Presidency of Theodore Roosevelt
 | |
| Presidency of Theodore Roosevelt September 14, 1901 – March 4, 1909 | |
| Cabinet | See list |
|---|---|
| Party | Republican |
| Election | 1904 |
| Seat | White House |
 Seal of the President (1894–1945) | |
| Library website | |
| ||
|---|---|---|
33rd Governor of New York
25th Vice President of the United States
26th President of the United States
First term
Second term
Post Presidency
|
||
The presidency of Theodore Roosevelt started on September 14, 1901, when Theodore Roosevelt became the 26th president of the United States upon the assassination of President William McKinley, and ended on March 4, 1909. Roosevelt had been the vice president for only 194 days when he succeeded to the presidency. A Republican, he ran for and won by a landslide a four-year term as president in 1904. He was succeeded by his protégé and chosen successor, William Howard Taft.
A Progressive reformer, Roosevelt earned a reputation as a "trust buster" through his regulatory reforms and antitrust prosecutions. His presidency saw the passage of the Pure Food and Drug Act, which established the Food and Drug Administration to regulate food safety, and the Hepburn Act, which increased the regulatory power of the Interstate Commerce Commission. Roosevelt took care, however, to show that he did not disagree with trusts and capitalism in principle, but was only against monopolistic practices. His "Square Deal" included regulation of railroad rates and pure foods and drugs; he saw it as a fair deal for both the average citizen and the businessmen. Sympathetic to both business and labor, Roosevelt avoided labor strife, most notably negotiating a settlement to the great Coal Strike of 1902. He vigorously promoted the conservation movement, emphasizing efficient use of natural resources. He dramatically expanded the system of national parks and national forests. After 1906, he moved to the left, attacking big business, proposing a welfare state, and supporting labor unions.
In foreign affairs, Roosevelt sought to uphold the Monroe Doctrine and to establish the United States as a strong naval power and took charge of building the Panama Canal, which greatly increased access to the Pacific and increased American security interests and trade opportunities. He inherited the colonial empire acquired in the Spanish–American War (1898). He ended the United States Military Government in Cuba and committed to a long-term occupation of the Philippines. Much of his foreign policy focused on the threats posed by Japan in the Pacific and Germany in the Caribbean Sea. Seeking to minimize European power in Latin America, he mediated the Venezuela Crisis and declared the Roosevelt Corollary. Roosevelt mediated the Russo-Japanese War (1904–1905), for which he won the 1906 Nobel Peace Prize. He pursued closer relations with Great Britain. Biographer William Harbaugh argues:
- In foreign affairs, Theodore Roosevelt’s legacy is judicious support of the national interest and promotion of world stability through the maintenance of a balance of power; creation or strengthening of international agencies, and resort to their use when practicable ; and implicit resolve to use military force, if feasible, to foster legitimate American interests. In domestic affairs, it is the use of government to advance the public interest. "If on this new continent," he said, "we merely build another country of great but unjustly divided material prosperity, we shall have done nothing."[1]
Historian Thomas Bailey, who generally disagreed with Roosevelt's policies, nevertheless concluded, "Roosevelt was a great personality, a great activist, a great preacher of the moralities, a great controversialist, a great showman. He dominated his era as he dominated conversations...the masses loved him; he proved to be a great popular idol and a great vote-getter."[2] His image stands alongside George Washington, Thomas Jefferson and Abraham Lincoln on Mount Rushmore. Although Roosevelt has been criticized by some for his imperialism stance, he is often ranked by historians among the top-five greatest U.S. presidents of all time.[3][4]
Accession[]

Roosevelt served as assistant secretary of the navy and governor of New York before winning election as William McKinley's running mate in the 1900 presidential election. Roosevelt became president following the assassination of McKinley by anarchist Leon Czolgosz in Buffalo, New York; Czolgosz shot McKinley on September 6, 1901, and McKinley died on September 14. Roosevelt was sworn into office on the day of McKinley's death at the Ansley Wilcox House in Buffalo. John R. Hazel, U.S. District Judge for the Western District of New York, administered the oath of office.[5] Being just a few weeks short of his 43rd birthday, Roosevelt became the youngest president in U.S. history, a distinction he still retains.[6]
When asked whether he was ready to take the oath, Roosevelt answered,[7]
I will take the oath. And in this hour of deep and terrible national bereavement, I wish to state that it shall be my aim to continue, absolutely without variance, the policy of President McKinley, for the peace and honor of our beloved country.
Roosevelt would later state that he came into office without any particular domestic policy goals. He broadly adhered to most Republican positions on economic issues, with the partial exception of the protective tariff. Roosevelt had stronger views on the particulars of his foreign policy, as he wanted the United States to assert itself as a great power in international relations.[8]
Administration[]
Cabinet[]
| The Roosevelt Cabinet | ||
|---|---|---|
| Office | Name | Term |
| President | Theodore Roosevelt | 1901–1909 |
| Vice President | none | 1901–1905 |
| Charles W. Fairbanks | 1905–1909 | |
| Secretary of State | John Hay | 1901–1905 |
| Elihu Root | 1905–1909 | |
| Robert Bacon | 1909 | |
| Secretary of the Treasury | Lyman J. Gage | 1901–1902 |
| L. M. Shaw | 1902–1907 | |
| George B. Cortelyou | 1907–1909 | |
| Secretary of War | Elihu Root | 1901–1904 |
| William Howard Taft | 1904–1908 | |
| Luke Edward Wright | 1908–1909 | |
| Attorney General | Philander C. Knox | 1901–1904 |
| William Henry Moody | 1904–1906 | |
| Charles Joseph Bonaparte | 1906–1909 | |
| Postmaster General | Charles Emory Smith | 1901–1902 |
| Henry Clay Payne | 1902–1904 | |
| Robert Wynne | 1904–1905 | |
| George B. Cortelyou | 1905–1907 | |
| George von Lengerke Meyer | 1907–1909 | |
| Secretary of the Navy | John Davis Long | 1901–1902 |
| William Henry Moody | 1902–1904 | |
| Paul Morton | 1904–1905 | |
| Charles Joseph Bonaparte | 1905–1906 | |
| Victor H. Metcalf | 1906–1908 | |
| Truman Handy Newberry | 1908–1909 | |
| Secretary of the Interior | Ethan A. Hitchcock | 1901–1907 |
| James Rudolph Garfield | 1907–1909 | |
| Secretary of Agriculture | James Wilson | 1901–1909 |
| Secretary of Commerce and Labor | George B. Cortelyou | 1903–1904 |
| Victor H. Metcalf | 1904–1906 | |
| Oscar Straus | 1906–1909 | |

At far left: Roosevelt
Left to right in back of table: George B. Cortelyou, Charles Joseph Bonaparte, Robert Bacon, James Wilson, Truman Handy Newberry.
Left to right in front of table: Oscar S. Straus, Luke Edward Wright, George von Lengerke Meyer, James Rudolph Garfield
Anxious to ensure a smooth transition, Roosevelt convinced the members of McKinley's cabinet, most notably Secretary of State John Hay and Secretary of the Treasury Lyman J. Gage, to remain in office after McKinley's death.[9] Another holdover from McKinley's cabinet, Secretary of War Elihu Root, had been a Roosevelt confidante for years, and he continued to serve as President Roosevelt's close ally.[10] Attorney General Philander C. Knox, who McKinley had appointed in early 1901, also emerged as a powerful force within the Roosevelt administration.[11] McKinley's personal secretary, George B. Cortelyou, remained in place under Roosevelt.[12] Once Congress began its session in December 1901, Roosevelt replaced Gage with L. M. Shaw and appointed Henry C. Payne as Postmaster General, earning the approval of powerful Senators William B. Allison and John Coit Spooner.[13] He also replaced his former boss, Secretary of the Navy John D. Long, with Congressman William H. Moody.[14][a] In 1903, Roosevelt named Cortelyou as the first head of the Department of Commerce and Labor, and William Loeb Jr. became Roosevelt's secretary.[15]
Root returned to the private sector in 1904 and was replaced by William Howard Taft, who had previously served as the governor-general of the Philippines.[16] Knox accepted appointment to the Senate in 1904 and was replaced by William Moody, who in turn was succeeded as attorney general by Charles Joseph Bonaparte in 1906. After Hay's death in 1905, Roosevelt convinced Root to return to the Cabinet as secretary of state, and Root remained in office until the final days of Roosevelt's tenure.[17] In 1907, Roosevelt replaced Shaw with Cortelyou, while James R. Garfield became the new secretary of the interior.[18]
Press Corps[]
Building on McKinley's effective use of the press, Roosevelt made the White House the center of news every day, providing interviews and photo opportunities. Noticing the White House reporters huddled outside in the rain one day, he gave them their own room inside, effectively inventing the presidential press briefing.[19] The grateful press, with unprecedented access to the White House, rewarded Roosevelt with ample coverage, rendered the more possible by Roosevelt's practice of screening out reporters he didn't like.[19]
Judicial appointments[]
Roosevelt appointed three associate justices of the Supreme Court.[20] Roosevelt's first appointment, Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr. had served as chief justice of the Massachusetts Supreme Court since 1899 and had earned notoriety within legal circles for his moral skepticism and deference to elected officials. Confirmed in December 1902, Holmes served on the Supreme Court until 1932.[21] Roosevelt's second appointment, former Secretary of State William R. Day, became a reliable vote for Roosevelt's antitrust prosecutions and remained on the court from 1903 to 1922.[22] In 1906, after considering Democratic appellate judge Horace Harmon Lurton for a Supreme Court vacancy, Roosevelt instead appointed Attorney General William Moody.[23] Moody served on the court until health problems forced his retirement in 1910.
