South Shetland Islands
 Map of the South Shetland Islands | |
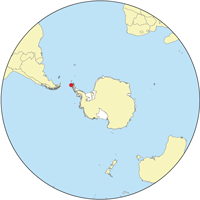 Location of the South Shetlands | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Antarctica   |
| Coordinates | 62°0′S 58°0′W / 62.000°S 58.000°W |
| Area | 3,687 km2 (1,424 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 2,105 m (6906 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Foster |
| Administration | |
| Administered under the Antarctic Treaty System | |
| Demographics | |
| Population | around 500[citation needed] |
| Ethnic groups | Chileans, others |




The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of 3,687 km2 (1,424 sq mi). They lie about 120 km (75 mi) north of the Antarctic Peninsula,[1] and between 430 km (270 mi) to 900 km (560 mi) southwest from the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories[citation needed] and they are free for use by any signatory for non-military purposes.
The islands have been claimed by the United Kingdom since 1908 and as part of the British Antarctic Territory since 1962. They are also claimed by the governments of Chile (since 1940, as part of the Antártica Chilena province) and Argentina (since 1943, as part of Argentine Antarctica, Tierra del Fuego Province).
Several countries maintain research stations on the islands. Most of them are situated on King George Island, benefitting from the airfield of the Chilean base Eduardo Frei.
There are sixteen research stations to date in different parts of the islands, with Chilean stations being the greatest in number.
History[]
The islands were discovered by the British mariner William Smith in 1819. Although it has been postulated that Dutch mariner Dirck Gerritsz in 1599 or Spanish Admiral Gabriel de Castilla in 1603 might have sighted the South Shetlands, or North or South American sealers might have visited the archipelago before Smith, there is insufficient historical evidence to sustain such assertions. Smith's discovery, by contrast, was well documented and had wider historical implications beyond its geographic significance.[2]
Chilean scientists have claimed that Amerinds visited the islands, due to stone artifacts recovered from bottom-sampling operations in Admiralty Bay, King George Island, and Discovery Bay, Greenwich Island;[3] however, the artifacts — two arrowheads — were later found to have been planted.[4][5] In 1818 Juan Pedro de Aguirre obtained permission from the Buenos Aires authorities to establish a base for sealing on "some of the uninhabited islands near the South Pole".[6]
Captain William Smith in the British merchant brig Williams, while sailing to Valparaíso, Chile in 1819 deviated from his route south of Cape Horn, and on 19 February 1819 sighted Williams Point, the northeast extremity of Livingston Island. Thus Livingston Island became the first land ever discovered farther than 60° south. Smith revisited the South Shetlands, landed on King George Island on 16 October 1819, and claimed possession for Britain.
Meanwhile, the Spanish Navy ship San Telmo sank in September 1819 whilst trying to go through the Drake Passage. Parts of her presumed wreckage were found months later by sealers on the north coast of Livingston Island. The crew of San Telmo and the troops onboard, led by brigadier Rosendo Porlier (a total of 644 men), are believed to be the first known humans to land in Antarctica.[7]
From December 1819 to January 1820, the islands were surveyed and mapped by Lieutenant Edward Bransfield on board the Williams, which had been chartered by the Royal Navy.
On 15 November 1819, the United States agent in Valparaíso, Jeremy Robinson, informed the United States Secretary of State John Quincy Adams of Smith's discovery and Bransfield's forthcoming mission, and suggested dispatching a United States Navy ship to explore the islands where "new sources of wealth, power and happiness would be disclosed and science itself be benefited thereby".
The discovery of the islands attracted British and American sealers. The first sealing ship to operate in the area was the brig Espirito Santo, chartered by British merchants in Buenos Aires. The ship arrived at Rugged Island off Livingston Island, where its British crew landed on Christmas Day 1819, and claimed the islands for King George III. A narrative of the events was published by the brig's master, Joseph Herring, in the July 1820 edition of the Imperial Magazine. The Espirito Santo was followed from the Falkland Islands by the American brig Hersilia, commanded by Captain James Sheffield (with second mate Nathaniel Palmer), the first US sealer in the South Shetlands.
The first wintering over in Antarctica took place on the South Shetlands, when at the end of the 1820–1821 summer season eleven British men from the ship Lord Melville failed to leave King George Island, and survived the winter to be rescued at the beginning of the next season.
Having circumnavigated the Antarctic continent, the Russian Antarctic Expedition of Fabian von Bellingshausen and Mikhail Lazarev arrived at the South Shetlands in January 1821. The Russians surveyed the islands and named them, landing on both King George Island and Elephant Island. While sailing between Deception and Livingston islands, Bellingshausen was visited by Nathaniel Palmer, master of the American brig Hero, who informed him of the activities of dozens of American and British sealing ships in the area.
The name "New South Britain" was used briefly, but was soon changed to South Shetland Islands (in reference to the Shetland Islands in the north of Scotland). The name South Shetland Islands is now established in international usage. Both island groups lie at similar distances from the equator, but the South Shetlands are much colder. (See section Climate)
Seal hunting and whaling was conducted on the islands during the 19th and early 20th century. The sealing era lasted from 1820 to 1908 during which time 197 vessels are recorded visiting the islands.[8] Twelve of those vessels were wrecked. Relics of the sealing era include iron try-pots, hut ruins and inscriptions.
Beginning in 1908, the islands were governed as part of the Falkland Islands Dependency, but they have only been permanently occupied by humans since the establishment of a scientific research station in 1944. The archipelago, together with the nearby Antarctic Peninsula and South Georgia Island, is an increasingly popular tourist destination during the southern summer.
Geography[]

