Norfolk International Airport
Norfolk International Airport | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
 The Main Departures Building at ORF | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner | Norfolk Airport Authority | ||||||||||||||
| Operator | Norfolk Airport Authority | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | Hampton Roads, Northeast North Carolina | ||||||||||||||
| Location | Norfolk, Virginia, U.S. | ||||||||||||||
| Focus city for | Breeze Airways | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 26 ft / 8 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 36°53′41″N 076°12′04″W / 36.89472°N 76.20111°WCoordinates: 36°53′41″N 076°12′04″W / 36.89472°N 76.20111°W | ||||||||||||||
| Website | NorfolkAirport.com | ||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||
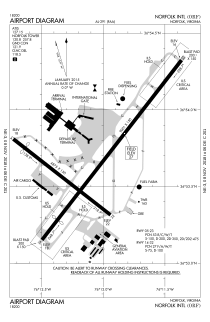 Diagram | |||||||||||||||
 ORF Location | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2020) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Source: Norfolk Airport Authority and Federal Aviation Administration[2] | |||||||||||||||
Norfolk International Airport (IATA: ORF[3], ICAO: KORF, FAA LID: ORF) is seven miles (11 km) northeast of downtown Norfolk, an independent city in Virginia, United States.[2] It is owned and operated by the Norfolk Airport Authority: a bureau under the municipal government. The airport serves the Hampton Roads metropolitan area of southeast Virginia (along with Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport in Newport News) as well as northeast North Carolina. Despite its name, the airport does not have any international destinations.
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2019–2023 categorized it as a small-hub primary commercial service facility.[4] Federal Aviation Administration records say the airport had 3,663,996 passengers in calendar year 2018, an increase of 9% from 3,380,902 in 2017.[5]
As of 2017, Norfolk International was ranked as the 70th-busiest airport in the United States and the fourth-busiest in Virginia in terms of passengers served annually, behind Dulles International Airport, Reagan National Airport and Richmond International.[6] Delta Air Lines has the largest share of passenger traffic, followed by Southwest Airlines and American Airlines.
Facilities[]
The airport covers 1,300 acres (526 ha) at an elevation of 27 feet (8 m). Its main runway, 5–23, is 9,001 by 150 feet (2,744 x 46 m) and crosswind runway 14–32 is 4,875 by 150 feet (1,486 x 46 m).[2]




The crosswind runway (14–32) was closed for renovations on December 19, 2009, and reopened in Spring 2011. The airport's long-term plan calls for this runway to be destroyed to make way for a parallel runway (5R-23L) east of runway 5–23, but the FAA grounded the plan in summer 2016 due to diminishing demand, limited space, and environmental impacts.
In 2017 the airport had 67,679 aircraft operations, average 185 per day: 39% airline, 27% air taxi, 27% general aviation, and 2% military. In November 2018, 95 aircraft were based at the airport: 52 single-engine, 20 multi-engine, 20 jet, and 3 helicopter.[2]
General aviation services, or fixed based operations, are provided by Landmark Aviation with full-service facilities for maintaining and housing private and corporate aircraft. The modern 54,000-square-foot (5,000 m2) terminal facility offers everything from aircraft rental to sightseeing flights and aircraft repair.
Daily scheduled aircraft include ERJ140/145 (United, American), CRJ200/700/900 (Delta, United, American), ERJ170/175 (American, United), A300 (FedEx), A319/320 (United, Allegiant, American, Frontier), B717 (Delta), B737 (Southwest, American, Delta), and B757 (UPS and Delta)
FAA control tower[]
Built in 1995, the FAA Norfolk Air Traffic Control Tower stands 134 feet (41 m) high. Operated and managed by the Federal Aviation Administration, the Norfolk Tower handles about 1,100 aircraft per day, 24 hours per day and 365 days per year. Radar coverage is provided by the ASR-9 terminal system with a six-level weather detection capability. Also available for use is an Enhanced Target Generator (ETG) lab with two radar scopes to accomplish training objectives, as well as the IDS4 system, a specialized microcomputer network system designed to distribute and display both static and real-time data regarding weather and other rapidly changing critical information to air traffic controllers.
Gates[]
Norfolk International Airport has two passenger concourses: Concourse A (gates A1-A11), and Concourse B (gates B16-B30). American Airlines and Southwest Airlines occupy Concourse A while Allegiant Air, Delta Airlines, Frontier Airlines, and United Airlines occupy Concourse B. International flights are handled at gate A1, however, there are currently no scheduled international flights. Specific gate locations are the following: American A2, A4, A6-A11, Delta B21-B25, Southwest A3 and A5, United B27-B30, with Allegiant and Frontier using common gates of B16, B17, B18, B20. Concourse B gates B22 and B26 are no longer in use.