Roosevelt also appointed 71 other federal judges: 18 to the United States Courts of Appeals, and 53 to the United States district courts.
Domestic policy[]
Progressivism[]
Determined to create what he called a "Square Deal" between business and labor, Roosevelt pushed several pieces of progressive legislation through Congress. Progressivism was among the most powerful political forces of the day, and Roosevelt was its most articulate spokesperson. Progressivism had dual aspects. First, progressivism promoted use of science, engineering, technology, and social sciences to address the nation's problems, and identify ways to eliminate waste and inefficiency and promote modernization.[24] Those promoting progressivism also campaigned against corruption among political machines, labor unions, and trusts of new, large corporations, which emerged at the turn of the century.[25] In describing Roosevelt's priorities and characteristics as president, historian G. Warren Chessman noted Roosevelt's
insistence upon the public responsibility of large corporations; publicity as a first remedy for trusts; regulation of railroad rates; mediation of the conflict of capital and labor; conservation of natural resources; and protection of the less fortunate members of society.[26]
Trust busting and regulation[]
In the late-nineteenth century, several large businesses, including Standard Oil, had either bought their rivals or had established business arrangements that effectively stifled competition. Many companies followed the model of Standard Oil, which organized itself as a trust in which several component corporations were controlled by one board of directors. While Congress had passed the 1890 Sherman Antitrust Act to provide some federal regulation of trusts, the Supreme Court had limited the power of the act in the case of United States v. E. C. Knight Co..[27] By 1902, the 100 largest corporations held control of 40 percent of industrial capital in the United States. Roosevelt did not oppose all trusts, but sought to regulate trusts that he believed harmed the public, which he labeled as "bad trusts."[28]
First term[]
Upon taking office, Roosevelt proposed federal regulations of trusts. As the states had not prevented the growth of what he viewed as harmful trusts, Roosevelt advocated the creation of Cabinet department designed to regulate corporations engaged in interstate commerce.[29] He also favored amending the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887, which had failed to prevent the consolidation of railroads.[30] In February 1902, the Justice Department announced that it would file an antitrust suit against the Northern Securities Company, a railroad holding company that had been formed in 1901 by J. P. Morgan, James J. Hill, and E. H. Harriman.[31] As the Justice Department lacked an antitrust division, Attorney General Knox, a former corporate lawyer, personally led the suit. While the case was working its way through court, Knox filed another case against the "Beef Trust," which had become unpopular due to rising meat prices.[32] Combined with his earlier rhetoric, the suits signaled Roosevelt's resolve to strengthen the federal regulation of trusts.[31]
After the 1902 elections, Roosevelt called for a ban on railroad rebates to large industrial concerns, as well as for the creation of a Bureau of Corporations to study and report on monopolistic practices.[33] To pass his antitrust package through Congress, Roosevelt appealed directly to the people, casting the legislation as a blow against the malevolent power of Standard Oil. Roosevelt's campaign proved successful, and he won congressional approval of the creation of the Department of Commerce and Labor, which included the Bureau of Corporations.[34] The Bureau of Corporations was designed to monitor and report on anti-competitive practices; Roosevelt believed that large companies would be less likely to engage in anti-competitive practices if such practices were publicized. At Knox's request, Congress also authorized the creation of the Antitrust Division of the Department of Justice. Roosevelt also won passage of the Elkins Act, which restricted the granting of railroad rebates.[35]
In March 1904, the Supreme Court ruled for the government in the case of Northern Securities Co. v. United States. According to historian Michael McGerr, the case represented the federal government's first victorious prosecution of a "single, tightly integrated interstate corporation."[36] The following year, the administration won another major victory in Swift and Company v. United States, which broke up the Beef Trust. The evidence at trial demonstrated that, prior to 1902, the "Big Six" leading meatpackers had engaged in a conspiracy to fix prices and divide the market for livestock and meat in their quest for higher prices and higher profits. They blacklisted competitors who failed to go along, used false bids, and accepted rebates from the railroads. After they were hit with federal injunctions in 1902, the Big Six had merged into one company, allowing them to continue to control the trade internally. Speaking for the unanimous court, Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr. held that interstate commerce included actions that were part of the chain where the chain was clearly interstate in character. In this case, the chain ran from farm to retail store and crossed many state lines.[37]
Second term[]
Following his re-election, Roosevelt sought to quickly enact a bold legislative agenda, focusing especially on legislation that would build upon the regulatory accomplishments of his first term. Events during his first term had convinced Roosevelt that legislation enacting additional federal regulation of interstate commerce was necessary, as the states were incapable of regulating large trusts that operated across state lines and the overworked Department of Justice was unable to provide an adequate check on monopolistic practices through antitrust cases alone.[38] Roused by reports in McClure's Magazine, many Americans joined Roosevelt in calling for an enhancement to the Elkins Act, which had done relatively little to restrict the granting of railroad rebates.[39] Roosevelt also sought to strengthen the powers of the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC), which had been created in 1887 to regulate railroads.[38] Roosevelt's call for regulatory legislation, published in his 1905 message to Congress, encountered strong opposition from business interests and conservative congressmen.[40]
When Congress reconvened in late 1905, Roosevelt asked Senator Jonathan P. Dolliver of Iowa to introduce a bill that would incorporate Roosevelt's railroad regulatory proposals, and set about mobilizing public and congressional support for the bill. The bill was also taken up in the House, where it became known as the Hepburn Bill, named after Congressman William Peters Hepburn.[41] While the bill passed the House with relative ease, the Senate, dominated by conservative Republicans like Nelson Aldrich, posed a greater challenge.[42] Seeking to defeat reform efforts, Aldrich arranged it so that Democrat Benjamin Tillman, a Southern senator who Roosevelt despised, was left in charge of the bill.[43] Because railroad regulation was widely popular, opponents of the Hepburn Bill focused on the role of courts in reviewing the ICC's rate-setting. Roosevelt and progressives wanted to limit judicial review to issues of procedural fairness, while conservatives favored "broad review" that would allow judges to determine whether the rates themselves were fair.[43]
After Roosevelt and Tillman were unable to assemble a bipartisan majority behind a bill that restricted judicial review, Roosevelt accepted an amendment written by Senator Allison that contained vague language allowing for court review of the ICC's rate-setting power.[44] With the inclusion of the Allison amendment, the Senate passed the Hepburn Bill in a 71-to-3 vote.[45] After both houses of Congress passed a uniform law, Roosevelt signed the Hepburn Act into law on June 29, 1906. In addition to rate-setting, the Hepburn Act also granted the ICC regulatory power over pipeline fees, storage contracts, and several other aspects of railroad operations.[46] Though some conservatives believed that the Allison amendment had granted broad review powers to the courts, a subsequent Supreme Court case limited judicial power to review the ICC's rate-setting powers.[45]
In response to public clamor largely arising from the popularity of Upton Sinclair's novel, The Jungle, Roosevelt also pushed Congress to enact food safety regulations. Opposition to a meat inspection bill was strongest in the House, due to the presence of conservative Speaker of the House Joseph Gurney Cannon and allies of the meatpacking industry.[47] Roosevelt and Cannon agreed to a compromise bill that became the Meat Inspection Act of 1906. Congress simultaneously passed the Pure Food and Drug Act, which received strong support in both the House and the Senate.[48] Collectively, the laws provided for the labeling of foods and drugs and the inspection of livestock, and mandated sanitary conditions at meatpacking plants.[49]
Seeking to bolster antitrust regulations, Roosevelt and his allies introduced a bill to enhance the Sherman Act in 1908, but it was defeated in Congress.[50] In the aftermath of a series of scandals involving major insurance companies, Roosevelt sought to establish a National Bureau of Insurance to provide federal regulation, but this proposal was also defeated.[51] Roosevelt continued to launch antitrust suits in his second term, and a suit against Standard Oil in 1906 would lead to that company's break-up in 1911.[52] In addition to the antitrust suits and major regulatory reform efforts, the Roosevelt administration also won the cooperation of many large trusts, who consented to regulation by the Bureau of Corporations.[53] Among the companies that voluntarily agreed to regulation was U.S. Steel, which avoided an antitrust suit by allowing the Bureau of Corporations to investigate its operations.[54]
