedian 1989, p. 308.
- ^ Petrosian, S. (1978). "Թադեի վանք [Monastery of Thaddeus]". Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia Volume 4 (in Armenian). p. 115.
Եկեղեցու աղոթասրահն ընդլայնելու նպատակով 1819-1830-ին արմ-ից, պատի բացվածքը մեծացնելով մույթերի հեռավորության չափով, կցվել է քառամույթ գմբթավոր, Էջմիածնի Մայր տաճարի (V դ.) հորինվածքով (առանց Ավագ խորանի, որին փոխարինում է հին եկեղեցին իր խորանով) դեղնավուն քարին կառույց:
- ^ Hasratyan, Murad. "Շուշիի Ղազանչեցոց Ս. Ամենափրկիչ եկեղեցի [Ghazanchetsots Church of Shushi]". Institute of Armenian Studies of Yerevan State University. Archived from the original on 28 February 2017. Retrieved 18 August 2014.
Նրա արտաքուստ խաչաձև, չորս մույթերի վրա դրված բարձր գմբեթով ծավալատարած. հորինվածքում ակնհայտ է Էջմիածնի Մայր տաճարին նմանեցնելու ձգտումը:
- ^ Chorbajian, Levon (1994). The Caucasian Knot: The History & Geopolitics of Nagorno-Karabagh. London: Zed Books. p. 84. ISBN 978-1-85649-288-1.
Thus when it was decided to construct the Cathedral of Our Savior, called Ghazanchetsots (one of the grandest churches in all of Armenia), in 1868–1888 in Shushi, it was to Etchmiadzin, the most important sanctuary for Armenians, that they looked for inspiration, at least for the plan.
- ^ Nanu, Yon Sava (1979). "Բուխարեստի հայկական եկեղեցի [Armenian Church of Bucharest]". Etchmiadzin (in Armenian). Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin. 36 (1): 56–60. Archived from the original on 12 August 2018. Retrieved 12 August 2018.
- ^ "Arhitectii Catedralei" (PDF). Ararat. New Series (in Romanian). 16 (20): 4. 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 October 2012.
- ^ Buxton 1975, p. 74.
- ^ Buxton 1975, p. 98.
- ^ Strzygowski, Josef (1904). Der dom zu Aachen und seine entstellung (in German). Leipzig: J. C. Hinrichs'sche Buchhandlung. pp. 39-41.
- ^ Buxton 1975, p. 100.
- ^ Hasratyan 2003, p. 270.
- ^ "Cathedral and Churches of Echmiatsin and the Archaeological Site of Zvartnots". UNESCO. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 26 October 2013.
- ^ Government of Armenia (2002). "Հայաստանի Հանրապետության Արմավիրի Մարզի Պատմության և Մշակույթի Անշարժ Հուշարձանների Պետական Ցուցակը [List of the Immovable Historical And Cultural Monuments in the Armavir Province of the Republic of Armenia]" (in Armenian). Armenian Legal Information System. Archived from the original on 12 March 2014.
- ^ Zenian, David (1 July 1996). "The Holy Etchmiadzin Museum: History of a Long Journey". AGBU Magazine. Armenian General Benevolent Union. Archived from the original on 22 October 2017.
- ^ Safran, William (2007). "The territorial dimension: holy places and sacred spaces". In Young, Mitchell; Zuelow, Eric; Sturm, Andreas (eds.). Nationalism in a Global Era: The Persistence of Nations. Routledge. p. 37. ISBN 978-0-415-41405-0.
- ^ Vazgen I (1991). "Ամենայն Հայոց Վեհափառ Հայրապետի կոնդակը Հայաստանի ազատ ու ինքնիշխան պետության հռչակման առթիվ". Etchmiadzin (in Armenian). 48 (1–3): 29. Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
Սուրբ Էջմիածինը՝ մեր Սողոմոնի տաճարն է...
- ^ Fischer, Louis (1935). Soviet Journey. New York: Harrison Smith and Robert Haas. p. 270.
In Echmiadzin, in the "Armenian Vatican," sits the Pope of the World Armenian Church...
- ^ Lord Warkworth (1898). Notes from a Diary in Asiatic Turkey. London: Edward Arnold. p. 97.
- ^ Davidson, Linda Kay; Gitlitz, David M. (2002). Pilgrimage: From the Ganges to Graceland: An Encyclopedia, Volume 1. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-57607-004-8.
