Outline of evolution
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to evolution:
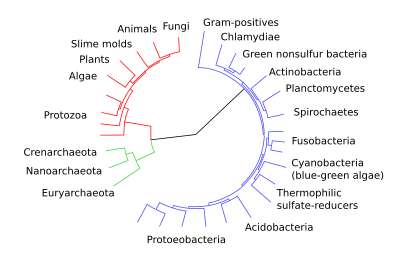
A diagram showing the relationships between various groups of organisms
| Part of a series on |
| Evolutionary biology |
|---|
 |
|
Evolution – change in heritable traits of biological organisms over generations due to natural selection, mutation, gene flow, and genetic drift. Also known as descent with modification. Over time these evolutionary processes lead to formation of new species (speciation), changes within lineages (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction). "Evolution" is also another name for evolutionary biology, the subfield of biology concerned with studying evolutionary processes that produced the diversity of life on Earth.
Fundamentals about evolution[]
−4500 — – — – −4000 — – — – −3500 — – — – −3000 — – — – −2500 — – — – −2000 — – — – −1500 — – — – −1000 — – — – −500 — – — – 0 — | Water Eukaryotes P l a n t s Arthropods Molluscs Flowers Dinosaurs Mammals Birds Primates H a d e a n A r c h e a n P r o t e r o z o i c P h a n e r o z o i c |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(million years ago) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Introduction[]
- Introduction to evolution – non-technical overview of the subject of biological evolution
- Evolution – Change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations
- Evolution as fact and theory – Discussion of the meaning and usage of the terms evolution, fact and theory
Basic principles[]
- Macroevolution – Evolution on a scale at or above the level of species
- Speciation – Evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species
- Natural speciation
- Allopatric speciation – Speciation that occurs between geographically isolated populations
- Peripatric speciation – Speciation in which a new species is formed from an isolated smaller peripheral population
- Parapatric speciation – Speciation within a population where subpopulations are reproductively isolated
- Sympatric speciation – Process through which new species evolve from a single ancestral species while inhabiting the same geographic region
- Artificial speciation
- Animal husbandry – Management, selective breeding, and care of farm animals by humans
- Plant breeding – Art and science of changing the traits of plants in order to produce desired characteristics
- Genetic engineering – Direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology
- Hybrid speciation – Form of speciation involving hybridization between two different species
- Natural speciation
- Despeciation – Loss of a unique species of animal due to its combining with another previously distinct species
- Anagenesis – Gradual evolutionary change in a species without splitting
- Extinction – Termination of a taxon by the death of the last member
- Speciation – Evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species
- Microevolution – Change in allele frequencies that occurs over time within a population
- Artificial selection – Breeding used to develop desired characteristics
- Natural selection – Mechanism of evolution by differential survival and reproduction of individuals
- Sexual selection – Mode of natural selection involving the choosing of and competition for mates
- Mutation – Alteration in the nucleotide sequence of a genome
- Gene flow – Transfer of genetic variation from one population to another
- Genetic drift – Change in the frequency of an existing gene variant in a population
Subfields[]
- Biology – Science that studies life
- Evolutionary biology – Study of the processes that produced the diversity of life
- Evolutionary developmental biology – Field of research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer the ancestral relationships
- Genetics – Science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms
- Evolutionary biology – Study of the processes that produced the diversity of life
- Biogeography – Study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time
- Ecological genetics – Study of genetics in natural populations
- Evolutionary biology – Study of the processes that produced the diversity of life
- Evolutionary developmental biology – Field of research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer the ancestral relationships
- Evolutionary ecology – Interaction of biology and evolution
- Evolutionary physiology – Study of changes over time in a population's physiological characteristics in response to natural selection
- Evolutionary taxonomy – Form of biological classification
- Experimental evolution – Use of laboratory and field experiments to explore evolutionary dynamics
- Molecular evolution – Process of change in the sequence composition of cellular molecules across generations
- Phylogenetics – Study of evolutionary relationships between organisms
- Population genetics – Study of genetic differences within and between populations including the study of adaptation, speciation, and population structure
- Paleontology – The scientific study of life prior to roughly 11,700 years ago
- Paleovirology – The study of ancient viruses
- Timeline of paleontology – Timeline of notable events in the sudy of ancient life
- Systematics – Study of the diversification and relationships among living things through time
