Mount Friesland
| Mount Friesland | |
|---|---|
 Mount Friesland from the west slopes of Lyaskovets Peak, with Presian Ridge in the foreground and ‘The Synagogue’ in the left background | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 1,700.2 m (5,578 ft)[1][2] |
| Prominence | 1,700.2 m (5,578 ft)[3] |
| Listing | Ultra |
| Coordinates | 62°40′14.9″S 60°11′10.7″W / 62.670806°S 60.186306°WCoordinates: 62°40′14.9″S 60°11′10.7″W / 62.670806°S 60.186306°W[1] |
| Geography | |
 Mount Friesland Antarctica | |
| Location | Livingston Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica |
| Parent range | Tangra Mountains |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 30 December 1991 Francesc Sàbat and Jorge Enrique |
Mount Friesland is a mountain rising to 1,700.2 metres (5,578 ft) in the homonymous Friesland Ridge, the summit of Tangra Mountains and Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Its north rib is connected to Pliska Ridge by Nesebar Gap on the west, and to Bowles Ridge by Wörner Gap on the north. On the east Mount Friesland is connected to Presian Ridge and further on to Catalunyan Saddle and Lyaskovets Peak. On the south-southwest it is connected by a short saddle to ‘The Synagogue’ a sharp-peaked rock-cored ice formation abutting neighbouring St. Boris Peak. The peak is heavily glaciated and crevassed, surmounting Huntress Glacier to the west, Perunika Glacier to the north-northwest, Huron Glacier to the northeast and Macy Glacier to the southeast. The local weather is notoriously unpleasant and challenging; according to the seasoned Antarctic mountaineer Damien Gildea who climbed in the area, 'just about the worst weather in the world'.[4]
History[]
The feature was known to American and British sealers as early as 1820–21, and variously referred to as "Peak of Frezeland", "Friezland Peak", and "Friesland Peak". In the early 1900s the name "Barnard", applied by James Weddell in 1825 to nearby Needle Peak, was transferred to this mountain. The original name has now been restored with the spelling "Friesland" that appears to have been more frequently used than any of the other versions. In order to preserve the historical memory of the area, the name Barnard Point has since been approved for the nearby point on the southeast side of the entrance to False Bay.[5][6]
The first ascent of Mount Friesland was made from Juan Carlos I Base on 30 December 1991 by the Catalan climbers and , after whom Sàbat Hill and Enrique Hill, respectively, were named. The peak was climbed and GPS surveyed by the Australian Damien Gildea and and the Chilean on 20 December 2003, who produced a new map of the island in 2004, based on Spanish satellite imagery and their GPS data. The third ascent was made by the Bulgarians Lyubomir Ivanov and Doychin Vasilev from Camp Academia on 15 December 2004. All these used the Sàbat–Enrique eastern route to the peak, from Camp Academia locality (541 m) via Catalunyan Saddle (1,260 m) and Presian Ridge (1,456 m).
Elevation[]
The summit elevation was estimated at 1,684 metres (5,525 ft) by a 1995–96 Bulgarian survey;[7] the present figure was produced by a 2003 Australian GPS survey,[8][1][2] and closely matched (as 1,702 metres (5,584 ft)) by the Bulgarian survey Tangra 2004/05. The local ice relief is subject to changes, causing variations in the feature's elevation. According to a Bulgarian GPS survey by D. Boyanov and N. Petkov the elevation of Mt. Friesland was 1,693 metres (5,554 ft) in December 2016, making the peak lower than the adjacent St. Boris Peak (the latter's northernmost ice formation ‘The Synagogue’ rising to 1,699 metres (5,574 ft)) at that time.[9][10][11] According to the American high accuracy Reference Elevation Model of Antarctica (REMA), Mount Friesland is 8 m (26 ft) higher than the central summit of St. Boris Peak and 14 m (46 ft) higher than ‘The Synagogue’.[12]
Location[]
Mount Friesland is situated 12.5 kilometres (7.8 mi) northeast of Barnard Point, 9.7 kilometres (6.0 mi) east-southeast of St. Kliment Ohridski Base, 3.6 kilometres (2.2 mi) southeast of the summit of Pliska Ridge, 6.1 kilometres (3.8 mi) south by east of Mount Bowles, 2.9 kilometres (1.8 mi) south-southwest of Camp Academia, 6.7 kilometres (4.2 mi) west of Great Needle Peak, and 6.85 kilometres (4.26 mi) north by west of Samuel Point. British mapping in 1968, Chilean in 1971, Argentine in 1980, Spanish in 1991, US in 2004, and Bulgarian in 1996, 2005 and 2009. Bulgarian surveys 1995/96 (estimated elevation 1684 m) and 2004–05.
Maps[]
- Chart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c. from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822
- South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:200000 topographic map. DOS 610 Sheet W 62 60. Tolworth, UK, 1968.
- Islas Livingston y Decepción. Mapa topográfico a escala 1:100000. Madrid: Servicio Geográfico del Ejército, 1991.
- L.L. Ivanov. Livingston Island: Central-Eastern Region. Scale 1:25000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 1996.
- S. Soccol, D. Gildea and J. Bath. Livingston Island, Antarctica. Scale 1:100000 satellite map. The Omega Foundation, USA, 2004.
- L.L. Ivanov et al., Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands (from English Strait to Morton Strait, with illustrations and ice-cover distribution), 1:100000 scale topographic map, Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, Sofia, 2005
- L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2010. ISBN 978-954-92032-9-5 (First edition 2009. ISBN 978-954-92032-6-4)
- Antarctic Digital Database (ADD). Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly upgraded and updated.
- L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Smith Island. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2017. ISBN 978-619-90008-3-0
See also[]
Gallery[]
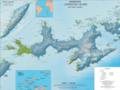
Topographic map of Livingston Island and Smith Island