Conservation[]

Roosevelt was a prominent conservationist, putting the issue high on the national agenda.[55] Roosevelt's conservation efforts were aimed not just at environment protection, but also at ensuring that society as a whole, rather than just select individuals or companies, benefited from the country's natural resources.[56] His key adviser and subordinate on environmental matters was Gifford Pinchot, the head of the Bureau of Forestry. Roosevelt increased Pinchot's power over environmental issues by transferring control over national forests from the Department of the Interior to the Bureau of Forestry, which was part of the Agriculture Department. Pinchot's agency was renamed to the United States Forest Service, and Pinchot presided over the implementation of assertive conservationist policies in national forests.[57]
Roosevelt encouraged the Newlands Reclamation Act of 1902, which promoted federal construction of dams to irrigate small farms and placed 230 million acres (360,000 mi2 or 930,000 km2) under federal protection. In 1906, Congress passed the Antiquities Act, granting the president the power to create national monuments in federal lands. Roosevelt set aside more federal land, national parks, and nature preserves than all of his predecessors combined.[58][59] Roosevelt established the Inland Waterways Commission to coordinate construction of water projects for both conservation and transportation purposes, and in 1908 he hosted the Conference of Governors to boost support for conservation.[b] After the conference, Roosevelt established the National Conservation Commission to take an inventory of the nation's natural resources.[61]
Roosevelt's policies faced opposition from both environmental activists like John Muir and opponents of conservation like Senator Henry M. Teller of Colorado.[62] While Muir, the founder of the Sierra Club, wanted nature preserved for the sake of pure beauty, Roosevelt subscribed to Pinchot's formulation, "to make the forest produce the largest amount of whatever crop or service will be most useful, and keep on producing it for generation after generation of men and trees."[63] Teller and other opponents of conservation, meanwhile, believed that conservation would prevent the economic development of the West and feared the centralization of power in Washington. The backlash to Roosevelt's ambitious policies prevented further conservation efforts in the final years of Roosevelt's presidency and would later contribute to the Pinchot–Ballinger controversy during the Taft administration.[64]
Labor relations[]

Roosevelt was generally reluctant to involve himself in labor-management disputes, but he believed that presidential intervention was justified when such disputes threatened the public interest.[65] Labor union membership had doubled in the five years preceding Roosevelt's inauguration, and at the time of his accession, Roosevelt saw labor unrest as the greatest potential threat facing the nation. Yet he also sympathized with many laborers due to the harsh conditions that many faced.[66] Resisting the more extensive reforms proposed by labor leaders such as Samuel Gompers of the American Federation of Labor (AFL), Roosevelt established the open shop as the official policy civil service employees.[67]
In 1899, the United Mine Workers (UMW) had expanded its influence from bituminous coal mines to anthracite coal mines. The UMW organized an anthracite coal strike in May 1902, seeking an eight-hour day and pay increases. Hoping to reach a negotiated solution with the help of Mark Hanna's National Civic Federation, UMW president John Mitchell prevented bituminous coal miners from launching a sympathy strike. The mine owners, who wanted to crush the UMW, refused to negotiate, and the strike continued. In the ensuing months, the price of coal increased from five dollars per ton to above fifteen dollars per ton. Seeking to help the two parties arrive at a solution, Roosevelt hosted the UMW leaders and mine operators at the White House in October 1902, but the mine owners refused to negotiate. Through the efforts of Roosevelt, Root, and J.P. Morgan, the mine operators agreed to the establishment of a presidential commission to propose a solution to the strike. In March 1903, the commission mandated pay increases and a reduction in the workday from ten hours to nine hours. At the insistence of the mine owners, the UMW was not granted official recognition as the representative of the miners.[68]
Roosevelt refrained from major interventions in labor disputes after 1902, but state and federal courts increasingly became involved, issuing injunctions to prevent labor actions.[69] Tensions were particularly high in Colorado, where the Western Federation of Miners led a series of strikes that became part of a struggle known as the Colorado Labor Wars. Roosevelt did not intervene in the Colorado Labor Wars, but Governor James Hamilton Peabody dispatched the Colorado National Guard to crush the strikes. In 1905, radical union leaders like Mary Harris Jones and Eugene V. Debs established the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), which criticized the conciliatory policies of the AFL.[70]
Civil rights[]
Although Roosevelt did some work improving race relations, he, like most leaders of the Progressive Era, lacked initiative on most racial issues. Booker T. Washington, the most important black leader of the day, was the first African American to be invited to dinner at the White House, dining there on October 16, 1901.[71] Washington, who had emerged as an important adviser to Republican politicians in the 1890s, favored accommodation with the Jim Crow laws that instituted racial segregation.[72] News of the dinner reached the press two days later, and public outcry from whites was so strong, especially from the Southern states, that Roosevelt never repeated the experiment.[71] Nonetheless, Roosevelt continued to consult Washington regarding appointments and shunned the "lily-white" Southern Republicans who favored excluding blacks from office.[citation needed]
After the dinner with Washington, Roosevelt continued to speak out against lynchings, but did little to advance the cause of African-American civil rights.[73] In 1906, he approved the dishonorable discharges of three companies of black soldiers who all refused his direct order to testify regarding their actions during a violent episode in Brownsville, Texas, known as the Brownsville Raid. Roosevelt was widely criticized by contemporary newspapers for the discharges, and Senator Joseph B. Foraker won passage of a congressional resolution directing the administration to turn over all documents related to the case.[74] The controversy hung over the remainder of his presidency, although the Senate eventually concluded that the dismissals had been justified.[75]
Panic of 1907[]
In 1907, Roosevelt faced the greatest domestic economic crisis since the Panic of 1893. The U.S. stock market entered a slump in early 1907, and many in the financial markets blamed Roosevelt's regulatory policies for the decline in stock prices.[76] Lacking a strong central banking system, the government was unable to coordinate a response to the economic downturn.[77] The slump reached a full-blown panic in October 1907, when two investors failed to take over United Copper. Working with Secretary of the Treasury Cortelyou, financier J.P. Morgan organized a group of businessmen to avert a crash by pledging their own money. Roosevelt aided Morgan's intervention by allowing U.S. Steel to acquire the Tennessee Coal, Iron and Railroad Company despite antitrust concerns, and by authorizing Cortelyou to raise bonds and commit federal funds to the banks.[78] Roosevelt's reputation in Wall Street fell to new lows following the panic, but the president remained broadly popular.[79] In the aftermath of the panic, most congressional leaders agreed on the need to reform the nation's financial system. With the support of Roosevelt, Senator Aldrich introduced a bill to allow National Banks to issue emergency currency, but his proposal was defeated by Democrats and progressive Republicans who believed that it was overly favorable to Wall Street. Congress instead passed the Aldrich–Vreeland Act, which created the National Monetary Commission to study the nation's banking system; the commission's recommendations would later form the basis of the Federal Reserve System.[80]
Tariffs[]
Many Republicans viewed the tariff as the key plank of their economic policy in the aftermath of the Panic of 1893.[81] The tariff protected domestic manufacturing against foreign competition, and was also a major source of government funding, constituting over one-third of federal revenue in 1901.[82] McKinley had been a committed protectionist, and the Dingley Tariff of 1897 represented a major increase in tariff rates. McKinley also negotiated bilateral reciprocity treaties with France, Argentina, and other countries in an attempt to expand foreign trade while still keeping overall tariff rates high.[81] Unlike McKinley and other nineteenth-century Republican presidents, Roosevelt had never been a strong advocate of the protective tariff, nor did he place a high emphasis on tariffs in general.[83] When Roosevelt took office, McKinley's reciprocity treaties were pending before the Senate, and many assumed that they would be ratified despite the opposition of Aldrich and other conservatives. After conferring with Aldrich, Roosevelt decided not to push Senate ratification of the treaties in order to avoid an intra-party conflict.[84] He did, however, successfully pressure Congress to ratify reciprocal tariff treaties with the Philippines and, after overcoming domestic sugar interests, with Cuba.[85]