History[]
- Charles Darwin – English naturalist and biologist (1809–1882)
- On the Origin of Species – 1859 book on evolutionary biology by Charles Darwin
- Caricatures of Charles Darwin and his evolutionary theory in 19th-century England – {{original research
- Darwinism – Theory of biological evolution
- History of evolutionary thought – History of evolutionary thought in biology
- By period or event
- Evolutionary ideas of the Renaissance and Enlightenment – Changes in thinking about evolution from religious and spiritual to more mechanistic and biological over the 17th and 18th centuries
- Transmutation of species – 19th-century evolutionary ideas for the altering of one species into another that preceded Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection
- 1860 Oxford evolution debate – Famous discussion about evolution featuring an exchange between Wilberforce and Huxley
- Neo-Darwinism – Used to describe the combination of natural selection and genetics
- The eclipse of Darwinism – Period when evolution was widely accepted, but natural selection was not
- Evolutionary progress – Hypothesis that organisms have an innate tendency to evolve towards some goal
- Scopes Trial – 1925 legal case in Tennessee, US, testing the legality of teaching evolution in schools
- Modern synthesis – Combination of Darwins theory of evolution with natural selection and Mendel's findings on heredity
- Extended evolutionary synthesis
- Current research – Study of the processes that produced the diversity of life
- By field
- Evolutionary developmental biology – Field of research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer the ancestral relationships
- History of evolutionary psychology
- History of molecular evolution – History of the field of study of molecular evolution
- History of paleontology – History of the effort to understand the history of life on Earth by studying the fossil record
- By period or event
- Social effect of evolutionary theory
Evolutionary theory and modelling[]
See also Basic principles (above)
Population genetics[]
- Population genetics – Study of genetic differences within and between populations including the study of adaptation, speciation, and population structure
- Process
- Mutation – Alteration in the nucleotide sequence of a genome
- Selection
- Natural selection – Mechanism of evolution by differential survival and reproduction of individuals
- Sexual selection – Mode of natural selection involving the choosing of and competition for mates
- Artificial selection – Breeding used to develop desired characteristics
- Ecological selection – Natural selection without sexual selection
- Natural selection – Mechanism of evolution by differential survival and reproduction of individuals
- Gene flow – Transfer of genetic variation from one population to another
- Genetic drift – Change in the frequency of an existing gene variant in a population
- Small population size – Statistical effects of small numbers on a population
- Population bottleneck – Effects of a sharp reduction in numbers on the diversity and robustness of a population
- Founder effect – Loss of genetic variation resulting from a few individuals establishing a new population in the world
- Coalescent theory – Model for tracing the history of genetic variation
- Variation
- Genetic variation – The concept and mechanisms of variation in alleles of genes
- Genetic diversity – Total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species
- Gene frequency – The relative frequency of a variant of a gene at a particular locus in a population
- Polymorphism (biology) – Occurrence of two or more clearly different morphs or forms in the population of a species
- Genetic variation – The concept and mechanisms of variation in alleles of genes
- Key concepts
- Hardy-Weinberg law – Principle within genetics
- Genetic linkage – tendency of DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together
- Identity by descent – Identical nucleotide sequence due to inheritance without recombination from a common ancestor
- Linkage disequilibrium – Non-random association of alleles at two or more genetic loci (either on the same or different chromosome)
- Fisher's fundamental theorem – Principle relating genetic variance to fitness
- Neutral theory
- Shifting balance theory – Theory suggesting that adaptive evolution may proceed most quickly when subpopulations have restricted gene flow
- Price equation – Description of how a trait or gene changes in frequency over time
- Coefficient of relationship – Measure of the degree of biological relationship between two individuals
- Fitness – Expected reproductive success
- Heritability – Estimation of effect of genetic variation on phenotypic variation of a trait
- Effects of selection
- Genetic hitchhiking – Incidental selection of non-harmful genes which are close to a beneficial gene on the same DNA chain
- Negative selection (natural selection) – Selective removal of alleles that are deleterious
- Related topics
- Microevolution – Change in allele frequencies that occurs over time within a population
- Evolutionary game theory – The application of game theory to evolving populations in biology
- Fitness landscape – Model used to visualise relationship between genotypes and reproductive success
