Jamaica Defence Force
| Jamaica Defence Force | |
|---|---|
 Jamaica Defence Force badge | |
| Founded | 31 July 1962 |
| Service branches |
|
| Headquarters | Up Park Camp, Kingston, Jamaica |
| Website | jdfweb.com |
| Leadership | |
| Commander-in-chief | Queen Elizabeth II |
| Prime Minister | Andrew Holness |
| Minister of Defence | Andrew Holness |
| Chief of Defence Staff | Lieutenant General Rocky Ricardo Meade |
| Manpower | |
| Military age | 16 years of age for selection process, 17 years of age is actual serving age (as of 2007) |
| Available for military service | 747,043, age 16–49 (2005 est.) |
| Fit for military service | 523,550, age 16–49 (2005 est.) |
| Reaching military age annually | 27,729 (2005 est.) |
| Expenditures | |
| Budget | $31,170,000 (ranked 141st) |
| Percent of GDP | 0.6% (2007) |
| Related articles | |
| Ranks | Military ranks of Jamaica |
The Jamaica Defence Force (JDF) is the combined military of Jamaica, consisting of an infantry Regiment and Reserve Corps, an Air Wing, a Coast Guard fleet and a supporting Engineering Unit.[1] The JDF is based upon the British military model, with similar organisation, training, weapons and traditions. Once chosen, officer candidates are sent to one of several British or Canadian basic officer courses depending upon the arm of service. Enlisted soldiers are given basic training at JDF Training Depot Newcastle. As on the British model, NCOs are given several levels of professional training as they rise up the ranks. Additional military schools are available for speciality training in Canada, China, the United States, and the United Kingdom.
History

The JDF is directly descended from the West India Regiments formed during the period of British rule. The regiments were used extensively by the British to garrison the Colony of Jamaica and possessions in the West Indies. 26. Other units in the JDF heritage tree include the early colonial Jamaica Militia, the Kingston Infantry Volunteers of WWI and reorganised into the Jamaican Infantry Volunteers in WWII. The West India Regiments were reformed in 1958 as part of the West Indies Federation. The dissolution of the Federation resulted in the establishment of the JDF.
The Jamaica Defence Force (JDF) comprises an infantry Regiment and Reserve Corps, an Air Wing, a Coast Guard fleet and a supporting Engineering Unit. The infantry regiment contains the 1st, 2nd and 3rd (National Reserve) battalions. The JDF Air Wing is divided into three flight units, a training unit, a support unit and the JDF Air Wing (National Reserve). The Coast Guard element is divided between seagoing crews and support crews. It conducts maritime safety and maritime law enforcement as well as defence-related operations. The support battalion contains a Military Police platoon as well as vehicle, armourers and supply units. The 1st Engineer Regiment provides military engineering support to the JDF. The Headquarters JDF contains the JDF commander, command staff as well as intelligence, judge advocate office, administrative and procurement sections.
In recent years the JDF has been called upon to assist the nation's police, the Jamaica Constabulary Force (JCF), in fighting drug smuggling and a rising crime rate which includes one of the highest murder rates in the world.[citation needed] JDF units actively conduct armed patrols with the JCF in high-crime areas and known gang neighbourhoods. There has been vocal controversy as well as support of this JDF role. In early 2005, an opposition leader, Edward Seaga, called for the merger of the JDF and JCF. This move did not garner support in either organisation nor among the majority of citizens.
Major units of the Jamaica Defence Force

