Posterior cerebral artery
| Posterior cerebral artery | |
|---|---|
 The outer surface of the human brain, with the area supplied by the posterior cerebral artery shown in yellow. | |
 The arterial circle and arteries of the brain (inferior view). The posterior cerebral arteries (bottom forks) arise from the basilar artery (center). | |
| Details | |
| Source | basilar artery (most common in adults) |
| Vein | cerebral veins |
| Supplies | occipital lobe of cerebrum |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria cerebri posterior |
| Acronym(s) | PCA |
| MeSH | D020769 |
| TA98 | A12.2.07.082 |
| TA2 | 4565 |
| FMA | 50583 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, part of the back of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery, where it bifurcates into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. These anastomose with the middle cerebral arteries and internal carotid arteries via the posterior communicating arteries.
Structure[]
The branches of the posterior cerebral artery are divided into two sets, ganglionic and cortical:
Central branches[]
Also known as the perforating branches:
- Thalamoperforating and thalamogeniculate or postero-medial ganglionic branches: a group of small arteries which arise at the commencement of the posterior cerebral artery: these, with similar branches from the posterior communicating, pierce the posterior perforated substance, and supply the medial surfaces of the thalami and the walls of the third ventricle.
- Peduncular perforating or postero-lateral ganglionic branches: small arteries which arise from the posterior cerebral artery after it has turned around the cerebral peduncle; they supply a considerable portion of the thalamus.

Posterior (choroidal) branches[]
The posterior choroidal branches of the posterior cerebral artery are sometimes referred to as a single posterior choroidal artery.
- Medial posterior choroidal branches: run forward beneath the splenium of the corpus callosum, and supply the tela choroidea of the third ventricle and the choroid plexus.
- Lateral posterior choroidal branches: small branches to the cerebral peduncle, fornix, thalamus, caudate nucleus, and choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle.[1]
Cortical branches[]
The cortical branches are:
- Anterior temporal, distributed to the uncus and the anterior part of the fusiform gyrus
- Posterior temporal, to the fusiform and the inferior temporal gyri
- Lateral occipital, which branches into the anterior, middle and posterior inferior temporal arteries
- Medial occipital, which branches into the:
- Calcarine sulcus, to the cuneus and lingual gyrus and the back part of the convex surface of the occipital lobe
- Parieto-occipital sulcus, to the cuneus and the precuneus
- Splenial, or the posterior pericallosal branch, sometimes anastomoses with the anterior cerebral artery (ACA), and may not be present if the ACA wraps around the corpus callosum
Development[]
The prenatal development of the posterior cerebral arteries in the fetus comes relatively late and arises from the fusion of several embryonic vessels near the caudal ends of the posterior communicating arteries supplying the mesencephalon and diencephalon.[2] The PCA begins as such, as a continuation of the PCommA in the fetus with only 10–30% of fetuses having a prominent basilar origin.[3]
The fetal carotid origin of the PCA usually regresses as the vertebral and basilar arteries develop with the PCommA reducing is size. In most adults, the PCA sources from the anterior portion of the basilar artery. Only about 19% of adults retain PCommA dominance of the PCA with 72% having dominant basilar origin, and the rest having either equal prominence between PCommA and basilar artery, or a single exclusive source.[3]
Clinical significance[]
This section does not cite any sources. (November 2021) |
Stroke[]
- Contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensations.
- Visual field defects (contralateral hemianopsia with macular sparing).
- Prosopagnosia with bilateral obstruction of the lingual and fusiform gyri.
- Superior Alternating Syndrome (Weber's syndrome)
- Ipsilateral deficits of oculomotor nerve,
- Contralateral deficits of facial nerve (only lower face, upper face receives bilateral input), vagus nerve and hypoglossal nerve
- Horner's Syndrome
Signs and symptoms: Structures involved
Peripheral territory (Cortical branches)[]
- Homonymous hemianopsia (often upper quadrantic): Calcarine cortex or optic radiation nearby.
- Bilateral homonymous hemianopsia, cortical blindness, awareness or denial of blindness; tactile naming, achromatopia (color blindness), failure to see to-and-fro movements, inability to perceive objects not centrally located, apraxia of ocular movements, inability to count or enumerate objects, tendency to run into things that the patient sees and tries to avoid: Bilateral occipital lobe with possibly the parietal lobe involved.
- Verbal dyslexia without agraphia, color anomia: Dominant calcarine lesion and posterior part of corpus callosum.
- Memory defect: Hippocampal lesion bilaterally or on the dominant side only.
- Topographic disorientation and prosopagnosia: Usually with lesions of nondominant, calcarine, and lingual gyrus.
- Simultanagnosia, hemivisual neglect: Dominant visual cortex, contralateral hemisphere.
- Unformed visual hallucinations, peduncular hallucinosis, metamorphopsia, teleopsia, illusory visual spread, palinopsia, distortion of outlines, central photophobia: Calcarine cortex.
- Complex hallucinations: Usually nondominant hemisphere.
Central territory (Ganglionic branches)[]
- Thalamic syndrome: sensory loss (all modalities), spontaneous pain and dysesthesias, choreoathetosis, intention tremor, spasms of hand, mild hemiparesis, contralateral hemianaethesia: Posteroventral nucleus of thalamus; involvement of the adjacent subthalamus body or its afferent tracts.
- Thalamoperforate syndrome: crossed cerebellar ataxia with ipsilateral third nerve palsy (Claude's syndrome): Dentatothalamic tract and issuing third nerve.
- Weber's syndrome: third nerve palsy and contralateral hemiplegia: Third nerve and cerebral peduncle.
- Contralateral hemiplegia: Cerebral peduncle.
- Paralysis or paresis of vertical eye movement, skew deviation, sluggish pupillary responses to light, slight miosis and ptosis (retraction nystagmus and "tucking" of the eyelids may be associated): Supranuclear fibers to third nerve, interstitial nucleus of Cajal, nucleus of Darkschewitsch, and posterior commissure.
- Contralateral rhythmic, ataxic action tremor; rhythmic postural or "holding" tremor (rubral tremor): Dentatothalamic tract.
Additional images[]

Arteriogram of the arterial supply.
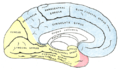
Medial surface of cerebral hemisphere, showing areas supplied by cerebral arteries. Areas supplied by the posterior cerebral artery shown in yellow.

The arteries of the base of the brain. Posterior cerebral artery labeled near center. The temporal pole of the cerebrum and a portion of the cerebellar hemisphere have been removed on the right side. Inferior aspect (viewed from below).
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Atlas of Human Anatomy, Frank Netter
- ^ Osborn, Anne G.; Jacobs, John M. (1999), Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, p. 153, ISBN 978-0-397-58404-8
- ^ a b Krayenbühl, Hugo; Yaşargil, Mahmut Gazi; Huber, Peter; Bosse, George (1982), Cerebral Angiography, Thieme, pp. 163–165, ISBN 978-0-86577-067-6
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Posterior cerebral artery. |
- neuro/322 at eMedicine – Posterior cerebral artery stroke
- Atlas image: n3a8p1 at the University of Michigan Health System
- Anatomy photo:28:09-0206 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- "Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-11-07.
- Overview
- Angiography at State University of New York Upstate Medical University
- Diagram
- Blood supply
- Arteries of the head and neck