The issue of the tariff lay dormant throughout Roosevelt's first term,[86] but it continued to be an important campaign topic for both parties.[87] Proponents of tariff reduction asked Roosevelt to call a special session of Congress to address the issue in early 1905, but Roosevelt was only willing to issue a cautious endorsement of a cut in tariff rates, and no further action was taken on the tariff during Roosevelt's tenure.[88] In the first decade of the 20th century, the country experienced a period of sustained inflation for the first time since the early 1870s, and Democrats and other free trade advocates blamed rising prices on high tariff rates.[89] Tariff reduction became an increasingly important national issue, and Congress would pass a major tariff law in 1909, shortly after Roosevelt left office.[90]
Move to Left Center, 1907–1909[]

By 1907, Roosevelt identified himself with the "left center" of the Republican Party.[91][92] He explained his balancing act:
- Again and again in my public career I have had to make head against mob spirit, against the tendency of poor, ignorant and turbulent people who feel a rancorous jealousy and hatred of those who are better off. But during the last few years it has been the wealthy corruptionists of enormous fortune, and of enormous influence through their agents of the press, pulpit, colleges and public life, with whom I've had to wage bitter war."[93]
Growing popular outrage at corporate scandals, along with reporting of muckraking journalists like Lincoln Steffens and Ida Tarbell, contributed to a split in the Republican Party between conservatives like Aldrich and progressives like Albert B. Cummins and Robert M. La Follette. Roosevelt did not fully embrace the left wing of his party, but he adopted many of their proposals.[94]
In his last two years in office, Roosevelt abandoned his cautious approach toward big business, lambasting his conservative critics and calling on Congress to enact a series of radical new laws.[95][96] Roosevelt sought to replace the laissez-faire economic environment with a new economic model which included a larger regulatory role for the federal government. He believed that 19th-century entrepreneurs had risked their fortunes on innovations and new businesses, and that these capitalists had been rightly rewarded. By contrast, he believed that 20th-century capitalists risked little but nonetheless reaped huge and unjust, economic rewards. Without a redistribution of wealth away from the upper class, Roosevelt feared that the country would turn to radicalism or fall to revolution.[97]
In January 1908, Roosevelt sent a special message to Congress, calling for the restoration of an employer's liability law, which had recently been struck down by the Supreme Court due to its application to intrastate corporations.[98] He also called for a national incorporation law (all corporations had state charters, which varied greatly state by state), a federal income tax and inheritance tax (both targeted at the rich), limits on the use of court injunctions against labor unions during strikes (injunctions were a powerful weapon that mostly helped business), an eight-hour work day for federal employees, a postal savings system (to provide competition for local banks), and legislation barring corporations from contributing to political campaigns.[99][100]
Roosevelt's increasingly radical stance proved popular in the Midwest and Pacific Coast, and among farmers, teachers, clergymen, clerical workers and some proprietors, but appeared as divisive and unnecessary to eastern Republicans, corporate executives, lawyers, party workers, and many members of Congress.[101] Populist Democrats such as William Jennings Bryan expressed admiration for Roosevelt's message, and one Southern newspaper called for Roosevelt to run as a Democrat in 1908, with Bryan as his running mate.[102] Despite the public support offered by Democratic congressional leaders like John Sharp Williams, Roosevelt never seriously considered leaving the Republican Party during his presidency.[103] Roosevelt's move to the left was supported by some congressional Republicans and many in the public, but conservative Republicans such as Senator Nelson Aldrich and Speaker Joseph Gurney Cannon remained in control of Congress.[104] These Republican leaders blocked the more ambitious aspects of Roosevelt's agenda,[105] though Roosevelt won passage of a new Federal Employers Liability Act and other laws, such as a restriction of child labor in Washington, D.C.[104]
States admitted[]
One new state, Oklahoma, was admitted to the Union while Roosevelt was in office. Oklahoma, which was formed out of Indian Territory and Oklahoma Territory, became the 46th state on November 16, 1907. Congress had established the Indian Territory after several Native American tribes had been relocated to the area following the passage of the Indian Removal Act of 1830. Congress had created Oklahoma Territory in 1890 out of a portion of Indian Territory, opening up the region to settlement by whites.[106] Native American leaders in the Indian Territory sought to create the State of Sequoyah, but their efforts were defeated in Congress. At Roosevelt's suggestion, Indian Territory and Oklahoma Territory were combined to form one state under the Oklahoma Enabling Act. The act also contained provisions encouraging New Mexico Territory and Arizona Territory to begin the process of gaining admission as states.[citation needed]
Foreign policy[]
Big Stick diplomacy[]
Roosevelt was good at coining phrases to concisely summarize his policies. "Big stick" was his catch phrase for his hard pushing foreign policy: "Speak softly and carry a big stick; you will go far."[107] Roosevelt described his style as "the exercise of intelligent forethought and of decisive action sufficiently far in advance of any likely crisis."[108] As practiced by Roosevelt, big stick diplomacy had five components. First it was essential to possess serious military capabilities that force the adversary to pay close attention. At the time that meant a world-class navy. Roosevelt never had a large army at his disposal. The other qualities were to act justly toward other nations, never to bluff, to strike only if prepared to strike hard, and the willingness to allow the adversary to save face in defeat.[109]
Great power politics[]
Victory in the Spanish–American War had made the United States a power in both the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean, and Roosevelt was determined to continue the expansion of U.S. influence.[110] Reflecting this view, Roosevelt stated in 1905, "We have become a great nation, forced by the face of its greatness into relations with the other nations of the earth, and we must behave as beseems a people with such responsibilities." Roosevelt believed that the United States had a duty to uphold a balance of power in international relations and seek to reduce tensions among the great powers.[111] He was also adamant in upholding the Monroe Doctrine, the American policy of opposing European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere.[112] Roosevelt viewed the German Empire as the biggest potential threat to the United States, and he feared that the Germans would attempt to establish a base in the Caribbean Sea. Given this fear, Roosevelt pursued closer relations with Britain, a rival of Germany, and responded skeptically to German Kaiser Wilhelm II's efforts to curry favor with the United States.[113] Roosevelt also attempted to expand U.S. influence in East Asia and the Pacific, where the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire exercised considerable authority. One important aspect of Roosevelt's strategy in East Asia was the Open Door Policy, which called for keeping China open to trade from all countries.[114]
A major turning point in establishing America's role in European affairs was the Moroccan crisis of 1905–1906. France and Britain had agreed that France would dominate Morocco, but Germany suddenly protested aggressively, with the disregard for quiet diplomacy characteristic of Kaiser Wilhelm. Berlin asked Roosevelt to serve as an intermediary, and he helped arrange a multinational conference at Algeciras, Morocco, where the crisis was resolved. Roosevelt advised Europeans in the future the United States would probably avoid any involvement in Europe, even as a mediator, so European foreign ministers stopped including the United States as a potential factor in the European balance of power.[115][116]
Aftermath of the Spanish–American War[]

Philippines[]
Roosevelt inherited a country torn by debate over the territories acquired in the Spanish–American War. Roosevelt believed that Cuba should be quickly granted independence and that Puerto Rico should remain a semi-autonomous possession under the terms of the Foraker Act. He wanted U.S. forces to remain in the Philippines to establish a stable, democratic government, even in the face of an insurrection led by Emilio Aguinaldo. Roosevelt feared that a quick U.S. withdrawal would lead to instability in the Philippines or an intervention by a major power such as Germany or Japan.[117]
