Hudson Bay drainage basin
| Hudson Bay drainage basin | |
|---|---|
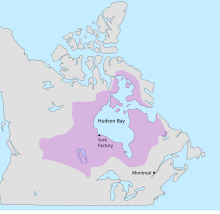
 The Hudson Bay drainage connects primarily to the Labrador Sea just south of Davis Strait as depicted on most atlases such as those of the National Geographic Society just north of the 60th parallel north and northeast of the Labrador Peninsula | |
| Geography | |
| Country | Canada, United States |
| Coordinates | 60°N 86°W / 60°N 86°W |
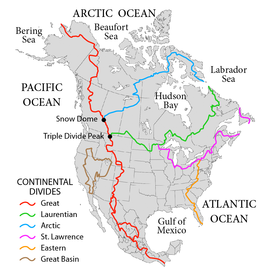
The Hudson Bay drainage basin is the drainage basin in northern North America where surface water empties into Hudson Bay and adjoining waters. Spanning an area of about 3,861,400 square kilometres (1,490,900 sq mi),[1] the basin is almost totally in Canada (spanning parts of the Prairies, central and northern Canada), with a small portion in the United States (in Montana, the Dakotas, and Minnesota). The watershed's connection to the Labrador Sea is at the Hudson Strait's mouth between Resolution Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region and Cape Chidley on the Labrador Peninsula.[2] The watershed's headwaters to the south-west are on the Continental Divide of the Americas, bounded at Triple Divide Peak to the south, and Snow Dome to the north. The western and northern boundary of the watershed is the Arctic Divide, and the southern and eastern boundary is the Laurentian Divide.
Hudson Bay is often considered part of the Arctic Ocean. For example, the International Hydrographic Organization (in its current unapproved working edition only[3] of Limits of Oceans and Seas) defines the Hudson Bay, with its outlet extending from 62.5 to 66.5 degrees north (just a few miles south of the Arctic Circle) as being part of the Arctic Ocean, specifically "Arctic Ocean Subdivision 9.11." Other authorities include it with the Atlantic Ocean, in part because of its greater water budget connection. [4][5]
The Hudson Bay drainage basin coincides almost completely with the former territory Rupert's Land, claimed by the Hudson's Bay Company in the 17th century, and an ideal area for the early fur trade in northern and central North America.
See also[]
References[]
- ^ "Canada Drainage Basins". The National Atlas of Canada, 5th edition. Natural Resources Canada. 1985. Retrieved 24 November 2010.
- ^ Limits of Oceans and Seas (PDF), 1953, archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-10-08, retrieved 29 December 2020
- ^ "IHO Publication S-23 Limits of Oceans and Seas; Chapter 9: Arctic Ocean". International Hydrographic Organization. 2002. Archived from the original on 2014-02-02. Retrieved 2017-07-01.
- ^ Earle, Sylvia A.; Glover, Linda K. (2008). Ocean: An Illustrated Atlas. National Geographic Society. p. 112. ISBN 978-1-4262-0319-0. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ Lewis, Edward Lyn; Jones, E. Peter; et al., eds. (2000). The Freshwater Budget of the Arctic Ocean. Springer. pp. 101, 282–283. ISBN 978-0-7923-6439-9. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- Hudson Bay drainage basin
- Watersheds of Canada
- Arctic Watershed of North America
