Orthodontics
 | |
| Occupation | |
|---|---|
| Names | Orthodontist |
Occupation type | Specialty |
Activity sectors | Dentistry |
| Description | |
Education required | Dental degree, specialty training |
Fields of employment | Private practices, hospitals |
Orthodontics[a][b] is a dentistry specialty that addresses the diagnosis, prevention, and correction of mal-positioned teeth and jaws, and misaligned bite patterns.[2] It may also address the modification of facial growth, known as dentofacial orthopedics.
Abnormal alignment of the teeth and jaws is very common. Nearly 50% of the developed world's population, according to the American Association of Orthodontics, has malocclusions severe enough to benefit from orthodontic treatment.[citation needed]: although this figure decreases to less than 10% according to the same AAO statement when referring to medically necessary orthodontics. Conclusive scientific evidence for the health benefits of orthodontic treatment, however, is lacking, although patients with completed orthodontic treatment have reported a higher quality of life than that of untreated patients undergoing orthodontic treatment.[3][4] Treatment may require several months to a few years, and entails using dental braces and other appliances to gradually adjust tooth position and jaw alignment. In cases where the malocclusion is severe, jaw surgery may be incorporated in the treatment plan. Treatment usually begins before a person reaches adulthood, insofar as pre-adult bones may be adjusted more easily before adulthood.
History[]
As a modern science, orthodontics dates to the mid 1800s.[5] The field's influential contributors include Norman William Kingsley[5] (1829–1913) and Edward Angle[6] (1855–1930). Angle created the first basic system for classifying malocclusions, a system which remains in use today.[5]
Until the mid-1970s, braces were made by wrapping metal around each tooth.[5] With advancements in adhesives it became possible to instead bond metal brackets to the teeth.[5]
Methods[]
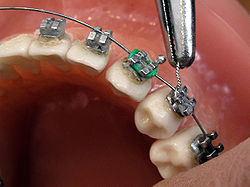
A typical treatment for incorrectly positioned teeth (malocclusion) takes from one to three years, with braces being adjusted every four to 10 weeks by specialists called orthodontists,[7] university-trained dental specialists versed in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of dental and facial irregularities. Orthodontists offer a wide range of treatment options to straighten crooked teeth, fix irregular bites and align the jaws correctly.[8] There are many ways to adjust malocclusion. In growing patients there are more options to treat skeletal discrepancies, either by promoting or restricting growth using functional appliances, orthodontic headgear or a reverse pull facemask. Most orthodontic work begins in the early permanent dentition stage before skeletal growth is completed. If skeletal growth has completed, jaw surgery is an option. Sometimes teeth are extracted to aid the orthodontic treatment (teeth are extracted in about half of all the cases, most commonly the premolars).[9]
Orthodontic therapy may include using fixed or removable appliances. Most orthodontic therapy is delivered using appliances that are fixed in place,[10] for example, with braces that are adhesively bonded to the teeth. Fixed appliances may provide greater mechanical control of the teeth; optimal treatment outcome is improved by using fixed appliances.
Fixed appliances may be used, for example, to rotate teeth that do not fit the arch shape of the other teeth in the mouth, to adjust multiple teeth to different places, to change tooth angle of teeth, or to change the position of a tooth's root. This treatment course is not preferred where a patient has poor oral hygiene, (as decalcification, tooth decay or other complications may result. If a patient is unmotivated (insofar as treatment takes several months and requires commitment to oral hygiene), or if malocclusions are mild.
Biology of tooth movement and how advances in gene therapy and molecular biology technology may shape the future of orthodontic treatment is an interesting area. [11]
Braces[]
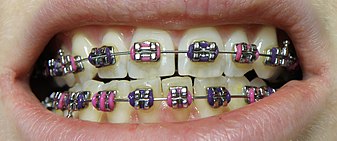
Braces are usually placed on the front side of the teeth, but may also be placed on the side facing the tongue (called lingual braces). Brackets made out of stainless steel or porcelain are bonded to the center of the teeth using an adhesive. Wires are placed in a slot in the brackets which allows for controlled movement in all three dimensions.