Cargo[]
About 70 million pounds of air cargo are shipped in and out of Norfolk International Airport each year.[7] NIA houses one of the most modern and efficient air cargo facilities in the state. Its two modern air cargo terminals have 88,000 square feet (8,200 m2) of space. A ramp provides direct access from plane to warehouse.
Airlines and destinations[]

Passenger[]
| Airlines | Destinations | Refs |
|---|---|---|
| Allegiant Air | Fort Lauderdale, Jacksonville, Orlando/Sanford, St. Petersburg/Clearwater Seasonal: Boston,[8] Cincinnati, Cleveland, Columbus–Rickenbacker, Nashville, Pittsburgh,[9] Punta Gorda (FL) | [10] |
| American Airlines | Charlotte, Dallas/Fort Worth | [11] |
| American Eagle | Charlotte, Chicago–O'Hare, Miami, New York–JFK (suspended until November 2, 2021), New York–LaGuardia, Philadelphia, Washington–National | [11] |
| Breeze Airways | Charleston (SC), Columbus–Glenn, Hartford, New Orleans, Pittsburgh, Providence, Tampa[12] | [13] |
| Delta Air Lines | Atlanta Seasonal: Detroit | [14] |
| Delta Connection | Boston, Detroit, New York–JFK (suspended until March 1, 2022), New York–LaGuardia | [14] |
| Frontier Airlines | Denver, Miami (begins November 2, 2021),[15] Orlando | [16] |
| Southwest Airlines | Baltimore, Chicago–Midway, Nashville, Orlando, San Diego Seasonal: Atlanta,[17] Dallas–Love, Denver, St. Louis | [18] |
| United Airlines | Chicago–O'Hare, Denver Seasonal: Washington–Dulles | [19] |
| United Express | Chicago–O'Hare, Houston–Intercontinental, Newark, Washington–Dulles Seasonal: Denver | [19] |
| showDestinations map |
|---|
Cargo[]
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| FedEx Express | Indianapolis, Manteo, Memphis, Newark, Richmond |
| UPS Airlines | Columbia (SC), Louisville, Raleigh/Durham, Richmond |
| showCargo destinations map |
|---|
Statistics[]
[]
| Carrier | Passengers (arriving and departing) |
|---|---|
| Delta | 276,000(18.70%)
|
| Southwest | 255,000(17.29%)
|
| PSA | 223,000(13.23%)
|
| American | 195,000(15.12%)
|
| United | 107,000(7.25%)
|
| Other | 419,000(28.42%)
|
Top destinations[]
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Atlanta, GA | 134,000 | Delta, Southwest |
| 2 | Charlotte, NC | 117,000 | American |
| 3 | Baltimore, MD | 88,000 | Boutique Air, Southwest |
| 4 | Dallas/Fort Worth, TX | 65,000 | American |
| 5 | Chicago–O'Hare, IL | 65,000 | American, United |
| 6 | Washington D.C. Dulles | 36,000 | United |
| 7 | Detroit, MI | 34,000 | Delta |
| 8 | Philadelphia, PA | 30,000 | American |
| 9 | Miami, FL | 24,000 | American |
| 10 | Newark, NJ | 24,000 | United |
Annual traffic[]
| 2000s | 2010s | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Passengers | Year | Passengers |
| 2010 | 3,332,466 | ||
| 2011 | 3,193,388 | ||
| 2002 | 3,464,246 | 2012 | 3,299,712 |
| 2003 | 3,436,391 | 2013 | 3,112,355 |
| 2004 | 3,778,216 | 2014 | 2,965,306 |
| 2005 | 3,884,422 | 2015 | 3,034,407 |
| 2006 | 3,703,664 | 2016 | 3,209,185 |
| 2007 | 3,714,323 | 2017 | 3,380,902 |
| 2008 | 3,549,204 | 2018 | 3,663,996 |
| 2009 | 3,409,456 | 2019 | 3,981,139 |
| 2020 | 1,785,135 | ||
Passenger development[]
 |
Ground transportation[]
There are no bus or shuttle services to and from Norfolk International Airport. The nearest bus (HRT Route 15) connection is 1.5 miles (2.4 km) away at the intersection of Military Highway (Route 165) and Norview Avenue (Route 247).[23]
All ground transportation services are located in the arrivals terminal. There are several on-site rental car companies, an authorized shuttle service providing door-to-door service to the entire Hampton Roads area, and taxis available through several companies. Both Uber and Lyft service the airport through an agreement with the airport authority.
