Magdalena River turtle
| Magdalena River turtle | |
|---|---|

| |
| From Medellin, Colombia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Pleurodira |
| Family: | Podocnemididae |
| Genus: | Podocnemis |
| Species: | P. lewyana
|
| Binomial name | |
| Podocnemis lewyana Duméril, 1852
| |

| |
| Range in red | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Podocnemis coutinhii Göldi, 1886 | |
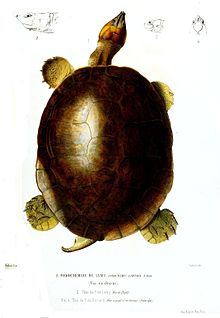
The Magdalena River turtle, or Rio Magdalena river turtle, (Podocnemis lewyana) is a species of turtle in the family Podocnemididae,[2] which diverged from other turtles in the Cretaceous Period, 100 million years ago.[3] It is endemic to northern Colombia, where its home range consists of the Sinú, San Jorge, Cauca, and Magdalena river basins.[4]
The species has been classified as "Critically Endangered" by the IUCN in 2015 and is considered the most threatened species of the family Podocnemididae.[5][6] In less than 25 years, the species exhibited a population decline of over 80%.[3] The decline is attributed to habitat destruction, pollution, over-harvest, commercial exploitation, hydrological changes due to electrical generation facilities, and climate change.[4] While early conservation attempts were unsuccessful or unenforced, there has been a resurgence in studies aimed at discovering the most effective approaches.[7]
Description[]
Magdalena River turtles exhibit sexual dimorphism.[8] Both males and females have a shell composed of shield-like plates that are primarily brown in color.[3] Their necks extend to a robust head.[3]
Males have grayish-brown head scales, while females display head scales more reddish-brown in color.[8] Adult males, on average, weigh 1.6 kg and measure 24.6 cm in carapace length.[5] Whereas females, on average, weigh 5.6 kg and measure 37 cm in carapace length.[5]
The species is regarded as having a mostly herbivorous diet, however opportunistic insectivorous behavior has been observed.[8] At times, juveniles pursue piscivorous behavior.[8] Average life span is 10–15 years in the wild.[5]
Ecology[]
Reproduction[]
Magdalena River turtles are iteroparous.[4] Males sexually mature at 3–4 years old, while females mature at 5–6 years old.[5] Females nest in the sandy riverbanks that result from areas of shallow water.[7]
There are two nesting seasons: December–January and June–July.[7] It is unclear if individual females nest during both seasons in the same year.[3] Higher egg counts are observed in the June–July nesting season.[7]
While average egg weight is significantly greater in the December–January nesting season.[7] Therefore, researchers have proposed it is equally vital to protect both seasons, as egg weight is positively correlated to hatching weight.[7]
Average clutch size is 22 eggs.[3] The embryos within the eggs have temperature-dependent sex determination.[9] The species' pivotal temperature (Tpiv), incubation temperature that produces 1:1 sex ratio, is 33.4 °C.[9] Incubation temperatures below the pivotal temperature produce a greater percentage of male hatchlings, while temperatures above produce a greater percentage of female hatchlings.[9] Concerns have been raised about the effects of climate change on this evolved developmental strategy.[9]
Movement[]
Among freshwater turtles, podocnemidids have among the longest aquatic migratory patterns, rarely leaving the water except to bask.[6] Their average home range spans between 0.3 and 14.6 ha.[5] Movement patterns are predicated on sex, body size, food availability, habitat quality, season, reproductive status, and life stage.[6]
Seasonal movements are most prominent due to changing water levels.[6] Research has shown increased movement to deeper waters, likely as a result of climate change.[9]
Conservation[]
Threats[]
As of 2018, 37% of all freshwater and terrestrial turtle species found in Colombia were classified as "Threatened".[10] Despite legislation passed in 1964 aimed at protecting these species (Ministry of Agriculture Resolution No. 0214-1964), their populations have continually decreased.[10] While many anthropogenic factors have contributed to the decline of Magdalena River turtles, over-harvest and climate change are the most prominent.[4] Over-harvest results from human demand for Magdalena River turtle consumption.[3]
Locals believe that feeding on the turtles offer many medicinal qualities.[3] These include easing pregnancy recovery, curing diseases, boosting strength and longevity, and creating natural aphrodisiacs.[3] Climate change has led to discernible changes in temperature-dependent sex determination and movement patterns.[9][6] It has also contributed to nesting site flooding and other habitat alterations.[6]