Apart from wires, forces can be applied using elastic bands,[12] and springs may be used to push teeth apart or to close a gap. Several teeth may be tied together with ligatures and different kinds of hooks can be placed to allow for connecting an elastic band.[13][12]
Clear aligners are an alternative to braces, but insufficient evidence exists to determine their effectiveness.[14]
Treatment Duration[]
The time required for braces varies from person to person, depending on the severity of the problem; the amount of room available; the distance the teeth must travel; the health of the teeth, gums, and supporting bone; and how closely the patient follows instructions. On average, however, once the braces are put on, they usually remain in place for one to three years. After braces are removed, most patients will need to wear a retainer all the time for the first six months, then only during sleep for many years.[15]
Headgear[]
Orthodontic headgear—sometimes referred to as an "extra-oral appliance"—is a treatment approach that requires the patient to have a device strapped onto his or her head to help correct malocclusion—typically used when the teeth do not align properly. Headgear is most often used along with braces or other orthodontic appliances. While braces correct the position of teeth, orthodontic headgear—which as the name suggests is worn on or is strapped onto the patient's head—is most often added to orthodontic treatment to help alter the alignment of the jaw, although there are some situations in which such an appliance can help move teeth, particularly molars.
Whatever the purpose, orthodontic headgear works by exerting tension on the braces via hooks, a facebow, coils, elastic bands, metal orthodontic bands, and other attachable appliances directly into the patient's mouth. It is most effective for children and teenagers because their jaws are still developing and can be easily manipulated. (If an adult is fitted with headgear, it is usually to help correct the position of teeth that have shifted after other teeth have been extracted.) Thus Headgear is typically used to treat a number of jaw alignment or bite problems such as overbite and underbite.[16]
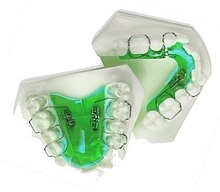
Palatal expansion[]
Palatal expansion can be achieved using either fixed or removable appliances.[17]
Jaw surgery[]
Jaw surgery may be required to fix severe malocclusions. The bone is broken during surgery and is stabilised with titanium (or bioresorbable) plates and screws to allow for healing to take place.[18] After surgery, regular orthodontic treatment is used to move the teeth into their final position.[19]
During treatment[]
To reduce pain during the orthodontic treatment, low-level laser therapy (LLLT), vibratory devices, chewing adjuncts, brainwave music or cognitive behavioral therapy can be used. However, the supporting evidence is of low quality and the results are inconclusive.[20]
Post treatment[]
After orthodontic treatment has completed, there is a tendency for teeth to return, or relapse, back to their pre-treatment positions. Over 50% of patients have some reversion to pre-treatment positions within 10 years following treatment.[21] To prevent relapse, the majority of patients will be offered a retainer once treatment has completed, and will benefit from wearing their retainers. Retainers can be either fixed or removable.
Removable retainers[]
Removable retainers are made from a clear plastic, and they are custom-fitted for the patient's mouth. It has a tight fit and holds all of the teeth in position. There are many types of brands for clear retainers including, Zendura Retainer, Essix Retainer and Vivera Retainer.[22] Hawley retainer is also a removable orthodontic appliance made from a combination of plastic and metal that is molded custom to fit the patient's mouth. Removable retainers will be worn for different periods of time depending on patient need to stabilise the dentition.[23]
Fixed retainers[]
Fixed retainers are a simple wire fixed to the tongue-facing part of the incisors using dental adhesive and can be specifically useful to prevent rotation in incisors. Other types of fixed retainers can include labial or lingual braces, with brackets fixed to the teeth.[23]

Palatal expander
An X-ray taken for skull analysis

Top and bottom retainers
Clear Aligners (Invisalign)[]
Invisalign is another form of Orthodontics that is commonly used today. Many patients do not like the appearance of traditional metal braces, so they opt for clear removable aligners. There was a lot of controversy about the effectiveness of Invisalign, but with years of advancements, Invisalign's results can now be closely compared to traditional braces but with a lot more freedom and faster results.[24]
Process[]
After booking an appointment with a dentist, the patient set up for a consultation. During the consultation the dentist or the dental assistant will scan the individual's teeth with a machine called iTero. The iTero machine digitally scans the structure of the teeth and gums. The dentist is able to see a 3D model of the patient's teeth on the screen. Unlike traditional braces, with Invisalign one is able to see the entire process from start to finish during consultation. Being that aligners are used, there is a lot of flexibility in fixing the smile. The dentist is able to make any changes that one wants to their treatment.[25]
Traditional braces, require metal brackets; with Invisalign, depending on the case, a patient will have "attachments" on the teeth. They are clear little buttons that help move teeth. Also, depending on the case, an individual might need interproximal reduction, also known as IPR. The dentist will take a little tool and "shave" off in-between the teeth, to help with overcrowded teeth. The reduction is very minimal, at most 0.3mm.[25]
Once the individual receives their aligners, they will have to wear them every day for 20–22 hours. One is supposed to remove them when eating and drinking. Unlike traditional metal braces, the person is able to eat anything when the aligners are removed; there are no restrictions.[25]
Depending on the severity of the case, one will have a new smile in a matter of months. Unlike traditional braces, which take about two years to remove, Invisalign can take less than a year (again, depending on the severity of the specific case).