Parking[]

A nine-level parking garage adjacent to the new arrivals terminal opened in July 2002. It provides 2,800 covered spaces for short term, long term and rental parking. Overall, NIA parking facilities can accommodate 7,000 vehicles.[24] In February 2019, the airport announced it would begin construction of a brand new 1.09 million square foot parking garage. Construction started in July 2019. This new parking garage will consolidate all parking lots at ORF. It will also replace the employee shuttle that costs over $600,000 a year to operate.[25]
Accidents and incidents[]
- On January 19, 1967 a United Airlines Vickers 754D Viscount collided with a snow plow which had entered the runway in the path of the United plane upon landing. All 50 passengers and crew on board the aircraft survived, the aircraft suffered major damage to its airframe and was written off.[26]
- On September 1, 1974 a Martin 4-0-4 which was sitting empty on the ramp caught fire, damaging the airframe beyond repair. The cause of the fire was never determined.[27]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ "Press Room - Norfolk International Airport". www.norfolkairport.com.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d FAA Airport Form 5010 for ORF PDF. Federal Aviation Administration. effective November 8, 2018.
- ^ "IATA Airport Code Search (ORF: Norfolk / International)". International Air Transport Association. Retrieved December 31, 2012.
- ^ "NPIAS Report 2019-2023 Appendix A" (PDF). Federal Aviation Administration. October 3, 2018. Retrieved November 7, 2018.
- ^ "Enplanements for CY 2011" (PDF, 1.7 MB). faa.gov. Federal Aviation Administration. October 9, 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Passenger Boarding (Enplanement) and All-Cargo Data for U.S. Airports – Airports 2015". www.faa.gov. Retrieved March 5, 2017.
- ^ "Press Room". Norfolk International Airport. Archived from the original on January 17, 2012.
- ^ https://www.allegiantair.com/
- ^ https://pittsburgh.cbslocal.com/2021/01/19/allegiant-air-pittsburgh-norfolk/
- ^ "Allegiant Air". Archived from the original on February 24, 2011. Retrieved January 7, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Flight schedules and notifications". Retrieved January 7, 2017.
- ^ https://www.dailypress.com/business/vp-bz-norfolk-flights-20210521-5a5jofhcwvfzdjlvnhdr4bsqu4-story.html
- ^ "Breeze Home Page". Retrieved May 21, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "FLIGHT SCHEDULES". Retrieved January 7, 2017.
- ^ "Frontier Airlines Announces 15 New Nonstop Routes, Including Service To Aruba And Turks & Caicos From Miami". Aviator. August 3, 2021. Retrieved August 3, 2021.
- ^ "Frontier". Retrieved January 7, 2017.
- ^ "Start Summer Vacation Planning Today: Southwest Airlines Extends Flight Schedule Through August 10, 2020". Southwest Airlines Newsroom. Retrieved March 3, 2020.
- ^ "Check Flight Schedules". Retrieved January 7, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Timetable". Archived from the original on January 28, 2017. Retrieved January 7, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Norfolk, VA: Norfolk International (ORF)". Bureau of Transportation Statistics (BTS), Research and Innovative Technology Administration (RITA), U.S. Department of Transportation. May 24, 2021.
- ^ "Passenger Boarding (Enplanement) and All-Cargo Data for U.S. Airports - Previous Years – Airports Previous Years". www.faa.gov. Retrieved March 5, 2017.
- ^ "Statistics" (PDF). norfolkairport.com.
- ^ "Distance from airport to intersection of Route 165 & Route 247". Google Maps.
- ^ "Norfolk Airport, ACS and MasterCard Worldwide Introduce Contactless Payments to Airport Parking". MasterCard.com. June 8, 2009.
- ^ "New Parking Garage coming to Norfolk International". WKTR. March 7, 2019.
- ^ Accident description for N7431 at the Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved on November 19, 2018.
- ^ Accident description for N40427 at the Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved on November 19, 2018.
 This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency website http://www.afhra.af.mil/.
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency website http://www.afhra.af.mil/.
External links[]
- Official website

- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective August 12, 2021
- FAA Terminal Procedures for ORF, effective August 12, 2021
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KORF
- ASN accident history for ORF
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations: current, past three days
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KORF
- FAA current ORF delay information
- Live webcam image from WAVY-TV
- Airport pictures
- Airports in Virginia
- Transportation in Norfolk, Virginia
- Airfields of the United States Army Air Forces in Virginia
- 1938 establishments in Virginia
- Airports established in 1938