Houthi movement
| Houthi movement ٱلْحُوثِيُّون Ansar Allah أَنْصَار ٱللَّٰه | |
|---|---|
 Houthi slogan reading "God is Greatest, Death to America, Death to Israel, Curse on the Jews, Victory to Islam". | |
| Leaders |
|
| Spokesperson | Mohammed Abdul Salam[1] |
| Dates of operation | 1994–ongoing (armed since 2004) |
| Headquarters | Saada and Sanaa, Yemen |
| Active regions |
|
| Ideology | Zaidi revivalism[2] Social justice[3][4][5][6] Anti-imperialism[7] Irredentism[8] Anti-Zionism[7] Antisemitism[9] (officially denied)[10] Yemeni nationalism[11][12] Big tent populism[11] Anti-Americanism |
| Size | 100,000 (2011)[13][14] |
| Allies | State allies
Non-state allies
|
| Opponents | State opponents
Non-state opponents |
| Battles and wars | Houthi insurgency in Yemen, Yemeni Crisis (the Yemeni Revolution, the Yemeni Civil War, the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen and the Saudi–Yemeni border conflict (2015–present)) |
| Designated as a terrorist group by | |
| Website | Ansarollah.com |
The Houthi movement[a] (/ˈhuːθi/; Arabic: ٱلْحُوثِيُّون al-Ḥūthīyūn [al.ħuː.θiː.juːn]), officially called Ansar Allah (ʾAnṣār Allāh أَنْصَار ٱللَّٰه "Supporters of God") and colloquially simply Houthis, is an Islamist political and armed movement that emerged from Saada in north Yemen in the 1990s. The Houthi movement is a predominately Zaidi Shia force,[51] whose leadership is drawn largely from the Houthi tribe.[52]
The Houthis have a complex relationship with Yemen's Sunni Muslims; the movement has discriminated against Sunnis, but also recruited and allied with them.[53][11][54][55] Under the leadership of Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, the group emerged as an opposition to former Yemeni president Ali Abdullah Saleh, whom they charged with massive financial corruption and criticized for being backed by Saudi Arabia and the United States[40] at the expense of the Yemeni people[56] and Yemen's sovereignty.[57] Resisting Saleh's order for his arrest,[58] Hussein was killed in Sa'dah in 2004 along with a number of his guards by the Yemeni army, sparking the Houthi insurgency in Yemen.[59] Since then, except for a short intervening period, the movement has been led by his brother Abdul-Malik al-Houthi.[58]
The Houthi movement attracts its Zaidi-Shia followers in Yemen by promoting regional political-religious issues in its media, including the overarching U.S.–Israeli conspiracy theory and Arab "collusion".[60][61] In 2003, the Houthis' slogan, "God is great, death to the US, death to Israel, curse the Jews, and victory for Islam", became the group's trademark.[61] Houthi officials, however, have rejected the literal interpretation of the slogan.[62]
The movement's expressed goals include combating economic underdevelopment and political marginalization in Yemen while seeking greater autonomy for Houthi-majority regions of the country.[63] They also claim to support a more democratic non-sectarian republic in Yemen.[64][65] The Houthis have made fighting corruption the centerpiece of their political program.[40]
The Houthis took part in the 2011 Yemeni Revolution by participating in street protests and by coordinating with other opposition groups. They joined the National Dialogue Conference in Yemen as part of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) initiative to broker peace following the unrest. However, the Houthis would later reject the November 2011 GCC deal's provisions stipulating formation of six federal regions in Yemen, claiming that the deal did not fundamentally reform governance and that the proposed federalization "divided Yemen into poor and wealthy regions". Houthis also feared the deal was a blatant attempt to weaken them by dividing areas under their control between separate regions.[55][63] In late 2014, Houthis repaired their relationship with the former president Ali Abdullah Saleh, and with his help, they took control of the capital and much of the north.[66]
In 2014–2015, Houthis took over the government in Sanaa with the help of the former president Ali Abdullah Saleh, and announced the fall of the current government of Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi.[67][68] Houthis have gained control of most of the northern part of Yemen's territory and since 2015 have been resisting the Saudi-led military intervention in Yemen that claims to seek to restore the internationally recognized Yemeni government[69] to power. Additionally, the Islamic State militant group has attacked all of the conflict's major parties including Houthis, Saleh forces, the Yemeni government, and the Saudi Arabian–led coalition forces.[70][71] The Houthis have launched repeated missile and drone attacks against Saudi cities. The conflict is widely seen as a proxy war between Saudi Arabia and Iran.[72]
History

According to Ahmed Addaghashi, a professor at Sanaa University, the Houthis began as a moderate theological movement that preached tolerance and held a broad-minded view of all the Yemeni peoples.[73] Their first organization, "the Believing Youth" (BY), was founded in 1992 in Saada Governorate[74]: 1008 by either Mohammed al-Houthi,[75]: 98 or his brother Hussein al-Houthi.[76]
The Believing Youth established school clubs and summer camps[75]: 98 in order to "promote a Zaidi revival" in Saada.[76] By 1994–1995, 15–20,000 students had attended BY summer camps. The religious material included lectures by Mohammed Hussein Fadhlallah (a Lebanese shia scholar) and Hassan Nasrallah (Secretary General of Lebanon's Hezbollah Party)."[75]: 99 [77]
The formation of the Houthi organisations has been described by Adam Baron of the European Council on Foreign Relations as a reaction to foreign intervention. Their views include shoring up Zaidi support against the perceived threat of Saudi-influenced ideologies in Yemen and a general condemnation of the former Yemeni government's alliance with the United States, which, along with complaints regarding the government's corruption and the marginalisation of much of the Houthis' home areas in Saada, constituted the group's key grievances.[78]
Although Hussein al-Houthi, who was killed in 2004, had no official relation with Believing Youth, according to Zaid, he contributed to the radicalisation of some Zaydis after the 2003 invasion of Iraq. BY-affiliated youth adopted anti-American and anti-Jewish slogans which they chanted in the Saleh Mosque in Sanaa after Friday prayers. According to Zaid, the followers of Houthi's insistence on chanting the slogans attracted the authorities' attention, further increasing government worries over the extent of the al-Houthi movement's influence. "The security authorities thought that if today the Houthis chanted `Death to America', tomorrow they could be chanting 'Death to the president [of Yemen]". 800 BY supporters were arrested in Sanaa in 2004. President Ali Abdullah Saleh then invited Hussein al-Houthi to a meeting in Sanaa, but Hussein declined. On 18 June 2004 Saleh sent government forces to arrest Hussein.[58] Hussein responded by launching an insurgency against the central government, but was killed on 10 September 2004.[56] The insurgency continued intermittently until a ceasefire agreement was reached in 2010.[73] During this prolonged conflict, the Yemeni army, and air force was used to suppress the Houthi rebellion in northern Yemen. The Saudis joined these anti-Houthi campaigns, but the Houthis won against both Saleh and the Saudi army. According to the Brookings Institution, this particularly humiliated the Saudis, who spent tens of billions of dollars on their military.[40]
Later, the Houthis participated in the 2011 Yemeni Revolution, as well as the ensuing National Dialogue Conference (NDC).[79] However, they rejected the provisions of the November 2011 Gulf Cooperation Council deal on the ground that "it divide[d] Yemen into poor and wealthy regions" and also in response to assassination of their representative at NDC.[80][81]
As the revolution went on, Houthis gained control of greater territory. By 9 November 2011, Houthis were said to be in control of two Yemeni governorates (Saada and Al Jawf) and close to taking over a third governorate (Hajjah),[82] which would enable them to launch a direct assault on the Yemeni capital of Sanaa.[83] In May 2012, it was reported that the Houthis controlled a majority of Saada, Al Jawf, and Hajjah governorates; they had also gained access to the Red Sea and started erecting barricades north of Sanaa in preparation for more conflict.[84]

By 21 September 2014, Houthis were said to control parts of the Yemeni capital, Sanaa, including government buildings and a radio station.[85] While Houthi control expanded to the rest of Sanaa, as well as other towns such as Rada', this control was strongly challenged by Al-Qaeda. The Gulf States believed that the Houthis had accepted aid from Iran while Saudi Arabia was aiding their Yemeni rivals.[86]
On 20 January 2015, Houthi rebels seized the presidential palace in the capital. President Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi was in the presidential palace during the takeover, but was not harmed.[87] The movement officially took control of the Yemeni government on 6 February, dissolving parliament and declaring its Revolutionary Committee to be the acting authority in Yemen.[67] On 20 March 2015, The al-Badr and al-Hashoosh mosques came under suicide attack during midday prayers, and the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant quickly claimed responsibility. The blasts killed 142 Houthi worshippers and wounded more than 351, making it the deadliest terrorist attack in Yemen's history.[88]
