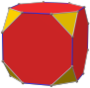
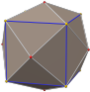
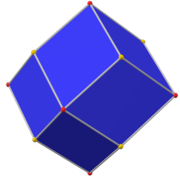
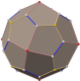
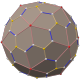
Truncated cube
| Truncated cube | |
|---|---|
 (Click here for rotating model) | |
| Type | Archimedean solid Uniform polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 14, E = 36, V = 24 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 8{3}+6{8} |
| Conway notation | tC |
| Schläfli symbols | t{4,3} |
| t0,1{4,3} | |
| Wythoff symbol | 2 3 | 4 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | Oh, B3, [4,3], (*432), order 48 |
| Rotation group | O, [4,3]+, (432), order 24 |
| Dihedral angle | 3-8: 125°15′51″ 8-8: 90° |
| References | U09, C21, W8 |
| Properties | Semiregular convex |
 Colored faces |
 3.8.8 (Vertex figure) |
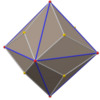 Triakis octahedron (dual polyhedron) |
 Net |

In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces (6 octagonal and 8 triangular), 36 edges, and 24 vertices.
If the truncated cube has unit edge length, its dual triakis octahedron has edges of lengths 2 and 2 + √2.
Area and volume[]
The area A and the volume V of a truncated cube of edge length a are:
Orthogonal projections[]
The truncated cube has five special orthogonal projections, centered, on a vertex, on two types of edges, and two types of faces: triangles, and octagons. The last two correspond to the B2 and A2 Coxeter planes.
| Centered by | Vertex | Edge 3-8 |
Edge 8-8 |
Face Octagon |
Face Triangle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid |  |

|

| ||
| Wireframe | 
|

|

|

|
|
| Dual | 
|

|

|

|
|
| Projective symmetry |
[2] | [2] | [2] | [4] | [6] |
Spherical tiling[]
The truncated cube can also be represented as a spherical tiling, and projected onto the plane via a stereographic projection. This projection is conformal, preserving angles but not areas or lengths. Straight lines on the sphere are projected as circular arcs on the plane.

|
 octagon-centered |
 triangle-centered |
| Orthographic projection | Stereographic projections | |
|---|---|---|
Cartesian coordinates[]

Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a truncated hexahedron centered at the origin with edge length 2ξ are all the permutations of
- (±ξ, ±1, ±1),
where ξ = √2 − 1.
The parameter ξ can be varied between ±1. A value of 1 produces a cube, 0 produces a cuboctahedron, and negative values produces self-intersecting octagrammic faces.
If the self-intersected portions of the octagrams are removed, leaving squares, and truncating the triangles into hexagons, truncated octahedra are produced, and the sequence ends with the central squares being reduced to a point, and creating an octahedron.
Dissection[]

The truncated cube can be dissected into a central cube, with six square cupolae around each of the cube's faces, and 8 regular tetrahedra in the corners. This dissection can also be seen within the runcic cubic honeycomb, with cube, tetrahedron, and rhombicuboctahedron cells.
This dissection can be used to create a Stewart toroid with all regular faces by removing two square cupolae and the central cube. This excavated cube has 16 triangles, 12 squares, and 4 octagons.[1][2]
Vertex arrangement[]
It shares the vertex arrangement with three nonconvex uniform polyhedra:
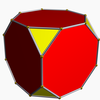 Truncated cube |
 Nonconvex great rhombicuboctahedron |
 Great cubicuboctahedron |
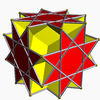 Great rhombihexahedron |
Related polyhedra[]
The truncated cube is related to other polyhedra and tilings in symmetry.
The truncated cube is one of a family of uniform polyhedra related to the cube and regular octahedron.
| Uniform octahedral polyhedra | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [4,3], (*432) | [4,3]+ (432) |
[1+,4,3] = [3,3] (*332) |
[3+,4] (3*2) | |||||||
| {4,3} | t{4,3} | r{4,3} r{31,1} |
t{3,4} t{31,1} |
{3,4} {31,1} |
rr{4,3} s2{3,4} |
tr{4,3} | sr{4,3} | h{4,3} {3,3} |
h2{4,3} t{3,3} |
s{3,4} s{31,1} |
= |
= |
= |
||||||||
| Duals to uniform polyhedra | ||||||||||
| V43 | V3.82 | V(3.4)2 | V4.62 | V34 | V3.43 | V4.6.8 | V34.4 | V33 | V3.62 | V35 |
Symmetry mutations[]
This polyhedron is topologically related as a part of sequence of uniform truncated polyhedra with vertex configurations (3.2n.2n), and [n,3] Coxeter group symmetry, and a series of polyhedra and tilings n.8.8.
| *n32 symmetry mutation of truncated spherical tilings: t{n,3} | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *n32 [n,3] |
Spherical | Euclid. | Compact hyperb. | Paraco. | |||||||
| *232 [2,3] |
*332 [3,3] |
*432 [4,3] |
*532 [5,3] |
*632 [6,3] |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3]... |
*∞32 [∞,3] | ||||
| Truncated figures |

