Outer Manchuria
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2016) |
This article may be expanded with text translated from the corresponding article in Russian. (August 2020) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
This article may be expanded with text translated from the corresponding article in Chinese. (December 2011) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|

Outer Manchuria (Russian: Приаму́рье, romanized: Priamurye;[note 1] Chinese: 外滿洲; pinyin: Wài Mǎnzhōu), alternatively called Outer Northeast China (Chinese: 外東北; pinyin: Wài Dōngběi; lit. 'Outer Northeast') or Russian Manchuria, refers to a territory in Northeast Asia that is currently part of Russia and had formerly belonged to a series of Chinese dynasties, including the Tang, Liao, Jin, Eastern Xia, Yuan, Northern Yuan, Ming, Later Jin, and Qing dynasties.[1] It is considered part of the larger region of Manchuria. The Russian Empire annexed this territory from Qing China by way of the Treaty of Aigun in 1858 and the Treaty of Peking in 1860. The northern part of the area was disputed by Qing China and the Russian Empire between 1643 and 1689.
Outer Manchuria comprises the modern-day Russian areas of Primorsky Krai, southern Khabarovsk Krai, the Jewish Autonomous Oblast, the Amur Oblast and the island of Sakhalin.
The Treaty of Nerchinsk signed in 1689 after a series of conflicts, defined the Sino–Russian border as the Stanovoy Mountains and the Argun River, making Outer Manchuria a part of Qing China. After losing the Opium Wars, Qing China was forced to sign a series of treaties that gave away territories and ports to the imperialist Western powers as well as to Russia and Japan; these were known as the Unequal Treaties. Starting with the Treaty of Aigun in 1858 and the Treaty of Peking in 1860, the Sino–Russian border was realigned in Russia's favor along the Amur and Ussuri rivers. As a result, China lost Outer Manchuria (an area of more than 1 million km2) and access to the Sea of Japan.
History of the term[]
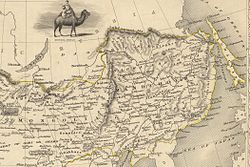
The terms "Outer Manchuria" and "Inner Manchuria", modeled on Inner and Outer Mongolia, were coined to support Chinese claims to Russian territory and were never used in scientific literature.[citation needed] "Manchuria" (subdivided into Northern and Southern Manchuria) is an accepted term for the area now belonging to China. Critics of this analogy, however, suggest that while Mongols under the Qing dynasty were a recognized ethnic group, "Manchus" were a group constructed by the chieftain Nurhaci in the early 17th century, mainly for the purposes of conquering the Ming dynasty. According to this view, there were no Manchus north of the Nen River and the Songhua River, so that region cannot properly be called "Outer Manchuria". However, the native population of Outer Manchuria were southern Tungusics, closely related to the Manchu and no more different from them than the differences found among various Mongol groups. The only exception was the Nivkh people inhabiting the lowest reaches of the Amur River and the island of Sakhalin.
Place names[]
Today, there are reminders of the ancient Manchu domination in English-language toponyms: for example, the Sikhote-Alin, the great coastal range; the Khanka Lake; the Amur and Ussuri rivers; the Greater Khingan, Lesser Khingan and other small mountain ranges; and the Shantar Islands. Evenks, who speak a closely related Tungusic language, make up a significant part of the indigenous population.
History[]
| History of Manchuria |
|---|
 |
The original inhabitants of the region were apparently the Mohe and other Tungusic tribes. Other entities occupying parts of Outer Manchuria include the ancient mixed Mohe and proto-Korean kingdoms of Goguryeo and Balhae, whose territories extended from the northern Korean peninsula to the southern and central parts of Inner and Outer Manchuria.

According to the Treaty of Nerchinsk in 1689, the Manchu-Russian border was the Argun River and the Stanovoy Mountains until the Pacific coast. The eastern end of the boundary was generally held to be the Uda River, leaving Outer Manchuria to China. However, the Qing dynasty ceded Outer Manchuria to Russia in the Treaty of Aigun in 1858 and the Treaty of Peking in 1860. A small region to the north of the Amur, known as the Sixty-Four Villages East of the (Heilongjiang) River, was kept by the Qing dynasty under the Treaty of Aigun, but was invaded and annexed by Russia in 1900. Outer Manchuria formed part of the far eastern provinces of the Soviet Union and was used as the launch-pad for the Soviet assault on Japanese-occupied Inner Manchuria in 1945. During the Chinese Civil War, Chinese communist forces began the war with large amounts of Inner Manchuria already in their hands; in 1949, the victorious communists established the present-day People's Republic of China.
In 2004, Russia agreed to transfer Yinlong Island and half of Heixiazi Island to China, ending a longstanding border dispute between Russia and China. Both islands are found at the confluence of the Amur and Ussuri rivers, and were until then administered by Russia and claimed by China. The transfer was meant to foster reconciliation and cooperation between the two countries, but it has also sparked different degrees of discontent on both sides. Russians, especially Cossack farmers in Khabarovsk who had plowlands on the islands, were unhappy about the loss of territory. The transfer has been ratified by both the Chinese National People's Congress and the Russian State Duma. The official transfer ceremony was held on-site on 14 October 2008.
Disputes[]

Outstanding boundary issues between China and Russia were officially settled in the 1991 Sino-Soviet Border Agreement. Article 6 of the 2001 Sino-Russian Treaty of Friendship provides that the contracting parties—the People's Republic of China and the Russian Federation—have no territorial claims.
As the Republic of China, now based in Taiwan, has never recognized the People's Republic of China nor its border treaties with other countries, some maps published in Taiwan still show the entire Heixiazi Island and the Sixty-Four Villages East of the River as Chinese territories. However, these maps show Outer Manchuria, sometimes called "lost territories in the Northeast" (東北失地), to be Russian territory.
Some Manchu and Han Chinese regard Outer Manchuria as territory that was unfairly taken away, as in Mao's comments leading up to the Sino-Soviet border conflict.
See also[]
- 1991 Sino-Russian Border Agreement
- Hulun
- Inner Manchuria
- Outer Mongolia
- Tannu Uriankhai
- Outer Northwest China
- Sixty-Four Villages East of the River
- Blagoveshchensk massacre and Sixty-Four Villages East of the River massacre
- Amur Annexation
Notes[]
- ^ Now Priamurye usually refers to a narrower region of Amur Oblast and parts of Khabarovsk Krai.
References[]
- ^ Karaoğlu, Semiha. "The Legacy of a War: How the Legacy of the Russo-Japanese War Affected the US-Japan Relations". researchgate.
- ^ E.g. Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society, Volumes 11–12, 1867, p. 162
- Fletcher, Joseph. "Sino-Russian Relations, 1800-62: The loss of north-east Manchuria". In Fairbank, John K (ed.). The Cambridge History of China. Vol. 10. Cambridge University Press. pp. 332–351.
External links[]
- Books.google.com: Russia in Manchuria — 1903 illustrated article.
- Manchuria
- East Asia
- Inner Asia
- Geography of Northeast Asia
- Geography of the Russian Far East
- Historical regions of China
- Historical regions in Russia
- History of Manchuria
- China–Russia border
- China–Russian Empire relations
- China–Russia relations