On 27 March 2015, in response to perceived Houthi threats to Sunni factions in the region, Saudi Arabia along with Bahrain, Qatar, Kuwait, UAE, Egypt, Jordan, Morocco, and Sudan led a gulf coalition airstrike in Yemen.[89] The military coalition included the United States which helped in planning of airstrikes, as well as logistical and intelligence support.[90]
According to a 2015 September report by Esquire magazine, the Houthis, once the outliers, are now one of the most stable and organised social and political movements in Yemen. The power vacuum created by Yemen's uncertain transitional period has drawn more supporters to the Houthis. Many of the formerly powerful parties, now disorganised with an unclear vision, have fallen out of favour with the public, making the Houthis—under their newly branded Ansar Allah name—all the more attractive.[7]
Houthi spokesperson Mohamed Abdel Salam stated that his group had spotted messages between the UAE and Saleh three months before his death. He told Al-Jazeera that there was communication between Saleh, UAE and a number of other countries such as Russia and Jordan through encrypted messages.[91] The alliance between Saleh and the Houthi broke down in late 2017,[92] with armed clashes occurring in Sanaa from 28 November.[93] Saleh declared the split in a televised statement on 2 December, calling on his supporters to take back the country[94] and expressed openness to a dialogue with the Saudi-led coalition.[92] On 4 December 2017, Saleh's house in Sanaa was assaulted by fighters of the Houthi movement, according to residents.[95] Saleh was killed by the Houthis on the same day.[96][97]
In January 2021, the United States designated the Houthis a terrorist organization, creating fears of an aid shortage in Yemen,[98] but this stance was reversed a month later after Joe Biden became president.[99]
Membership and support

There is a difference between the al-Houthi family[75]: 102 and the Houthi movement. The movement was called by their opponents and foreign media "Houthis". The name came from the surname of the early leader of the movement Hussein al-Houthi who died in 2004.[100]
The Houthis avoid assuming a singular tribal identity. Instead, the group strategically draws support from tribes of the northern Bakil federation, rival to the Hashid federation which had been a traditional ally of the central government. The Houthis' lack of centralised command structure allows them to generate immense support, as Yemenis from diverse backgrounds have joined their cause.[101]
Membership of the group had between 1,000 and 3,000 fighters as of 2005[102] and between 2,000 and 10,000 fighters as of 2009.[103] In 2010, the Yemen Post claimed that they had over 100,000 fighters.[104] According to Houthi expert Ahmed Al-Bahri, by 2010, the Houthis had a total of 100,000–120,000 followers, including both armed fighters and unarmed loyalists.[105]
As of 2015, the group is reported to have attracted new supporters from outside their traditional demographics.[78][106]
Ideology
The Houthi movement follows a mixed ideology with religious, Yemeni nationalist, and big tent populist tenets, imitating Hezbollah. Outsiders have argued that their political views are often vague, contradictory, and many of their slogans do not accurately reflect their aims. The Houthis have portrayed themselves as national resistance, defending all Yemenis from outside aggression and influences, as champions against corruption, chaos, and extremism, and as representative for the interests of marginalized tribal groups and the Zaidi sect.[11][12][108] The group has also exploited the popular discontent over corruption and reduction of government subsidies.[55][16] According to a February 2015 Newsweek report, Houthis are fighting "for things that all Yemenis crave: government accountability, the end to corruption, regular utilities, fair fuel prices, job opportunities for ordinary Yemenis and the end of Western influence".[109] In forging alliances, the Houthi movement has been opportunistic, at times allying with countries it later declared its enemy such as the United States.[12]
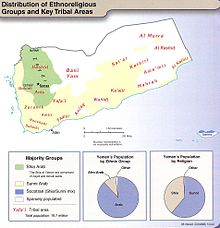
In general, the Houthi movement has centered its belief system on the Zaydi branch of Islam,[11][b] a sect of Islam almost exclusively present in Yemen.[110] Zaydis make up about 25 percent of the population, Sunnis make up 75 percent. Zaydi-led governments ruled Yemen for 1,000 years up until 1962.[58] Since its foundation, the Houthi movement has often acted as advocate for the Zaydi population of Yemen.[16]
Although they have framed their struggle in religious terms and put great importance in their Zaydi roots, the Houthis are not an exclusively Zaydi group. In fact, they have outright rejected their portrayal by others as a faction which is purportedly only interested in Zaydi-related issues. They have not publicly advocated for the restoration of the old Zaydi imamate,[11] although analysts have argued that they might plan to restore it in the future.[55] The movement has also recruited and allied with Sunni Muslims;[116][11][53][55][108] according to researcher Ahmed Nagi, several themes of the Houthi ideology "such as Muslim unity, prophetic lineages, and opposition to corruption [...] allowed the Houthis to mobilize not only northern Zaidis, but also inhabitants of predominantly Shafi'i areas."[55] However, the group is known to have discriminated against Sunni Muslims as well, closing Sunni mosques and primarily placing Zaidis in leadership positions in Houthi-controlled areas.[11][53][54][55][108] The Houthis lost significant support among Sunni tribes after killing ex-President Saleh.[117] Many Zaydis also oppose the Houthis, regarding them as Iranian proxies and the Houthis' form of Zaydi revivalism an attempt to "establish Shiite rule in the north of Yemen".[111]
The Houthis have asserted that their actions are to fight against the expansion of Salafism in Yemen,[111][55] and for the defence of their community from discrimination, whereas their opponents have argued that they desire to institute Zaidi religious law,[118] destabilising the government and stirring anti-American sentiment.[119][120] Hassan al-Homran, a former spokesperson for Ansar Allah, has said that "Ansar Allah supports the establishment of a civil state in Yemen. We want to build a striving modern democracy. Our goals are to fulfil our people's democratic aspirations in keeping with the Arab Spring movement."[121] In an interview with Yemen Times, Hussein al-Bukhari, a Houthi insider, said that Houthis' preferable political system is a republic with elections where women can also hold political positions, and that they do not seek to form a cleric-led government after the model of Islamic Republic of Iran, for "we cannot apply this system in Yemen because the followers of the Shafi (Sunni) doctrine are bigger in number than the Zaydis".[64] In 2018, the Houthi leadership proposed the establishment of a non-partisan transitional government composed of technocrats.[65]
As a result of their strong support among the northern tribes, the Houthis have also been described as tribalist faction in opposition to republicanism. Regardless, they have managed to rally many people outside of their traditional bases to their cause, and became a major nationalist force.[12] When armed conflict for the first time erupted back in 2004 between the Yemeni government and Houthis, the President Ali Abdullah Saleh accused the Houthis and other Islamic opposition parties of trying to overthrow the government and the republican system. However, Houthi leaders, for their part, rejected the accusation by saying that they had never rejected the president or the republican system, but were only defending themselves against government attacks on their community.[122] The Houthis have an ambivalent stance on the possible transformation of Yemen into a federation or the separation into two fully independent countries to solve the country's crisis. Though not opposed to these plans per se, they have declined any plans which would in their eyes marginalize the northern tribes politically.[11][55]
Ali Akbar Velayati, International Affairs Advisor to Supreme Iranian Leader Ayatollah Seyyed Ali Khamenei, stated in October 2014 that "We are hopeful that Ansar-Allah has the same role in Yemen as Hezbollah has in eradicating the terrorists in Lebanon".[123]
Mohammed Ali al-Houthi criticized the Trump-brokered peace agreement between Israel and the United Arab Emirates as treason against the Palestinians and the cause of pan-Arabism.[124] Houthi spokesman Mohammed Abdelsalam said the deal was a provocation against Arab and Islamic nations, and it also showed that countries like the UAE involved in the Yemeni Civil War were trying to fulfil Israel's agenda.[125]
Slogan
The group's slogan reads as following: "God Is Great, Death to America, Death to Israel, Curse on the Jews, Victory to Islam".[126] This motto is partially modelled on the motto of revolutionary Iran, which reads "Death to U.S., and death to Israel".[127]
Some Houthi supporters stress that their ire for the U.S. and Israel is directed toward the governments of America and Israel. Ali al-Bukhayti, the spokesperson and official media face of the Houthis, rejected the literal interpretation of the slogan by stating in one of his interviews that "We do not really want death to anyone. The slogan is simply against the interference of those governments [i. e., U.S. and Israel]".[62] In the Arabic Houthi-affiliated TV and radio stations they use religious connotations associated with jihad against Israel and the US.[61]
Relationship with the Yemeni Jews