- Headquarters, Jamaica Defence Force (HQ JDF) - divided into the Operations Branch and Adjutant Quartermaster's Branch, this is the main command of the entire JDF.
- The Jamaica Regiment - The Jamaica Regiment is the operationalization of a terrestrial and combat focused Regular Force formation with an overarching operational headquarters in command of five battalions; the First, Second, Fourth and Fifth Battalions the Jamaica Regiment (1, 2, 4, 5 JR) and the Combat Support Battalion (Cbt Sp Bn).
- The Support Brigade (Sp Bde) - The Support Brigade is a Regular Force formation that will provide both combat support and service support functions with an overarching operational headquarters for five units; the Directorate of Training and Doctrine ( Dir of Trg and Doct), 1 Engineer Regiment JDF (1 Engr Regt (JDF), the Support and Services Battalion (Sp and Svcs Bn), the Military Police Battalion (MP Bn) and the Health Services Corps (HSC). In addition it will also see the creation of the Caribbean Military Academy (CMA). The CMA is the academic institutional arm of the JDF that will provide internationally recognized, accredited, doctrinally relevant professional military education and training to a common standard in support of the operational needs of Jamaica and also to partner military and paramilitary organizations across the Caribbean region and around the world.
- The Maritime, Air and Cyber Command (MACC) - The Maritime, Air and Cyber Command (MACC) is a multi-domain focused Regular Force formation with an operational headquarters in command of six units; the First and Second Districts Jamaica Defence Force Coast Guard (1stand 2ndDist JDF CG), the Jamaica Defence Force Air Wing (JDF AW), the Military Intelligence Unit (MIU), the Special Activities Regiment (SPEAR) and the Military Cyber Corps (MCC).
- The Jamaica National Reserve (JNR) - The Jamaica National Reserve (JNR) is a multi-domain focused Reserve Force formation that has been expanded to include a headquarters element in command of four units; the Third, Sixth and Ninth Battalions the Jamaica Regiment (3, 6 and 9 JR (NR)) in addition to the Support Battalion (National Reserve) (Sp Bn (NR).
- The Jamaica National Service Corps (JNSC) - The Jamaica National Service Corps (JNSC) is the newest category of service in the JDF. It was designed to instill positive values and attitudes, whilst providing young men and women with a range of life skills in order to make them better equipped for success in their chosen career path; which may on completion include service in the JDF.
Bands
The JDF also supports two military bands;
- Jamaica Military Band - this is the band that is descended from the band of the West India Regiment, and was formed in February 1927. It is one of only two units in the world (the other being the Band of the Barbados Regiment) that wears the uniform of the zouaves.[2][3]
- Jamaica Regiment Band - this band was originally formed as the Band of the West India Regiment formed in 1959 as the military force of the Federation of the West Indies. With the Federation's break up and the independence of Jamaica, it became the Band of the 1st Battalion, Jamaica Regiment. It gained its current name with the formation of the 2nd Battalion in 1979.[4]
Army equipment


JDF Air Wing
Current inventory

| Aircraft | Origin | Type | Variant | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maritime Patrol | |||||
| Super King Air | United States | maritime patrol | 350 | 1[9] | |
| Helicopter | |||||
| Bell 206 | United States | trainer | 1[10] | ||
| Bell 407 | United States | utility / patrol | 3[10] | ||
| Bell 412 | United States | utility / SAR | 2 | 1 on order[10] | |
| Bell 429 | United States | utility / SAR | 7 | 2 on order[10] | |
| Trainer Aircraft | |||||
| Bell 505 | United States | trainer | 6 on order [11][12] | ||
| Diamond DA40 | Canada | trainer | DA40 CS | 4 [13] | |
| Diamond DA42 | Canada | multi-engine trainer | DA42 NG | 2[10] | |
Retired
Previous aircraft operated by the Air Force consisted of the Aero Commander 500 family, BN-2 Islander, Beechcraft Duke, Beechcraft King Air, Cessna Skymaster, Cessna 185 Skywagon, Cessna 210, DHC-6 Twin Otter, Eurocopter AS355 Écureuil 2, Bell UH-1 Iroquois, Bell 47G, Bell 212, Bell 204/205, and the Bell 222UT helicopter[14][15][16]
Incidents
On July 1, 2009, a Jamaica Defence Force Air Wing Bell 412EP helicopter was on its way back to Up Park Camp from a training mission when it began experiencing mechanical issues. The helicopter crashed into the ground at Up Park Camp, injuring the captain, his co-pilot and a crew member.[17]
JDF Coast Guard

A year after the JDF was formed in 1962, a naval arm, the Jamaica Sea Squadron was added. The squadron’s initial vessels were three 63 ft wooden World War II torpedo recovery boats provided by the United States. They were commissioned “Her Majesty’s Jamaican Ship” HMJS Yoruba (P1), HMJS Coromante (P2) and HMJS Mandingo (P3). A training team from the Royal Navy assisted with the unit’s early development. In 1966 they changed names from the Jamaica Sea Squadron to the Jamaica Defence Force Coast Guard.[18]
As of 2016, the Jamaica Defence Force Coast Guard was staffed by 241 individuals.[1]
Equipment

| Vessel | Origin | Type | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMJS Nanny of the Maroons | Netherlands | Fast Crew Supplier | 1[19] | Honour-class |
| HMJS Cornwall | Netherlands | Patrol Vessel | 1[20] | County-class |
| HMJS Middlesex | Netherlands | Patrol Vessel | 1[20] | County-class |
| HMJS Fort Charles | United States | Patrol Boat | 1 | Fort-class |
| HMJS Paul Bogle | United States | Patrol Boat | 1 | Hero-class |
| Boston Whaler | United States | Interceptor | 2[21] | 37 foot Justice model |
Ranks of the JDF
- Commissioned Officers
The rank insignia for commissioned officers for the army and Coast Guard respectively.
| Rank group | General/flag officers | Field/senior officers | Junior officers | Officer cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lieutenant general | Major general | Brigadier | Colonel | Lieutenant colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | Second lieutenant | Officer Cadet
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
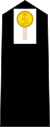
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander | Lieutenant | Lieutenant (junior grade) | Sub-Lieutenant | Midshipman
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lieutenant Colonel | Major | Captain | First Lieutenant | Second Lieutenant | Officer Cadet
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rank group | General/flag officers | Field/senior officers | Junior officers | Officer cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Enlisted
The rank insignia for enlisted personnel for the army and Coast Guard respectively.
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant officer class 1 | Warrant officer class 2 | Staff sergeant | Sergeant | Corporal | Lance corporal | Private (or equivalent)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|
No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Master chief petty officer 1 | Master chief petty officer | Chief petty officer | Petty officer | Leading seaman | Able seaman | Ordinary seaman
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|