The Filipino insurrection largely ended with the capture of Miguel Malvar in 1902.[118] In remote Southern areas, the Muslim Moros resisted American rule in an ongoing conflict known as the Moro Rebellion,[119] but elsewhere the insurgents came to accept American rule. Roosevelt continued the McKinley policies of removing the Catholic friars (with compensation to the Pope), upgrading the infrastructure, introducing public health programs, and launching a program of economic and social modernization. The enthusiasm shown in 1898-99 for colonies cooled off, and Roosevelt saw the islands as "our heel of Achilles." He told Taft in 1907, "I should be glad to see the islands made independent, with perhaps some kind of international guarantee for the preservation of order, or with some warning on our part that if they did not keep order we would have to interfere again."[120] By then the president and his foreign policy advisers turned away from Asian issues to concentrate on Latin America, and Roosevelt redirected Philippine policy to prepare the islands to become the first Western colony in Asia to achieve self-government.[121] Though most Filipino leaders favored independence, some minority groups, especially the Chinese who controlled much of local business, wanted to stay under American rule indefinitely.[122]
The Philippines was a major target for the progressive reformers. A report to Secretary of War Taft provided a summary of what the American civil administration had achieved. It included, in addition to the rapid building of a public school system based on English teaching:
- steel and concrete wharves at the newly renovated Port of Manila; dredging the River Pasig,; streamlining of the Insular Government; accurate, intelligible accounting; the construction of a telegraph and cable communications network; the establishment of a postal savings bank; large-scale road-and bridge-building; impartial and incorrupt policing; well-financed civil engineering; the conservation of old Spanish architecture; large public parks; a bidding process for the right to build railways; Corporation law; and a coastal and geological survey.[123]
Cuba[]
While the Philippines would remain under U.S. control until 1946, Cuba gained independence in 1902.[124] The Platt Amendment, passed during the final year of McKinley's tenure, made Cuba a de facto protectorate of the United States.[125] Roosevelt won congressional approval for a reciprocity agreement with Cuba in December 1902, thereby lowering tariffs on trade between the two countries.[126] In 1906, an insurrection erupted against Cuban President Tomás Estrada Palma due to the latter's alleged electoral fraud. Both Estrada Palma and his liberal opponents called for an intervention by the U.S., but Roosevelt was reluctant to intervene.[127] When Estrada Palma and his Cabinet resigned, Secretary of War Taft declared that the U.S. would intervene under the terms of the Platt Amendment, beginning the Second Occupation of Cuba.[128] U.S. forces restored peace to the island, and the occupation ceased shortly before the end of Roosevelt's presidency.[129]
Puerto Rico[]
Puerto Rico had been something of an afterthought during the Spanish–American War, but it assumed importance due to its strategic position in the Caribbean Sea. The island provided an ideal naval base for defense of the Panama Canal, and it also served as an economic and political link to the rest of Latin America. Prevailing racist attitudes made Puerto Rican statehood unlikely, so the U.S. carved out a new political status for the island. The Foraker Act and subsequent Supreme Court cases established Puerto Rico as the first unincorporated territory, meaning that the United States Constitution would not fully apply to Puerto Rico. Though the U.S. imposed tariffs on most Puerto Rican imports, it also invested in the island's infrastructure and education system. Nationalist sentiment remained strong on the island and Puerto Ricans continued to primarily speak Spanish rather than English.[130]
Military reforms[]

Roosevelt placed an emphasis on expanding and reforming the United States military.[131] The United States Army, with 39,000 men in 1890, was the smallest and least powerful army of any major power in the late 19th century. By contrast, France's army consisted of 542,000 soldiers.[132] The Spanish–American War had been fought mostly by temporary volunteers and state national guard units, and it demonstrated that more effective control over the department and bureaus was necessary.[133] Roosevelt gave strong support to the reforms proposed by Secretary of War Elihu Root, who wanted a uniformed chief of staff as general manager and a European-style general staff for planning. Overcoming opposition from General Nelson A. Miles, the Commanding General of the United States Army, Root succeeded in enlarging West Point and establishing the U.S. Army War College as well as the general staff. Root also changed the procedures for promotions, organized schools for the special branches of the service, devised the principle of rotating officers from staff to line,[134] and increased the Army's connections to the National Guard.[135]
Upon taking office, Roosevelt made naval expansion a priority, and his tenure saw an increase in the number of ships, officers, and enlisted men in the Navy.[135] With the publication of The Influence of Sea Power upon History, 1660–1783 in 1890, Captain Alfred Thayer Mahan had been immediately hailed as an outstanding naval theorist by the leaders of Europe. Roosevelt paid very close attention to Mahan's emphasis that only a nation with a powerful fleet could dominate the world's oceans, exert its diplomacy to the fullest, and defend its own borders.[136][137] By 1904, the United States had the fifth largest navy in the world, and by 1907, it had the third largest. Roosevelt sent what he dubbed the "Great White Fleet" around the globe in 1908–1909 to make sure all the naval powers understood the United States was now a major player. Though Roosevelt's fleet did not match the overall strength of the British fleet, it became the dominant naval force in the Western Hemisphere.[138][139][140]
Rapprochement with Great Britain[]

The Great Rapprochement between Britain and the United States had begun with British support of the United States during the Spanish–American War, and it continued as Britain withdrew its fleet from the Caribbean in favor of focusing on the rising German naval threat.[141] Roosevelt sought a continuation of close relations with Britain in order to ensure peaceful, shared hegemony over the Western hemisphere. With the British acceptance of the Monroe Doctrine and American acceptance of the British control of Canada, only two potential major issues remained between the U.S. and Britain: the Alaska boundary dispute and construction of a canal across Central America. Under McKinley, Secretary of State Hay had negotiated the Hay–Pauncefote Treaty, in which the British consented to U.S. construction of the canal. Roosevelt won Senate ratification of the treaty in December 1901.[142]
The boundary between Alaska and Canada had become an issue in the late 1890s due to the Klondike Gold Rush, as American and Canadian prospectors in Yukon and Alaska competed for gold claims. A treaty on the border between Alaska and Canada had been reached by Britain and Russia in the 1825 Treaty of Saint Petersburg, and the United States had assumed Russian claims on the region through the 1867 Alaska Purchase. The United States argued that the treaty had given Alaska sovereignty over disputed territories which included the gold rush boom towns of Dyea and Skagway.[143] The Venezuela Crisis briefly threatened to disrupt peaceful negotiations over the border, but conciliatory actions by the British during the crisis helped defuse any possibility of broader hostilities.[144] In January 1903, the U.S. and Britain reached the Hay–Herbert Treaty, which would empower a six-member tribunal, composed of American, British, and Canadian delegates, to set the border between Alaska and Canada. With the help of Senator Henry Cabot Lodge, Roosevelt won the Senate's consent to the Hay–Herbert Treaty in February 1903.[145] The tribunal consisted of three American delegates, two Canadian delegates, and Lord Alverstone, the lone delegate from Britain itself. Alverstone joined with the three American delegates in accepting most American claims, and the tribunal announced its decision in October 1903. The outcome of the tribunal strengthened relations between the United States and Britain, though many Canadians were outraged by the tribunal's decision.[146]
Venezuela Crisis and Roosevelt Corollary[]
In December 1902, an Anglo-German blockade of Venezuela began an incident known as the Venezuelan Crisis. The blockade originated due to money owed by Venezuela to European creditors. Both powers assured the U.S. that they were not interested in conquering Venezuela, and Roosevelt sympathized with the European creditors, but he became suspicious that Germany would demand territorial indemnification from Venezuela. Roosevelt and Hay feared that even an allegedly temporary occupation could lead to a permanent German military presence in the Western Hemisphere.[113] As the blockade began, Roosevelt mobilized the U.S. fleet under the command of Admiral George Dewey.[147] Roosevelt threatened to destroy the German fleet unless the Germans agreed to arbitration regarding the Venezuelan debt, and Germany chose arbitration rather than war.[148] Through American arbitration, Venezuela reached a settlement with Germany and Britain in February 1903.[149]

Though Roosevelt would not tolerate European territorial ambitions in Latin America, he also believed that Latin American countries should pay the debts they owed to European credits.[150] In late 1904, Roosevelt announced his Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine. It stated that the U.S. would intervene in the finances of unstable Caribbean and Central American countries if they defaulted on their debts to European creditors and, in effect, guarantee their debts, making it unnecessary for European powers to intervene to collect unpaid debts. Roosevelt's pronouncement was especially meant as a warning to Germany, and had the result of promoting peace in the region, as the Germans decided to not intervene directly in Venezuela and in other countries.[151]