As a group of islands, the South Shetland Islands are located at 62°0′S 58°0′W / 62.000°S 58.000°WCoordinates: 62°0′S 58°0′W / 62.000°S 58.000°W. They are within the region 61° 00'–63° 37' South, 53° 83'–62° 83' West. The islands lie 940 km (580 mi) south of the Falkland Islands, and between 93 km (58 mi) (Deception Island) and 269 km (167 mi) (Clarence Island) northwest and north from the nearest point of the Antarctic continent, Graham Land.

The South Shetlands consist of 11 major islands and several minor ones, totalling 3,687 km2 (1,424 sq mi) of land area. Between 80 and 90% of the land area is permanently glaciated. The highest point on the island chain is Mount Irving on Clarence Island at 2,300 m (7,500 ft) above sea level.
The South Shetland Islands extend about 450 km (280 mi) from Smith Island and Low Island in the west-southwest to Elephant Island and Clarence Island in the east-northeast.
Volcanoes[]
Various volcanoes with activity in the Quaternary exist in the islands. These volcanoes are associated with the tectonics of Bransfield Rift. From west to east known volcanoes are Sail Rock, Deception Island, Rezen Knoll, Gleaner Heights, Edinburgh Hill, Inott Point, Penguin Island, Melville Peak and Bridgeman Island.[9] Most of the volcanic rock and tephra is of basalt or basaltic andesite.[9] An exception is the tephra of Deception Island which is of trachyte and basaltic trachyandesite, richer in potassium and sodium.[9]
Quaternary volcanic products of the islands tend to have less potassium and sodium at a given silica range, and lower Nb/Y ratios, than those associated with the on the Antarctic Peninisula.[9]
Climate[]
The islands are the same distance from the equator as the Faroe Islands in the North Atlantic, but their proximity to Antarctica means that they have a much colder climate. The sea around the islands is closed by ice from early April to early December and the monthly average temperature is below 0 °C (32 °F) for eight months of the year (April to November).
The islands have experienced measurable glacier retreat during recent years, but despite this, they remain more than 80% snow and ice covered throughout the summer.
The climate is cloudy and humid all year round and very strong westerly winds blow at all seasons. Some of the sunniest weather is associated with outbreaks of very cold weather from the south in late winter and spring. Mean summer temperatures are only about 1.5 °C (34.7 °F) and those in winter are about −5 °C (23 °F). The effect of the ocean tends to keep summer temperatures low and prevent winter temperatures from falling as low as they do inland to the south.[10]
Flora and fauna[]

Despite the harsh conditions, the islands do support vegetation and are part of the Scotia Sea Islands tundra ecoregion, along with South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, the South Orkney Islands and Bouvet Island. All of these islands lie in the cold seas below the Antarctic Convergence. These areas support tundra vegetation consisting of mosses, lichens and algae, while seabirds, penguins, and seals feed in the surrounding waters.
Diptera[]
- Diptera
- Chironomidae
Islands[]