While anthropogenic causes are most pronounced, several life history factors contribute to the Magdalena River turtles endangerment, as well.[4] High rates of mortality are seen in eggs, hatchlings, and juveniles.[4] Despite their high rates of survival as subadults and adults, their slow, r-selected growth means it takes a while for those stages to be reached.[4] They also require multiple habitats, one for nesting and another for feeding, which result in strenuous migrations.[4]
Conservation approaches[]
The most commonly used conservation approach for Magdalena River turtle conservation is "head-starting".[3] However, research efforts have been focused on finding more effective means on conservation, as understanding of the turtles' endangered nature is relatively novel.[10][5] A study that compiled 16 ecological knowledge criteria of Colombian freshwater and tortoise species suggested that the Magdalena River turtle should receive top conservation priority.[11] Studies are applying faster demographic modeling and surveying to better understand the species and establish practical conservation efforts.[4][10] Faster demographic modeling of the species' vital rates is focused on analyzing the contributions of each life stage and intrinsic growth rates (r).[4] Surveying has shown that local Magdalena River turtle consumption habits have changed and knowledge of their ecological role has improved.[10] This suggests that community-based strategies, including distribution of educational material, is proving effective in the conservation effort of Magdalena River turtles.[10]
References[]
- ^ Páez, V.; Gallego-Garcia, N.; Restrepo, A. (2016). "Podocnemis lewyana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T17823A1528580. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T17823A1528580.en. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ Podocnemis lewyana, Reptile Database
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Magdalena River Turtle | Podocnemis lewyana". EDGE of Existence. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Paez, VP; Bock, BC; Espinal-Garcia, PA; Rendon-Valencia, BH; Alzate-Estrada, D; Cartagena-Otalvaro, VM; Heppell, SS (2015). "Life History and Demographic Characteristics of the Magdalena River Turtle ( Podocnemis lewyana): Implications for Management". Copeia. 103: 1058–1074.
- ^ a b c d e f g Páez, Vivian; Restrepo, Adriana; Gallego-Garcia, Natalia (2015-07-01). "IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: Magdalena River Turtle". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ a b c d e f Alzate-Estrada, Diego A.; Páez, Vivian P.; Cartagena-Otálvaro, Viviana M.; Bock, Brian C. (2020). "Linear Home Range and Seasonal Movements of Podocnemis lewyana in the Magdalena River, Colombia". Copeia. 108 (1): 29–38.
- ^ a b c d e f Ceballos, Claudia P.; Romero, Isabel; Gómez-Saldarriaga, Catalina; Miranda, Karla (2014). "REPRODUCTION AND CONSERVATION OF THE MAGDALENA RIVER TURTLE (Podocnemis lewyana) IN THE CLAROCOCORNÁ SUR RIVER, COLOMBIA". Acta Biológica Colombiana. 19 (3): 393–400.
- ^ a b c d Paez, VP; Restrepo, A; Vargas-Ramirez, M; Bock, BC (2009). "Podocnemis lewyana Dumeril 1852- Magdalena River Turtle". Chelonian Research Monographs. 5.
- ^ a b c d e f Gallego-García, Natalia; Páez, Vivian P. (2016). "Geographic Variation in Sex Determination Patterns in the River Turtle Podocnemis lewyana: Implications for Global Warming". Journal of Herpetology. 50 (2): 256–262.
- ^ a b c d e f Vallejo-Betancur, Margarita M.; Páez, Vivian P.; Quan-Young, Lizette I. (2018). "Analysis of People's Perceptions of Turtle Conservation Effectiveness for the Magdalena River Turtle Podocnemis lewyana and the Colombian Slider Trachemys callirostris in Northern Colombia: An Ethnozoological Approach". Tropical Conservation Science. 11: 194008291877906.
- ^ Forero-Medina, German; Páez, Vivian P.; Garcés-Restrepo, Mario F.; Carr, John L.; Giraldo, Alan; Vargas-Ramírez, Mario (2016). "Research and Conservation Priorities for Tortoises and Freshwater Turtles of Colombia". Tropical Conservation Science. 9 (4).
- IUCN Red List critically endangered species
- Podocnemis
- Turtles of South America
- Endemic fauna of Colombia
- Magdalena River
- Reptiles of Colombia
- Critically endangered animals
- Critically endangered biota of South America
- Reptiles described in 1852
- Taxa named by André Marie Constant Duméril