Location of Tangra Mountains on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands

Topographic map of central-eastern Livingston Island featuring Mount Friesland

The survey route of Tangra 2004/05 including Mount Friesland

Panoramic northeast view from St. Boris Peak centred on Mount Friesland

The main building of St. Kliment Ohridski Base, with Balkan Snowfield in the middle, and (left to right) Mount Friesland, St. Boris Peak and Simeon Peak in the background

Friesland Ridge from Bransfield Strait, with St. Methodius Peak, St. Cyril Peak, Simeon Peak, St. Boris Peak, Mount Friesland and Lyaskovets Peak in the background, and Needle Peak, Macy Glacier and Peshev Ridge in the foreground
Mount Friesland from upper Perunika Glacier near Orpheus Gate, with Pliska Ridge on the right
The summit of Mount Friesland, with the open extension of a partially hidden crevasse

St. Boris Peak from Mount Friesland, with ‘The Synagogue’ ice form in the foreground

Southern Hurd Peninsula from Mount Friesland, with False Bay on the left and South Bay on the right, and Smith Island seen on the horizon

The Spanish base area from Mount Friesland, with Napier Peak and Johnsons Glacier in the foreground, Charrúa Ridge on the right and Mount Reina Sofia in the background, and South Bay, Hannah Point and western Livingston Island farther away
Bulgarian Beach from Mount Friesland, with Castillo Nunatak and Willan Nunatak in the foreground, Balkan Snowfield in the middle, and left to right in the background Atlantic Club Ridge, Hesperides Hill, Pesyakov Hill and Sinemorets Hill with the Bulgarian base in between, and Spanish Knoll
Notes[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Gildea, Damien. "Omega Livingston Island GPS Expedition 2003". USA: The Omega Foundation. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gildea, Damien (2004). "Antarctica, Antarctic Peninsula, Livingston Island, South Shetland Islands, Second Ascent of Mt. Friesland and New Altitude". American Alpine Journal. 46 (78): 329–331. Retrieved 11 April 2015.
- ^ "Mount Friesland, Antarctica". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 11 April 2015.
- ^ D. Gildea. Omega Livingston Island GPS Expedition 2003. Dispatches, 17 December 2003
- ^ "Friesland, Mount". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 10 April 2012.
- ^ "Mount Friesland". SCAR Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ^ L.L. Ivanov. Livingston Island: Central-Eastern Region. Scale 1:25000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 1996.
- ^ AUSPOS Online GPS Processing Report: Job number #101306. Space Geodesy Analysis Centre, The National Mapping Division. Geoscience Australia, 22 December 2003. 5 pp.
- ^ D. Boyanov. NSA third time in Antarctica. National Sports Academy, 2017. (in Bulgarian)
- ^ D. Boyanov. This Saturday and this Sunday. BTV, 28 January 2017. (in Bulgarian)
- ^ D. Boyanov and N. Petkov. The peaks of Tangra Mountains: Project report Part Two 2016/17. Sofia, February 2017 (in Bulgarian)
- ^ I.M. Howat, C. Porter, B.E. Smith, M.-J. Noh and P. Morin. The Reference Elevation Model of Antarctica. The Cryosphere 13, 2019. pp. 665–674 (Antarctic REMA Exlorer)
References[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mount Friesland. |
- "Mount Friesland". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Mount Friesland. SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer.
- Mount Friesland, Antarctica. Peakbagger.com.
- D. Gildea. Antarctic Mountains: Climbing in Antarctica.
- L. Ivanov. General Geography and History of Livingston Island. In: Bulgarian Antarctic Research: A Synthesis. Eds. C. Pimpirev and N. Chipev. Sofia: St. Kliment Ohridski University Press, 2015. pp. 17–28. ISBN 978-954-07-3939-7
External links[]
- Mount Friesland. Copernix satellite image
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the United States Geological Survey document: "Friesland, Mount". (content from the Geographic Names Information System)
This article incorporates public domain material from the United States Geological Survey document: "Friesland, Mount". (content from the Geographic Names Information System)
- Mountains of Antarctica
- Tangra Mountains













