Frankenthal
show This article may be expanded with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (June 2017) Click [show] for important translation instructions. |
Frankenthal (Pfalz) | |
|---|---|
 Town hall | |
 Coat of arms | |
show Frankenthal (red) in the Rhein-Neckar region | |
 Frankenthal (Pfalz) | |
| Coordinates: 49°32′N 8°21′E / 49.533°N 8.350°ECoordinates: 49°32′N 8°21′E / 49.533°N 8.350°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Rhineland-Palatinate |
| District | urban district |
| Government | |
| • Lord mayor (2015–23) | Martin Hebich[1] (CDU) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 43.78 km2 (16.90 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 96 m (315 ft) |
| Population (2020-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 48,750 |
| • Density | 1,100/km2 (2,900/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 67227 |
| Dialling codes | 06233 |
| Vehicle registration | FT |
| Website | frankenthal.de |
Frankenthal (Pfalz) is a town in southwestern Germany, in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate.
History[]
Frankenthal was first mentioned in 772. In 1119 an Augustinian monastery was built here, the ruins of which — known, after the founder, as the Erkenbertruine — still stand today in the town centre.
In the second half of the 16th century, people from Flanders, persecuted for their religious beliefs, settled in Frankenthal. They were industrious and artistic and brought economic prosperity to the town. Some of them were important carpet weavers, jewellers and artists whose Frankenthaler Malerschule ("Frankenthal school of painting") acquired some fame. In 1577 the settlement was raised to the status of a town by the Count Palatine Johann Casimir.
In 1600 Frankenthal was converted to a fortress. In 1621 it was besieged by the Spanish during the Thirty Years' War, and then successively occupied by troops of the opposing sides. Trade and industry were ruined and the town was not reconstructed until 1682.
In 1689 the town was burnt to the ground by French troops in the War of the Grand Alliance. The town did not fully recover from this for more than fifty years.
However, in 1750, under the rule of the Elector (Kurfürst) Charles Theodore, Frankenthal was established as a centre of industry. Numerous factories were opened and mulberry trees were planted for silk production. In 1755 the famous Frankenthal porcelain factory was opened, which remained in production until 1800.
In 1797 the town came under French occupation during the French Revolutionary Wars. It passed into the rule of Bavaria in 1816.
The beginning of modern industrialisation is dated from 1859.
In 1938 the Jewish synagogue, built in 1884, was burnt to the ground during the Kristallnacht.
In 1943 during a bombing raid the centre of the town was almost completely destroyed. In 1945, at the end of World War II, its industries in ruins, it was occupied first by the Americans and then by the French.
From 1946 Frankenthal has been part of the federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate. Today the town is again the site of some medium-sized industries.
Number of inhabitants[]
- 1850: 4,767
- 1900: 16,899
- 2000: around 50,000
- 2015: 48,363
Lord Mayors[]
|
|
Twin towns – sister cities[]
Frankenthal is twinned with:[3]
 Colombes, France (1958)
Colombes, France (1958) Rosolini, Italy (2018)
Rosolini, Italy (2018) Sopot, Poland (1991)
Sopot, Poland (1991) Strausberg, Germany (1990)
Strausberg, Germany (1990)
Since 1982, Frankenthal also cooperates with the community of Butamwa in Nyarugenge, Rwanda.
Sons and daughters of the town[]


- Abraham Heidanus (1597-1678), a reformed theologian
- Esther Moscherosch née Ackermann (1602-1632), wife of the statesman and baroque poet Johann Michael Moscherosch
- Jacob Marrel (1614-1681), still life painter
- Johann Philipp Becker (1809-1886), revolutionary
- Georg Vierling (1820-1901), composer (dedication of the Vierlingstrasse )
- Konrad Maurer (1823-1902), a Bavarian legal historian
- Julius von Michel (1843-1911), ophthalmologist
- Richard Reverdy (1851-1915), civil engineer
- Karl Wendling (1857-1918), pianist and music pedagogue
- Karl Perron (1858-1928), opera singer
- Franz Nissl (1860-1919), neurologist and psychiatrist
- August von Parseval (1861-1942), designer of airships (dedication of the Parsevalplatz)
- Hermann Wilker (1874-1941), rower
- Karl Gentner (1876–1922), operatic tenor
- Oskar Perron (1880-1975), mathematician
- Ludwig Marum (1882-1934), lawyer and politician, victims of the Holocaust
- Arnold Fanck (1889-1974), director and pioneer of the mountain film
- Paul Martini (1889-1964), medical doctor
- Carl Neubronner (1892-1961), politician
- Georg Gehring (1903-1943), wrestler
- Karl Huber (1904-1965), politician and trade unionist
- (1906-1971), politician (SPD)
- Werner Knab (1908-1945), jurist and SS leader
- Hans Carste (1909-1971), composer and conductor
- Adolf Metzner (1910-1978), Leichtathlet
- Rudi Fischer (1925-2012), Football goalkeeper
- Michael Werner (publisher) (1965-), founder of the Pennsylvania German newspaper Hiwwe wie Driwwe
- Tobias Eckmeier (1995-), vlogger and Instagram personality known as EXSL95
- , operatic soprano
Family name[]
The family name "Frankenthal" is attested among people scattered in many countries - especially among Jews - and indicates an ultimate origin of the family in the town, though it might be centuries old and leaving no memory other than the name.
Gallery[]

Ruins of the monastery

The two churches in the centre

Wormser Tor

Outskirts
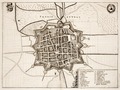
Fortress Franckenthal
References[]
- ^ Wahl der Oberbürgermeister der kreisfreien Städte, Landeswahlleiter Rheinland-Pfalz, accessed 30 July 2021.
- ^ "Bevölkerungsstand 2020, Kreise, Gemeinden, Verbandsgemeinden". Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz (in German). 2021.
- ^ "Partnerstädte". frankenthal.de (in German). Frankenthal (Pfalz). Retrieved 2021-02-03.
External links[]
- . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.
- . Collier's New Encyclopedia. 1921.
- Towns in Rhineland-Palatinate
- Frankenthal
- Anterior Palatinate
- Palatinate (region)







