List of Japanese Navy ships and war vessels in World War II
This list is incomplete; you can help by . (November 2018) |
This List of Japanese Naval ships and war vessels in World War II is a list of seafaring vessels of the Imperial Japanese Navy of World War II. It includes submarines, battleships, oilers, minelayers and other types of Japanese sea vessels of war and naval ships used during wartime.
Aircraft carrier[]
Heavy carriers[]
| Fleet Carrier (11) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships (Years in Service) | Displacement | Note |
| Akagi-class | 
|
Aircraft carrier | Akagi (1927–1942) | 36,500 tonnes | Converted from an Amagi-class battlecruiser. Sunk at Midway on June 5, 1942 |
| Kaga-class | 
|
Aircraft carrier | Kaga (1928–1942) | 38,200 tonnes | Converted from a Tosa-class battleship. Sunk at Midway on June 4, 1942 |
| Sōryū-class | 
|
Aircraft carrier | Sōryū (1937–1942) Hiryū (1939–1942) |
16,200 tonnes | Hiryū is often considered to be a separated class. Sunk at Midway on June 5, 1942
Soryu took part in the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Battle of Wake Island, and supported the conquest of the Dutch East Indies. She was sunk at Midway on June 4, 1942 |
| Shōkaku-class | 
|
Aircraft carrier | Shōkaku (1941–1944) Zuikaku (1941–1944) |
25,675 tonnes | With the exception of the Battle of Midway, Shōkaku and Zuikaku participated in every major naval action of the Pacific War, including the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Indian Ocean Raid, the Battle of the Coral Sea, and the Guadalcanal Campaign. Both carriers were sunk during the 1944 Pacific campaigns. |
| Unryū-class | 
|
Aircraft carrier | Unryū (1944–1944) Amagi (1944–1945) Katsuragi (1944–1945) |
17,480 tonnes | The design for these ships was based on the aircraft carrier Hiryū. IJN Planned to build 16 ships, however only 3 were completed and 2 almost completed (one of which was sunk as a target then salvaged and later scrapped) before the project was abandoned in favour of Shinano's construction. Unryū was sunk by the USS Redfish, Amagi capsized after air attacks and Katsuragi was the only heavy carrier to survive the war |
| Taihō-class | 
|
Aircraft carrier | Taihō (1944–1944) | 30,250 tonnes | A bit of a break from traditional Japanese carrier design, Taiho was a heavily armoured carrier expected to withstand multiple bombs and torpedo strikes. However, design faults and poor damage control allowed it to be sunk with one torpedo from the USS Albacore on June 19, 1944 |
| Shinano-class | 
|
Aircraft carrier | Shinano (1944–1944) | 65,800 tonnes | Initially laid down as the third of the Yamato-class battleships, Shinano was converted into an aircraft carrier due to the Japanese defeat at Midway. She was sunk on November 29, 1944, by torpedoes from USS Archerfish. |
Light carriers[]
| Light Aircraft Carrier (9) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Hōshō-class | 
|
Light aircraft carrier | Hōshō (1922–1945) | 7,470 tonnes | First purpose-built carrier in the world. Scrapped 1946. |
| Ryūjō-class | 
|
Light aircraft carrier | Ryūjō (1931–1942) | 8,000 tonnes | Sunk 1942. |
| Hiyō-class | 
|
Light aircraft carrier | Hiyō (1942–1944) Jun'yō (1942–1946) |
24,150 tonnes | Converted from an ocean liner in 1939. Hiyō sunk and Jun'yō scrapped 1946–1947. |
| Zuihō-class | 
|
Light aircraft carrier | Zuihō (1940–1944) Shōhō (1939–1942) |
11,443 tonnes | Both sunk during WWII. |
| Chitose-class | 
|
Light aircraft carrier | Chitose (1938/1944–1944) Chiyoda (1938/1944–1944) |