A crisis in the Dominican Republic became the first test case for the Roosevelt Corollary. Deeply in debt, the nation struggled to repay its European creditors. Fearing another intervention by Germany and Britain, Roosevelt reached an agreement with Dominican President Carlos Felipe Morales to take temporary control of the Dominican economy, much as the U.S. had done on a permanent basis in Puerto Rico. The U.S. took control of the Dominican customs house, brought in economists such as Jacob Hollander to restructure the economy, and ensured a steady flow of revenue to the Dominican Republic's foreign creditors. The intervention stabilized the political and economic situation in the Dominican Republic, and the U.S. role on the island would serve as a model for Taft's dollar diplomacy in the years after Roosevelt left office.[152]
Panama Canal[]


Roosevelt sought the creation of a canal through Central America which would link the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. Most members of Congress preferred that the canal cross through Nicaragua, which was eager to reach an agreement, but Roosevelt preferred the isthmus of Panama, under the loose control of Colombia. Colombia had been engulfed in a civil war since 1898, and a previous attempt to build a canal across Panama had failed under the leadership of Ferdinand de Lesseps. A presidential commission appointed by McKinley had recommended the construction of the canal across Nicaragua, but it noted that a canal across Panama could prove less expensive and might be completed more quickly.[153] Roosevelt and most of his advisers favored the Panama Canal, as they believed that war with a European power, possibly Germany, could soon break out over the Monroe Doctrine and the U.S. fleet would remain divided between the two oceans until the canal was completed.[154] After a long debate, Congress passed the Spooner Act of 1902, which granted Roosevelt $170 million to build the Panama Canal.[155] Following the passage of the Spooner Act, the Roosevelt administration began negotiations with the Colombian government regarding the construction of a canal through Panama.[154]
The U.S. and Colombia signed the Hay–Herrán Treaty in January 1903, granting the U.S. a lease across the isthmus of Panama.[154] The Colombian Senate refused to ratify the treaty, and attached amendments calling for more money from the U.S. and greater Colombian control over the canal zone.[156] Panamanian rebel leaders, long eager to break off from Colombia, appealed to the United States for military aid.[157] Roosevelt saw the leader of Colombia, José Manuel Marroquín, as a corrupt and irresponsible autocrat, and he believed that the Colombians had acted in bad faith by reaching and then rejecting the treaty.[158] After an insurrection broke out in Panama, Roosevelt dispatched the USS Nashville to prevent the Colombian government from landing soldiers in Panama, and Colombia was unable to re-establish control over the province.[159] Shortly after Panama declared its independence in November 1903, the U.S. recognized Panama as an independent nation and began negotiations regarding construction of the canal. According to Roosevelt biographer Edmund Morris, most other Latin American nations welcomed the prospect of the new canal in hopes of increased economic activity, but anti-imperialists in the U.S. raged against Roosevelt's aid to the Panamanian separatists.[160]
Secretary of State Hay and French diplomat Philippe-Jean Bunau-Varilla, who represented the Panamanian government, quickly negotiated the Hay–Bunau-Varilla Treaty. Signed on November 18, 1903, it established the Panama Canal Zone—over which the United States would exercise sovereignty—and insured the construction of an Atlantic to Pacific ship canal across the Isthmus of Panama. Panama sold the Canal Zone (consisting of the Panama Canal and an area generally extending five miles (8.0 km) on each side of the centerline) to the United States for $10 million and a steadily increasing yearly sum.[161] In February 1904, Roosevelt won Senate ratification of the treaty in a 66-to-14 vote.[162] The Isthmian Canal Commission, supervised by Secretary of War Taft, was established to govern the zone and oversee the construction of the canal.[163] Roosevelt appointed George Whitefield Davis as the first governor of the Panama Canal Zone and John Findley Wallace as the Chief Engineer of the canal project.[57] When Wallace resigned in 1905, Roosevelt appointed John Frank Stevens, who built a railroad in the canal zone and initiated the construction of a lock canal.[164] Stevens was replaced in 1907 by George Washington Goethals, who saw construction through to its completion.[165] Roosevelt traveled to Panama in November 1906 to inspect progress on the canal,[18] becoming the first sitting president to travel outside of the United States.[166]
East Asia[]
Russo-Japanese War[]
Russia had occupied the Chinese region of Manchuria in the aftermath of the 1900 Boxer Rebellion, and the United States, Japan, and Britain all sought the end of its military presence in the region. Russia agreed to withdraw its forces in 1902, but it reneged on this promise and sought to expand its influence in Manchuria to the detriment of the other powers.[167] Roosevelt was unwilling to consider using the military to intervene in the far-flung region, but Japan prepared for war against Russia in order to remove it from Manchuria.[168] When the Russo-Japanese War broke out in February 1904, Roosevelt sympathized with the Japanese but sought to act as a mediator in the conflict. He hoped to uphold the Open Door policy in China and prevent either country from emerging as the dominant power in East Asia.[169] Throughout 1904, both Japan and Russia expected to win the war, but the Japanese gained a decisive advantage after capturing the Russian naval base at Port Arthur in January 1905.[170] In mid-1905, Roosevelt persuaded the parties to meet in a peace conference in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, starting on August 5. His persistent and effective mediation led to the signing of the Treaty of Portsmouth on September 5, ending the war. For his efforts, Roosevelt was awarded the 1906 Nobel Peace Prize.[171] The Treaty of Portsmouth resulted in the removal of Russian troops from Manchuria, and it gave Japan control of Korea and the southern half of Sakhalin Island.[172]
Relations with Japan[]
The American annexation of Hawaii in 1898 was stimulated in part by fear that otherwise Japan would dominate the Hawaiian Republic.[173] Likewise Japan was the alternative to American takeover of the Philippines in 1900.[174] These events were part of the American goal of transitioning into a naval world power, but it needed to find a way to avoid a military confrontation in the Pacific with Japan. One of Theodore Roosevelt's high priorities during his presidency and even afterwards, was the maintenance of friendly relations with Japan.[175]
In the late 19th century, the opening of sugar plantations in the Kingdom of Hawaii led to the immigration of large numbers of Japanese families. Recruiters sent about 124,000 Japanese workers to more than fifty sugar plantations. China, the Philippines, Portugal and other countries sent an additional 300,000 workers.[176] When Hawaii became part of the U.S. in 1898, the Japanese were the largest element of the population then. Although immigration from Japan largely ended by 1907, they have remained the largest element ever since.
President Roosevelt made sure there was a strategy to defend the islands against possible Japanese aggression, especially in 1907 when tensions were high. In June 1907 he met with military and naval leaders to decide on a series of operations to be carried in the Philippines which included shipments of coal, military rations, and the movement of guns and munitions.[177] The October 23, 1907 Puck magazine cover[178] shows President Theodore Roosevelt defending the nation of Japan from attack – Roosevelt is wearing a military uniform with the Japanese Imperial seal on his hat. He holds a rifle and confronts two rolled-up U.S. newspapers labeled the 'Sun' and 'World' who are also holding rifles and confronting Roosevelt – In the magazine caption, Roosevelt stated that the war talk predicting a future conflict between the U.S. and Japan was based entirely on these incendiary newspapers, which sought to increase their sales, and for that reason, these newspapers had attacked Roosevelt's representative Minister William Howard Taft, who Roosevelt had again sent to Tokyo to promote improved communications between their two nations. Much of the confrontation was sparked by racism shown against Japanese Americans living in California.[179]
Roosevelt saw Japan as the rising power in Asia, in terms of military strength and economic modernization. He viewed Korea as a backward nation and did not object to Japan's attempt to gain control over Korea. With the withdrawal of the American legation from Seoul and the refusal of the Secretary of State to receive a Korean protest mission, the Americans signaled they would not intervene militarily to stop Japan's planned takeover of Korea.[180] In mid-1905, Taft and Japanese Prime Minister Katsura Tarō jointly produced the Taft–Katsura agreement. Nothing new was decided but each side clarified its position. Japan stated that it had no interest in the Philippines, while the U.S. stated that it considered Korea to be part of the Japanese sphere of influence.[181]
Regarding China, the two nations cooperated with the European powers in suppressing the Boxer Rebellion in China in 1900, but the U.S. was increasingly troubled about Japan's denial of the Open Door Policy that would ensure that all nations could do business with China on an equal basis.