- ^ Villari, Luigi (1906). Fire and Sword in the Caucasus. London: T. F. Unwin. p. 233.
- ^ Saxon, Wolfgang (19 August 1994). "Vazgen I, Head of Armenian Church, Dies at 85". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 12 December 2019. Retrieved 12 December 2019.
- ^ Historical Section of the Foreign Office (1920). Caucasia. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office. p. 49.
Echmiadzin, in the Government of Erivan, the residence of the Armenian Patriarch, was regarded as the national capital of the Armenians.
- ^ Williams, W. Llewelyn (1916). Armenia: Past and Present. London: P.S. King & Son. p. 132.
- ^ Tavernier, Jean-Baptiste (1713). Les six voyages de Jean-Baptiste Tavernier Volume 1 (in French). Paris: Pierre Ribou. p. 33.
- ^ Chardin, Jean (1686). Journal du voiage du Chevalier Chardin en Perse (in French). Paris: Daniel Horthemels. p. 308.
- ^ Joseph Pitton de Tournefort (1718). A voyage into the Levant [Relation d'un voyage du Levant] Volume II. London. pp. 248–251.
- ^ Morier, James (1818). A second journey through Persia, Armenia, and Asia Minor, to Constantinople, between the year 1810 and 1816. London: Longman. p. 323.
- ^ Porter, Robert Ker (1821). Travels in Georgia, Persia, Armenia, ancient Babylonia, &c. &c. Volume 1. London: Longman, Hurst, Rees, Orme, and Brown. p. 634.
- ^ Parrot, Friedrich (2016) [1846]. Journey to Ararat. Translated by William Desborough Cooley. Introduction by Pietro A. Shakarian. London: Gomidas Institute. pp. 81–82. ISBN 978-1-909382-24-4.
- ^ Haxthausen, Baron August von (2016) [1854–55]. Transcaucasia and the Tribes of the Caucasus. Translated by John Edward Taylor. Introduction by Pietro A. Shakarian. Foreword by Dominic Lieven. London: Gomidas Institute. pp. 200–201. ISBN 978-1-909382-31-2.
- ^ Wagner, Moritz (1848). Reise nach dem Ararat und dem Hochland Armenien (in German). Stuttgart: J.G. Cotta. p. 94.
- ^ Bryce 1878, p. 29.
- ^ Lynch, H. F. B. (1901). Armenia, travels and studies. Volume I: The Russian Provinces. London: Longmans, Green, and Co. p. 228.
- ^ Александр Грибоедов. Его жизнь и литературная деятельность
- ^ Русская художественная литература и геноцид армян: - Page 244, Михаил Давидович Амирханян - 1988
- ^ "«Армения оставила глубочайший след…»". Archived from the original on 27 November 2020. Retrieved 5 November 2021.
- ^ "Նանսենը եւ հայերը". Archived from the original on 19 August 2016. Retrieved 26 June 2016.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ Советская музыка - Issues 7–12 - Page 111
- ^ Владимир Высоцкий: воспоминания, Давид Карапетян
- ^ "Ереванские этюды Иосифа Бродского". Archived from the original on 11 January 2017. Retrieved 26 June 2016.
- ^ "Елена Боннэр. До дневников, Журнал «Знамя», #11, 2005". Archived from the original on 29 July 2021. Retrieved 29 July 2021.
- ^ "Modern history [part 2]. How Cher arrived in "freezing" Armenia". Archived from the original on 5 September 2019. Retrieved 6 March 2021.
- ^ Juneau, Jen (11 October 2019). "Kim Kardashian Reveals She Was Baptized with Her Kids in Armenia and Shares Photos from Ceremony". People. Archived from the original on 23 July 2021. Retrieved 23 July 2021.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 20 April 2019. Retrieved 20 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 20 April 2019. Retrieved 20 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Apostolic Voyage in Armenia Prayer Visit Address of John Paul II, Apostolic Cathedral, Etchmiadzin". vatican.va. 25 September 2001. Archived from the original on 11 April 2014. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 23 October 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Patriarch of Antioch Visits Etchmiadzin". Asbarez. 21 October 2002. Archived from the original on 19 November 2015. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ "Patriarch Kirill's speech at Echmiadzin cathedral". Russian Orthodox Church Department for External Church Relations. 16 March 2010. Archived from the original on 18 November 2015. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ "Visit and Prayer to the Armenian Apostolic Cathedral". vatican.va. Holy See. 24 June 2016. Archived from the original on 7 February 2021. Retrieved 15 January 2021.
