Landmarkism
Landmarkism is a type of Baptist ecclesiology developed in the American South in the mid-19th century. It is committed to a strong version of the perpetuity theory of Baptist origins, attributing an unbroken continuity and unique legitimacy to the Baptist movement since the apostolic period. It includes belief in the exclusive validity of Baptist churches and invalidity of non-Baptist liturgical forms and practices. It led to intense debates and splits in the Baptist community.
History[]
The movement began in the Southern United States in 1851, shaped by James Robinson Graves of Tennessee,[1][2] and Ben M. Bogard of Arkansas.[3] The movement was a reaction to religious progressivism earlier in the century.[2] At the time it arose, its proponents claimed Landmarkism was a return to what Baptists had previously believed, while scholars since then have claimed it was "a major departure".[1]
In 1859, the Southern Baptist Convention approved several resolutions disapproving of Landmarkism, which led to adherents gradually withdrawing from the Southern Baptist Convention "to form their own churches and associations and create an independent Landmark Baptist tradition."[4]
The main baptist groups adhering to Landmark principles and doctrines in the present day are the churches of the American Baptist Association (founded by Bogard), Baptist Missionary Association of America, and the Interstate & Foreign Landmark Missionary Baptist Association.[5]
Major personalities[]
The Great Triumvirate[]

James Robinson Graves[]
Through his Tennessee Baptist newspaper, James Robinson Graves popularized Landmarkism,[6] building for it a virtual hegemony among Baptists west of the Appalachians. He and Amos Cooper Dayton, who was also influential, were members of the First Baptist Church of Nashville, Tennessee. Graves was especially popular in the states of the lower Mississippi River Valley and Texas. In 1851, Graves called a meeting of like-minded Baptists at the Cotton Grove Baptist Church near Jackson, Tennessee, to address five questions:
- Can Baptists with their principles on the Scriptures, consistently recognize those societies not organized according to the Jerusalem church, but possessing different government, different officers, a different class of members, different ordinances, doctrines and practices as churches of Christ?
- Ought they to be called gospel churches or churches in a religious sense?
- Can we consistently recognize the ministers of such irregular and unscriptural bodies as gospel ministers?
- Is it not virtually recognizing them as official ministers to invite them into our pulpits or by any other act that would or could be construed as such recognition?
- Can we consistently address as brethren those professing Christianity who not only have not the doctrine of Christ and walk not according to his commandments but are arrayed in direct and bitter opposition to them?
The majority of the gathered Baptists resolved these questions by non-recognition of non-Baptist congregations, and then published their findings as the "Cotton Grove Resolutions".[7] The "Cotton Grove Resolutions" essentially comprise the organizational document of the Landmark Baptist movement.
James Madison Pendleton[]
James Madison Pendleton was a Baptist pastor from Kentucky whose article An Old Landmark Re-Set, a treatise against pulpit affiliation with non-Baptist ministers, gave the movement its name. His Church Manual was also influential in perpetuating Landmark Baptist ecclesiology. Although Pendleton was the only native Southerner in the Landmark Triumvirate, he was in favor of emancipation and opposed secession. As a result, his influence among Southern Baptists declined precipitously in the days leading up to the American Civil War and he took a pastorate in Pennsylvania during the war.[8]

Amos Cooper Dayton[]
Amos Cooper Dayton's major contribution to Landmarkism was the novel Theodosia Ernest (1857), which expressed religious issues and was first published in The Tennessee Baptist.[9]
Other influential Landmark Baptists[]
- (1849–1905), publisher of the Kentucky Baptist Flag newspaper, was a forceful advocate of both Landmarkism and the Gospel Mission Movement.
- Ben M. Bogard, after leading a schism out of the Arkansas Baptist State Convention became the most popular leader of Landmarkism into the twentieth century.
- Samuel Augustus Hayden led a schismatic movement in Texas that many have associated with Landmarkism.
- championed Landmark sentiment in Kentucky and led the charge against anti-Landmark scholar .
- John T. Christian prolifically defended the Landmark Baptist conception of Baptist successionism.
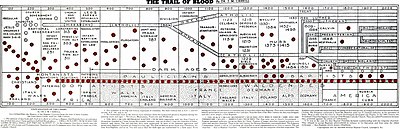
- James Milton Carroll wrote one of the most enduring Landmark Baptist works, The Trail of Blood, a history of the Baptist movement.
- A number of prominent Southern Baptist leaders were also Landmark Baptists although their primary contributions to Baptist history lay in fields other than ecclesiology.
See also[]
References[]
- ^ a b Garrett Jr., James Leo (2009). Baptist Theology: A Four-Century Study. Mercer University Press. p. 213. ISBN 978-0-88146-129-9.
- ^ a b Stookey, Stephen (2008). "Baptists and Landmarkism and the Turn toward Provincialism: 1851". In Williams, Michael Edward and Walter B. Shurden (ed.). Turning Points in Baptist History. Mercer University Press. pp. 178–181. ISBN 978-0-88146-135-0. Retrieved October 16, 2011.
- ^ J. Kristian Pratt, The Father of Modern Landmarkism: The Life of Ben M. Bogard (Mercer University Press; 2013)
- ^ Johnson, Robert E. (2010). A Global Introduction to Baptist Churches. Cambridge University Press. p. 148. ISBN 978-0-521-70170-9. Retrieved February 15, 2012.
- ^ Parsons, George. "Landmark Baptists". Middletownbiblechurch.org. Middletown Bible church.
- ^ "James Robinson Graves". Southern Baptist Historical Library & Archives. Retrieved January 14, 2018.
- ^ Hughey, Sam. "Preface". Old Landmarkism. The Reformed Reader. Retrieved June 30, 2008.
- ^ Tull, James E (1960). A History of Southern Baptist Landmarkism in the Light of Historical Baptist Ecclesiology.
- ^ Dayton, Amos Cooper (1857). Theodosia Ernest.
Further reading[]
- Moritz, Fred. The Landmark Controversy: A Study in Baptist History and Polity (The Maranatha Series) (2013); 22pp
External links[]
- Old Landmarkism: What Is It?
- Three Witnesses for the Baptists, Curtis Pugh
- A Study of the Antecedents of Landmarkism, by LeRoy Benjamin Hogue
- Perpetuity of the Lord’s Church
- Baptist Christianity in the United States
- Landmarkism
- Anti-Protestantism
- Ecclesiology
- 1851 in Christianity
- Christian theology stubs