- Genetic genealogy – Use of DNA testing in combination with traditional genealogical methods to infer relationships between individuals and find ancestors
- Quantitative genetics – Study of the inheritance of continuously variable traits
Evolutionary phenomena[]
- Adaptation – Trait with a current functional role in the life history of an organism maintained and evolved by natural selection
- Adaptive radiation – A process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species
- Coevolution – Two or more species influencing each other's evolution
- Concerted evolution
- Convergent evolution – Independent evolution of similar features in species of different lineages which creates analogous structures
- List of examples of convergent evolution – Wikipedia list article
- Divergent evolution – Accumulation of differences between closely related species populations, leading to speciation
- Divergent evolution in animals
- Evolution of ageing – Study of the evolutionary development of ageing processes
- Evolution of biological complexity – Tendency for maximum complexity to increase over time, though without any overall direction
- Evolution of multicellularity – The development of organisms that consists of more than one cell from unicellular ancestors
- Evolution of photosynthesis – Origin and subsequent evolution of the process by which light energy is used to synthesize sugars
- Evolution of sexual reproduction – How sexually reproducing multicellular organisms could have evolved from a common ancestor species
- Evolutionary arms race – Competition of sets of genes, traits, or species, that develop adaptations and counter-adaptations against each other
- Evolutionary capacitance – Hypothetical mechanism to activate and deactivate phenotypic effect of accumulated genetic variation
- Evolutionary fauna
- Evolutionary pressure – Any cause that reduces reproductive success in a proportion of a population
- Evolutionary radiation – Increase in taxonomic diversity or morphological disparity, due to adaptive change or the opening of ecospace
- Evolutionary trap – Cases in which an evolved, and presumably adaptive, trait has suddenly become maladaptive
- Evolvability – capacity of a system for adaptive evolution
- Exaptation – A shift in the function of a trait during evolution
- Extinction – Termination of a taxon by the death of the last member
- Fitness (biology) – Expected reproductive success
- Inclusive fitness – Measure of evolutionary success based on the number of offspring the individual supports
- Kin selection – The evolutionary strategy that favours the reproductive success of an organism's relatives, even at a cost to the organism's own survival and reproduction
- Reproductive success – The passing of genes on to the next generation in a way that they too can pass on those genes
- Inclusive fitness – Measure of evolutionary success based on the number of offspring the individual supports
- Genetic recombination – Production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent
- Horizontal gene transfer in evolution – The evolutionary consequences of transfer of genetic material between organisms of different taxa
- Human evolution (origins of society and culture)
- Inversion (evolutionary biology) – Hypothesis that during the course of chordate evolution, the structures along the dorsoventral axis have taken on an orientation opposite that of the ancestral form
- Mosaic evolution – Evolution of characters at various rates both within and between species
- Parallel evolution – Similar development of a trait in distinct species that are not closely related, in response to similar evolutionary pressure
- Quantum evolution – Evolution where transitional forms are particularly unstable and do not last long
- Recurrent evolution – The repeated evolution of a particular character
- Robustness (evolution)
- Speciation – Evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species
Modelling[]
- Emergent evolution – Evolutionary biology
- Epic of evolution – Evolutionay narrative that blends views
- Evolution window – Narrow band of mutation step size that is conducive to significant evolutionary progress
- Evolutionary dynamics – Study of the mathematical principles according to which biological organisms and cultural ideas evolve
- Evolutionary game theory – The application of game theory to evolving populations in biology
- Evolutionary graph theory – Approach to studying how topology affects evolution of a population
- Evolutionary invasion analysis – Mathematical modeling techniques that use differential equations to study the long-term evolution of traits in asexually reproducing populations
- Largest-scale trends in evolution – Low end minimum limit for complexity of living organisms may result in a general gradual trend for increased complexity over time
Taxonomy, systematics, and phylogeny[]
Fundamentals[]
- Taxonomy – Science of naming, defining and classifying organisms
- Alpha taxonomy – The discipline of finding, describing, and naming taxa, particularly species
- Biological classification – The science of identifying, describing, defining and naming groups of biological organisms
- Binomial nomenclature – System of identifying species of organisms using a two-part name