From north to south the main and some minor islands of the South Shetlands are:
- Cornwallis Island (minor)
- Elephant Island (Mordvinova by Russia)
- Clarence Island (Shishkova by Russia)
- Rowett Island (minor)
- Gibbs Island (minor)
- Eadie Island (minor)
- King George Island (the largest, called May 25 island by Argentina, or Vaterloo by Russia)
- Bridgeman Island (minor)
- Penguin Island (minor - one of several Penguin Islands in the Antarctic region)
- Nelson Island (Leipzig by Russia)
- Robert Island (Polotsk by Russia)
- The Watchkeeper (minor)
- Table Island (minor)
- Aitcho Islands (minor)
- Greenwich Island (Berezina by Russia)
- Half Moon Island (minor)
- Desolation Island (minor)
- Livingston Island (second largest, Smolensk by Russia)
- Rugged Island (minor - one of several in the Antarctic region)
- Snow Island (one of several in the Antarctic region; Maly Yaroslavets by Russia)
- Smith Island (Borodino by Russia)
- Deception Island (Teylya by Russia)
- Low Island
- Seal Islands (minor)
- Middle Island (phantom)
The Russian names above are historical, and no longer the official Russian names. (See the end of the article for a complete list of islands.)
Research stations[]


Several nations maintain research stations on the Islands:
 Argentina – Cámara (since 1953, Summer only)
Argentina – Cámara (since 1953, Summer only) Argentina – Carlini (since 1953, Year-round)
Argentina – Carlini (since 1953, Year-round) Argentina – Base Decepción (since 1948, Summer only)
Argentina – Base Decepción (since 1948, Summer only) Bulgaria – St. Kliment Ohridski (since 1988, Summer only)
Bulgaria – St. Kliment Ohridski (since 1988, Summer only) Brazil – Comandante Ferraz Antarctic Station (since 1984, Year-round)
Brazil – Comandante Ferraz Antarctic Station (since 1984, Year-round) Chile – Presidente Eduardo Frei Base (since 1969, Year-round)
Chile – Presidente Eduardo Frei Base (since 1969, Year-round) Chile – Profesor Julio Escudero Base (since 1994, Year-round)
Chile – Profesor Julio Escudero Base (since 1994, Year-round) Chile – Captain Arturo Prat Base (since 1947, Year-round)
Chile – Captain Arturo Prat Base (since 1947, Year-round) Chile – Dr. Guillermo Mann Base (since 1991, Summer only)
Chile – Dr. Guillermo Mann Base (since 1991, Summer only) China – Chang Cheng / Great Wall (since 1985, Year-round)
China – Chang Cheng / Great Wall (since 1985, Year-round) Ecuador – Pedro Vicente Maldonado Base (since 1990, Summer only)
Ecuador – Pedro Vicente Maldonado Base (since 1990, Summer only) Spain – Juan Carlos I Antarctic Base (since 1988, Summer only)
Spain – Juan Carlos I Antarctic Base (since 1988, Summer only) Spain – Gabriel de Castilla Base (since 1989, Summer only)
Spain – Gabriel de Castilla Base (since 1989, Summer only) South Korea – King Sejong Station (since 1988, Year-round)
South Korea – King Sejong Station (since 1988, Year-round) Peru – Machu Picchu Research Station (since 1989, Summer only)
Peru – Machu Picchu Research Station (since 1989, Summer only) Poland – Henryk Arctowski Polish Antarctic Station (since 1977, Year-round)
Poland – Henryk Arctowski Polish Antarctic Station (since 1977, Year-round) Russia – Bellingshausen Station (since 1968, Year-round)
Russia – Bellingshausen Station (since 1968, Year-round) United States – Shirreff Base (since 1996, Summer only)
United States – Shirreff Base (since 1996, Summer only) Uruguay – Artigas Base (since 1984, Year-round)
Uruguay – Artigas Base (since 1984, Year-round)
Field camps[]

 Argentina – Camp Livingston
Argentina – Camp Livingston Bulgaria – Camp Academia
Bulgaria – Camp Academia Spain – Camp Byers
Spain – Camp Byers
See also[]
- Cape Plenty
- Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica – Authoritative international gazetteer containing all the Antarctic toponyms
- Deception Island – Active volcanic island in the South Shetland archipelago
- Greenwich Island – Island of the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica
- King George Island – Island of the South Shetland Islands
- List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands
- Livingston Island – Island of the South Shetland Islands
- Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research
- Sherratt Bay
- Territorial claims in Antarctica
- Shetland Plate – Tectonic microplate off the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula
- Stancomb Cove
- Stanley Patch
- Stump Rock
- Wensleydale Beacon
Maps[]

- Chart of South Shetland including Coronation Island from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822.
- King George Island Geographic Information System.
- L. L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands (from English Strait to Morton Strait, with illustrations and ice-cover distribution). Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, Sofia, 2005.
- L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2010. ISBN 978-954-92032-9-5 (First edition 2009 ISBN 978-954-92032-6-4)
- L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Smith Island. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2017, ISBN 978-619-90008-3-0
- Antarctic Digital Database (ADD) Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly upgraded and updated.