After the treatment is complete, the individual will have to wear clear removable retainers.
Training[]
There are several specialty areas in dentistry, but the specialty of orthodontics was the first to be recognized within dentistry.[26] Specifically, the American Dental Association recognized orthodontics as a specialty in the 1950s.[26] Each country has their own system for training and registering orthodontic specialists.
Australia[]
In Australia, to obtain an accredited three-year full-time university degree in orthodontics, one will need to be a qualified dentist (complete an AHPRA registered general dental degree) with a minimum of two years of clinical experience. There are several universities in Australia that offer orthodontic programs: University of Adelaide, University of Melbourne, University of Sydney, University of Queensland, University of Western Australia, University of Otago.[27] Orthodontic Courses are accredited by the Australian Dental Council and reviewed by the (ASO). Prospective applicants should obtain information from the relevant institution before applying for admission.[28] After completing a degree in orthodontics, specialists are required to be registered with the Australian Health Practitioners Regulation Agency (AHPRA) in order to practice.[29][30]
Bangladesh[]
Dhaka Dental College in Bangladesh is one of the many schools recognized by the Bangladesh Medical and Dental Council (BM&DC) that offer post-graduation orthodontic courses.[31][32] Before applying to any post-graduation training courses, an applicant must have completed the Bachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS) examination from any dental college.[31] After application, the applicant must take an admissions test held by the specific college.[31] When successful, selected candidates undergo training for six months.[33]
Canada[]
In Canada, obtaining a dental degree, such as a Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) or Doctor of Medical Dentistry (DMD), would be required before being accepted by a school for orthodontic training.[34] Currently, there are 10 schools in the country offering the orthodontic specialty.[34] Candidates should contact the individual school directly to obtain the most recent pre-requisites before entry.[34] The Canadian Dental Association expects orthodontists to complete at least two years of post-doctoral, specialty training in orthodontics in an accredited program, after graduating from their dental degree.
Pakistan[]
In Pakistan to be enrolled as a student or resident in a postgraduation orthodontic course approved by Pakistan Medical and Dental Council, the dentist must graduate with a Bachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS) or equivalent degree. Pakistan Medical & Dental Council (PMDC) has a recognized program in Orthodontics[35] as Master in Dental Surgery (MDS) orthodontics and FCPS orthodontics as 4 years post-graduate degree programs, the latter of which is conducted by CPSP Pakistan.