- ^ "Владимир Путин прибыл в Эчмиадзин [Putin visits Echmiadzin]" (in Russian). RIA Novosti. 25 March 2005. Archived from the original on 18 November 2015. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ "Ժակ Շիրակը այցելել է Մայր Աթոռ Ս. Էջմիածին [Jacques Chirac visits Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin]". A1plus (in Armenian). 1 October 2006. Archived from the original on 3 August 2014.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 1 February 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "French President visits Armenia". Rustavi 2. 6 October 2011. Retrieved 22 August 2014.[dead link]
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 19 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Georgian president Giorgi Margvelashvili visits Etchmiadzin". PanARMENIAN.Net. 28 February 2014. Archived from the original on 18 November 2015. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Lebanon president visits Holy Etchmiadzin". news.am. 21 February 2018. Archived from the original on 23 February 2018. Retrieved 22 February 2018.
- ^ Harutyunyan, Aneta (25 August 2018). "Catholicos of All Armenians Garegin II holds meeting with German Chancellor Angela Merkel". Armenpress. Archived from the original on 2 September 2018. Retrieved 1 September 2018.
- ^ "Անգելա Մերկելն այցելեց Մայր Աթոռ Սուրբ Էջմիածին". 168.am (in Armenian). 25 August 2018. Archived from the original on 1 September 2018. Retrieved 1 September 2018.
- ^ Рукописные сокровища Матенадарана - Page 7, Ашот Гарегини Абрахамян - 1959
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Prince Charles visits the Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin". Public Radio of Armenia. 30 May 2013. Archived from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ ""Էջմիածին" ամսագիր [Etchmiadzin monthly]" (in Armenian). Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin. Archived from the original on 31 March 2014.
- ^ "Mayrig/Mother (Full Movie in French)". YouTube. Archived from the original on 10 February 2016. Retrieved 31 March 2014.
- ^ "Banknotes in circulation - 50000 drams". Central Bank of Armenia. Archived from the original on 27 March 2014.
- ^ "Dish, Decorated". amnh.org. American Museum of Natural History. Archived from the original on 3 February 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2016.
Bibliography[]
Academic articles[]
- Corley, Felix (1996). "The Armenian Church Under the Soviet Regime" (PDF). Religion, State & Society. Keston Institute. 24 (1): 9–53. doi:10.1080/09637499608431724. ISSN 0963-7494. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- Grigoryan, Vahagn (2012a). "Ագաթանգեղոսի "Հայոց պատմությունը" և Հայաստանի վաղ միջնադարի ճարտարապետության ուսումնասիրության խնդիրները [Agathangeghos's "History of Armenia" and Problems in the Study of the Early Medieval Armenian Architecture]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences (1): 14–37. ISSN 0135-0536. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 12 June 2014.
- Grigoryan, Vahagn (2012b). "Մայր տաճարի հնագույն երեք քանդակների թվագրման խնդիրը [The Problem of Dating the Three Earliest Reliefs of the Echmiadzin Cathedral]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences (3): 3–20. ISSN 0135-0536. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
- Grigoryan, Vahagn (1986). "Էջմիածնի մայր տաճարը [Cathedral of Etchmiadzin]". Lraber Hasarakakan Gitutyunneri (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences (7): 77–85. ISSN 0320-8117. Archived from the original on 19 August 2014. Retrieved 26 June 2014.
- Harutyunyan, Varazdat (1984). "Էջմիածնի Մայր տաճարի հիմնական վերանորոգումը (1954–1955) [Fundamental restoration of Echmiadzin Cathedral temple (1954—1955)]". Lraber Hasarakakan Gitutyunneri (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences (10): 56–67. ISSN 0320-8117. Archived from the original on 19 August 2014. Retrieved 26 June 2014.
- Harutiunian, Z. (1978). "Էջմիածին. Պատմական ակնարկ (Etchmiadzin: Historical Overview)". Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia Volume 4 (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Encyclopedia Publishing. pp. 654–68.
