Polish Special Forces
| Special Troops Command | |
|---|---|
| Wojska Specjalne | |
 | |
| Founded | 1990 |
| Country | |
| Allegiance | Polish Armed Forces |
| Type | special forces |
| Size | 5,000 (April 2021)[1] |
| Garrison/HQ | Kraków |
| Engagements | Operation Uphold Democracy War in Afghanistan Iraq War Syrian civil war (Personnel recovery, Emergency evacuation) |
| Commanders | |
| Chief of the General Staff | gen. broni Rajmund Andrzejczak |
| General Commander | gen. broni Jarosław Mika |
| Special Operations Component Commander | gen. bryg. Sławomir Drumowicz |
| Insignia | |
| Flag[2] |  |
Special Troops Command (Pol.: Wojska Specjalne) is the fourth military branch of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Poland and was officially formed in early 1990 after the fall of communism in 1989, in which the Polish Special Forces were first deployed into the conflict in Lebanon. The conflict in Lebanon was the first official battlefield experience in post-communist times. Polish Special Forces most notably train with American Navy SEALS and NATO Alliance members. It is composed of special forces units and command.
Composition[]
Special Troops Command () based in Kraków:[3]
- Jednostka Wojskowa GROM, or GROM, based in Warszawa and Gdańsk – Poland's premier special operations force. The unit was named after the Silent Unseen of World War II and trains regularly with the best special operation units from around the world.[3]
- Jednostka Wojskowa Komandosów, or JWK, based in Lubliniec – With a varied skill set, comparable to that of the U.S. Army Special Forces (Green Berets), JWK is responsible for asymmetrical warfare, embedding with, training, and leading host nation forces, as well as counterinsurgency operations.
- Jednostka Wojskowa Formoza, or JW FORMOZA, is based in Gdynia - Created as a maritime sabotage unit in the 1970s and it is the smallest of the STCs special forces units. The unit works closely with GROM and JWK and is often referred to as Poland's equivalent of the Navy SEALs.
- Jednostka Wojskowa Agat, or AGAT, based in Gliwice – A relatively new unit, being stood up in 2011, its name is shortened for “anti-gestapo” in honor of a WWII Polish Home Army Combat Diversion unit. A specialized light infantry unit, its role is comparable to that of the 75th Ranger Regiment.
- , or NIL, is based in Kraków – Formed in 2008 as the Special Operations Support unit, the unit is responsible for intelligence analysis, electronic warfare, technical surveillance, and unmanned aircraft operations. The unit is named after general Emil August Fieldorf “Nil”, a WWII Polish hero.
- based in Powidz – Created in 2011, dedicated to support SOF if needed while still being part of the Air Force.
Structure[]

GROM - Operational-Maneuver Response Group "Cichociemni" (Silent Unseen)
- Command and Support Staff – in Warsaw
- A Squadron (ZB A) – Land Element located in Warsaw
- B Squadron (ZB B) – Maritime Element located in Gdańsk
- C Squadron (ZB C) – Specialty unknown located in Warsaw
- Logistic and Security Unit - located in Warsaw
JW Komandosów - Army Commandos
- Command and Security - insignia of the Batalion Zośka from the Polish Home Army
- A Squadron (ZB A)- insignia of the Batalion Miotła from the Polish Home Army and insignia of PSBS
- B Squadron (ZB B)- Combined Operations insignia of the No. 10 (Inter-Allied) Commando unit and its No. 6 Troop (Polish)
- C Squadron (ZB C)- insignia of the Batalion Parasol from the Polish Home Army
- D Squadron (ZB D)- set up in 2016
- Information Support Group
- Special Forces Training Center
JW Formoza - name comes from the colloquial name of the units base, the post-German torpedo house in Gdynia, called "Formoza".[4]
- Special Operations Squadron - at least six special operations sections and a base unit

JW AGAT - formed on the basis of the Special Branch of the Military Police in Gliwice[5]
- HQ Staff and Command Group
- "A" Company
- "B" Company
- "C" Company
- Combat Support Team
- Logistics Security Team
- Medical Security Group
JW NIL - Support Unit of Command and Security of Special Forces[6]
- HQ Staff
- Command Team
- Logistics Security Team
- Information Support Team
- Medical Security Group
7 Special Operations Aviation Squadron - based in Powidz
- HQ staff
- Aerospace Group - equipped with 8 Mi-17, including 4 Mi-17-1W and 4 Sikorsky S-70i[7][8] all helicopters are to be equipped with M134Gs[9]
- Maintenance Group
Gallery[]