United States[]
Similar to Canada, there are several colleges and universities in the United States that offer orthodontic programs. Every school has a different enrollment process, but every applicant is required to have graduated with a DDS or DMD from an accredited dental school.[36][37] Entrance into an accredited orthodontics program is extremely competitive, and begins by passing a national or state licensing exam.[38]
The program generally lasts for two to three years, and by the final year, graduates are to complete the written American Board of Orthodontics (ABO) exam.[38] This exam is also broken down into two components: a written exam and a clinical exam.[38] The written exam is a comprehensive exam that tests for the applicant's knowledge of basic sciences and clinical concepts.[38] The clinical exam, however, consists of a Board Case Oral Examination (BCOE), a Case Report Examination (CRE), and a Case Report Oral Examination (CROE).[38] Once certified, certification must then be renewed every ten years.[38] Orthodontic programs can award the Master of Science degree, Doctor of Science degree, or Doctor of Philosophy degree depending on the school and individual research requirements.[39]
United Kingdom[]
Throughout the United Kingdom, there are several Orthodontic Specialty Training Registrar posts available.[40] The program is full-time for three years, and upon completion, trainees graduate with a degree at the Masters or Doctorate level.[40] Training may take place within hospital departments that are linked to recognized dental schools.[40] Obtaining a Certificate of Completion of Specialty Training (CCST) allows an orthodontic specialist to be registered under the General Dental Council (GDC).[40] An orthodontic specialist can provide care within a primary care setting, but to work at a hospital as an orthodontic consultant, higher-level training is further required as a post-CCST trainee.[40] To work within a university setting, as an academic consultant, completing research toward obtaining a Ph.D. is also required.[40]
See also[]
- Orthodontic technology
- Orthodontic indices
- List of orthodontic functional appliances
- Molar distalization
- Mouth breathing
- Obligate nasal breathing
- Orthodontic Tooth Movement: Gene Therapy and Molecular Biology Aspect
Notes[]
References[]
- ^ "Definition of orthodontics | Dictionary.com". www.dictionary.com. Retrieved 2019-08-28.
- ^ "What is orthodontics?// Useful Resources: FAQ and Downloadable eBooks". Orthodontics Australia. Retrieved 2020-08-13.
- ^ "Evidence and Orthodontics: Does Your Child Really Need Braces?". Undark Magazine. 2020-07-20. Retrieved 2020-07-27.
- ^ "Controversial report finds no proof that dental braces work". British Dental Journal. 226 (2): 91. 2019-01-01. doi:10.1038/sj.bdj.2019.65. ISSN 1476-5373. S2CID 59222957.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "A Brief History of Orthodontic Braces – ArchWired". www.archwired.com. 17 July 2019.[self-published source]
- ^ Peck S (November 2009). "A biographical portrait of Edward Hartley Angle, the first specialist in orthodontics, part 1". The Angle Orthodontist. 79 (6): 1021–7. doi:10.2319/021009-93.1. PMID 19852589.
- ^ Fleming PS, Fedorowicz Z, Johal A, El-Angbawi A, Pandis N, et al. (The Cochrane Collaboration) (June 2015). "Surgical adjunctive procedures for accelerating orthodontic treatment". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. (6): CD010572. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd010572. PMC 6464946. PMID 26123284.
- ^ "What is an Orthodontist?". Orthodontics Australia. 5 December 2019.
- ^ Dardengo C, Fernandes LQ, Capelli Júnior J (February 2016). "Frequency of orthodontic extraction". Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics. 21 (1): 54–9. doi:10.1590/2177-6709.21.1.054-059.oar. PMC 4816586. PMID 27007762.
- ^ "Child Dental Health Survey 2013, England, Wales and Northern Ireland". digital.nhs.uk. Retrieved 2018-03-08.
- ^ Atsawasuwan, Phimon; Shirazi, Sajjad (2019-04-10), Işık Aslan, Belma; Deniz Uzuner, Fatma (eds.), "Advances in Orthodontic Tooth Movement: Gene Therapy and Molecular Biology Aspect", Current Approaches in Orthodontics, IntechOpen, doi:10.5772/intechopen.80287, ISBN 978-1-78985-181-6, retrieved 2021-05-16
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Elastics For Braces: Rubber Bands in Orthodontics". Orthodontics Australia. 2019-12-15. Retrieved 2020-12-13.
- ^ Mitchell L (2013). An Introduction to Orthodontics. Oxford Medical Publications. pp. 220–233.
- ^ Rossini G, Parrini S, Castroflorio T, Deregibus A, Debernardi CL (September 2015). "Efficacy of clear aligners in controlling orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review". The Angle Orthodontist. 85 (5): 881–9. doi:10.2319/061614-436.1. PMID 25412265. S2CID 10787375.
The quality level of the studies was not sufficient to draw any evidence-based conclusions.
- ^ "Dental Braces and Retainers".
- ^ Millett DT, Cunningham SJ, O'Brien KD, Benson PE, de Oliveira CM (February 2018). "Orthodontic treatment for deep bite and retroclined upper front teeth in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2: CD005972. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005972.pub4. PMC 6491166. PMID 29390172.
