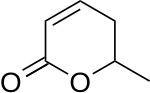
Parasorbic acid
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
6-methyl-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-one
| |
| Other names
2-methyl-2,3-dihydropyran-6-one, 2-Hexen-5-olide, 5-hydroxy-2-Hexenoic acid δ-lactone, parasorbic acid, sorbic oil, γ-Hexenolactone
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 112.128 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.0 g/mL (estimated) |
| Boiling point | 227 °C (441 °F; 500 K) estimated |
| 50 g/L | |
| Solubility | estimated |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-360.03 kJ·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
Signal word
|
Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
2
2
0 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Parasorbic acid is the cyclic lactone of sorbic acid. Thermal treatment or hydrolysis converts the lactone to sorbic acid.[1]
Toxicity[]
Parasorbic acid is toxic and causes indigestion and nausea, however cooking and exposure to moisture convert it to the benign food preservative sorbic acid.[2]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ A. S. Naidu, ed. (2000). Natural food antimicrobial systems. p. 637. ISBN 0-8493-2047-X.
- ^ Mason PL, Gaunt IF, Hardy J, Kiss IS, Butterworth KR, Gangolli SD (1976). "Long-term toxicity of parasorbic acid in rats". Food Cosmet Toxicol. 14 (5): 387–394. doi:10.1016/S0015-6264(76)80174-5. PMID 1010506.
Categories:
- Delta-lactones
- Preservatives
- Enones