In fiction[]
- The archipelago provides the mise-en-scène of the 2016 Antarctica thriller novel The Killing Ship authored by Elizabeth Cruwys and Beau Riffenburgh (under their joint alias Simon Beaufort), with action spreading from Hannah Point to Byers Peninsula via Ivanov Beach, skirting Verila Glacier and Rotch Dome in the process.[11][12]
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "South Shetland Islands". North Dakota State University. Retrieved 21 August 2009.
- ^ Ivanov, L. General Geography and History of Livingston Island. In: Bulgarian Antarctic Research: A Synthesis. Eds. C. Pimpirev and N. Chipev. Sofia: St. Kliment Ohridski University Press, 2015, pp. 17–28, ISBN 978-954-07-3939-7
- ^ G. Hattersley-Smith (June 1983). "Fuegian Indians in the Falkland Islands". Polar Record. Cambridge University Press. 21 (135): 605–606. doi:10.1017/S003224740002204X.
- ^ "Authentication of aboriginal remains in the South Shetland Islands". NASA. 15 October 2012. Archived from the original on 2 January 2014. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Griffiths, Tom (2007). Slicing the Silence: Voyaging to Antarctica. Harvard University Press. pp. 344–345. ISBN 978-0674026339.
- ^ "Dirección Nacional del Antártico | Ministerio de Relaciones Exteriores, Comercio Internacional y Culto". cancilleria.gob.ar. Archived from the original on 18 June 2015.
- ^ Martinez-Bahamonde, Rafael (2019). "El navio San Telmo: Los Primeros en pisar la Antartida. Una reparación histórica". University of the Basque Country – Escuela de Ingeniería de Bilbao (in Spanish).
- ^ R.K. Headland (ed.), Historical Antarctic sealing industry, Scott Polar Research Institute (Cambridge University), 2018, p.168, ISBN 978-0-901021-26-7
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Kraus, Stefan; Kurbatov, Andrei; Yates, Martin (2013). "Geochemical signatures of tephras from Quaternary Antarctic Peninsula volcanoes". Andean Geology. 40 (1): 1–40. doi:10.5027/andgeoV40n1-a01.
- ^ GHCN Climate data, GISS data publications, period 1978-2007
- ^ Beaufort, Simon, (pseudonym); Cruwys, Elizabeth; Riffenburgh, Beau (2016). The Killing Ship. Sutton, Surrey, UK: Severn House Publishers. pp. 1–224. ISBN 978-0-7278-8639-2 – via Google Books.
- ^ "The Killing Ship". Susanna Gregory website. Simon Beaufort. 2019. (Susanna Gregory is pseudonyms of author Elizabeth Cruwys, and Simon Beaufort is a pseudonym she and Beau Riffenburgh use jointly.)
Bibliography[]
- A. G. E. Jones, Captain William Smith and the Discovery of New South Shetland, Geographical Journal, vol. 141, no. 3 (November 1975), pp. 445–461.
- Alan Gurney, Below the Convergence: Voyages Toward Antarctica, 1699-1839, Penguin Books, New York, 1998.
- R. J. Campbell ed., The Discovery of the South Shetland Islands: The Voyage of the Brig Williams 1819-1820 and the Journal of Midshipman C. W. Poynter, the Hakluyt Society, London, 2000.
- Capt. Hernán Ferrer Fougá, El hito austral del confín de América. El cabo de Hornos. (Siglo XIX, 1800-1855.) (Segunda parte.). Revista de Marina, Valparaíso, 2004, n° 1.
- General Survey of Climatology V12, Landsberg ed., 1984, Elsevier.
- J. Stewart. Antarctica: An Encyclopedia. Jefferson, N.C. and London: McFarland, 2011. 1771 pp. ISBN 978-0-7864-3590-6
- B. Riffenburgh, ed. Encyclopedia of the Antarctic. New York, N.Y.: Routledge, 2006. 1272 pp. ISBN 978-1-1358-7866-5
- E. Serrano. Espacios protegidos y política territorial en las islas Shetland del Sur (Antártida). Boletín de la A.G.E. N.º 31 - 2001, págs. 5-21
External links[]
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for South Shetland Islands. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to South Shetland Islands. |
- Commonwealth Secretariat Website describing BAT
- United Kingdom, British Antarctic Territory Government
- Argentine Government Website with a map of the South Shetland Islands
- Argentine Government website about the history of Antarctica
| Look up south shetland islands in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Argentine Antarctic Sector: Historical Documents
- Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica
- Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria
- South Shetland Islands
- Falkland Islands in World War II
- Archipelagoes of the Southern Ocean
- Seal hunting