11,200 tonnes | Both ships were seaplane tenders before their conversion in 1943. Both ships sunk in 1944. |
| Ryūhō-class | 
|
Light aircraft carrier | Ryūhō (1934/1942–1945) | 16,700 tonnes | Converted from the submarine tender Taigei 1941–1942. Recommissioned as Ryūhō 1942. Scrapped 1946. |
Escort carriers[]
| Escort Carrier (10) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Taiyō-class | 
|
Escort carrier | Taiyō (1941–44) Chūyō (1942–43) Unyō (1942–44) |
17,830 tonnes | All sunk. |
| Kaiyō-class | 
|
Escort carrier | Kaiyō (1943–1945) | 13,600 tonnes. Converted from ocean liner Argentina Maru. | Scrapped 1946. |
| Shin'yō-class | 
|
Escort carrier | Shin'yō (1943–1944) | 17,500 tonnes | |
| Akitsu Maru-class | 
|
Escort carrier | Akitsu Maru (1942–1944) Nigitsu Maru (1942?–1944) |
11,800 tonnes | Operated by the Imperial Japanese Army. Worlds' first Amphibious Assault ships. |
| Shimane Maru-class | 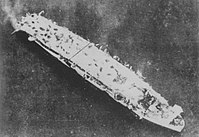
|
Escort carrier | Shimane Maru (1945–1945) | 11,989 tonnes | |
| Yamashio Maru-class | 
|
Escort carrier | Yamashio Maru (1945–1945) | 16,119 tonnes | |
| Kumano Maru-class | 
|
Escort carrier | Kumano Maru (1945–1945) | 8,258 tonnes | Operated by Imperial Japanese Army. |
Seaplane tenders[]
| Seaplane Tender (9) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Nisshin-class | 
|
Seaplane tender | Nisshin (1942–1943) | 11,499 tonnes | Also midget submarine carrier and minelayer |
| Kamikawa Maru-class | 
|
Seaplane tender | Kamikawa Maru (1937–1943) Kiyokawa Maru (1941–1946) Kimikawa Maru (1937–1944) Kunikawa Maru (1937–1945) |
6,862 tonnes | Hirokawa Maru of the same class was converted to auxiliary (anti-aircraft) cruiser instead of seaplane tender when impressed for Navy service |
| Akitsushima-class | 
|
Seaplane tender | Akitsushima (1942–1944) | 4,725 tonnes | |
| Kamoi-class | 
|
Seaplane tender | Kamoi (1922-1947) | 17,273 tonnes | |
| Notoro-class | 
|
Seaplane tender | Notoro (1934-1947) | 15,647 tonnes | Of 7 oilers in class, Notoro was converted to seaplane tender and Shiretoko to munition ship |
| Mizuho-class | 
|
Seaplane tender | Mizuho (1939-1942) | 10,930 tonnes | Also midget submarine carrier |
Armoured vessels[]
Battlecruisers[]
| Fast Battleship (4) - former battlecruisers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Kongō-class | 
|
Fast battleship | Kongō Hiei Kirishima Haruna |
32,156 tonnes | Laid down and commissioned as Battlecruisers in early 20th century, remodelled into Battleships because of Washington Naval Treaty in the late 20' and into Fast Battleships in 1935, allowing them to accompany growing carrier force. All four were sunk during the war |
Battleships[]
| Battleship (8) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Fusō-class | 
|
Battleship | Fusō Yamashiro |
29,330 tonnes | There was a plan to convert these ships into Aviation Battleships in 1943. The plan was cancelled and the two Ise-class battleships were converted instead. |
| Ise-class | 
|
Battleship | Ise Hyūga |
27,384 tonnes | Converted into Aviation Battleship in 1943. |
| Nagato-class | 
|
Battleship | Nagato Mutsu |
32,720 tonnes | Both ships underwent significant modernization on 1934–1936, rebuilding the superstructure into the more familiar pagoda mast style. |
| Yamato-class | 
|
Battleship | Yamato Musashi |
69,988 tonnes | 5 planned, 1 converted into an Aircraft carrier, 2 cancelled. Yamato was sunk during a one-way trip to Okinawa during operation Ten-Go. She never saw action there and was sunk by aircraft on the way. |