The Houthis have been accused of expelling or restricting members of the rural Yemeni Jewish community, which had about 50 remaining members.[128] Reports of abuse include Houthi supporters bullying or attacking the country's Jews.[129][10] Houthi officials, however, have denied any involvement in the harassment, asserting that under Houthi control, Jews in Yemen would be able to live and operate freely as any other Yemeni citizen. "Our problems are with Zionism and the occupation of Palestine, but Jews here have nothing to fear", said Fadl Abu Taleb, a spokesman for the Houthis. But despite insistence by Houthi leaders that the movement is not sectarian, a Yemeni Jewish rabbi has reportedly said that many Jews remain terrified by the movement's slogan.[10] As a result, Yemeni Jews reportedly retain a negative sentiment towards the Houthis, who they allege have committed persecutions against them.[9] According to Israeli Druze politician Ayoob Kara, Houthi militants had given an ultimatum telling Jews to "convert to Islam or leave Yemen".[130]
In March 2016, a UAE-based newspaper reported that one of the Yemeni Jews, who emigrated to Israel in 2016, was fighting with the Houthis. In the same month a Kuwaiti newspaper, al-Watan, reported that a Yemeni Jew named Haroun al-Bouhi was killed in Najran while fighting with the Houthis against Saudi Arabia. The Kuwaiti newspaper added that the Yemeni Jews had a good relationship with Ali Abdullah Salah, who was at that time allied with the Houthis and were fighting in different fronts with the Houthis.[131][132]
Al-Houthi has said through his fascicles: “Arab countries and all Islamic countries will not be safe from Jews except through their eradication and the elimination of their entity.”[133] A New York Times journalist reported being asked why they were speaking to a "dirty Jew" and that the Jews in the village were unable to communicate with their neighbors.[134]
Allegations of harassment against Baháʼí minority
The Houthis have been accused of detaining, torturing, arresting, and holding incommunicado Baháʼí Faith members on charges of espionage and apostasy, which are punishable by death.[135][136] Houthi leader Abdel-Malek al-Houthi has targeted Baháʼís in public speeches, and accused the followers of Baháʼí Faith of being "satanic"[137] and agents for the western countries, citing a 2013 fatwa issued by Iran's supreme leader.[135]
Leaders
- Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi – former leader (killed 2004)
- Abdul-Malik Badreddin al-Houthi – leader
- Yahia Badreddin al-Houthi – senior leader
- Abdul-Karim Badreddin al-Houthi – high-ranking commander
- Badr Eddin al-Houthi – spiritual leader (died 2010)
- Abdullah al-Ruzami – former military commander
- Abu Ali Abdullah al-Hakem al-Houthi – military commander
- Saleh Habra – political leader[138]
- Fares Mana'a – Houthi-appointed governor of Sa'dah,[139] and former head of Saleh's presidential committee[140]
Activism and tactics
Political
During their campaigns against Hadi government, Houthis used civil disobedience. Following the Yemeni government's decision on 13 July 2014 to increase fuel prices, Houthi leaders succeeded in organising massive rallies in the capital Sanaa to protest the decision and to demand resignation of the incumbent government of Abd Rabbuh Mansur Hadi for "state-corruption".[141] These protests developed into the 2014–2015 phase of the insurgency. Similarly, following 2015 Saudi-led airstrikes against Houthis which claimed civilians lives, Yemenis responded to the Abdul-Malik al-Houthi's call and took to streets of the capital, Sanaa, in tens of thousands to voice their anger at the Saudi invasion.[142]
Cultural

The Houthis have also held a number of mass gatherings since the revolution. On 24 January 2013, thousands gathered in Dahiyan, Sa'dah and Heziez, just outside Sanaa, to celebrate Mawlid al-Nabi, the birth of Mohammed. A similar event took place on 13 January 2014 at the main sports' stadium in Sanaa. On this occasion, men and women were completely segregated: men filled the open-air stadium and football field in the centre, guided by appointed Houthi safety officials wearing bright vests and matching hats; women poured into the adjacent indoor stadium, led inside by security women distinguishable only by their purple sashes and matching hats. The indoor stadium held at least five thousand women—ten times as many attendees as the 2013 gathering.[7]
Media
The Houthis are said to have "a huge and well-oiled propaganda machine". They have established "a formidable media arm" with the Lebanese Hezbollah's technical support. The format and content of the group's leader, Abdul-Malik al-Houthi's televised speeches are said to have been modeled after those of Hezbollah's Secretary General, Hassan Nasrallah. Following the peaceful youth uprising in 2011, the group launched its official TV channel, Almasirah. "The most impressive part" of Houthi propaganda, though, is their media print which includes 25 print and electronic publications.[61]
Houthis also utilize radios as an effective means of spreading influence, storming radio stations and confiscating equipment of radio stations that do not adhere to what they're allowed to broadcast by the Houthis.[143] A Houthi fundraising campaign through a radio station affiliated with Iran-backed Houthi rebels has collected 73.5 million Yemeni rials ($132,000) for the Lebanese militant group Hezbollah.[144]
Another western-based media, "Uprising Today", is also known to be extensively pro-Houthi.[145]
Combat and military
In 2009, US Embassy sources have reported that Houthis used increasingly more sophisticated tactics and strategies in their conflict with the government as they gained more experience, and that they fought with religious fervor.[146][147]
Armed strength

Late in 2015, Houthis announced the local production of short-range ballistic missile Qaher-1 on Al-Masirah TV. On 19 May 2017 Saudi Arabia intercepted a Houthi-fired ballistic missile targeting a deserted area south of the Saudi capital and most populous city Riyadh. The Houthi militias have captured dozens of tanks and masses of heavy weaponry from the Yemeni Armed Forces.[148][149][150]
In June 2019, the Saudi-led coalition stated that the Houthis had launched 226 ballistic missiles during the insurgency so far.[151]
The 2019 Abqaiq–Khurais attack targeted the Saudi Aramco oil processing facilities at Abqaiq and Khurais in eastern Saudi Arabia on 14 September 2019. The Houthi movement claimed responsibility, though the United States has asserted that Iran was behind the attack. Iranian President Hassan Rouhani said that "Yemeni people are exercising their legitimate right of defence ... the attacks were a reciprocal response to aggression against Yemen for years."[152]
In course of the Yemeni Civil War, the Houthis developed tactics to combat their opponents' navies. At first, their anti-ship operations were unsophisticated and limited to rocket-propelled grenades being shot at vessels close to the shore.[153] After seizing power in Sanaa, the Houthis took control of numerous coastal missile batteries and patrol boats belonging to the Yemeni military. From 2015, these were gradually converted, adapted and modernized to be effectively used in combat. The Houthis increasingly began to employ specialised anti-ship missile and naval mines, some of them taken from old Yemeni arsenals, others newly constructed or imported from outside supporters such as Iran.[153][154] Patrol boats were fitted with anti-tank guided missiles, about 30 coast-watcher stations were set up, disguised "spy dhows" were constructed, and the maritime radar of docked ships used to create targeting solutions for attacks.[154] One of the most notable features of the Houthis' naval arsenal became its remote-controlled drone boats which carry explosives and ram enemy warships.[153][155][156] Among these, the self-guiding Shark-33 explosive drone boats originated as patrol boats of the old Yemeni coast guard.[155] In addition, the Houthis have begun to train combat divers on the Zuqar and Bawardi islands.[154]
Allegations of Iranian and North Korean support
Former Yemeni president Ali Abdullah Saleh had accused the Houthis of having ties to external backers, in particular the Iranian government.[157] Saleh stated in a New York Times' interview that "The real reason they received unofficial support from Iran was because they repeat same slogan that is raised by Iran death to America, death to Israel". He also said "The Iranian media repeats statements of support for these Houthi elements. They are all trying to take revenge against the USA on Yemeni territories".[60][158] Tehran has denied allegations of Houthis receiving arms support from Iran.[159] The Houthis in turn accused the Saleh government of being backed by Saudi Arabia and of using Al-Qaeda to repress them.[160] Under the next President Hadi, Gulf Arab states accused Iran of backing the Houthis financially and militarily, though Iran denied this, and they were themselves backers of President Hadi.[161] Despite confirming statements by Iranian and Yemeni officials in regards to Iranian support in the form of trainers, weaponry, and money, the Houthis denied reception of substantial financial or arm support from Iran.[16][162] Joost Hiltermann of Foreign Policy wrote that whatever little material support the Houthis may have received from Iran, the intelligence and military support by US and UK for the Saudi Arabian-led coalition exceed that by many factors.[163]
In April 2015, the United States National Security Council spokesperson Bernadette Meehan remarked that "It remains our assessment that Iran does not exert command and control over the Houthis in Yemen".[164] Joost Hiltermann wrote that Iran does not control the Houthis' decision-making as evidenced by Houthis' flat rejection of Iran's demand not to take over Sanaa in 2015.[163] Thomas Juneau, writing in the journal, International Affairs, states that even though Iran's support for Houthis has increased since 2014, it remains far too limited to have a significant impact in the balance of power in Yemen.[158]