- Evolutionary taxonomy – Form of biological classification
- Catalogue of life – Online database and index of taxa
- Homonym (biology) – Scientific name that is identical in spelling to a name with a different type
- Integrated Taxonomic Information System – Authoritative taxonomic information on plants, animals, fungi, and microbes
- International Code of Zoological Nomenclature – Code of scientific nomenclature for animals
- International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants – Code of scientific nomenclature
- Linnaean taxonomy – Rank based classification system for organisms
- Phenetics – Attempt to classify organisms based on overall similarity
- Species 2000 – Federated taxonomic database system for species checklists
- Taxon – Group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms which have distinguishing characteristics in common
- Taxonomic rank – Level in a taxonomic hierarchy
- Type (biology) – Specimen(s) to which a scientific name is formally attached
- Species description – Formal description and naming of a new recognised species
- Systematics – Study of the diversification and relationships among living things through time
- Cladogram – Diagram used to show relations among groups of organisms with common origins
- Phylogenetic tree – Branching diagram of evolutionary relationships between organisms
- Phylogenetics – Study of evolutionary relationships between organisms
- Cladistics – Method of biological systematics in evolutionary biology
- Computational phylogenetics – Application of computational algorithms, methods and programs to phylogenetic analyses
- Common descent – Characteristic of a group of organisms with a common ancestor
- Evidence of common descent – Evidence that a given group of organisms have a common ancestor, and therefore that evolution has taken place.
- Evolutionary grade – Non-monophyletic grouping of organisms united by morphological or physiological characteristics
- Lineage (evolution) – Sequence of populations, organisms, cells, or genes that form a line of descent
- Molecular phylogenetics – Branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences
- Most recent common ancestor – Most recent individual from which all organisms in a group are directly descended
Basic concepts of phylogenetics[]
- Phylogenetic tree – Branching diagram of evolutionary relationships between organisms
- Phylogenetic network – Graph used to visualize evolutionary relationships, including reticulation events
- Long branch attraction – Form of systematic error whereby distantly related lineages are incorrectly inferred to be closely related
- Clade – Group of a common ancestor and all descendants
- Grade – Non-monophyletic grouping of organisms united by morphological or physiological characteristics
- Ghost lineage – Phylogenetic lineage that is inferred to exist but has no fossil record
Inference methods[]
- Maximum parsimony (phylogenetics) – Optimality criterion in which the shortest possible tree that explains the data is considered best
- Minimum evolution
- Probabilistic methods
- Maximum likelihood estimation – Method of estimating the parameters of a statistical model, given observations
- Bayesian inference – Statistical method for molecular phylogenetics
- Distance matrices in phylogeny – Matrices used in construction of phylogenetic trees
- Neighbor joining – Bottom-up clustering method for creating phylogenetic trees
- Unweighted Pair Group Method with Arithmetic Mean (UPGMA) – Agglomerative hierarchical clustering method
- Least squares inference in phylogeny – Generation of phylogenetic trees based on an observed matrix of pairwise genetic distances
- Three-taxon analysis – Cladistic based method of phylogenetic reconstruction
Current topics[]
- PhyloCode, also known as International Code of Phylogenetic Nomenclature
- DNA barcoding – Method of species identification using a short section of DNA
- Molecular phylogenetics – Branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences
- Phylogenetic comparative methods – Use of information on the historical relationships of lineages to test evolutionary hypotheses
- Phylogenetic network – Graph used to visualize evolutionary relationships, including reticulation events
- Phylogenetic niche conservatism – tendency of lineage to retain ancestral traits
- List of phylogenetics software – Compilation of software used to produce phylogenetic trees
- Phylogenomics – Intersection of the fields of evolution and genomics
- Phylogeography – Field of study
Group Traits[]
- Symplesiomorphy – An ancestral character or trait state shared by two or more taxa
- Apomorphy – Shared distinguishing characteristic of a clade
- Synapomorphy – Shared distinguishing characteristic of a clade
- Autapomorphy – Distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon
Group Types[]
- Monophyly – Property of a group of including all taxa descendant from a common ancestral species
- Paraphyly – Property of a group which includes only descendants of a common ancestor, but excludes at least one monophyletic subgroup
- Polyphyly – Set of organisms that do not share an immediate common ancestor
Evolution of biodiversity[]
- Biodiversity – Variety and variability of life forms
Origin and evolutionary history of life[]
- Abiogenesis – Natural process by which life arises from non-living matter