Heavy cruisers[]
| Heavy Cruiser (18) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Furutaka-class | 
|
Heavy cruiser | Furutaka Kako |
7,100 tonnes | |
| Aoba-class | 
|
Heavy cruiser | Aoba Kinugasa |
7,100 tonnes | Variation of the Furutaka class |
| Myōkō-class | 
|
Heavy cruiser | Myōkō Nachi Haguro Ashigara |
11,633 tonnes | |
| Takao-class | 
|
Heavy cruiser | Takao Atago Maya Chōkai |
11,633 tonnes | Variation of the Myōkō class |
| Mogami-class | 
|
Heavy cruiser | Mogami Mikuma Suzuya Kumano |
8,500 tonnes | Suzuya and Kumano is Considered as Suzuya Sub-class. Mogami considered as an Aviation Cruiser by IJN (1943). |
| Tone-class | 
|
Heavy cruiser | Tone Chikuma |
11,213 tonnes | Considered as Aviation Cruisers by IJN |
Light cruisers[]
| Light Cruiser (26) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Tenryū-class | 
|
Light cruiser | Tenryū Tatsuta |
3,948 tonnes | |
| Kuma-class | 
|
Light cruiser | Kuma Tama Kitakami Ōi Kiso |
5,500 tonnes | Kitakami, Ōi and Kiso later converted to a torpedo cruiser under a short-lived Imperial Japanese Navy program. |
| Nagara-class | 
|
Light cruiser | Nagara Isuzu Yura Natori Kinu Abukuma |
5,570 tonnes | |
| Yūbari-class | 
|
Light cruiser | Yūbari | 2,890 t tonnes | An experimental light cruiser. |
| Sendai-class | 
|
Light cruiser | Sendai Jintsu Naka |
5,195 tonnes | 8 planned; 5 cancelled. |
| Katori-class | 
|
Light cruiser | Katori Kashima Kashii |
5,890 tonnes | 4 planned; 1 cancelled.
Originally served as a training ship. |
| Agano-class | 
|
Light cruiser | Agano Noshiro Yahagi Sakawa |
6,652 tonnes | |
| Ōyodo-class | 
|
Light cruiser | Ōyodo | 8,164 tonnes | 2 planned; 1 cancelled. |
| Yasoshima-class | 
|
Light cruiser | Yasoshima | 2,448 tonnes | Served under the Republic of China Navy under the name of Ping Hai, until seized and re-floated in 1938 by IJN, having been sunk the year before. |
Destroyers[]
Destroyers[]
| Destroyer (169) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Momi-class | 
|
Destroyer | Momi | Kaya | Nashi | Take | Kaki | Tsuga | Nire | Kuri | Kiku | Aoi | Hagi | Fuji | Susuki | Hishi | Hasu | Warabi | Tade | Sumire | Tsuta | Ashi | Yomogi | 850 tonnes | 28 vessel planned 21 completed. 7 re-ordered as the new Wakatake-class. Relegated to mostly secondary roles. |
| Minekaze-class | 
|
Destroyer | Minekaze | Sawakaze | Okikaze | Shimakaze | Nadakaze | Yakaze | Hakaze | Shiokaze | Akikaze | Yūkaze | Tachikaze | Hokaze | Nokaze | Namikaze | Numakaze | 1,345 tonnes | |
| Wakatake-class | 
|
Destroyer | | | | | | | | Karukaya | 900 tonnes | 23 vessel planned 8 completed. Relegated to mostly secondary roles. |
| Kamikaze-class | 
|
Destroyer | Kamikaze | Asakaze | Harukaze | Matsukaze | Hatakaze | Oite | Hayate | Asanagi | Yūnagi | 1,400 tonnes | |
| Mutsuki-class | 
|
Destroyer | Mutsuki Kisaragi Yayoi Uzuki Satsuki Minazuki Fumizuki Nagatsuki Kikuzuki Mikazuki Mochizuki Yūzuki |
1,315 tonnes | |
| Fubuki-class | 
|
Destroyer | Fubuki Shirayuki Hatsuyuki Miyuki Murakumo Shinonome Usugumo Shirakumo Isonami Uranami |
1,750 tonnes | |
| Ayanami-class | 
|
Destroyer | Ayanami Shikinami Asagiri Yūgiri Amagiri Sagiri Oboro Akebono Sazanami Ushio |
1,750 tonnes | Also known as Type II Fubuki-class. |
| Akatsuki-class | 
|
Destroyer | Akatsuki Hibiki Ikazuchi Inazuma |
1,750 tonnes | Also known as Type III Fubuki-class. |
| Hatsuharu-class | 
|
Destroyer | Hatsuharu Nenohi Wakaba Hatsushimo Ariake Yūgure |
1,530 tonnes | |
| Shiratsuyu-class | 
|