A December 2009 cable between Sanaa and various intelligence agencies disseminated by WikiLeaks states that US State Dept. analysts believed the Houthis obtained weapons from the Yemeni black market and corrupt members of the Yemenis Republican Guard.[146] On the edition of 8 April 2015 of PBS Newshour, Secretary of State John Kerry stated that the US knew Iran was providing military support to the Houthi rebels in Yemen, adding that Washington "is not going to stand by while the region is destabilised".[165]
Phillip Smyth of the Washington Institute for Near East Policy told Business Insider that Iran views Shia groups in the Middle East as "integral elements to the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC)". Smyth claimed that there is a strong bond between Iran and the Houthi uprising working to overthrow the government in Yemen. According to Smyth, in many cases Houthi leaders go to Iran for ideological and religious education, and Iranian and Hezbollah leaders have been spotted on the ground advising the Houthi troops, and these Iranian advisers are likely responsible for training the Houthis to use the type of sophisticated guided missiles fired at the US Navy.[166] For Iran, supporting the revolt in Yemen is "a good way to bleed the Saudis", Iran's regional and ideological rival. Essentially, Iran is backing the Houthis to fight against a Saudi-led coalition of Gulf States fighting to maintain government control of Yemen.[167] The discord has led some publishers to fear that further confrontations may lead to an all-out Sunni-Shia war.[168]
In 2013, photographs released by the Yemeni government show the United States Navy and Yemen's security forces seized a class of shoulder-fired anti-aircraft missiles not publicly known to have been out of state control.[169]
In April 2016, the U.S. Navy intercepted a large Iranian arms shipment, seizing thousands of weapons, AK-47 rifles and rocket-propelled grenade launchers. The Pentagon stated that the shipment was likely headed to Yemen.[170]
In August 2018, the United Nations had found out the North Korean government had armed the Houthis via Syria after a meeting between a Houthi member and a North Korean government official.[171][19][20]
The Houthis have repeatedly used a drone that is nearly identical to Iran Aircraft Manufacturing Industrial Company's Ababil-T drone in strikes against Saudi Arabia.[172]
IRGC involvement
In 2013, an Iranian vessel was seized and discovered to be carrying Katyusha rockets, heat-seeking surface-to-air missiles, RPG-7s, Iranian-made night vision goggles and artillery systems that track land and navy targets 40 km away. That was en route to the Houthis.[173]
In March 2017, Qasem Soleimani, the head of Iran's Quds Force, met with Iran's Revolutionary Guard Corps to look for ways to what was described as "empowering" the Houthis. Soleimani was quoted as saying, "At this meeting, they agreed to increase the amount of help, through training, arms and financial support." Despite the Iranian government, and Houthis both officially denying Iranian support for the group. Brigadier General Ahmad Asiri, the spokesman of the Saudi-led coalition told Reuters that evidence of Iranian support was manifested in the Houthi use of Kornet anti-tank guided missiles which had never been in use with the Yemeni military or with the Houthis and that the arrival of Kornet missiles had only come at a later time.[174] In the same month the IRGC had altered the routes used in transporting equipment to the Houthis by spreading out shipments to smaller vessels in Kuwaiti territorial waters in order to avoid naval patrols in the Gulf of Oman due to sanctions imposed, shipments reportedly included parts of missiles, launchers, and drugs.[175]
In May 2018, the United States imposed sanctions on Iran's IRGC, which was also listed as a designated terrorist organization by the US over its role in providing support for the Houthis, including help with manufacturing ballistic missiles used in attacks targeting cities and oil fields in Saudi Arabia.[176]
In August 2018, despite previous Iranian denial of military support for the Houthis, IRGC commander Nasser Shabani was quoted by the Fars News Agency which has been described as the semi-official news agency of the Iranian government as saying, "We (IRGC) told Yemenis [Houthi rebels] to strike two Saudi oil tankers, and they did it," on 7 August 2018. In response to Shabani's account, the IRGC released a statement saying that the quote was a "Western lie" and that Shabani was a retired commander, despite no actual reports of his retirement after 37 years in the IRGC, and media linked to the Iranian government confirming he was still enlisted with the IRGC.[177] Furthermore, while the Houthis and the Iranian government have previously denied any military affiliation,[178] Iranian supreme leader Ali Khamenei openly announced his "spiritual" support of the movement in a personal meeting with the Houthi spokesperson Mohammed Abdul Salam in Tehran, in the midst of ongoing conflicts in Aden in 2019.[179][180]
Allegations of human rights violations
Houthis have been accused of violations of international humanitarian law such as using child soldiers,[181][182][183] shelling civilian areas,[184] forced evacuations and executions.[146] According to Human Right Watch, Houthis intensified their recruitment of children in 2015. The UNICEF mentioned that children with the Houthis and other armed groups in Yemen comprise up to a third of all fighters in Yemen.[185] Human Rights Watch has further accused Houthi forces of using landmines in Yemen's third-largest city of Taizz which has caused many civilian casualties and prevent the return of families displaced by the fighting.[186] HRW has also accused the Houthis of interfering with the work of Yemen's human rights advocates and organizations.[187]
An HRW researcher, quoted in 2009 US embassy report, has downplayed the allegations by the former government of Yemen accusing the Houthis of using civilians as human shields, by saying that they did not have enough evidence to conclude that the Houthis have been intentionally using civilians as human shields.[146][147]
According to the Human Rights Watch, the Houthis also use hostage taking as a tactic to generate profit. Human Rights Watch documented 16 cases in which Houthi authorities held people unlawfully, in large part to extort money from relatives or to exchange them for people held by opposing forces.[188]
The United Nations World Food Programme has accused the Houthis of diverting food aid and illegally removing food lorries from distribution areas, with rations sold on the open market or given to those not entitled to it.[189] The WFP has also warned that aid could be suspended to areas of Yemen under the control of Houthi rebels due to "obstructive and uncooperative" Houthi leaders that have hampered the independent selection of beneficiaries.[190] WFP spokesman Herve Verhoosel stated "The continued blocking by some within the Houthi leadership of the biometric registration ... is undermining an essential process that would allow us to independently verify that food is reaching ... people on the brink of famine". The WFP has warned that "unless progress is made on previous agreements we will have to implement a phased suspension of aid". The Norwegian Refugee Council has stated that they share the WPF frustrations and reiterate to the Houthis to allow humanitarian agencies to distribute food.[191][192]
UN-funded investigators have uncovered proof that Houthis conscripted tens of teenage girls as informants, nurses, and guards; an unusual phenomenon in a society as conservative as Yemen. Twelve girls suffered sexual violence, arranged marriages, and child marriages as a result of their recruitment. It alleged the Houthis recruited children as young as seven years old with monetary incentives. The report cited hundreds of accounts and took place between summer 2019 and summer 2020.[193]
Governance
According to the 2009 US Embassy cable leaked by WikiLeaks, Houthis have reportedly established courts and prisons in areas they control. They impose their own laws on local residents, demand protection money, and dispense rough justice by ordering executions. AP's reporter, Ahmad al-Haj argued that the Houthis were winning hearts and minds by providing security in areas long neglected by the Yemeni government while limiting the arbitrary and abusive power of influential sheikhs. According to the Civic Democratic Foundation, Houthis help resolve conflicts between tribes and reduce the number of revenge killings in areas they control. The US ambassador believed that the reports that explain Houthi role as arbitrating local disputes were likely.[146][147]
Areas under administration
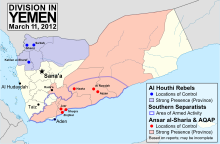
The Houthis exert de facto authority over the bulk of North Yemen.[194] As of 28 April 2020, they control all of North Yemen except for Marib Governorate.[195][196] The Houthis' direct administration includes the following territories:
- Saada Governorate[139]
- Marib Governorate
- Sirwah
- 'Amran Governorate[197]
- Al Jawf Governorate[195][196]
- Hajjah Governorate[198]
- Sanaa Governorate[199]
- Dhamar Governorate[200]
- Al Mahwit Governorate
- Raymah Governorate[201]
- Ibb Governorate[202]
- Al Hudaydah Governorate[203]
- Al Bayda Governorate[204]
- Taiz Governorate
Notes
References
- ^ "Mohammed Abdul Salam denies news in Saudi channel". Yemen Press. Archived from the original on 27 August 2018. Retrieved 28 August 2018.
