History of Karelia

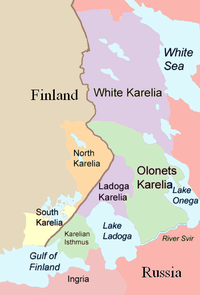



The History of Karelia is about the cultural and geopolitical region of Karelia, in present-day eastern Finland and northwestern Russia in northern Europe. The Karelian people's presence can be dated back to the 7th millennium BC–6th millennium BC.[1]
Prehistoric[]
Karelia is primarily within the Scandinavian and Russian taiga habitat and ecoregion, which was rich in natural resources for prehistoric people's food and shelter needs. The mining of copper in Karelia began between 1 AD and 1000 AD.[1] The ethnic composition of Karelia at the end of the 1st millennium consisted of Finnic tribes.[1]
13th century[]
Swedish–Novgorodian era[]
Karelia was bitterly fought over by Sweden and the Novgorod Republic during the 13th-century Swedish–Novgorodian Wars. The Treaty of Nöteborg (Finnish: Pähkinäsaaren rauha) in 1323 divided Karelia between the two. The Baltic Sea port city of Viborg (Finnish: Viipuri) became the capital of the new Swedish province, with the Fief of Viborg existing from 1320 to 1534. The Novgorodians (occupied, annexed and genocided by Muscovites in 1478) received East Karelia.[1] Since the 13th century the Karelians have lived in the tension between the East and the West, between the Eastern Christianity of Eastern Orthodoxy and Western Christianity of Catholicism and then Lutheranism.
18th century[]
Imperial Russian era[]
The Treaty of Nystad (Finnish: Uudenkaupungin rauha) in 1721 between Imperial Russia and Sweden ceded most of Karelia, as the Vyborg Governorate, to Russia. The Treaty of Åbo in 1743 between Sweden and Russia then ceded South Karelia to Russia. After Finland had been occupied by Russia in the Finnish War, parts of the ceded provinces 'Old Finland' were incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Finland, in the Russian Empire.[1]
20th century[]
Independence era[]
In 1917, with Finland's declaration of independence, Finland became independent and the border was confirmed in 1920 by the Russian–Finnish Treaty of Tartu.[1] This included the Finnish Viipuri Province in Karelia from 1917 to 1947.
Following the Russian Revolution and the Finnish Civil War, Finns were involved in attempts to overthrow the Bolshevists in Russian Karelia (East Karelia), for instance in the failed Aunus expedition. These mainly private expeditions ended after the peace Treaty of Tartu. After the end of the Russian Civil War, and the establishment of the Soviet Union in 1922, the Russian part of Karelia became the Karelian Autonomous republic of the Soviet Union (ASSR) in 1923.[1]
During Soviet Union's first five-year plan (1928 to 1932) tens of thousands of gulag prisoners were used to dig the White Sea–Baltic Canal. In the years of the Stalin's Great Purge (1936 to 1938) around 6,000 people were executed in the woods at Sandormokh near the Solovetsky Islands.[2]
World War II[]
In 1939 the Soviet Union attacked Finland starting the Winter War. The Moscow Peace Treaty of 1940 handed the eastern half of Finnish Karelia to the Soviet Union. About 400,000 people, virtually the whole population, had to be relocated within Finland. In 1941 Finland attacked the Soviet Union alongside the Axis powers as co-belligerents. The Finnish military administration in Eastern Karelia administered the region during 1941–1944.
The ceding of the eastern half of Finnish Karelia to the Soviets caused considerable bitterness in Finland, which had lost its fourth largest city, Viipuri, its industrial heartland along the River Vuoksi, its Saimaa canal that connected central Finland to the Gulf of Finland, and its access to the fishing waters of Lake Ladoga (Finnish: Laatokka). The serious loss also made of an eighth of the Finnish population displaced refugees, without a chance of return to their Karelian homeland.
Soviet era[]
As a consequence of the peace treaty, the Karelian ASSR was incorporated with the Karelo-Finnish SSR 1941–1956, after which it became an ASSR again.[1] Karelia was the only Soviet republic that was "demoted" from an SSR to an ASSR within the Russian SFR. Unlike autonomous republics, soviets republics had the constitutional right to secede. The possible fear of secession, as well as the Russian ethnic majority in Karelia may have resulted in its "demotion."
Russian Federation era[]
In 1991 the Republic of Karelia was created out of the ASSR, in the Russian Federation.[1]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i From the History of Karelia Archived 3 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine – Official Government Site of the Republic of Karelia
- ^ Gulag grave hunter unearths uncomfortable truths in Russia Archived 3 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine The Guardian, 2017
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to History of Karelia. |
- History of Karelia