Destroyer | Shiratsuyu Shigure Murasame Yūdachi Harusame Samidare Umikaze Yamakaze Kawakaze Suzukaze |
1,685 tonnes | |
| Asashio-class | 
|
Destroyer | Asashio | Ōshio | Michishio | Arashio | Natsugumo | Yamagumo | Minegumo | Asagumo | Arare | Kasumi | 1,685 tonnes | |
| Kagerō-class | 
|
Destroyer | Kagerō | Shiranui | Kuroshio | Oyashio | Hayashio | Natsushio | Hatsukaze | Yukikaze | Amatsukaze | Tokitsukaze | Urakaze | Isokaze | Hamakaze | Tanikaze | Nowaki | Arashi | Hagikaze | Maikaze | Akigumo | 2,000 tonnes | Called Destroyer Type-A by IJN. |
| Yūgumo-class | 
|
Destroyer | Yūgumo | Makigumo | Kazagumo | Naganami | Makinami | Takanami | Ōnami | Kiyonami | Tamanami | Suzunami | Fujinami | Hayanami | Hamanami | Okinami | Kishinami | Asashimo | Hayashimo | Akishimo | Kiyoshimo | 2,077 tonnes | Called Destroyer Type-A by IJN. |
| Akizuki-class | 
|
Destroyer | Akizuki | Teruzuki | Suzutsuki | Hatsuzuki | Niizuki | Wakatsuki | Shimotsuki | 2,700 tonnes | |
| Fuyutsuki-class | 
|
Destroyer | Fuyutsuki Harutsuki Yoizuki Natsuzuki |
2,700 tonnes | Akizuki-subclass. |
| Michitsuki-class | 
|
Destroyer | Hanazuki | 2,700 tonnes | 16 vessel planned however only 1 completed. Akizuki-subclass. |
| Shimakaze-class | 
|
Destroyer | Shimakaze | 2,570 tonnes | She was an experimental destroyer, with new high-temperature, high-pressure steam turbines and mounting a total of 15 torpedo tubes. Also called Type-C by IJN. |
| Matsu-class | 
|
Destroyer | Matsu | Take | Ume | Momo | Kuwa | Kiri | Sugi | Maki | Momi | Kashi | Kaya | Nara | Sakura | Yanagi | Tsubaki | Hinoki | Kaede | Keyaki | 1,260 tonnes | |
| Tachibana-class | 
|
Destroyer | Tachibana | Kaki | Kaba | Tsuta | Hagi | Sumire | Kusunoki | Hatsuzakura | Nire | Nashi | Shii | Enoki | Odake | Hatsuume | 1,350 tonnes | Matsu-subclass. |
Torpedo boats[]
| Torpedo Boat (12) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Boats | Displacement | Note |
| Chidori-class | 
|
Torpedo boat | | | Tomozuru | | 600 tonnes | 20 vessel planned however only 4 completed. 16 replaced by Ōtori-class. |
| Ōtori-class | 
|
Torpedo boat | | Hiyodori | | | | | | | | 960 tonnes | 16 vessel planned however only 8 completed. |
Destroyer escorts (Kaibōkan)[]
| Kaibōkan (178) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Boats | Displacement | Note |
| Shimushu-class | 
|
Kaibōkan | Shimushu | Kunashiri | Ishigaki | Hachijo | 874 tonnes | |
| Etorofu-class | 
|
Kaibōkan | Etorofu | Matsuwa | | | | | Tsushima | | | | Amakusa | | | | 884 tonnes | |
| Mikura-class | 
|
Kaibōkan | Mikura | Miyake | Awaji | | Kurahashi | | | | 955 tonnes | |
| Ukuru-class | 
|
Kaibōkan | | | | | Okinawa | | | | | Aguni | | | | | | | | | | Kanawa | | | | | | | | | | 955 tonnes | Includes the 9 vessels of the Hiburi subclass |
| Type C-class | 
|
Kaibōkan | | | | | | | CD-13 | | CD-17 | CD-19 | | CD-23 | | | | | | CD-35 | | | | CD-43 | | CD-47 | | CD-51 | CD-53 | | | | | CD-63 | | | | | | CD-75 | | | | | | | | | | | CD-207 | | | | | | | | 757 tonnes | |
| Type D-class | 
|
Kaibōkan | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | CD-40 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | CD-76 | | | | | | CD-104 | | | | CD-118 | | | | | | | CD-142 | | | CD-154 | | | CD-160 | CD-186 | CD-190 | CD-192 | CD-194 | CD-196 | CD-198 | CD-200 | CD-202 | CD-204 | 752 tonnes | |
Patrol boats[]
| Patrol Boat | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Boats | Displacement | Note |
| No.1-class auxiliary patrol boat | 
|
Patrol boat | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 238 tons | 280 planned, 27 completed |