- History of life – Processes by which organisms evolved on Earth
- Timeline of the evolutionary history of life – Current scientific theory outlining the major events during the development of life
Evolution of organisms[]
Evolution of tetrapods[]
- Evolution of tetrapods – The evolution of four legged vertebrates and their derivatives
- Evolution of dinosaurs
- Evolution of birds – Derivation of birds from a dinosaur precursor, and the adaptive radiation of bird species
- Evolution of mammals – Derivation of mammals from a synapsid precursor, and the adaptive radiation of mammal species
- Evolution of cetaceans – Derivation of cetaceans from an artiodactyl precursor, and the adaptive radiation of cetacean species
- Evolution of horses – Derivation of horses from an ungulate precursor
- Evolution of primates – Origin and diversification of primates through geologic time
- Evolution of humans – Evolutionary process leading up to the appearance of anatomically modern humans
- Evolution of human intelligence – Development of intelligence in humans and association with evolution of the brain and the origin of language
- Human evolutionary genetics – study of differences between human genomes
- Sexual selection in human evolution – The evolutionary effects of sexual selection on humans
- Timeline of human evolution – Chronological outline of major events in the development of the human species
- Evolution of lemurs – History of primate evolution on Madagascar
- Evolution of humans – Evolutionary process leading up to the appearance of anatomically modern humans
- Evolution of sirenians – Development from a Tethytherian ancestor and radiation of species
- Evolution of reptiles – The origin and diversification of reptiles through geologic time
- Evolution of dinosaurs
Evolution of other animals[]
- Evolution of brachiopods – The origin and diversification of brachiopods through geologic time
- Evolution of cephalopods – Origin and diversification of cephalopods through geologic time
- Evolution of fish – Origin and diversification of fish through geologic time
- Evolution of insects – Development of insects from an ancestral crustacean and their subsequent radiation
- Evolution of butterflies – Origin and diversification of butterflies through geologic time
- Peppered moth evolution – Significance of the peppered moth in evolutionary biology
- Evolution of molluscs – The origin and diversification of molluscs through geologic time
- Evolution of spiders – Origin from a chelicerate ancestor and diversification of spiders through geologic time
Evolution of plants[]
- Evolution of plants – The origin and diversification of plants through geologic time
- Evolutionary anachronism – Attributes of living species that arose due to coevolution with other now-extinct species
- Plant evolution – subset of evolutionary phenomena that concern plants
- Plant evolutionary developmental biology – Study of developmental programs and patterns in plants from an evolutionary perspective
- Timeline of plant evolution – Chronological outline of major events in the development of plants
Evolution of other taxa[]
- Evolution of fungi – The origin and diversification of fungi through geologic time
- Evolution of viruses – Subfield of evolutionary biology and virology concerned with the evolution of viruses
- E. coli long-term evolution experiment – Scientific study
Evolution of cells, organs, and systems[]
- Evolution of cells – The evolutionary origin and subsequent development of cells
- Evolution of flagella – Origin of three known varieties of flagella
- Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles – An evolutionary event in which bones from the jaws of reptiles became part of the hearing apparatus in mammals
- Evolution of nervous systems – Origin and subsequent variation and development of neurons and neural tissues and organs
- Evolution of snake venom – The origin and diversification of snake venom through geologic time
- Evolution of the brain – Overview of the evolution of the brain
- Evolution of the eye – Origins and diversification of the organs of sight through geologic time
- Evolution of color vision – Origin and variation of colour vision across various lineages through geologic time
- Evolution of color vision in primates – Loss and regain of colour vision during the evolution of primates
- Immune system – Biological system protecting an organism against disease
- Evolution of metabolism – Set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of organisms
Evolution of molecules and genes[]
- Directed evolution – Method used in protein engineering that mimics the process of natural selection to steer proteins or nucleic acids toward a user-defined goal
- Error threshold (evolution) – Limit on the number of base pairs a self-replicating molecule may have before mutation will destroy the information in subsequent generations of the molecule
- Gene-centered view of evolution – Reasoning that since heritable information is passed from generation to generation almost exclusively by DNA, natural selection and evolution are best considered from the perspective of genes
- Genome evolution – Process by which a genome changes in structure or size over time