Vituperative anti-Japanese sentiment (especially on the West Coast) soured relations in the early 20th century.[182] President Theodore Roosevelt did not want to anger Japan by passing legislation to bar Japanese immigration to the U.S. as had been done for Chinese immigration. Instead there was an informal "Gentlemen's Agreement of 1907" between the foreign ministers Elihu Root and Japan's Tadasu Hayashi. The Agreement said Japan would stop emigration of Japanese laborers to the U.S. or Hawaii, and there would not be segregation in California. The agreements remained effect until 1924 when Congress forbade all immigration from Japan—a move that angered Japan.[183][184]
Charles Neu concludes that Roosevelt's policies were a success:
By the close of his presidency it was a largely successful policy based upon political realities at home and in the Far East and upon a firm belief that friendship with Japan was essential to preserve American interests in the Pacific ... Roosevelt's diplomacy during the Japanese-American crisis of 1906-1909 was shrewd, skillful, and responsible.[185]
Algeciras Conference[]
In 1906, at the request of Kaiser Wilhelm II, Roosevelt convinced France to attend the Algeciras Conference as part of an effort to resolve the First Moroccan Crisis. After signing the Entente Cordiale with Britain, France had sought to assert its dominance over Morocco, and a crisis had begun after Germany protested this move. By asking Roosevelt to convene an international conference on Morocco, Kaiser Wilhelm II sought to test the new Anglo-British alliance, check French expansion, and potentially draw the United States into an alliance against France and Britain.[186] Senator Augustus Octavius Bacon protested U.S. involvement in European affairs, but Secretary of State Root and administration allies like Senator Lodge helped defeat Bacon's resolution condemning U.S. participation in the Algeciras Conference.[187] The conference was held in the city of Algeciras, Spain, and 13 nations attended. The key issue was control of the police forces in the Moroccan cities, and Germany, with a weak diplomatic delegation, found itself in a decided minority. Hoping to avoid an expansion of German power in North Africa, Roosevelt secretly supported France, and he cooperated closely with the French ambassador. An agreement among the powers, reached on April 7, 1906, slightly reduced French influence by reaffirming the independence of the Sultan of Morocco and the economic independence and freedom of operations of all European powers within the country. Germany gained nothing of importance but was mollified and stopped threatening war.[188]
Elections[]
Election of 1904[]
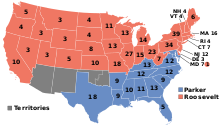
Before and during his presidency, Roosevelt built up a strong following within the Republican Party, but his re-nomination in 1904 was far from certain at the end of 1901.[189] Many expected Senator Mark Hanna, a confidante of former President McKinley, to win the party's 1904 presidential nomination.[190] Support for Hanna was especially strong among conservative businessmen who opposed many of Roosevelt's policies,[191] though Hanna lacked his own national organization, and even in his home state he was opposed by influential Senator Joseph Foraker.[192] Hanna and another prominent party leader, Matthew Quay of Pennsylvania, both died in 1904.[193] Other potential rivals for the 1904 Republican presidential nomination, including Leslie Shaw and Charles W. Fairbanks, failed to galvanize support for their candidacies.[189] At the 1904 Republican National Convention, Roosevelt secured his own nomination, but his preferred vice-presidential running mate, Robert R. Hitt, was not nominated.[194] Senator Fairbanks, a favorite of conservatives, gained the vice-presidential nomination.[193]
The Democratic Party's presidential nominee in 1904 was Alton B. Parker, the chief judge of the New York Court of Appeals. Democratic leaders hoped that Parker, whose political positions were largely unknown, would be able unify the populist followers of William Jennings Bryan with the conservative supporters of former President Grover Cleveland. Parker was unable to unite the party, and many Democrats supported Roosevelt.[195] Democrats alleged that the Republican campaign extorted large contributions from corporations, but these allegations had little impact on the election.[196] As Parker moved his party in a conservative direction, Republicans performed well among progressives and centrists.[197] Roosevelt won 56% of the popular vote while Parker received 38% of the popular; Roosevelt also won the electoral vote 336 to 140. Roosevelt's victory made him first president to be elected to a full term of his own after having succeeded to the presidency upon the death of a predecessor. His popular vote margin of 18.8% was the largest margin in U.S. history until the 1920 presidential election.[198] On election night, as it became clear that he had won in a landslide, Roosevelt pledged not to run for a third term.[199]
Election of 1908 and transition[]

Roosevelt had mixed feelings about a third term, as he enjoyed being president and was still relatively youthful, but felt that a limited number of terms provided a check against dictatorship. Roosevelt ultimately decided to stick to his 1904 pledge not to run for a third term, and he threw his support behind a successor so as to avoid a potential pro-Roosevelt delegate stampede at the 1908 Republican National Convention. Roosevelt personally favored Secretary of State Elihu Root, but Root's ill health made him an unsuitable candidate. New York Governor Charles Evans Hughes loomed as a potentially strong candidate and shared Roosevelt's progressivism, but Roosevelt disliked him and considered him to be too independent. Instead, Roosevelt settled on his Secretary of War, William Howard Taft, who had ably served under Presidents Harrison, McKinley, and Roosevelt in various positions. Roosevelt and Taft had been friends since 1890, and Taft had consistently supported President Roosevelt's policies.[200] Many conservatives wanted to re-take leadership of the party from the progressive Roosevelt.[201] Senator Joseph Foraker, who like Taft was from Ohio, briefly emerged as the main conservative candidate for the GOP nomination.[202] However, Taft defeated Foraker's attempt to win control of the Ohio Republican Party and entered the convention as the strong favorite over Foraker, Hughes, and Senator Philander Knox.[203]
At the 1908 Republican convention, many chanted for "four years more" of a Roosevelt presidency, but Taft won the nomination after Roosevelt's close friend, Henry Cabot Lodge, made it clear that Roosevelt was not interested in a third term.[204] In a speech accepting the Republican nomination, Taft promised to continue the policies of Roosevelt, but as the campaign progressed he minimized his reliance on Roosevelt, and did not ask the president to publicly campaign for him.[205] The Democrats nominated William Jennings Bryan, who had been the party's presidential candidate in 1896 and 1900. Bryan, a populist Democrat widely regarded as a strong speaker, thought that Taft was a weak candidate and hoped that the public would tire of the Republican leadership the country had experienced since the 1896 election.[206] The platforms of the two parties differed little: both called for antitrust actions, railroad and labor regulations, and a revision of the tariff.[207] As election day approached, it became clear that Taft would retain the loyalty of Republican voters and win a wide victory over Bryan, who had failed to find a winning issue on which to campaign. Taft won 321 of the 483 electoral votes and 51.6% of the popular vote. Republicans also retained control of both houses of Congress. Roosevelt regarded the victory of his chosen successor as a vindication of his policies and presidency.[208] As he left office, Roosevelt was widely regarded as the most powerful and influential president since Abraham Lincoln.[209] Taft's decision to retain few members of Roosevelt's Cabinet alienated Roosevelt, although Roosevelt continued to support his successor throughout the transition period.[210]
Historical reputation[]

Roosevelt was popular as he left office, and he remained a major world figure until his death in 1919. His own contemporaries viewed his presidency as influential; former Senator William E. Chandler wrote in January 1909 that Roosevelt "changed the course of American politics. We can never go back to where we were under Hanna."[211] After his death, Roosevelt was overshadowed by other figures, but the interest of historians and the American public in Roosevelt was reinvigorated after World War II. Historian John Morton Blum's 1954 book, The Republican Roosevelt, advanced the thesis that Roosevelt had been the first truly modern president, and many historians have argued that Roosevelt's presidency served as a model to subsequent presidents.[212]
Historian Lewis L. Gould summarizes the consensus view of historians, stating that Roosevelt was "a strong, effective executive whose policies foreshadowed the welfare state."[212] Gould also writes, "if Roosevelt fell short of the first rank of president, he qualified for that ambivalent rating of 'near great,' conferred upon him in the polls that historians take with each other.[213] A 2018 poll of the American Political Science Association ranked Roosevelt as the fourth greatest president in history, after George Washington, Abraham Lincoln, and Franklin D. Roosevelt.[214]
Roosevelt is a hero to modern liberals for his proposals in 1907–12 that presaged the modern welfare state of the New Deal Era, and put the environment on the national agenda. Conservatives admire his "big stick" diplomacy and commitment to military values. Dalton says, "Today he is heralded as the architect of the modern presidency, as a world leader who boldly reshaped the office to meet the needs of the new century and redefined America's place in the world."[215] However, the New Left has criticized him for his interventionist and imperialist approach to nations he considered "uncivilized". Conservatives reject his vision of the welfare state and emphasis on the superiority of government over private action.[216][217]
Notes[]
References[]
- ^ William H. Harbaugh, "Roosevelt, Theodore (27 October 1858–06 January 1919)" American National Biography (1999) online
- ^ Thomas A. Bailey, Presidential Greatness (1966) p. 308
- ^ "Impact and Legacy", Biography, American President, The Rector and Visitors of the University of Virginia, 2005, retrieved March 7, 2006.