Submarine chasers[]
| Submarine chaser | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Boats | Displacement | Note |
| No.1-class auxiliary submarine chaser | 
|
Submarine chaser | | Cha-2 | Cha-3 | | Cha-5 | | | | | | | Cha-12 | Cha-13 | Cha-14 | | | | | Cha-19 | | | | | | | | | Cha-28 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Cha-43 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Cha-156 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Cha-214 | Cha-215 | Cha-216 | Cha-217 | | Cha-219 | | Cha-221 | Cha-222 | | | | | | Cha-228 | | | Cha-231 | Cha-232 | | | | | | | | | Cha-241 | | | | Cha-245 | Cha-246 | | | Cha-249 | | 130 tons | 200 planned, 200 completed |
Submarine[]
| Submarine (213) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Boats | Displacement | Note |
| I-1-class | 
|
Submarine | I-1 | I-2 | I-3 | I-4 | I-5 | I-6 | I-7 | I-8 | 1,970 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Junsen-type submarine |
| I-9-class | 
|
Submarine | I-9 | I-10 | I-11 | I-12 | I-13 | I-14 | 2,434 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Type A (Ko) submarine. |
| I-15-class | 
|
Submarine | I-15 | I-17 | I-19 | I-21 | I-23 | I-25 | I-26 | I-27 | I-29 | I-30 | I-31 | I-32 | I-33 | I-34 | I-35 | I-36 | I-37 | I-38 | I-39 | I-40 | I-41 | I-42 | I-43 | I-44 | I-45 | I-54 | I-56 | I-58 | 2,184 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Type B (Otsu) submarine. |
| I-16-class | 
|
Submarine | I-16 | I-18 | I-20 | I-22 | I-24 | I-46 | I-47 | I-48 | I-52 | I-53 | I-55 | 2,184 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Type C (Hei) submarine. |
| I-361-class | 
|
Submarine | I-361 | I-362 | I-363 | I-364 | I-365 | I-366 | I-367 | I-368 | I-369 | I-370 | I-371 | I-372 | I-373 | 1,440 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Type D (Tei) submarine |
| I-51-class | 
|
Submarine | I-51 | I-152 | I-153 | I-154 | I-155 | I-156 | I-157 | I-158 | I-159 | I-60 | I-63 | I-61 | I-162 | I-164 | I-165 | I-66 | I-67 | I-168 | I-169 | I-70 | I-171 | I-73 | I-174 | I-175 | I-176 | I-177 | I-178 | I-179 | I-180 | I-181 | I-182 | I-183 | I-184 | I-185 | 1,575 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Kaidai-type submarine |
| I-121-class | 
|
Submarine | I-121 | I-122 | I-123 | I-124 | 1,142 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Kiraisen-type submarine |
| I-351-class | 
|
Submarine | I-351 | 3,512 tonnes | Planned 6. Completed 1. The official designation of the submarine was Senho-type submarine |
| I-201-class | 
|
Submarine | I-201 I-202 I-203 |
1,503 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Sentaka-type submarine |
| I-501-class | Submarine | I-501 | 1,616 tonnes | Was German Kriegsmarine submarine under the name U-181, until given to Japan May 1945. | |
| I-502-class | Submarine | I-502 | 1,610 tonnes | Was German Kriegsmarine submarine under the name U-862, until given to Japan May 1945. | |
| I-503-class | 
|
Submarine | I-503 | 1,610 tonnes | Was a Regia Marina submarine under the name Comandante Cappelini then captured by IJN after Italy's capitulation then given to Kriegsmarine in September 1943 under the name UIT-24. After that captured again by IJN in May 1945 after Nazi-Germany's surrender. |
| I-504-class | Submarine | I-504 | 1,763 tonnes | Was Regia Marina submarine under the name Luigi Torelli then it was temporarily interned to IJN after Italy's capitulation then given to Kriegsmarine in September 1943 under the name UIT-25. After that captured again by IJN in May 1945 after Nazi-Germany's surrender. | |