|

|

|
No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant officer class 1 | Warrant officer class 2 | Staff sergeant | Sergeant | Corporal | Lance corporal | Private (or equivalent) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
Citations
- ^ Jump up to: a b Sanjay Badri-Maharaj (2016-12-11). "Jamaica Defence Force: Balancing Priorities With Resources – Analysis". . Archived from the original on 2016-12-12. Retrieved 2016-12-11.
The Jamaica Defence Force is a brigade-sized unit comprising land, sea and air formations and is possibly the largest military establishment within the English-speaking Caribbean.
- ^ "Jamaica Military Band". Jamaica Defence Force. Archived from the original on 2016-04-04.
- ^ "Jamaica Defense Force Band Archives". Archived from the original on 2018-08-13. Retrieved 2018-08-12.
- ^ "Jamaica Regiment Band (TU)". Jamaica Defence Force. Archived from the original on 2016-03-08.
- ^ "Jamaica". Armies of the World. Archived from the original on 2016-12-26.
The military budget is 48 million dollars (2001).
- ^ "Equipment". Jamaica Defence Force. Archived from the original on 2016-06-30.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "PM Commissions JDF's Protected Mobility Vehicles Squadron". 2016-01-14. Archived from the original on 2018-01-17. Retrieved 2018-01-10.
- ^ "JDF to Acquire New Fleet of Armoured Vehicles". 2013-12-03. Archived from the original on 2018-01-11. Retrieved 2018-01-10.
- ^ "World Air Forces 2020". Flightglobal Insight. 2020. Retrieved 16 January 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "World Air Forces 2021". Flightglobal Insight. 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2021.
- ^ "Bell Announces Delivery of 300th Bell 505 Jet Ranger X". 11 May 2021.
- ^ "Bell Announces Sale of Six Bell 505s to Jamaica Defence Force". 8 February 2021.
- ^ "Ministry of National Security invests over US$90 million in border security | the Ministry of National Security".
- ^ "World Air Forces 1975 pg. 303". flightglobal.com. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- ^ "World Air Forces 1987 pg. 66". flightglobal.com. Archived from the original on 6 March 2016. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- ^ "Aerospatiale AS 355 | Jamaican Defence Force".
- ^ "3 JDF soldiers injured in helicopter crash". The Jamaica Observer. 2 July 2009. Archived from the original on 5 July 2009.
- ^ "MOTTO:Service for the Lives of Others". Jamaica Defense Fund. Archived from the original on 2017-01-18. Retrieved 2017-02-20.
The Sea Squadron was renamed the Jamaica Defence Force Coast Guard (JDF CG) in 1966 and the naval White Ensign, naval rank insignia and Royal Navy - patterned uniforms were adopted.
- ^ "JDF welcomes 'HMJS Nanny of the Maroons' to maritime fleet | Buzz". 27 June 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Jamaica Defence Force returns to Damen for fleet renewal Share this page". Damen Group. 2016-11-17. Archived from the original on 2017-02-18. Retrieved 2017-02-20.
- ^ "JDF Coast Guard gets two new vessels from United States". The Jamaica Observer. 27 August 2015. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "BADGES OF RANK". Official Jamaica Defence Force Website. 2019. Archived from the original on 20 August 2020. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
Cite error: A list-defined reference named "JDF-Aircraft" is not used in the content (see the help page).
Bibliography
- "JDF Senior Officers Biography". Jamaica Defence Force.
- "JDF Ships". Jamaica Defence Force.
- "JDF Aircraft". Jamaica Defence Force. Archived from the original on 2013-05-11. Retrieved 2010-05-30.
- "History of the JDF". Jamaica Defence Force. Archived from the original on 2012-07-01. Retrieved 2012-05-06.
- "Change of Guard - Jamaica Defence Force (JDF) Chief of Staff, Commish walk". Jamaica Gleaner. 10 October 2007. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011.
- "Chronological List of Jamaica Army chiefs". Land Forces of Britain, The Empire and Commonwealth. Archived from the original on 15 September 2006.
- "Latin American Light Weapons National Inventories". Federation of American Scientists. Archived from the original on 15 March 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Military of Jamaica. |
- Military of Jamaica