- ^ "What is the Houthi Movement?". Tony Blair Faith Foundation. 25 September 2014. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ Tucker, Spencer C. (8 October 2010). The Encyclopedia of Middle East Wars: The United States in the Persian Gulf, Afghanistan, and Iraq Conflicts [5 volumes]: The United States in the Persian Gulf, Afghanistan, and Iraq Conflicts. ABC-CLIO. p. 539. ISBN 9781851099481 – via Google Books.
- ^ Council, American Foreign Policy (27 October 2011). The World Almanac of Islamism: 2011. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 250. ISBN 9781442207158 – via Google Books.
- ^ Wells, Madeleine. "Yemen's Houthi movement and the revolution". Archived from the original on 24 January 2015. Retrieved 18 September 2019.
- ^ Hill, Ginny (18 September 2017). Yemen Endures: Civil War, Saudi Adventurism and the Future of Arabia. Oxford University Press. p. 266. ISBN 9780190842369 – via Google Books.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Plotter, Alex (4 June 2015). "Yemen in crisis". Esquire. Archived from the original on 23 July 2018. Retrieved 5 September 2015.
- ^ "Yemen Issue and Solution Alternatives". ResearchGate. Archived from the original on 2 March 2019. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Persecution Defines Life for Yemen's Remaining Jews". The New York Times. 19 February 2015. Archived from the original on 15 October 2016. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c ""Damn the Jews" proving more than just a slogan". Yemen Times. Archived from the original on 16 February 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i Cameron Glenn (29 May 2018). "Who are Yemen's Houthis?". Wilson Center. Archived from the original on 20 April 2019. Retrieved 20 April 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Asher Orkaby (25 March 2015). "Houthi Who? A History of Unlikely Alliances in an Uncertain Yemen". Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 12 August 2019. Retrieved 20 April 2019.
- ^ Almasmari, Hakim. "Medics: Militants raid Yemen town, killing dozens Archived 29 November 2011 at the Wayback Machine", CNN, 27 November 2011.
- ^ Houthis Kill 24 in North Yemen Archived 19 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine, 27 November 2011.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 4 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Iranian support seen crucial for Yemen's Houthis". Reuters. 15 December 2014. Archived from the original on 2 February 2015. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- ^ "North Korea's Balancing Act in the Persian Gulf". The Huffington Post. 17 August 2015. Archived from the original on 17 August 2015. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
North Korea's military support for Houthi rebels in Yemen is the latest manifestation of its support for anti-American forces.
- ^ "The September 14 drone attack on Saudi oil fields: North Korea's potential role | NK News". 30 September 2019. Archived from the original on 11 October 2019. Retrieved 11 October 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "North Korea is hiding nukes and selling weapons, alleges confidential UN report". CNN. 5 February 2019. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
The summary also accuses North Korea of violating a UN arms embargo and supplying small arms, light weapons and other military equipment to Libya, Sudan, and Houthi rebels in Yemen, through foreign intermediaries.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Secret UN report reveals North Korea attempts to supply Houthis with weapons". Al-Arabiya. 4 August 2018. Retrieved 4 August 2018.
The report said that experts were investigating efforts by the North Korean Ministry of Military Equipment and Korea Mining Development Trading Corporation (KOMID) to supply conventional arms and ballistic missiles to Yemen’s Houthi group.
- ^ "Panel investigates North Korean weapon used in Mogadishu attack on UN compound". 3 March 2021.
- ^ "Just how neutral is Oman in Yemen war?". AL-MONITOR. 12 October 2016. Archived from the original on 18 October 2018. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
Just how neutral is Oman in Yemen war?"
- ^ "Yemen War and Qatar Crisis Challenge Oman's Neutrality". Middle East Institute. 6 July 2017. Archived from the original on 18 October 2018. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
Yemen War and Qatar Crisis Challenge Oman’s Neutrality
- ^ "Oman is a mediator in Yemen. Can it play the same role in Qatar?". The Washington Post. 22 July 2017. Archived from the original on 18 October 2018. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
Oman is a mediator in Yemen. Can it play the same role in Qatar?
- ^ "Oman denies arms smuggled through border to Houthis". Middle East Eye. Archived from the original on 26 April 2019. Retrieved 13 June 2018.
- ^ "Houthi rise in Yemen raises alarm in Horn of Africa". www.worldbulletin.net. Archived from the original on 13 August 2019. Retrieved 13 August 2019.
- ^ "Mana'a and al-Ahmar received money from Gaddafi to shake security of KSA, Yemen". 4 September 2011. Archived from the original on 10 February 2013. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ^ Shahbazov, Fuad. "Russia's Growing Role in Yemen". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ^ "Yemen's Houthi-led govt appoints new envoy to Syria". Middle East Monitor. 12 November 2020. Archived from the original on 13 November 2020. Retrieved 30 March 2021.
Yemen's Houthi-led National Salvation Government (NSG) has appointed a new ambassador to Syria, one of the countries alongside Iran which recognises the Sanaa-based government.
- ^ "Yemen's Military: From the Tribal Army to the Warlords". 19 March 2018. Archived from the original on 14 June 2018. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- ^ "Yemen's General People's Congress calls for 'uniting against Iranian project'". English.AlArabiya.net. 3 December 2017. Archived from the original on 24 June 2018. Retrieved 1 January 2018.
- ^ "Death of a leader: Where next for Yemen's GPC after murder of Saleh?". Middle East Eye. 23 January 2018. Archived from the original on 23 January 2018. Retrieved 31 May 2018.
- ^ "Source: Hezbollah, Iran helping Hawthi rebels boost control of Yemen's capital". Haaretz. 27 September 2014. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- ^ Rafi, Salman (2 October 2015). "How Saudi Arabia's aggressive foreign policy is playing against itself". Asia Times. Archived from the original on 29 September 2020. Retrieved 23 January 2016.
- ^ "Iraq's Nujaba, Yemen's Ansarullah Discuss US Threats - World news". Archived from the original on 11 May 2019. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- ^ https://iranprimer.usip.org/blog/2018/oct/04/state-department-report-1-iran%E2%80%99s-support-terrorism
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f "Egypt, Jordan, Sudan and Pakistan ready for ground offensive in Yemen: report". The Globe and Mail. 26 March 2015. Archived from the original on 26 March 2015. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia launches airstrikes in Yemen". CNN. 26 March 2015. Archived from the original on 20 June 2019. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ^ "SOMALIA: Somalia finally pledges support to Saudi-led coalition in Yemen – Raxanreeb Online". RBC Radio. 7 April 2015. Archived from the original on 7 April 2015. Retrieved 7 April 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Riedel, Bruce (18 December 2017). "Who are the Houthis, and why are we at war with them?". Brookings Institution. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 12 June 2018.
- ^ "Yemen's Houthis: New members of Iran's anti-Israeli/anti-American axis". JPost.com. Retrieved 1 January 2018.
- ^ "Yemen's Houthis: New members of Iran's anti-Israeli/anti-American axis". Jerusalem Post.
- ^ "Al-Qaeda Announces Holy War against Houthis- Yemen Post English Newspaper Online". yemenpost.net. Archived from the original on 21 October 2017. Retrieved 6 November 2011.
- ^ "Islamic State leader urges attacks in Saudi Arabia: speech". Reuters. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- ^ Hamas supports military operation for political legitimacy in Yemen, https://www.arabnews.com/saudi-arabia/news/725241 (29 March 2015). "Hamas supports military operation for political legitimacy in Yemen".
- ^ "Australian mercenary reportedly killed in Yemen clashes". 8 December 2015. Archived from the original on 3 November 2018. Retrieved 20 December 2018 – via www.theguardian.com.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia designates Muslim Brotherhood terrorist group". Reuters. 7 March 2014. Archived from the original on 27 June 2018. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
- ^ "مجلس الوزراء يعتمد قائمة التنظيمات الإرهابية. | Wam". Archived from the original on 17 November 2014.