| I-505-class | Submarine | I-505 | 1,763 tonnes | Was German Kriegsmarine submarine under the name U-219, until given to Japan May 1945. | |
| I-506-class | Submarine | I-506 | 1,610 tonnes | Was German Kriegsmarine submarine under the name U-195, until given to Japan May 1945. | |
| Ro-11-class | 
|
Submarine | Ro-11 | Ro-12 | Ro-13 | Ro-14 | Ro-15 | Ro-16 | Ro-17 | Ro-18 | Ro-19 | Ro-20 | Ro-21 | Ro-22 | Ro-23 | Ro-24 | Ro-25 | Ro-26 | Ro-27 | Ro-28 | Ro-29 | Ro-30 | Ro-31 | Ro-32 | Ro-33 | Ro-34 | Ro-35 | Ro-36 | Ro-37 | Ro-37 | Ro-38 | Ro-39 | Ro-40 | Ro-41 | Ro-42 | Ro-43 | Ro-44 | Ro-45 | Ro-46 | Ro-47 | Ro-48 | Ro-49 | Ro-50 | Ro-55 | Ro-56 | 720 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Type Kaichū submarine. |
| Ro-51-class | 
|
Submarine | Ro-51 | Ro-52 | Ro-53 | Ro-54 | Ro-55 | Ro-56 | Ro-57 | Ro-58 | Ro-59 | Ro-60 | Ro-61 | Ro-62 | Ro-63 | Ro-64 | Ro-65 | Ro-66 | Ro-67 | Ro-68 | 893 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Type L submarine |
| Ro-100-class | 
|
Submarine | Ro-100 | Ro-101 | Ro-102 | Ro-103 | Ro-104 | Ro-105 | Ro-106 | Ro-107 | Ro-108 | Ro-109 | Ro-110 | Ro-111 | Ro-112 | Ro-113 | Ro-114 | Ro-115 | Ro-116 | Ro-117 | 525 tonnes | |
| Ha-201-class | 
|
Submarine | Ha-201 | Ha-202 | Ha-203 | Ha-204 | Ha-205 | Ha-207 | Ha-208 | Ha-209 | Ha-210 | Ha-216 | 320 tonnes | Never saw combat The official designation of the submarine was Sentaka-Shō type submarine. |
| Ro-500-class | 
|
Submarine | Ro-500 | 1,120 tonnes | Was German Kriegsmarine submarine under the name U-511, until given to Japan 16 September 1943. |
| Ro-501-class | Submarine | Ro-501 | 1,144 tonnes | Was German Kriegsmarine submarine under the name U-1224, until given to Japan 15 February 1944. | |
| Submarine aircraft carrier (3) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Boats | Displacement | Note |
| I-400-class | 
|
Submarine aircraft carrier | I-400 I-401 I-402 |
6,560 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Sentoku type Submarine. |
| Transport Submarine (49) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Boats | Displacement | Note |
| Ha-101-class | 
|
Ha-101 | Ha-102 | Ha-103 | Ha-104 | Ha-105 | Ha-106 | Ha-107 | Ha-108 | Ha-109 | Ha-111 | 370 tonnes | The official designation of the submarine was Sen'yu type submarine | |
| Yu-class | 
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 274 tonnes | Used by Imperial Japanese Army. | |
Submarine tender[]
| Submarine Tender (3) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Jingei-class | 
|
Submarine tender | Jingei Chōgei |
6,240 tonnes | |
| Taigei-class | 
|
Submarine tender | Taigei | 16,700 tonnes | Converted into Light aircraft carrier. |
Gunboats[]
| Gunboats (20) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Japanese gunboat Saga | 
|
River gunboat | Saga | 793 | Improvement of Uji (1903) |
| Hashidate-class | 
|
Gunboat | Hashidate Uji |
1,009 | |
| Japanese gunboat Ataka | 
|
River gunboat | Ataka | 880 | |
| Fushimi-class | 
|
River gunboat | Fushimi Sumida |
356 | |
| Luzon-class | 
|
River gunboat | Karatsu | 509 | Salvaged from the US wreck |
| USS Wake (PR-3) | 
|
River gunboat | Tatara | 360 | The only US ship surrendered to Japanese during World War II |
| Azio-class | 
|
Gunboat | Okitsu | 625 | Salvaged from the Italian wreck |
| Insect-class | 
|
River gunboat | Suma | 635 | Salvaged from the British wreck |
| Atami-class | 
|
River gunboat | Atami Futami |
249 | |
| Seta-class | 
|
