Garabet Yazmaciyan
Garabet Yazmaciyan Կարապետ Եազմաճեան | |
|---|---|
 Self-portrait of Garabet Yazmaciyan | |
| Born | 1868 |
| Died | 1929 (aged 61) |
| Occupation | Painter |
Garabet Yazmaciyan (Armenian: Կարապետ Եազմաճեան, 1868 – 1929) was a prominent Ottoman painter of Armenian descent.[1]
Life[]
According to the register of deaths in the Church of Surp Takavor in Kadıköy, Yazmaciyan was born in Üsküdar and his wife's name was Deruni.[1] Yazmaciyan came from a family of three children who were born and grew up in Üsküdar. He was an introvert man, and a skilled violinist.[1] His first wife, a relative of Nubar Pasha, was twenty years older than himself and died four years after they got married. Yazmaciyan's house burned down, and nothing but a few paintings were saved. While carrying these paintings to a friend's shop in Kadıköy, he was attacked and beaten by thieves, who took the paintings.[1] For some time after this, Yazmaciyan was unable to speak from shock.[1] He lived in the shop of this same friend in Kadıköy for a while, until he made the acquittance of a widow named Sirpuhi, whose daughter was studying Latin in Italy. Sirpuhi and Garabet ended up getting married. After the daughter of Sirpuhi, Alis, returned from Italy, the family moved to Cevizli and eight months later Garabet Yazamaciyan died of a heart attack in Istanbul, Turkey.[1]
Style[]
Yazmacıyan used scenery, color harmonies, and subjects that are of very close resemblance to Mıgırdiç Civanyan (1848–1906). His brushstrokes however are a little more careless and slovenly.[2] In order to be able to make a living from painting like Civanyan, Yazmacıyan had to produce quite quickly. Yazmaciyan also painted for the local Armenian churches. His paintings for the churches are more elaborate, attentive, and refined.[2]
One of his works is the double-sided tin shop sign he painted for his own business. On one of the sides, the artist has depicted himself painting. On the rear of the sign one can see a still-life painting. This proclaimed to the potential customers that he was open to conduct business and receive orders of both still-life and portraits.[2] In a way this shop sign is also proof that a painter in late 19th and early 20th century Istanbul was at the same time a tradesman. Similarly this fact suggests that paintings during that period were seen as objects.[2] They were ordered and considered as goods in the Ottoman society and economy, especially among the non-Muslim minorities.[2]
The Alluring Woman with Poison in her Mouth is also one of Yazmaciyan's more interesting works. This painting depicts a naked man standing and is wrapped around a half-snake half-human Basilisk that has long claws similar to nails. The Basilisk appears as though it is looking up to god; enraged at being unable to fulfill her desires. There is a stark contrast between the pink body of the man against the blue-black snake like creature with red tinsels. What is open to discussion however is the content of the red-white bohemian cup the man is holding and what it symbolizes.[2]
Paintings[]

Beyazit'da Yangin (Fire at Beyazit)

Galata Tower looking towards Haliç

Storm at Sea (1906)
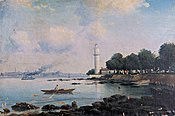
Lighthouse at Fener

Bosphorus View (1912)

Galata Fire

Hisar and Robert College

Boaters (1898)

Boating in Gardens (1904)

Rumeli Hisar

Galata Tower during Winter

The Alluring Woman with Poison in her Mouth
References[]
- ^ a b c d e f Kürkman, Garo (2004). Armenian painters in the Ottoman empire: 1600-1923. Istanbul: Matusalem publ. p. 846. ISBN 9789759201531.
- ^ a b c d e f "Çıracıyan ve Yazmacıyan'ın İstanbul'u..." (in Turkish). Sanal Muze (Museum). Archived from the original on 23 August 2015. Retrieved 11 December 2012.
- 1868 births
- 1929 deaths
- Armenians of the Ottoman Empire
- People from Üsküdar
- Armenian portrait painters
- 19th-century painters of the Ottoman Empire
- 20th-century painters of the Ottoman Empire
- People from Constantinople
- Artists from Istanbul
- 19th-century Armenian painters
- 20th-century Armenian painters