GROM operator conducting a port security exercise

Polish GROM and US Navy SEALs conducting joint field exercises

GROM unit conducting ship seizure training

GROM operator conducting a pistol training exercise
Equipment[]
Weaponry[]
| Name | Type | Photo | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard firearms of the Polish Armed Forces | |||
| AKM | Assault rifle | Outdated technology, virtually phased out and replaced | |
| Kbs wz. 1996 Beryl | Assault rifle | 
|
Most commonly used weapon |
| Pallad grenade launcher | Grenade launcher | Polish made grenade launcher, used from its introduction to the army | |
| SWD | Sniper rifle |  |
|
| Sako TRG | Sniper Rifle | ||
| PKM | General purpose machine gun |  |
|
| UKM-2000 | General purpose machine gun |  |
|
| Standard firearms of the Polish Special Forces | |||
| Heckler & Koch USP | Semi-auto pistol |  |
Standard pistol in JW Grom |
| Glock 17 | Semi-auto pistol |  |
Standard pistol in JW Komandosów and JW Agat |
| SIG P226 | Semi-auto pistol |  |
Standard pistol in JW Formoza (Navy Unit) |
| FN Five-seven | Semi-auto pistol |  |
Standard pistol for close protection in JW Grom |
| CZ Scorpion Evo 3 | Submachine gun |  |
New addition SMG for direct force operations in JW Grom |
| Heckler & Koch MP5 | Submachine gun |  |
Standard SMG for direct force operations in JW Grom |
| FN P90 | Submachine gun | Standard SMG for close protection in JW Grom | |
| Colt M4A1 | Assault rifle |  |
Mostly supplanted the Beryl in JW GROM. Less prevalent in other units. |
| Heckler & Koch HK416 | Assault rifle |  |
Assault rife used by the Polish SOF, JW Grom, JW Komandosów and JW Agat. Various barrel options used (10, 14.5 and 16.5 inch). Most commonly used assault rifle of the Special Forces |
| Heckler & Koch AG-C/GLM | Grenade launcher |  |
Standard under-barrel grenade launcher used with the HK416 |
| Heckler & Koch G36 | Assault rifle | Used in JW Formoza | |
| Heckler & Koch AG36 | Grenade launcher | Standard grenade launcher used with the G36 | |
| FN Minimi | Light machine gun |  |
Most common light machine gun in the Polish SOF |
| Carl Gustav | Recoilless rifle |  |
|
| Other firearms | |||
| Beretta 92 | Semi-auto pistol |  |
|
| M4 Carbine | Assault rifle |  |
Clones made by KAC and Bushmaster |
| F2000 | Assault rifle |  |
|
| M14 rifle | Battle rifle | Upgraded to EBR standard | |
| M203 | Grenade launcher |  |
|
| Grenade launcher | |||
| Remington 870 | Shotgun | ||
| Heckler & Koch PSG-1 | Sniper rifle | ||
| Remington 700 | Sniper rifle |  |
|
| Mauser SP66 | Sniper rifle |  |
|
| Mauser 86 | Sniper rifle | ||
| Barrett M82 | Anti-material rifle | ||
Vehicles[]
| Name | Type | Variant | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMMWV | Four-wheel drive multi-purpose vehicle | M1165A1 | 5 | The Polish Armed Forces currently operate 222 different variants of HMMWVes (217 are operated by the Polish Land Forces). |
| Oshkosh M-ATV | MRAP | M1240A1 | 45 | Donated by the United States[10] |
| Toyota | Four-wheel drive vehicle | Land Cruiser Hilux[11] |
Used by GROM and 1 Pułk Specjalny Komandosów (1st Special Commando's Regiment) | |
| Land Rover Defender | Four-wheel drive vehicle | 90 110 |
4[12] 6 |
Used by JW GROM and JW Formoza |
| Mercedes-Benz | Four-wheel drive vehicle Truck |
G-class Atego 1323AK |
6 10[13] |
The Polish Armed forces currently operate a total of 140 G-class vehicles.[14] The Land forces operate 121 GD 290s and MB290GD WDs.[13] The military police uses 13 GD 290s.[13] |
| Tarpan Honker | 4x4 | Honker Skorpion 3 special version | Used by 1 Pułk Specjalny Komandosów | Polish made off-road vehicles, best variants are powered with Polish Andoria engines |
| Star | Truck | Star 1444 (MAN TGM 18.280 BB) | 1[13] | Polish made trucks, now modernised to adjust to new weaponry and specifications |
| Volvo | Truck | Volvo FM 8x4 Volvo FM 6x6 Volvo FM 4x4 |
10[13] 11[13] 2[13] |
Aircraft[]

