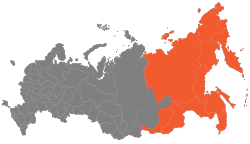
Far Eastern economic region
Far Eastern economic region | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Time zones | |
| Buryatia | UTC+08:00 (Irkutsk Time) |
| Amur Oblast, Zabaykalsky Krai and most of the Sakha Republic (excluding districts in UTC+10:00 and UTC+11:00 time zones) | UTC+09:00 (Yakutsk Time) |
| Jewish Autonomous Oblast, Khabarovsk Krai, Primorsky Krai, and the Oymyakonsky, Ust-Yansky and Verkhoyansky districts of the Sakha Republic | UTC+10:00 (Vladivostok Time) |
| Magadan Oblast, Sakhalin Oblast, and the Abyysky, Allaikhovsky, Momsky, Nizhnekolymsky, Srednekolymsky and Verkhnekolymsky districts of the Sakha Republic | UTC+11:00 (Magadan Time) |
| Chukotka and Kamchatka Krai | UTC+12:00 (Kamchatka Time) |
Far Eastern economic region (Russian: Дальневосто́чный экономи́ческий райо́н; tr.: Dalnevostochny ekonomichesky rayon) is one of twelve economic regions of Russia.
Composition[]
Until 2018 it encompassed the same area as the Far Eastern Federal District, which then was enlarged by Buryatia Republic and Zabaykalsky Krai.
In 2019 the economic region was enlarged by Buryatia Republic and Zabaykalsky Krai too [1]
The federal subjects are:
- Amur Oblast
- Buryatia Republic
- Chukotka Autonomous Okrug
- Jewish Autonomous Oblast
- Kamchatka Krai
- Khabarovsk Krai
- Magadan Oblast
- Primorsky Krai
- Sakha Republic
- Sakhalin Oblast
- Zabaykalsky Krai
Economy[]
This region accounted for 4 per cent of the national GRP in 2008. Bordering on the Pacific Ocean, the region has Komsomolsk-on-Amur, Khabarovsk, Yakutsk, and Vladivostok as its chief cities. Machinery is produced, and lumbering, fishing, hunting, and fur trapping are important. The Trans-Siberian Railroad follows the Amur and Ussuri Rivers and terminates at the port of Vladivostok.[2]
References[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Far Eastern economic region. |
- ^ "ИЗМЕНИТЬ / КонсультантПлюс".
- ^ Russia. The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. 2001-07 Archived February 3, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- Economic regions of Russia
- Economy of the Russian Far East