- Hologenome theory of evolution – Evolutionary view of an individual multicellular organism as a community of the host plus all of its symbiotic microbes
- Models of DNA evolution – Markov models used in phylogeny to describe rates of nucleotide exchanges during the evolution of DNA sequences
- Molecular evolution – Process of change in the sequence composition of cellular molecules across generations
- History of molecular evolution – History of the field of study of molecular evolution
- Neutral theory of molecular evolution
- Nearly neutral theory of molecular evolution – Modification of the neutral theory of molecular evolution that accounts for the fact that not all mutations are either so deleterious such that they can be ignored, or else neutral
- Neutral network (evolution) – Set of genes all related by point mutations that have equivalent function or fitness
- RNA-based evolution – Theory that RNA plays an independent role in determining phenotype
Evolution of behaviour[]
- Co-operation (evolution) – Evolutionary process where groups of organisms work or act together for common or mutual benefits
- Evolution of biparental care in tropical frogs – The evolution of the behaviour in frogs in which both the mother and father raise their offspring
- Evolution of emotion – Study of the evolution of emotions
- Evolution of empathy – Capacity to understand or feel what another person is experiencing
- Evolution of eusociality – Origins of cooperative brood care, overlapping generations within a colony of adults, and a division of labor into reproductive and non-reproductive groups.
- Monogamy in animals – Natural history of mating systems in which species pair bond to raise offspring
- Reciprocal altruism – Behaviour whereby an organism acts in a manner that temporarily reduces its fitness while increasing another organism's fitness in the expectation of reciprocity
- Reciprocity (evolution) – Mechanisms whereby the evolution of cooperative or altruistic behaviour may be favoured by the probability of future mutual interactions
Evolution of other processes[]
- Evolution of ageing – Study of the evolutionary development of ageing processes
- Evolution of aging and mortality – Permanent, irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism
- Origin of programmed cell death – Death of a cell mediated by intracellular program, often as part of development
- Origin of avian flight – Evolution of birds from non-flying ancestors
- Evolution of biological complexity – Tendency for maximum complexity to increase over time, though without any overall direction
- Mosaic evolution – Evolution of characters at various rates both within and between species
- Evolution of multicellularity – The development of organisms that consists of more than one cell from unicellular ancestors
- Evolution of sexual reproduction – How sexually reproducing multicellular organisms could have evolved from a common ancestor species
- Mating type – Term in biologys
- Gamete differentiation/sexes – Sexual reproduction involving a large, female gamete and a small, male gamete
- Sex-determination – Biological system that determines the development of organism’s sex
- Life cycles/nuclear phases – Life cycle of living species
Applications in other disciplines[]
- Applications of evolution – Practical application of biological evolution throughout biology and in other disciplines such as medicine and computer science
- Biological anthropology – Branch of anthropology that studies the physical development of the human species
- Evolutionary aesthetics – Evolutionary psychology theories in which the basic aesthetic preferences of Homo sapiens are argued to have evolved in order to enhance survival and reproductive success
- Evolutionary anthropology – Interdisciplinary study of the evolution of human physiology and human behaviour and the relation between hominids and non-hominid primates
- Evolutionary computation – Trial and error problem solvers with a metaheuristic or stochastic optimization character
- Evolutionary economics
- Kenneth Boulding's evolutionary perspective – Approach to economic theory based on an evolutionary model
- Evolutionary epistemology – Ambiguous term applied to several concepts
- Evolutionary ethics – Study of evolution on morality or ethics
- Evolutionary linguistics – An umbrella term for various sociobiological approaches to linguistics
- Evolutionary medicine – Application of modern evolutionary theory to understanding health and disease
- Evolutionary neuroscience – Study of the evolution of nervous systems
- Evolutionary psychology – Branch of Psychology
- Biosocial criminology – Psychosocial examination of crime
- Criticism of evolutionary psychology
- Evolution of morality – The emergence of human moral behavior over the course of human evolution
- Evolution of schizophrenia
- Evolutionary aesthetics – Evolutionary psychology theories in which the basic aesthetic preferences of Homo sapiens are argued to have evolved in order to enhance survival and reproductive success
- Evolutionary approaches to depression – Attempts by evolutionary psychologists to use the theory of evolution to shed light on the problem of mood disorders
- Evolutionary developmental psychology – Application of the basic principles of Darwinian evolution to understand the development of human behavior and cognition