- ^ Agostino, Paola; Ugolini, Alessandro; Signori, Alessio; Silvestrini-Biavati, Armando; Harrison, Jayne E.; Riley, Philip (2014). "Orthodontic treatment for posterior crossbites". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (8): CD000979. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000979.pub2. PMID 25104166.
- ^ Agnihotry A, Fedorowicz Z, Nasser M, Gill KS, et al. (The Cochrane Collaboration) (October 2017). Zbigniew F (ed.). "Resorbable versus titanium plates for orthognathic surgery". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. 10: CD006204. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd006204. PMC 6485457. PMID 28977689.
- ^ "British Orthodontic Society > Public & Patients > Your Jaw Surgery". www.bos.org.uk. Retrieved 2019-08-28.
- ^ Fleming PS, Strydom H, Katsaros C, MacDonald L, Curatolo M, Fudalej P, Pandis N (December 2016). Cochrane Oral Health Group (ed.). "Non-pharmacological interventions for alleviating pain during orthodontic treatment". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12: CD010263. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010263.pub2. PMC 6463902. PMID 28009052.
- ^ Yu Y, Sun J, Lai W, Wu T, Koshy S, Shi Z (September 2013). "Interventions for managing relapse of the lower front teeth after orthodontic treatment". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (9): CD008734. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008734.pub2. PMID 24014170.
- ^ "Clear Retainers | Maintain Your Hard to Get Smile with Clear Retainers". Retrieved 2020-01-13.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Littlewood SJ, Millett DT, Doubleday B, Bearn DR, Worthington HV, et al. (The Cochrane Collaboration) (January 2016). "Retention procedures for stabilising tooth position after treatment with orthodontic braces". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd (1): CD002283. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd002283. PMC 7138206. PMID 26824885.
- ^ Putrino, Alessandra; Barbato, Ersilia; Galluccio, Gabriella (January 2021). "Clear Aligners: Between Evolution and Efficiency—A Scoping Review". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 18 (6): 2870. doi:10.3390/ijerph18062870. PMC 7998651. PMID 33799682.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Azaripour, A.; Weusmann, J.; Mahmoodi, B.; Peppas, D.; Gerhold-Ay, A.; Van Noorden, C. J. F.; Willershausen, B. (2015-06-24). "Braces versus Invisalign®: gingival parameters and patients' satisfaction during treatment: a cross-sectional study". BMC Oral Health. 15 (1): 69. doi:10.1186/s12903-015-0060-4. ISSN 1472-6831. PMC 4478712. PMID 26104387.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Christensen GJ (March 2002). "Orthodontics and the general practitioner". Journal of the American Dental Association. 133 (3): 369–71. doi:10.14219/jada.archive.2002.0178. PMID 11934193.
- ^ "How to become an orthodontist". Orthodontics Australia. 26 September 2017.
- ^ "Studying orthodontics". Australian Society of Orthodontists. 26 September 2017.
- ^ "Specialties and Specialty Fields". Australian Health Practitioners Regulation Agency.
- ^ "Medical Specialties and Specialty Fields". Medical Board of Australia.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Dhaka Dental College". Dhaka Dental College. Archived from the original on October 28, 2017. Retrieved October 28, 2017.
- ^ "List of recognized medical and dental colleges". Bangladesh Medical & Dental Council (BM&DC). Retrieved October 28, 2017.
- ^ "Orthodontic Facts - Canadian Association of Orthodontists". Canadian Association of Orthodontists. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "FAQ: I Want To Be An Orthodontist - Canadian Association of Orthodontists". Canadian Association of Orthodontists. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- ^ "Orthodontics (Dental Braces)". Royal Dental Care. Retrieved 2020-08-16.
- ^ "RCDC - Eligibility". The Royal College of Dentists of Canada. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- ^ "Accredited Orthodontic Programs - AAO Members". www.aaoinfo.org.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f "About Board Certification". American Board of Orthodontists. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- ^ "Accredited Orthodontic Programs | AAO Members". American Association of Orthodontists. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f https://www.bos.org.uk/Portals/0/Public/docs/Careers/guidelines-on-orthodontic-specialty-training.pdf "Orthodontic Specialty Training in the UK" (PDF). British Orthodontic Society. British Orthodontic Society. Retrieved 28 October 2017.
| Look up orthodontics in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Orthodontics. |
- Orthodontics
- Dentistry branches



