Gallery of named graphs
Some of the finite structures considered in graph theory have names, sometimes inspired by the graph's topology, and sometimes after their discoverer. A famous example is the Petersen graph, a concrete graph on 10 vertices that appears as a minimal example or counterexample in many different contexts.
Individual graphs[]
Highly symmetric graphs[]
Strongly regular graphs[]
The strongly regular graph on v vertices and rank k is usually denoted srg(v,k,λ,μ).
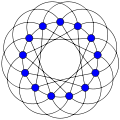
Paley graph of order 13

Local McLaughlin graph
Symmetric graphs[]
A symmetric graph is one in which there is a symmetry (graph automorphism) taking any ordered pair of adjacent vertices to any other ordered pair; the Foster census lists all small symmetric 3-regular graphs. Every strongly regular graph is symmetric, but not vice versa.

The Rado graph
Semi-symmetric graphs[]
Graph families[]
Complete graphs[]
The complete graph on vertices is often called the -clique and usually denoted , from German komplett.[1]
Complete bipartite graphs[]
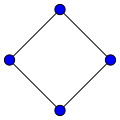
The complete bipartite graph is usually denoted . For see the section on star graphs. The graph equals the 4-cycle (the square) introduced below.
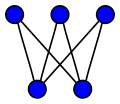

, the utility graph
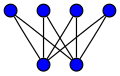
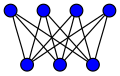
Cycles[]
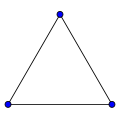
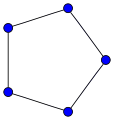
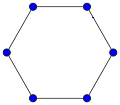
The cycle graph on vertices is called the n-cycle and usually denoted . It is also called a cyclic graph, a polygon or the n-gon. Special cases are the triangle , the square , and then several with Greek naming pentagon , hexagon , etc.
Friendship graphs[]
The friendship graph Fn can be constructed by joining n copies of the cycle graph C3 with a common vertex.[2]

Fullerene graphs[]
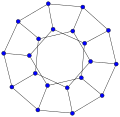
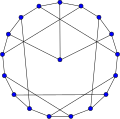
In graph theory, the term fullerene refers to any 3-regular, planar graph with all faces of size 5 or 6 (including the external face). It follows from Euler's polyhedron formula, V – E + F = 2 (where V, E, F indicate the number of vertices, edges, and faces), that there are exactly 12 pentagons in a fullerene and h = V/2 – 10 hexagons. Therefore V = 20 + 2h; E = 30 + 3h. Fullerene graphs are the Schlegel representations of the corresponding fullerene compounds.
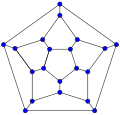
20-fullerene (dodecahedral graph)

24-fullerene (Hexagonal truncated trapezohedron graph)
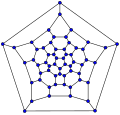
60-fullerene (truncated icosahedral graph)

70-fullerene
An algorithm to generate all the non-isomorphic fullerens with a given number of hexagonal faces has been developed by G. Brinkmann and A. Dress.[3] G. Brinkmann also provided a freely available implementation, called fullgen.
Platonic solids[]
The complete graph on four vertices forms the skeleton of the tetrahedron, and more generally the complete graphs form skeletons of simplices. The hypercube graphs are also skeletons of higher-dimensional regular polytopes.

Cube
,
Truncated solids[]
Snarks[]
A snark is a bridgeless cubic graph that requires four colors in any proper edge coloring. The smallest snark is the Petersen graph, already listed above.

Loupekine snark (first)

Loupekine snark (second)

Tietze graph
Star[]
A star Sk is the complete bipartite graph K1,k. The star S3 is called the claw graph.

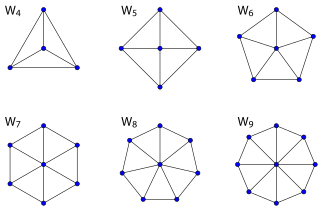
Wheel graphs[]
The wheel graph Wn is a graph on n vertices constructed by connecting a single vertex to every vertex in an (n − 1)-cycle.
References[]
- ^ David Gries and Fred B. Schneider, A Logical Approach to Discrete Math, Springer, 1993, p 436.
- ^ Gallian, J. A. "Dynamic Survey DS6: Graph Labeling." Electronic Journal of Combinatorics, DS6, 1-58, January 3, 2007. [1] Archived 2012-01-31 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Brinkmann, Gunnar; Dress, Andreas W.M (1997). "A Constructive Enumeration of Fullerenes". Journal of Algorithms. 23 (2): 345–358. doi:10.1006/jagm.1996.0806. MR 1441972.
- Graphs
- Graph families
- Image galleries