- Hasratyan, Murad (2003). "Էջմիածնի Մայր տաճարի ճարտարապետությունը Ղազար Փարպեցու օրոք [The Architecture of the Echmiadzin Cathedral in the Time of Lazarus Parpetsi]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences (2): 266–271. ISSN 0135-0536. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- Khatchatrian, Armen (1962). "Données historiques sur la fondation d'Edjmiatsin à la lumière des fouilles récentes [Historical data on the foundation of Edjmiatsin in the light of recent excavations]". Handes Amsorya (in French). Vienna: Mechitharisten-Congregation (1–2). ISSN 0017-7377. OCLC 26019166.
- Mnatsakanian, Stepan (1987). "Вопросы формирования Эчмиадзинского кафедрала в контексте эволюции крестовокупольных систем [Structural Principles of the Cathedral of Echmiadzin within the Context of Developing Systems of Cross-Shaped Cupolas]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences (1): 147–158. ISSN 0135-0536. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 26 June 2014.
- Sahinian, Alexander (1966). "Էջմիածնի Մայր տաճարի սկզբնական տեսքը [The Original Shape of the Cathedral of Echmiatsin]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences (3): 71–94. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- Sahinian, Alexander (1978). "Մոդուլային համակարգը Էջմիածնի Մայր տաճարի V դարի գմբեթակիր կառուցվածքում [The Module System in the 5th Century Cupola Structures of the Cathedral of Echmiadzin]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences (2): 140–158. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- Sahinian, Alexander; Zarian, A.; Ghazarian, M. (1978). "Էջմիածնի Մայր Տաճար [Etchmiadzin Cathedral]". Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia Volume 4 (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Encyclopedia Publishing. pp. 71–73.
- Ter-Movsisian, Mesrovb (1907). "Էջմիածին եւ հայոց հնագոյն եկեղեցիներ [Etchmiadzin and ancient Armenian churches]". Azgagrakan Handes (in Armenian). Tiflis: Yervand Lalayan. 16: 130–204. Archived from the original on 19 August 2014. Retrieved 23 June 2014.
Published books[]
- Specific
- Ashjian, Mesrob, ed. (2003). The Etchmiadzin chronicles (in English, Italian, Russian, German, French, and Armenian). Yerevan: Moughni Publishers. ISBN 99941-33-04-7.
- Balakian, Grigoris (1911). Ս. Էջմիածնի բարեկարգութեան պէտքը [Holy Ejmiatsin in Need of Renovation] (in Armenian). Constantinople: Shant.
- Bastamiants, Vahan (1877). Նկարագրութիւն Մայր եկեղեցիոյն հայոց Ս. Էջմիածնի [Description of Mother Church of Holy Ejmiatsin] (in Armenian and Russian). Vagharshapat.
- Harutyunyan, Varazdat (1978). Էջմիածին [Ējmiatsin] (in Armenian). Yerevan: Sovetakan Grogh. OCLC 19983186.
- Harutyunyan, Varazdat; Société pour la protection des monuments historiques et culturels de la RSS d'Arménie (1985). Etchmiadsin (in French). Yerevan: Hayastan. OCLC 78980119.
- Harutyunyan, Varazdat (1988). Եկայք շինեսցուք: Պատմութիւն Ս. Էջմիածնի Մայր Աթոռի շինարարական գործունէութեան Ամենայն Հայոց Կաթողիկոս Վազգէն Առաջինի գահակալութեան շրջանում (1955–1988) [History of construction activities at the Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin during the reign of Vazgen I (1955–1988)] (in Armenian). Los Angeles: Erebuni.
- Kazarian, Armen (2007). Кафедральный собор Сурб Эчмиадзин и восточнохристианское зодчество IV-VII веков [Cathedral of Holy Ejmiacin and the Eastern Christian architecture of the 4th-7th centuries] (in Russian). Moscow: Locus Standi. ISBN 978-5-94428-041-1.
- Miller, Julie A. (1996). "Echmiadzin (Armenia)". In Ring, Trudy; Salkin, Robert M.; La Boda, Sharon (eds.). International Dictionary of Historic Places: Middle East and Africa. 4. Chicago: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. pp. 250–253. ISBN 978-1-884964-03-9. Archived from the original on 22 March 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- Parsamian, Vardan (1931). Էջմիածինն անցյալում: Պատմական ուսումնասիրության փորձ [Etchmiadzin in the past: An attempt of historical research] (in Armenian). Pethrat: Yerevan.