- ^ "LIST OF INDIVIDUALS, ENTITIES AND OTHER GROUPS AND UNDERTAKINGS DECLARED BY THE MINISTER OF HOME AFFAIRS AS SPECIFIED ENTITY UNDER SECTION 66B(1)" (PDF). Ministry of Home Affairs of Malaysia. Retrieved 4 March 2020.
- ^ "Do not call the Ansar Allah movement "Houthi"!". IWN. 23 April 2021. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ "Yemen: Civil War and Regional Intervention" (PDF). Congressional Research. 8 December 2020. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
The Houthi movement (formally known as Ansar Allahor Partisans of God) is a predominantly Zaydi Shia revivalist political and insurgent movement formed in the northern Yemeni governorate of Saada under the leadership of members of the Houthi family.
- ^ Hoffman, Valerie J. (28 February 2019). Making the New Middle East: Politics, Culture, and Human Rights. Syracuse University Press. ISBN 9780815654575. Retrieved 18 September 2019 – via Google Books.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Yemen crisis: Who is fighting whom?". BBC News. 2018. Archived from the original on 10 July 2018. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Refugees, United Nations High Commissioner for. "Refworld | Yemen: Treatment of Sunni Muslims by Houthis in areas under Houthi control (2014-September 2017)". Refworld. Archived from the original on 17 June 2019. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i Ahmed Nagi (19 March 2019). "Yemen's Houthis Used Multiple Identities to Advance". Carnegie Middle East Center. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Yemeni forces kill rebel cleric". BBC News. 10 September 2004. Archived from the original on 21 November 2006.
- ^ Streuly, Dick (12 February 2015). "5 Things to Know About the Houthis of Yemen". Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Yemen: The conflict in Saada Governorate – analysis". IRIN. 24 July 2008. Archived from the original on 4 December 2014. Retrieved 29 November 2014.
- ^ "Debunking Media Myths About the Houthis in War-Torn Yemen · Global Voices". GlobalVoices.org. 1 April 2015. Archived from the original on 1 September 2017. Retrieved 1 January 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "An Interview With President Ali Abdullah Saleh". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 8 July 2016. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Houthi propaganda: following in Hizbullah's footsteps". alaraby. Archived from the original on 18 October 2016. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Photo Essay: Rise of the Houthis". Newsweek. 9 February 2015. Archived from the original on 12 November 2017. Retrieved 27 March 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Juneau, Thomas (May 2016). "Iran's policy towards the Houthis in Yemen: a limited return on a modest investment". International Affairs. 92 (3): 647–663. doi:10.1111/1468-2346.12599.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Al-Bukhari to the Yemen Times: "The Houthis' takeover can not be called an invasion"". Yemen Times. 21 October 2014. Archived from the original on 25 September 2015. Retrieved 17 February 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Naseh Shaker; Faisal Edroos (25 December 2018). "Mohammed al-Houthi: We want a united and democratic Yemen". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- ^ "Yemen". Human Rights Watch. Archived from the original on 23 April 2017. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Yemen's Houthis form own government in Sanaa". Al Jazeera. 6 February 2015. Archived from the original on 2 July 2018. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ Islam Hassan (31 March 2015). "GCC's 2014 Crisis: Causes, Issues and Solutions". Gulf Cooperation Council's Challenges and Prospects. Al Jazeera Research Center. Archived from the original on 4 September 2015. Retrieved 4 June 2015.
- ^ "International Support to Yemen's Legitimate Government". aawsat. Archived from the original on 10 April 2018. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ "Yemen govt vows to stay in Aden despite IS bombings". Yahoo News. 7 October 2015. Archived from the original on 22 December 2015. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ^ Agence France-Presse (7 October 2015). "Arab Coalition Faces New Islamic State Foe in Yemen Conflict". NDTV.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 8 October 2015.
- ^ Agence France-Presse (23 October 2019). "Yemeni government, separatists seen inking deal to end Aden standoff". Euronews. Archived from the original on 23 October 2019. Retrieved 25 October 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Al Batati, Saeed (21 August 2014). "Who are the Houthis in Yemen?". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 23 August 2014.
- ^ Freeman, Jack (2009). "The al Houthi Insurgency in the North of Yemen: An Analysis of the Shabab al Moumineen". Studies in Conflict & Terrorism. 32 (11): 1008–1019. doi:10.1080/10576100903262716. ISSN 1057-610X. S2CID 110465618.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Regime and Periphery in Northern Yemen: The Huthi Phenomenon" (PDF). RAND. 2010. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 January 2012. Retrieved 23 January 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Yemen's Abd-al-Malik al-Houthi". BBC News. 3 October 2014. Archived from the original on 2 March 2015. Retrieved 29 November 2014.
- ^ "Profile: The crisis in Yemen". thenational.scot. Archived from the original on 15 April 2015. Retrieved 11 April 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Adam Baron (25 March 2015). "What Went Wrong with Yemen". Politico. Archived from the original on 12 August 2015. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ^ "The Huthis: From Saada to Sanaa". Middle East Report N°154. International Crisis Group. 10 June 2014. Archived from the original on 9 April 2015. Retrieved 29 November 2014.
- ^ "Yemen Al Houthi rebels slam federation plan as unfair". Gulf News. 11 February 2014. Archived from the original on 12 March 2014. Retrieved 16 March 2014.
- ^ al-Hassani, Mohammed (6 February 2014). "HOUTHI SPOKESPERSON TALKS TO THE YEMEN TIMES". Yemen Times. Archived from the original on 16 March 2014. Retrieved 16 March 2014.
- ^ "Houthis Close to Control Hajjah Governorate, Amid Expectations of Expansion of Control over Large Parts of Northern Yemen". Islam Times. 29 November 2011. Archived from the original on 5 April 2012. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- ^ "Al-Houthi Expansion Plan in Yemen Revealed". Yemen Post. 9 November 2011. Archived from the original on 9 November 2011.
- ^ "New war with al-Houthis is looming". Yemen observer. Archived from the original on 19 September 2012. Retrieved 23 January 2013.
- ^ "Houthis seize government buildings in Sanaa". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 22 September 2014. Retrieved 21 September 2014.
- ^ Kareem Fahim (7 January 2015). "Violence Grows in Yemen as Al Qaeda Tries to Fight Its Way Back". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 8 January 2015. Retrieved 8 January 2015.
- ^ "Yemen Houthi rebels 'seize presidential palace'". BBC News. 20 January 2015. Archived from the original on 28 May 2018. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- ^ "Death toll hits 142 from attacks in Yemen mosques". Al Bawaba. 20 March 2015. Archived from the original on 22 March 2015.
- ^ "Saudi 'Decisive Storm' waged to save Yemen". Al Arabiya News. 26 March 2015. Archived from the original on 27 March 2015.
- ^ Keane, Angela Greiling (26 March 2015). "U.S. Backs Saudi-Led Yemeni Bombing With Logistics, Spying". Bloomberg News. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015.
- ^ "الحوثيون: رصدنا رسائل بين صالح وأبوظبي قبل 3 شهور" (in Arabic). Al Khaleej. 4 December 2017. Archived from the original on 15 June 2018. Retrieved 5 December 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Edroos, Faisal (4 December 2017). "How did Yemen's Houthi-Saleh alliance collapse?". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 19 May 2019. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ Leith Fadel (2 December 2017). "Violence escalates in Sanaa as Saleh loyalists battle Houthis". Al Masdar News. Archived from the original on 19 May 2019. Retrieved 2 December 2017.
- ^ Yemen: Conflict intensifies between former rebel allies Archived 25 December 2019 at the Wayback Machine, 0:24, Al Jazeera English (3 December 2017)
- ^ "Yemen's Houthis blow up ex-president Saleh's house". Reuters. 4 December 2017. Archived from the original on 25 November 2018. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ "Yemen's former President Ali Abdullah Saleh killed trying to flee Sanaa". CNN. 4 December 2017. Archived from the original on 11 December 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ "Yemen's ex-president Saleh shot dead after switching sides in civil war". Reuters. 4 December 2017. Archived from the original on 4 December 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ "'Diplomatic vandalism': aid groups' fury as US puts Houthis on terror list". The Guardian. Retrieved 11 January 2021.
- ^ Nick Schifrin; Ali Rogin (16 February 2021). "In foreign policy shift, Biden lifts terrorist designation for Houthis in Yemen". PBS. Retrieved 12 April 2021.