| Name | Type | Variant | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-70i Black Hawk | Medium-lift transport/utility helicopter | S-70i | 4/8 | 4 on order, 2 scheduled for delivery in 2023, remaining in 2024.[15] In 2019 7 S-70i Black Hawks were ordered and received. 4 to Special Forces and 3 to the Police.[16] |
Rank insignia[]
- Officers
| NATO Code | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Special Forces |

|

|

|

|

|

|
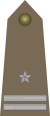
|

|

|

|
| Polish name | Generał1 | Generał broni |
Generał dywizji |
Generał brygady |
Pułkownik | Podpułkownik | Major | Kapitan | Porucznik | Podporucznik |
| Abbreviation | gen. | gen. broni | gen. dyw. | gen. bryg. | płk | ppłk | mjr | kpt. | por. | ppor. |
|
1 Until 2004 Generał armii | ||||||||||
- Enlisted
| NATO Code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Special Forces |

|

|

|

|

|

|
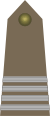
|

|

|

|

|
| Polish name | Starszy chorąży sztabowy |
Starszy chorąży |
Chorąży | Młodszy chorąży |
Starszy sierżant |
Sierżant | Plutonowy | Starszy kapral |
Kapral | Starszy szeregowy |
Szeregowy |
| Abbreviation | st. chor. szt. | st. chor. | chor. | mł. chor. | st. sierż. | sierż. | plut. | st. kpr. | kpr. | st. szer. | szer. |
See also[]
References[]
- ^ http://www.dz.urz.mon.gov.pl/zasoby/dziennik/pozycje/zalaczniki/2020/02/zalaczniki-sig.pdf
- ^ "Ustawa z dnia 19 lutego 1993 r. o znakach Sił Zbrojnych Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej" [Act of February 19, 1993 on the symbols of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Poland] (PDF). isap.sejm.gov.pl (in Polish). Internet System of Legal Acts. pp. 24–28. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ a b "Polish Special Forces 2018 GROM / JWK / FORMOZA / AGAT / NIL". funker530.com. 26 February 2018. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "JW FORMOZA - USSE". usse.pl. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "Jednostka Wojskowa "Agat"". www.jednostki-wojskowe.pl. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "Jednostka Wojskowa "Nil"". www.jednostki-wojskowe.pl. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ Siminski, Jacek (2019-12-23). "Polish Special Ops Component Receives S-70i Black Hawk Helicopters". The Aviationist. Retrieved 2020-04-21.
- ^ "Mil Mi-17-1V Hip, lokalizacja: Powidz - (EPPW), autor: Marek Purat". Galeria Aviateam.pl. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "Miniguny w końcu kupione". www.altair.com.pl. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "Polskie Wojska Specjalne otrzymały od Amerykanów 45 pojazdów opancerzonych M-ATV". technologie.onet.pl. 26 February 2015. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ Nowa Technika Wojskowa magazine, issue 03/09
- ^ "Nadjeżdża Huzar". 4 January 2005.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Zakupy pojazdów dla Wojska Polskiego". Gdzie zaczyna się wojsko... 3 January 2011.
- ^ Nowa Technika Wojskowa magazine, issue 03/09 96
- ^ "Poland Purchases Four New S-70i Black Hawk Helicopters". 17 December 2021.
- ^ "Poland Purchases Four New S-70i Black Hawk Helicopters". 17 December 2021.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Special forces of Poland. |
- Special forces of Poland