- Evolutionary developmental psychopathology
- Evolutionary educational psychology
- Evolutionary ethics – Study of evolution on morality or ethics
- Evolutionary leadership theory – Analysis of leadership from an evolutionary perspective
- Evolutionary musicology
- Evolutionary origin of religions – Emergence of religious behavior discussed in terms of natural evolution
- Evolutionary psychology of language – Study of the evolutionary history of language assuming it is a result of Darwinian adaptation
- Evolutionary psychology of parenting
- Evolutionary psychology of religion – Study of religious belief using evolutionary psychology principles
- Theoretical foundations of evolutionary psychology – General and specific scientific theories that explain the ultimate origins of psychological traits in terms of evolution
- Evolutionary robotics
- Evolutionary systems
- Sociobiology – Subdiscipline of biology regarding social behavior
- Sociocultural evolution – Evolution of societies
- Cultural evolution
- Universal Darwinism – Application of Darwinian theory to other fields
Evolutionary issues[]
Controversy about evolution[]
- Creation–evolution controversy
- Outline of the creation–evolution controversy – Overview of and topical guide to the creation–evolution controversy
- Criticism of evolutionary psychology
- Evolutionary argument against naturalism – A philosophical argument asserting a problem with believing both evolution and philosophical naturalism simultaneously
- Level of support for evolution – Variation in support for the theory of evolution
- Objections to evolution – Arguments that have been made against evolution
- Social effects of evolutionary theory – Effects on human societies of the scientific explanation of life's diversity
- Theology of creationism and evolution – Topic in theology
Religious and philosophical views of evolution[]
- Acceptance of evolution by religious groups – General review of religious attitudes towards evolution
- Conscious evolution – Hypothetical ability of the human species to choose what they will become
- Buddhism and evolution
- Catholic Church and evolution
- Hindu views on evolution – Hindu views on evolution
- Islamic views on evolution – Islamic views on evolution are diverse, ranging from theistic evolution to Old Earth creationism
- Ahmadiyya views on evolution – Ahmadiyya Movement in Islam universally accepts a process of divinely guided evolution
- Jewish views on evolution – Jewish views on evolution includes a continuum of views about the theory of evolution
- Mormon views on evolution
- Theistic evolution – Views that regard religious teachings about God as compatible with modern science
Influence of evolutionary theory[]
- Social effects of evolutionary theory – Effects on human societies of the scientific explanation of life's diversity
- See also Applications in other disciplines
Publications and organizations concerning evolution[]
Books[]
- Evolution: The Modern Synthesis – book by Julian Huxley (grandson of Thomas Henry Huxley); one of the most important books of modern evolutionary synthesis, published in 1942
- The Genetical Theory of Natural Selection – Book by Ronald Aylmer Fisher – book by R.A. Fisher important in modern evolutionary synthesis, first published in 1930
- Genetics and the Origin of Species – 1937 book by Ukrainian-American evolutionary biologist Theodosius Dobzhansky
- On the Origin of Species – 1859 book on evolutionary biology by Charles Darwin – seminal book by Charles Darwin concerning evolution by natural selection, first published in 1859
- Systematics and the Origin of Species from the Viewpoint of a Zoologist – book by zoologist and evolutionary biologist Ernst Mayr, canonical publication of modern evolutionary synthesis, first published in 1942 by Columbia University Press
- The Structure of Evolutionary Theory – technical book on macroevolutionary theory by the Harvard paleontologist Stephen Jay Gould
- Evolutionary Biology
Journals[]
- Evolution – Monthly journal in the science of evolutionary biology
- Evolutionary Anthropology – Bimonthly review journal
- Evolutionary Bioinformatics – Peer-reviewed open access scientific journal focusing on computational biology in the study of evolution
- Evolutionary Psychology – Peer-reviewed open access academic journal
- Journal of Evolutionary Biology – Bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal
- Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research – Quarterly, peer reviewed, scientific journal
- Trends in Ecology & Evolution (TREE) – Series of journals that publish review articles in a range of areas of biology and chemistry
Organizations[]
- European Society for Evolutionary Biology – Organisation to support the study of organic evolution
- Society for the Study of Evolution – Professional organization of evolutionary biologists
- Evolutionary psychology research groups and centers
- I. M. Sechenov Institute of Evolutionary Physiology and Biochemistry – Research facility in Saint Petersburg, Russia
- Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology – research institute based in Leipzig, Germany
- Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology – Research institute located in Plön, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.