- ^ "Yemen war: Who are the Houthis and why is Saudi Arabia fighting them?". independent.co.uk. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ^ "Hothi / Houthi / Huthi; Ansar Allah; al-Shabab al-Mum'en / Shabab al-Moumineen (Believing Youth)". globalsecurity.org. Archived from the original on 4 January 2018. Retrieved 12 November 2009.
- ^ Philips, Sarah (28 July 2005). Cracks in the Yemeni System Archived 27 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Middle East Report Online.
- ^ "Pity those caught in the middle". The Economist. 19 November 2009. Archived from the original on 11 February 2010. Retrieved 20 November 2009.
- ^ Almasmari, Hakim (10 April 2010). "Editorial: Thousands Expected to die in 2010 in Fight against Al-Qaeda". Yemen Post. Archived from the original on 3 March 2011. Retrieved 22 January 2010.
- ^ Ahmed Al-Bahri: Expert in Houthi Affairs Archived 29 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine, 10 April 2010.
- ^ "Yemen: Houthis Send Children into Battle". 12 May 2015. Archived from the original on 26 August 2016. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ M. Izady. "Yemen:Ethno-Religious Composition Archived 22 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine" Columbia University. 2014. Accessed 12 April 2015
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Who are Yemen's Houthis?". NewsHour. PBS. 14 December 2018. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- ^ "Photo Essay: The Rise of the Houthis". Newsweek. 9 February 2015. Archived from the original on 12 November 2017. Retrieved 17 February 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Al-Shamahi, Abubakr (7 February 2014). "Yemen is more nuanced than 'Sunni' & 'Shia'". Yemen Times. Archived from the original on 2 January 2015. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Manuel Almeida (8 October 2014). "Profile: Who are Yemen's Houthis?". Al Arabiya. Archived from the original on 2 February 2015. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ^ "Hothi/Houthi/Huthi: al-Shabab al-Mum'en/Shabab al-Moumineen (Believing Youth)". GlobalSecurity. Archived from the original on 4 January 2018. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ^ Bengio, Ofra; Litvak, Meir, eds. (8 November 2011). The Sunna and Shi'a in History: Division and Ecumenism in the Muslim Middle East. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 244. ISBN 9780230370739.
- ^ Middle East Forum. "Harakat Ansar Allah (Yemen): Emblem". jihadintel.meforum.org. Retrieved 15 February 2020.
- ^ Ansar Allah (Houthis). "Ansar Allah". ansarollah.com (in Arabic). Retrieved 15 February 2020.
- ^ Refugees, United Nations High Commissioner for. "Refworld | Yemen: Treatment of Sunni Muslims by Houthis in areas under Houthi control (2014-September 2017)". Refworld. Archived from the original on 17 June 2019. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
[a]lthough the Huthis have widespread support among the Zaydi community, the movement also contains Sunni Muslims, [which is why] some Zaydis have denounced the Huthi movement [...] the Huthis are recruiting Yemenis of all faiths to fight for them
- ^ Maysaa Shuja al-Deen (23 April 2019). "The Houthi–Tribal Conflict in Yemen". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ "Deadly blast strikes Yemen mosque". BBC News. 2 May 2008. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- ^ Sultan, Nabil (10 July 2004).
- ^ "Asia Times – Asia's most trusted news source for the Middle East". atimes.com. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 3 May 2008.CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)
- ^ "Hassan al-Homran, spokesperson for Ansar Allah". Yemen Post. 22 November 2013. Archived from the original on 25 September 2015. Retrieved 25 September 2015.
- ^ Arrabyee, Nasser (25 May 2005). "Rebellion continues". Al-Ahram Weekly. Archived from the original on 24 October 2005. Retrieved 11 April 2007.
- ^ "Analysis: Iranian Reactions to Operation Decisive Storm". The Long War Journal. 31 March 2015. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- ^ Farrell, Stephen (13 August 2020). "Israel hails UAE deal but Palestinians - and settlers - dismayed". Reuters.
- ^ "World reacts to 'historic' Israel-UAE deal". Times of Malta. Agence France-Presse. 14 August 2020.
- ^ Arabic: الله أكبر، الموت لأمريكا، الموت لإسرائيل، اللعنة على اليهود، النصر للإسلام; Transliterated as "alllah 'akbara, almawt li'amrika, almawt li'iisrayiyla, alllaenat ealaa alyahud, alnnasr lil'iislam"
- ^ ShahidSaless, Shahir (30 March 2015). "Does Iran really control Yemen". Al Monitor. Archived from the original on 13 February 2015.
- ^ Toi Staff (16 April 2017). "Yemen minister says fate of country's last 50 Jews unknown". Times of Israel. Archived from the original on 1 August 2019. Retrieved 16 September 2019.
- ^ "Amid persecution, Yemeni Jews face extinction - Jewish World - Jerusalem Post". jpost.com. Archived from the original on 13 August 2019. Retrieved 13 August 2019.
- ^ Houthis militants to Jews: Convert or leave Yemen Archived 15 February 2016 at the Wayback Machine. 11 October 2015. Yemen Online. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
- ^ "يهودي يمني من أحضان الحوثي إلى أحضان إسرائيل". 24.ae (in Arabic). Retrieved 17 September 2019.
- ^ "الكشف عن جثة يهودي كان يشارك في القتال مع الحوثيين". Archived from the original on 7 March 2016. Retrieved 18 September 2019.
- ^ https://www.yemenembassy.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Houthi-Ideology.pdf
- ^ https://www.nytimes.com/2015/02/19/world/middleeast/persecution-defines-life-for-yemens-few-jews.html?auth=login-email&login=email
- ^ Jump up to: a b Majidyar, Ahmed; Al Jarallah, Lama (21 September 2018). "Iran-backed Houthi rebels step up persecution of Baha'i (sic) minority in Yemen". mei. mei. Archived from the original on 28 September 2018. Retrieved 28 September 2018.
- ^ "Yemen: Houthis Sentence Baha'i (sic) Man to Death". hrw. hrw. 27 February 2018. Archived from the original on 30 June 2018. Retrieved 28 September 2018.
- ^ Michael, Maggie. "404 Not Found". The Washington Post. Washington Post. Archived from the original on 18 September 2018. Retrieved 28 September 2018.
- ^ "Meetings push government and Houthis closer towards "reconciliation"". Yemen Times. 29 March 2012. Archived from the original on 23 January 2013. Retrieved 23 January 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Al-Batati, Saeed (28 March 2011). "Yemeni regime loses grip on four provinces". Arab News. Archived from the original on 31 March 2011.
- ^ "Sana'a Cards to Pressurize Houthis to Enter New Dialogue Rounds". Yemen Post. Archived from the original on 1 May 2012.
- ^ "Tens of thousands of Yemeni Houthis protest against fuel reform, government". Reuters. 18 August 2014.
- ^ "Coalition jets continue to hit Houthi targets in Yemen". Al Jazeera. 27 March 2015. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015.
- ^ https://www.jpost.com/Middle-East/Radio-becomes-new-battlefield-in-Yemen-war-601371/amp
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 8 July 2019. Retrieved 9 October 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Home – Uprising Today". Uprising Today Media. Archived from the original on 1 December 2019. Retrieved 11 May 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Cable:09SANAA2186_a". Wikileaks. 9 December 2009. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Cablegate: Who Are the Houthis, Part Two: How Are They". Scoop. Archived from the original on 25 September 2015. Retrieved 25 September 2015.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia intercepts Houthi rebel missile fired towards Riyadh – News – DW – 20.05.2017". DW.COM. Archived from the original on 19 January 2018. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ^ "ABC News". ABC News. Archived from the original on 24 May 2017. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ^ "فيديو+صور "قاهر1" أول صاروخ بالستي معدل محلياً يضرب قاعدة خميس مشيط | المسيرة نت – قناة المسيرة الفضائية". Archived from the original on 11 March 2016. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- ^ Lisa Barrington; Aziz El Yaakoubi (17 September 2019). "Yemen Houthi drones, missiles defy years of Saudi air strikes". Reuters. Archived from the original on 27 September 2019. Retrieved 27 September 2019.
- ^ "Putin proposes Russian missile defence for Saudi after oil attack". Al-Jazeera. 16 September 2019. Archived from the original on 18 September 2019. Retrieved 16 September 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Caleb Weiss (17 August 2019). "Analysis: Houthi naval attacks in the Red Sea". Long War Journal. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Knights 2018, p. 20.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Knights 2018, pp. 20–21.