|

|
|

|

|
|
| ||||
| Symbol | t{2,3} | t{3,3} | t{4,3} | t{5,3} | t{6,3} | t{7,3} | t{8,3} | t{∞,3} | |||
| Triakis figures |

|

|
|

|
|
|

| ||||
| Config. | V3.4.4 | V3.6.6 | V3.8.8 | V3.10.10 | V3.12.12 | V3.14.14 | V3.16.16 | V3.∞.∞ | |||
| *n42 symmetry mutation of truncated tilings: n.8.8 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *n42 [n,4] |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracompact | |||||||
| *242 [2,4] |
*342 [3,4] |
*442 [4,4] |
*542 [5,4] |
*642 [6,4] |
*742 [7,4] |
*842 [8,4]... |
*∞42 [∞,4] | ||||
| Truncated figures |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||
| Config. | 2.8.8 | 3.8.8 | 4.8.8 | 5.8.8 | 6.8.8 | 7.8.8 | 8.8.8 | ∞.8.8 | |||
| n-kis figures |

|

|

|
|

|

|

|

| |||
| Config. | V2.8.8 | V3.8.8 | V4.8.8 | V5.8.8 | V6.8.8 | V7.8.8 | V8.8.8 | V∞.8.8 | |||
Alternated truncation[]
Truncating alternating vertices of the cube gives the chamfered tetrahedron, i.e. the edge truncation of the tetrahedron.
The truncated triangular trapezohedron is another polyhedron which can be formed from cube edge truncation.
Related polytopes[]
The truncated cube, is second in a sequence of truncated hypercubes:
| Image | 
|
 
|
 
|
 
|
 
|
|
 
|
... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Octagon | Truncated cube | Truncated tesseract | Truncated 5-cube | Truncated 6-cube | Truncated 7-cube | Truncated 8-cube | |
| Coxeter diagram | ||||||||
| Vertex figure | ( )v( ) |  ( )v{ } |
 ( )v{3} |
 ( )v{3,3} |
( )v{3,3,3} | ( )v{3,3,3,3} | ( )v{3,3,3,3,3} |
Truncated cubical graph[]
| Truncated cubical graph | |
|---|---|
 4-fold symmetry Schlegel diagram | |
| Vertices | 24 |
| Edges | 36 |
| Automorphisms | 48 |
| Chromatic number | 3 |
| Properties | Cubic, Hamiltonian, regular, zero-symmetric |
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a truncated cubical graph is the graph of vertices and edges of the truncated cube, one of the Archimedean solids. It has 24 vertices and 36 edges, and is a cubic Archimedean graph.[3]
 Orthographic |
See also[]
- Spinning truncated cube
- Cube-connected cycles, a family of graphs that includes the skeleton of the truncated cube
References[]
- ^ B. M. Stewart, Adventures Among the Toroids (1970) ISBN 978-0-686-11936-4
- ^ http://www.doskey.com/polyhedra/Stewart05.html
- ^ Read, R. C.; Wilson, R. J. (1998), An Atlas of Graphs, Oxford University Press, p. 269
- Williams, Robert (1979). The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure: A Source Book of Design. Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-23729-X. (Section 3-9)
- Cromwell, P. Polyhedra, CUP hbk (1997), pbk. (1999). Ch.2 p. 79-86 Archimedean solids
External links[]
- Eric W. Weisstein, Truncated cube (Archimedean solid) at MathWorld.
- Klitzing, Richard. "3D convex uniform polyhedra o3x4x - tic".
- Editable printable net of a truncated cube with interactive 3D view
- The Uniform Polyhedra
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra www.georgehart.com: The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
- VRML model
- Conway Notation for Polyhedra Try: "tC"
- Uniform polyhedra
- Archimedean solids
- Truncated tilings