- Sahinian, Alexander (1978). Ս. Էջմիածին / Св. Эчмиадзин / St. Etchmiadzine (in Armenian, Russian, and French). Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin. OCLC 47168540.
- Shahkhatunian, Hovhannes (1842). Ստորագրութիւն Կաթուղիկէ Էջմիածնի եւ հինգ գաւառացն Արարատայ [Description of the Cathedral of Ejmiacin and of the Five Districts of Ararat], 2 vols (in Armenian). Holy Ejmiacin.
- Toramanian, Toros (1910). Էջմիածնի տաճարը: Ճարտարապետական եւ հնագիտական հետազօտութիւններ [Etchmiadzin Cathedral: Architectural and Archaeological Studies] (in Armenian). Tiflis: Aganiants Publishing.
- Նկարագրութիւն Սուրբ Էջմիածնի Մայր տաճարի [Description of the Holy Etchmiadzin Cathedral] (in Armenian). Vagharshapat: Holy Etchmiadzin Cathedral Publishing. 1890. OCLC 861620582.
- Ս. Էջմիածին 303-1903: Պատկերազարդ նկարագրութիւն [Holy Etchmiadzin 303-1903: Illustrated description] (in Armenian). San Lazzaro degli Armeni, Venice: Mechitarist Order. 1903. OCLC 35048877.
- Սուրբ Էջմիածին: 1600-րդ տարեդարձ (303-1903) [Holy Etchmiadzin: 1600th anniversary (303-1903)] (in Armenian). Saint Petersburg: Pushkinean Aragatip. 1903. OCLC 46338801.
- General
- Adalian, Rouben Paul (2010). Historical Dictionary of Armenia. Lanham, Maryland: Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-7450-3.
- Arakelian, Babken N.; Yeremian, Suren T.; Arevshatian, Sen S.; Bartikian, Hrach M.; Danielian, Eduard L.; Ter-Ghevondian, Aram N., eds. (1984). Հայ ժողովրդի պատմություն հատոր II. Հայաստանը վաղ ֆեոդալիզմի ժամանակաշրջանում [History of the Armenian People Volume II: Armenia in the Early Age of Feudalism] (PDF) (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian SSR Academy of Sciences Publishing. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- Atkin, Muriel (1980). Russia and Iran, 1780–1828. University of Minnesota Press. ISBN 978-0816609246.
- Behrooz, Maziar (2013). "From confidence to apprehension: early Iranian interaction with Russia". In Cronin, Stephanie (ed.). Iranian-Russian Encounters: Empires and Revolutions Since 1800. Routledge. ISBN 978-0415624336.
- Bournoutian, George A. (1992). The Khanate of Erevan Under Qajar Rule: 1795-1828. Mazda Publishers. ISBN 978-0939214181.
- Bryce, James (1878). Transcaucasia and Ararat: Being Notes of a Vacation Tour in Autumn of 1876 (3rd ed.). London: Macmillan and Co.
- Buxton, David Roden (1975). Russian Mediaeval Architecture with an Account of the Transcaucasian Styles and Their Influence in the West. New York: Hacker Art Books. ISBN 978-0-87817-005-0. Reprint of the 1934 ed. published by the Cambridge University Press
- Der Nersessian, Sirarpie (1945). Armenia and the Byzantine Empire. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.
- Hacikyan, Agop Jack; Basmajian, Gabriel; Franchuk, Edward S.; Ouzounian, Nourhan (2005). The Heritage of Armenian Literature: From the eighteenth century to modern times. 3. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. ISBN 978-0-8143-3221-4.
- Payaslian, Simon (2007). The History of Armenia. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4039-7467-9.
- Panossian, Razmik (2006). The Armenians: From Kings and Priests to Merchants and Commissars. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-51133-9.
- Thierry, Jean-Michel; Donabedian, Patrick (1989). Armenian Art. New York: Harry N. Abrams, Inc. ISBN 978-0-8109-0625-9.
- Churches in Armenia
- Armenian Apostolic cathedrals in Armenia
- Tourist attractions in Armavir Province
- World Heritage Sites in Armenia
- Buildings and structures in Armavir Province
- Church buildings with domes
- 4th-century churches
- 5th-century churches
- 4th-century establishments in Armenia
- Armenian Apostolic churches in Vagharshapat






