River gunboat | Seta Katata Hira Hozu |
343 | |
| Japanese gunboat Kotaka | 
|
River gunboat | Kotaka | 57 | Simplified Atami-class gunboat for shallow water (0.64m draft) operations |
| Japanese gunboat Toba | 
|
River gunboat | Toba | 220 | |
| Kozakura-class | 
|
River gunboat | 30 | ||
| Shōkai Maru-class | Gunboat | Official designation was a high-powered tugboat, however, they did not have any towing facilities. They were actually gunboats and escort ships. | |||
Mine warfare vessels[]
| Minesweepers (35), minelayers (33) and netlayers (1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement, tonnes | Note |
| Hatsutaka-class | 
|
Minelayer | Hatsutaka Aotaka Wakataka |
1,626 | |
| Japanese minelayer Shirataka | 
|
Netlayer | Shirataka | 1,540 | |
| Japanese cruiser Tokiwa | 
|
Minelayer | Tokiwa | 9,667 | Converted to minelayer in 1922 |
| Japanese minelayer Itsukushima | 
|
Minelayer | Itsukushima | 2,002 | First ever Japanese Navy diesel ship |
| Kamishima-class | 
|
Minelayer | Kamishima Awashima |
778 | |
| Japanese survey ship Katsuriki | 
|
Minelayer | Katsuriki | 1,565 | First purpose-built ocean-going minelayer of Japanese Navy, converted to survey ship in 1942 |
| Japanese minelayer Minoo | 
|
Minelayer | Minoo | 3,276 | |
| Japanese minelayer Okinoshima | 
|
Minelayer | Okinoshima | 4,359 | Carry a reconnaissance floatplane |
| Natsushima-class | 
|
Minelayer | Natsushima Nasami Sarushima |
483 | |
| Tsubame-class | 
|
Minelayer | Tsubame Kamome |
457 | |
| Sokuten-class | 
|
Minelayer | | | | | | | | | | | | 411 | 2 prototypes of this class decommissioned before World War II |
| MV Tenyo Maru (1935) | 
|
Minelayer | Tenyo Maru | 6,843 | |
| Japanese minelayer Tsugaru | 
|
Minelayer | Tsugaru | 4,064 | Carry a reconnaissance floatplane |
| Japanese minelayer Yaeyama | 
|
Minelayer | Yaeyama | 1,153 | Refit as anti-submarine warfare vessel in 1943 |
| Hashima-class | 
|
Minelayer | | | | | 1,585 | Used to lay remote-controlled mines in coastal fortifications |
| W-1-class | 
|
Minesweeper | | | | | | | 610 | |
| W-7-class | 
|
Minesweeper | W-7 | W-8 | | W-10 | | | 640 | Actually newer than W-13 class |
| W-13-class | 
|
Minesweeper | | | | | | | 533 | |
| W-19-class | 
|
Minesweeper | | | | | | | | W-26 | | | | | | | | | 658 | Primary Japanese minesweeper during World War II |
| Wa-1-class auxiliary minesweeper | 
|
Minesweeper | Wa-1 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | ||
Auxiliary vessels[]
Food Supply Ship[]
| Food Supply Ship (8) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Mamiya-class | 
|
Mamiya | 15,820 tonnes | ||
| Nosaki-class | 
|
Nosaki | 650 tonnes | ||
| Kinesaki-class | 
|
910 tonnes | |||
| Irako-class | 
|
Irako | 9,570 tonnes | ||
| 8,125 tonnes | |||||
| 498 tonnes | |||||
Repair ship[]
| Repair Ship (2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Asahi-class | 
|
Repair ship | Asahi | 15,200 tonnes | Converted from Pre-dreadnought battleship. |
| Akashi-class | 
|
Repair ship | Akashi | 9,000 tonnes | |
Survey ship[]
| Survey Ships (1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Picture | Type | Ships | Displacement | Note |
| Tsukushi-class | 
|
Survey ship | Tsukushi | 1,422 tonnes | Planned 2. Cancelled 1. |
See also[]
- Imperial Japanese Navy of World War II
- List of Japanese military equipment of World War II
- List of ships of the Japanese Navy
- List of ships of the Second World War
Categories:
- Ships of the Imperial Japanese Navy
- Japan in World War II-related lists
- World War II naval ships of Japan