Mińsk Mazowiecki
Mińsk Mazowiecki | |
|---|---|
 Aerial view of Mińsk Mazowiecki | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 Mińsk Mazowiecki | |
| Coordinates: 52°11′N 21°34′E / 52.183°N 21.567°ECoordinates: 52°11′N 21°34′E / 52.183°N 21.567°E | |
| Country | Poland |
| Voivodeship | |
| County | Mińsk |
| Gmina | Mińsk Mazowiecki (urban gmina) |
| Established | 14th century |
| Town rights | 1421, 29 May |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Marcin Jakubowski |
| Area | |
| • Total | 13.12 km2 (5.07 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 147 m (482 ft) |
| Population (2015) | |
| • Total | 40,211 |
| • Density | 3,100/km2 (7,900/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 05-300, 301, 303 |
| Area code(s) | +48 025 |
| Car plates | WM |
| Website | http://www.minsk-maz.pl |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mińsk Mazowiecki. |
Mińsk Mazowiecki [ˈmʲiɲsk mazɔˈvʲɛt͡skʲi] (![]() listen) "Masovian Minsk" is a town in eastern Poland with 40,211 inhabitants (2015). It is situated in the Masovian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Siedlce Voivodeship (1975–1998). It is the capital of Mińsk County.
listen) "Masovian Minsk" is a town in eastern Poland with 40,211 inhabitants (2015). It is situated in the Masovian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Siedlce Voivodeship (1975–1998). It is the capital of Mińsk County.
Name[]
The source of town name - Mińsk - is the Mienia River, which in turn derives from the verb 'mienić', which means 'to shine'. The postnominal adjective 'Mazowiecki' shows the historical connection to Mazovia and distinguishes Mińsk Mazowiecki from the Belarusian capital of Minsk.
Location[]
Mińsk Mazowiecki is located geographically in South Podlasie, historically in East Mazovia and administratively in the eastern part of Masovian Voivodeship, 37 kilometres (23 miles) east from Warsaw's Center.
Timeline of history[]
- XIV century – first mentions of a settlement with commercial function
- 1421, 29 May – Mińsk was granted town privileges by Janusz I of Warsaw
- 1422 – first wooden church was built (not preserved)
- 1549 – a second town Sendomierz, later merged with Mińsk, was located on the other side of Srebrna River
- 1629 – the present church opened
- 1695 – Sendomierz joined to Mińsk
- XVIII century – gradual decline of Mińsk connected with gradual decline of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
- 1795–1809 – under Austrian rule as a result of the Third Partition of Poland
- 1809–1815 – in the Duchy of Warsaw
- 1815–1916 – in the Congress Poland
- 1866 – Mińsk county established, first train arrival (Warsaw–Terespol Railway)
- 1867 – name of the town changed to Nowomińsk (Novominsk)
- 1870 – Dernałowicz Family became the last owners of the city (up to the Second World War)
- 1886 – first bookstore in east Mazovia
- XX century – found of famous manufacture
- 1912 (or 1910) – start of Maria Grochowska's School, today this is Polska Macierz Szkolna's High School
- 1914 – old church opened after reconstruction
- 1915 – present hospital opened
- 1915 to 1918, 11 November – German occupation during World War I
- 1916 – name's change (Novominsk > Mińsk Mazowiecki)
- 1920 – briefly occupied by Russians before the Battle of Warsaw during the Polish-Bolshevik War
- 1920–1939 – great development
- 1937 – first electric train arrived
- 1939–1944 – second German occupation (World War II)
- 1939, 12 September – German entry
- 1939, 13 September – battle for Mińsk Mazowiecki (led by gen. Władysław Anders)
- 1942, 21 July – liquidation of Mińsk Mazowiecki ghetto. Most of the Jewish residents were sent to the Treblinka death camp (one of the first episodes of the Holocaust)
- 1944, 30 July – liberation by Armia Krajowa (prelude to Warsaw Uprising)
- 1944, 30–31 July – Soviet liberation
- 1945, 2–3 March – Soviet killed Mińsk's elite (with Mayor Hipolit Konopka)
- 1952 – trains manufacture
- 1957 – military garrison
- 1979 – new train station
- 1985 – Solidarity events
- 1990 – first Mayor elected in free elections (since elections before Second World War): Zbigniew Grzesiak
- 1999 – Mińsk County established
Jewish history[]

In 1768 the restrictions on permanent residence for Jewish people in Mińsk had been lifted.[1] From the 19th century to the 1930s it became very popular. Before the Second World War, there were thousands of Jews living in Mińsk and they had a general synagogue and smaller temples. The Novominsk hasidic dynasty was founded here in the late 19th century by Rabbi Yaakov Perlow, a descendant of the Baal Shem Tov.
Soon after the war began, the Germans created the Mińsk Ghetto. It was liquidated on 21 July 1942. Most of the Jews were killed in Treblinka extermination camp sent in Holocaust trains by the thousands. The remaining Jewish population were killed in Mińsk on 10 January 1943 (500 people) and 5 June (the last 150 people).
Monuments[]

- layout of medieval settlement and later city
- Palace of Doria Dernałowicz Family – built probably in the 17th century (in place of 16th century residence), converted to classicism
- park
- Church of the Nativity of The Blessed Virgin Mary – built in the 17th century, converted to neo-baroque in the early 20th century
- internal furnishing
- cemetery
- county hall (former), 19th century, classicism
- county hall, 19th century
- post office, 19th century, empire
- church of Mariavite Church, 1911
- residential areas, 19th and early 20th century
- Jewish cemetery
- some school buildings (early 20th century)
Economy[]