- National Evolutionary Synthesis Center – Scientific research center in Durham, North Carolina
- Systematic and Evolutionary Biogeography Association
- Evolutionary Informatics Lab
Evolution scholars and researchers[]
- List of evolutionary psychologists – Wikipedia list article
- List of members of the National Academy of Sciences (Evolutionary biology)
Prominent evolutionary biologists[]
- Charles Darwin – English naturalist and biologist (1809–1882)
- Theodosius Dobzhansky – Russian-American geneticist and evolutionary biologist
- Richard Dawkins – English evolutionary biologist and author
- Stephen Jay Gould – American evolutionary biologist and historian of science (1941–2002)
- J. B. S. Haldane – Geneticist and evolutionary biologist
- Julian Huxley – British evolutionary biologist, philosopher, author
- Thomas Henry Huxley – English biologist and comparative anatomist
- Ronald Fisher – British statistician, evolutionary biologist, geneticist, eugenicist and high school teacher
- Ernst Mayr – German-American evolutionary biologist
- Alfred Russel Wallace – British naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist and biologist
- Sewall Wright – American geneticist
See also[]
- Outline of biology – Outline of subdisciplines within biology
- Outline of genetics – Hierarchical outline list of articles related to genetics
- Biogeography – Study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time
- Conscious evolution – Hypothetical ability of the human species to choose what they will become
- Ecology and Evolutionary Biology – Interdisciplinary field of study
- Effective evolutionary time – Hypothesis offering a causal explanation of diversity gradients
- Evolutionary acquisition of neural topologies – Method that evolves both the topology and weights of artificial neural networks
- Evolutionary anachronism – Attributes of living species that arose due to coevolution with other now-extinct species
- Evolutionary approaches to depression – Attempts by evolutionary psychologists to use the theory of evolution to shed light on the problem of mood disorders
- Evolutionary argument against naturalism – A philosophical argument asserting a problem with believing both evolution and philosophical naturalism simultaneously
- Evolutionary art – Branch of generative art where a system generates the art with an iterated process of selection by the artist and modification
- Evolutionary baggage – The part of the genome of a population that was advantageous in past circumstances but is currently disadvantageous
- Evolutionary Humanism
- Evolutionary informatics
- Evolutionary landscape – Metaphor used to visualize the processes of evolution
- Evolutionary Principle – The adaptation of species
- Extinction – Termination of a taxon by the death of the last member
- Extinction event – Widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth
- Human extinction – Hypothetical end of the human species
- Local extinction – The condition of a taxon ceasing to exist in a region which it previously inhabited
- MEGA, Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis
- Spandrel (biology)
- Speculative evolution – Science fiction genre exploring hypothetical scenarios in the evolution of life
- Transitional fossil – Fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group
External links[]
- General information
- Evolution on In Our Time at the BBC
- "Evolution". New Scientist. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- "Evolution Resources from the National Academies". U.S. National Academy of Sciences. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- "Understanding Evolution: your one-stop resource for information on Evolution". University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- "Evolution of Evolution – 150 Years of Darwin's "On the Origin of Species"". National Science Foundation. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- Human Timeline (Interactive) – Smithsonian, National Museum of Natural History (August 2016).
- Experiments concerning the process of biological evolution
- Lenski RE. "Experimental Evolution – Michigan State University". Retrieved July 31, 2013.
- Algorithms, games, and evolution, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA
- Online lectures
- Carroll SB. "The Making of the Fittest". Archived from the original on July 18, 2011. Retrieved May 30, 2011.
- Stearns SC. "Principles of Evolution, Ecology and Behavior". Archived from the original on March 23, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
Categories:
- Outlines of sciences
- Wikipedia outlines
- Evolution