- ^ Caleb Weiss (11 March 2020). "Houthis increase use of suicide drone boats in recent weeks". Long War Journal. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
- ^ "Cable Viewer". Wikileaks. 17 February 2010. Archived from the original on 7 June 2013. Retrieved 23 January 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Juneau, Thomas (1 May 2016). "Iran's policy towards the Houthis in Yemen: a limited return on a modest investment". International Affairs. 92 (3): 647–663. doi:10.1111/1468-2346.12599. ISSN 1468-2346.
- ^ Tisdall, Simon (26 March 2015). "Iran-Saudi proxy war in Yemen explodes into region-wide crisis". The guardian. Archived from the original on 5 June 2015. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
- ^ "Al-Qaeda Fighting for Yemeni Government Against Houthi Shia Rebels..." 29 December 2009. Archived from the original on 13 May 2020. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- ^ "BBC". BBC News. 30 January 2018. Archived from the original on 28 July 2018.
- ^ "Iranian ship unloads 185 tons of weapons for Houthis at Saleef port". Al Arabiya News. 20 March 2015. Archived from the original on 24 March 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The Houthis Are Not Hezbollah". Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on 28 July 2018. Retrieved 28 July 2018.
- ^ "United states senate committee on foreign relations" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 May 2017.
- ^ "Kerry Says U.S. Knew of Iran's Military Aid to Houthi Rebels". The New York Times. 10 April 2015. Archived from the original on 18 December 2016. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ cf. "US general suspects Iran role in Houthi attacks on US ships". The Times of Israel. 20 October 2016. Archived from the original on 25 October 2016. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ^ businessinsider. Why the US confronted Iranian-backed militants in Yemen, and the risks that lie ahead. Archived from the original on 22 October 2016. Retrieved 21 October 2016.
- ^ The Arab Revolts, 2013 David Mcmurray
- ^ "Seizure of Antiaircraft Missiles in Yemen Raises Fears That Iran Is Arming Rebels There". nytimes. nytimes. Archived from the original on 4 February 2017. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ "US seizes thousands of Iranian weapons, including grenade launchers, in Arabian Sea". fox news. Archived from the original on 19 October 2016. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ "North Korea has not stopped nuclear, missile program: confidential U.N. report". Reuters. 3 August 2018. Archived from the original on 6 December 2018. Retrieved 6 December 2018.
- ^ Frantzman, Seth J. (6 July 2019). "Iran Media Celebrates Houthi Drone Attacks on Saudi Arabia". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on 22 July 2019. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- ^ "Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC)". Counter Extremism Project. Archived from the original on 13 August 2019. Retrieved 12 August 2019.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 22 March 2017. Retrieved 12 August 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Exclusive: Iran Revolutionary Guards find new route to arm Yemen..." 2 August 2017. Archived from the original on 12 August 2019. Retrieved 13 August 2019 – via www.reuters.com.
- ^ "US hits Iran IRGC with sanctions over support of Yemen's Houthis". aljazeera.com. Archived from the original on 7 August 2019. Retrieved 12 August 2019.
- ^ "IRGC Claims General Who Spilled The Beans Is A 'Retired' Officer". RFE/RL. Archived from the original on 12 August 2019. Retrieved 12 August 2019.
- ^ "Iranian support seen crucial for Yemen's Houthis". Reuters. 15 December 2014. Archived from the original on 2 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "خامنهای خطاب به رهبران حوثی: در برابر عربستان و امارات بایستید". Euronews. 14 August 2019. Archived from the original on 15 August 2019. Retrieved 21 September 2019.
- ^ "Iran's Khamenei backs Yemen's Houthi movement, calls for dialogue". Reuters. 13 August 2019. Archived from the original on 21 September 2019. Retrieved 21 September 2019.
- ^ "WHO ARE THE HOUTHIS, PART TWO: HOW ARE THEY FIGHTING?". Archived from the original on 18 April 2015. Retrieved 17 April 2015.
- ^ "Checkpoint children: Armed Houthis under 18". Yemen Times. Archived from the original on 18 April 2015. Retrieved 17 April 2015.
- ^ "Q & A on The Conflict in Yemen and International Law – Human Rights Watch". hrw.org. 7 April 2015. Archived from the original on 11 February 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2016.
- ^ Al-Haj, Ahmed; Youssef, Nour. "Death toll from Yemen rebel shelling doubles to nearly 100". Yahoo! News. Archived from the original on 20 July 2015. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- ^ HRW (12 May 2015). "Yemen: Houthis Send Children into Battle". HRW. HRW. Archived from the original on 26 August 2016. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ HRW. "Yemen: Houthi Landmines Claim Civilian Victims". HRW. HRW. Archived from the original on 18 October 2016. Retrieved 14 October 2016.
- ^ HRW. "Yemen: Houthis Ban Rights Advocate's Travel". HRW. HRW. Archived from the original on 18 October 2016. Retrieved 14 October 2016.
- ^ "Yemen: Houthi Hostage-Taking". Human Rights Watch. 25 September 2018. Archived from the original on 27 September 2018. Retrieved 29 September 2018.
- ^ "Yemen war: WFP accuses Houthi rebels of diverting food aid". BBC. 31 December 2018. Archived from the original on 26 July 2019. Retrieved 12 June 2019.
- ^ "World Food Programme to consider suspension of aid in Houthi-controlled areas of Yemen". Releifweb. 20 May 2019. Archived from the original on 22 June 2019. Retrieved 12 June 2019.
- ^ "Yemen's Houthis and WFP dispute aid control as millions starve". Reuters. 4 June 2019. Archived from the original on 14 June 2019. Retrieved 12 June 2019.
- ^ "UN warns food aid to Yemen could be suspended". Al Jazeera. 20 May 2019. Archived from the original on 11 June 2019. Retrieved 12 June 2019.
- ^ "UN: Houthi rebels in Yemen recruited teenage girls". Al Jazeera. 9 September 2020.
- ^ AlAhmad, Safa (16 March 2015). "Meeting the Houthis – and their enemies". BBC News Magazine. Archived from the original on 5 April 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Audience Question: Did Ansar Allah Liberated 95% of al-Jawf?". Islamic World News. 30 April 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Yemen: Houthi army spokesman declares end of Jawf operation, holds 'key to Marib'". Middle East Monitor. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- ^ Heinze, Marie-Christine. "The primacy of stability over real change". Dialogue with the Islamic World. Qantara.de (Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung). Archived from the original on 6 February 2015. Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- ^ "Houthi rebels seize province, clash with al-Qaeda in Yemen's Rada'a". Middle East Eye. Archived from the original on 3 December 2014.
- ^ https://english.iswnews.com/12294/latest-updates-on-yemeni-fronts-in-the-period-march-2019-march-2020/
- ^ Oudah, Abdul-Aziz. "What's Next? Houthis Take Control of Four Northern Provinces, Two Governors Resign". Yemen Observer. Archived from the original on 21 February 2015.
- ^ Al-Moshki, Ali Ibrahim (1 January 2015). "Houthis take over Raima governorate". Yemen Times. Archived from the original on 26 March 2015. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ^ "More than 100 al Houthis killed in one week in Yemen". Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- ^ "Yemen government recaptures Red Sea town from Houthi rebels". Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- ^ "More than 20 Houthis killed in Yemen's al Bayda". Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
Works cited
- Knights, Michael (September 2018). "The Houthi War Machine: From Guerrilla War to State Capture" (PDF). CTC Sentinel. West Point, New York: Combating Terrorism Center. 11 (8): 15–23.
External links
- Brandt, Marieke (15 November 2017). Tribes and Politics in Yemen: A History of the Houthi Conflict. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780190911454.
- "Interview with exiled Houthi". Counterpunch. 3 February 2015. Archived from the original on 18 July 2011. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- John Pike. "al-Shabab al-Mum?en / Shabab al-Moumineen (Believing Youth)". Global Security. Retrieved 23 January 2013.
- Houthis
- Arab militant groups
- Antisemitism in Yemen
- Anti-Americanism
- Anti-imperialism
- Anti-Zionism in the Arab world
- Anti-Zionism in the Middle East
- Anti-Zionist organizations
- Houthi insurgency in Yemen
- Organizations designated as terrorist by Saudi Arabia
- Organizations designated as terrorist by the United Arab Emirates
- Organizations designated as terrorist in Asia
- Rebel groups in Yemen
- Rebel groups that actively control territory
- Islamic nationalism
- Shia organizations
- Shia Islamist groups
- Yemeni Crisis (2011–present)
- Yemeni Revolution
- Zaidiyyah
- Entities added to the Consolidated List by Australia
- Resistance movements
- Anti-ISIL factions
- Jihadist groups in Yemen
- Axis of Resistance