Trade:
- hypermarket Carrefour
- supermarkets (about 10)
- many other shops
- market
- developers
Service:
- 10 banks
- fast-foods, pubs and restaurants
- 3 hotels
- construction industry
- car service
- satellite communication
Industry:
- ZNTK "Mińsk Mazowiecki" (since 2008 a subsidiary PESA SA) — maintenance and repair of railway rolling stock
- Fabryka Urządzeń Dźwigowych – production of cranes and other heavy machinery
- cotton products
- yachts
- shoes
- foil
Population[]
|
|
Education[]

- Józef Majka College of Social Science (catholic)
- Stanisław Staszic Lifelong Learning Center
- University of Third Age
- Polska Macierz Szkolna Gymnasium and High School
- Salesian Elementary, Gymnasium and High School (catholic)
- Kazimierz Wielki Professional High School
- Powstańcy Warszawy Professional High School
- High School of Economy
- Maria Skłodowska-Curie High School
- 3 public gymnasiums
- 4 public elementary schools
- over 10 preschools (6 public)
- special school (for kids with problems)
- clinic of psychological and pedagogical help
Bureaus[]

- Regional Bureau of Environmental Protection Inspection
- Point of Conscription
- Above Forester Bureau (Nadleśnictwo Mińsk)
- County, city and commune bureaus
Safety[]
- Police Departament of Mińsk County – 2 building in Mińsk, dozens of cars (including sport cars and off-road cars)
- Fire Departament of Mińsk County – quite new fire engines (well equipped after big fire in industry area a few years ago)
- Public Hospital of Mińsk County
Culture and sports[]

Culture:
- House of Culture
- School of Art
- 2 libraries
- 2 museums
- Cinema
- Magazines (2 public and 3 commercial are published in Mińsk)
Sport:
- Miejski Ośrodek Sportu i Rekreacji (public sport and recreation departament)
- 2 stadiums
- Ice rink
- Other
- Mazovia-ZNTK
- Football team in local amateur league
- Other sports
- other clubs
Religions[]

- Roman Catholic Church (4 parishes and other structures)
- Mariavite Church (1 parish)
- Baptist (1 congregation)
- Mennonite (1 congregation)
Public transport[]
- Train station
- Regular service (39 trains in one way daily) to Warsaw
- Direct connections with many cities in Poland, and with Moscow
- 2 regular bus services to Warsaw
Lands[]
Overall: 13.12 square kilometres (5.07 sq mi)
- Residential: 30%
- Industrial: 6%
- Communication (roads, railroads etc.): 15%
- Agricultural: 29%
- Parks: 5%
- Other: 15%
Historical parts of city[]
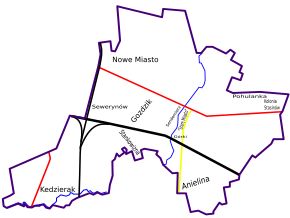

Cities:
- Mińsk – old town
- Sendomierz (found 1549, joined 1695)
Estates built as part of Mińsk:
- Nowe Miasto – Miasto Ogród – New Town – Garden Town (found 1936)
- Concrete estates built in socialist realism (about 1945–1990) without names
- Modern estates without names
Villages:
- Over railroad part of city (all existed in 1839 and earlier)
- Kędzierak (joined partly in 1954 and fully in 1984)
- Stankowizna (joined in 19th or 20th century)
- Anielina (joined in similar time as Kędzierak)
- Other
- Górki (joined in the 18th century)
- Goździk (joined during First War War)
- Kolonia Stasinów (joined in 1936)
- Pohulanka (joined partly in 1936)
- Sewerynów (joined in similar time as Kędzierak)
Military[]
- Military police
- 23rd Air Base with MIG-29 aircraft
Twin towns – sister cities[]
Mińsk Mazowiecki is twinned with:[2]
 Borodianka, Ukraine
Borodianka, Ukraine Krnov, Czech Republic
Krnov, Czech Republic Lacey, United States
Lacey, United States Pefki, Greece
Pefki, Greece Saint-Égrève, France
Saint-Égrève, France Telšiai, Lithuania
Telšiai, Lithuania
Notable people[]
- Julian Grobelny, Righteous Among the Nations
- Louis B. Mayer, Hollywood film producer and studio executive
- Czesław Mroczek, poseł
- , poseł
- Moshe Carmel, politician in Israel
- Stefan Żeromski, writer
- Jan Himilsbach, actor and author
- Leyb Rokhman, Yiddish writer in Israel
- Hanna Dunowska, actor
- Victor Prus, architect in Canada
- Yeshurun Keshet Israeli poet, essayist, translator and literary critic
- Jacques Kalisz, architect in France
- Stanislav Redens, secret police officer in the Soviet Union
- Hermann Birnbach, subject of a Stolperstein in Nordhausen
- Marek Piotrowski, World Champion in Kickboxing
- Rafał Jackiewicz, boxer
References[]
- ^ Mińsk Mazowiecki: The beginning of the Jewish settlement. Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine Museum of the History of Polish Jews, Virtual Shtetl.
- ^ "Współpraca zagraniczna". minsk-maz.pl (in Polish). Mińsk Mazowiecki. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
Books[]
- 585 lat Mińska Mazowieckiego, red. Janusz Kuligowski, Mińsk Mazowiecki, 2006, ISBN 8390693674
External links[]
- Co słychać? – weekly magazine, ISSN 1425-6185
- Web page of City Hall Minsk Maz.pl (English)
- Web page of County Hall Powiat Minski.pl
- Web page: virtual tour. Panoramas.
- Jewish cemetery
- Jewish cemetery
- Historical placards
- Mińsk Mazowiecki, Poland at JewishGen
- Cities and towns in Masovian Voivodeship
- Mińsk County
- Masovian Voivodeship (1526–1795)
- Warsaw Governorate
- Warsaw Voivodeship (1919–1939)
- Holocaust locations in Poland