- ^ "Legacy", T Roosevelt, PBS, retrieved March 7, 2006.
- ^ "The Swearing In of Theodore Roosevelt: September 14, 1901". Joint Congressional Committee on Inaugural Ceremonies. Retrieved April 24, 2017.
- ^ "Theodore Roosevelt". Washington, D.C.: The White House. Retrieved April 25, 2017.
- ^ Wilcox, Ansley (1902). "Theodore Roosevelt, President" (PDF). National Park Service, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved January 23, 2017.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 10–12.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 9-10
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 22-23
- ^ Morris (2001) p. 62
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 13–15.
- ^ Morris (2001) p. 78
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, p. 46.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 103, 122.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 308-309
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 394-395
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, p. 203.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Rouse, Robert (March 15, 2006). "Happy Anniversary to the first scheduled presidential press conference – 93 years young!". American Chronicle. Archived from the original on November 23, 2012. Retrieved November 11, 2008.
- ^ "U.S. Senate: Supreme Court Nominations: 1789-Present". Washington, D.C.: U.S. Senate. Retrieved March 25, 2017.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 129-131
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 313-314
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 458-464
- ^ see George Mowry, The Era of Theodore Roosevelt and the Birth of Modern America, 1900–1912 (1954), ch. 1
- ^ see Lewis L. Gould, The Presidency of Theodore Roosevelt. (1991), ch 1
- ^ Chessman, p 6
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 27–30
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 26–27.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 27–28, 31–32.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 37–38.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, pp. 45–47.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 49–50.
- ^ Morris (2001) p. 195–196
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 205–208
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 101–102.
- ^ McGerr (2003), p. 157
- ^ "The Supreme Court upholds Prosecution of the Beef Trust," in Frank N. Magill, ed., Great Events from History II: Business and Commerce Series Volume 1 1897-1923 (1994) pp 107-111
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, pp. 145–146.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 417–419
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 422–429
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 428–433
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 442–443
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, pp. 155–156.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 156–157.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, pp. 158–159.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 445–448
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 160–162.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 162–163.
- ^ Blum (1954) pp 43–44
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 272–274.
- ^ McGerr (2003), pp. 172–174
- ^ McGerr (2003), pp. 158–159
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 204–205.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 477–478
- ^ Benjamin Redekop, (2014). "Embodying the Story: The Conservation Leadership of Theodore Roosevelt" in Leadership DOI: 10.1177/1742715014546875. online Archived January 14, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 32-33
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, pp. 191–192.
- ^ W. Todd Benson, President Theodore Roosevelt's Conservations Legacy (2003)
- ^ Douglas Brinkley, The Wilderness Warrior: Theodore Roosevelt and the Crusade for America (2010)
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 198–199.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 515-519
- ^ McGerr (2003), pp. 166–167
- ^ Gifford Pinchot, Breaking New Ground, (1947) p. 32.
- ^ McGerr (2003), pp. 167–169
- ^ Morris (2001) p. 131
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 31–32
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 271–272
- ^ McGerr (2003), pp. 118–125
- ^ McGerr (2003), pp. 143–144
- ^ McGerr (2003), pp. 126, 138–142
- ^ Jump up to: a b Brands, TR (1999) pp 421–426
- ^ McGerr (2003), pp. 198–200
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 455, 472
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 471–473
- ^ Morris (2001) p. 511
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 495–496
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 112–113.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 497–501
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 501, 504–505
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 270–272.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, pp. 23–24.
- ^ Gould 2011, p. 35.
- ^ Gould 2003, p. 133.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 24–25.
- ^ Gould 2011, p. 104.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 25–26.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 60–61.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 141–142.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 32–33.
- ^ Gould 2003, pp. 174–175.
- ^ In December 1907 he wrote his British friend Arthur Hamilton Lee. "To use the terminology of Continental politics, I am trying to keep the left center together." Elting E. Morrison, ed., The Letters of Theodore Roosevelt (1952) vol 6 p 875.
- ^ See Nathan Miller, Theodore Roosevelt: A Life (1992) chapter 21, "'To Keep the Left Center Together'" pp 463-82, covering the last two years of his presidency.
- ^ Roosevelt to Arthur Hamilton Lee, December 16, 1907, in Morrison, ed., The Letters of Theodore Roosevelt (1952) vol 6 p 874.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 150–152.
- ^ Miller, pp 463-82.
- ^ Gary Murphy, "Theodore Roosevelt, Presidential Power and the Regulation of the Market" in Serge Ricard, ed. A companion to Theodore Roosevelt (2011) pp 154–172.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 430–431, 436
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 505–507
- ^ Brands, TR (1997) ch 21
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 235–236.
- ^ Mowry (1954)
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 508-509
- ^ Gould 2011, p. 270.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Morris (2001) pp. 510–511
- ^ Brands, TR (1997) ch 27
- ^ "Today in History: November 16". Washington, D.C.: Library of Congress.
- ^ Suzy Platt (1993). Respectfully Quoted: A Dictionary of Quotations. Barnes & Noble. p. 123.
- ^ David McCullough (2001). The Path Between the Seas: The Creation of the Panama Canal, 1870-1914. Simon and Schuster. p. 508. ISBN 9780743201377.
- ^ Cathal J. Nolan (2004). Ethics and Statecraft: The Moral Dimension of International Affairs. Greenwood. pp. 103–104. ISBN 9780313314933.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 13–14.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 167–168.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 71–72.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, pp. 72–73.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 81–82.
- ^ Ernest R. May, From Imperialism to Isolationism 1898-1919 (1964) pp 29-30.
- ^ Howard K. Beale, Theodore Roosevelt and the Rise of America to World Power (1955) pp 355-89.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 24-25
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 100-101
- ^ Federico V. Magdalena, "Moro-American Relations in the Philippines." Philippine Studies 44.3 (1996): 427-438. online
- ^ H. W. Brands, Bound to Empire: The United States and the Philippines. (1992) p. 84.
- ^ Stephen Wertheim, "Reluctant Liberator: Theodore Roosevelt's Philosophy of Self-Government and Preparation for Philippine Independence," Presidential Studies Quarterly, Sept 2009, Vol. 39 Issue 3, pp 494–518
- ^ Ellen H. Palanca, "Chinese business families in the Philippines since the 1890s." in R.S. Brown, Chinese business enterprise in Asia (1995).
- ^ Andrew Roberts, A History of the English-Speaking Peoples Since 1900 (2008), p 26.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 105–106
- ^ Morris (2001) p. 456
- ^ Morris (2001) p. 299
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 456–457
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 461–462
- ^ Morris (2001) p. 554
- ^ Herring, pp. 364-365
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 117–119.
- ^ Paul Kennedy, The Rise and Fall of the Great Powers (1987) p. 154, 203
- ^ Graham A. Cosmas, An Army for Empire: The United States Army and the Spanish–American War (1971)
- ^ James E. Hewes, Jr. From Root to McNamara: Army Organization and Administration, 1900-1963 (1975)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, pp. 118–119.
- ^ Peter Karsten, "The Nature of 'Influence': Roosevelt, Mahan and the Concept of Sea Power." American Quarterly 23#4 (1971): 585-600. in JSTOR
- ^ Richard W. Turk, The Ambiguous Relationship: Theodore Roosevelt and Alfred Thayer Mahan (1987) online
- ^ Carl Cavanagh Hodge, "The Global Strategist: The Navy as the Nation's Big Stick," in Serge Ricard, ed., A Companion to Theodore Roosevelt (2011) pp 257–273
- ^ Stephen G. Rabe, "Theodore Roosevelt, the Panama Canal, and the Roosevelt Corollary: Sphere of Influence Diplomacy," in Ricard, ed., A Companion to Theodore Roosevelt (2011) pp 274-92.
- ^ Gordon Carpenter O'Gara, Theodore Roosevelt and the Rise of the Modern Navy (1970)
- ^ Miller 1992, pp. 387–388.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 25–26
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 77–78.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 78–79.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 79–80.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 80–81.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 176–182
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 187–191
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 75–76.
- ^ Morris (2001) p. 201
- ^ Frederick W. Marks III, Velvet on Iron: The Diplomacy of Theodore Roosevelt (1979), p. 140
- ^ Herring, pp. 371–372
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 26, 67–68
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Morris (2001) pp. 201–202
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 115–116
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 262–263
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 276–278
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 85–89.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 282–283
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 293–298
- ^ Julie Greene, The Canal Builders: Making America's Empire at the Panama Canal (2009)
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 297–303, 312
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 320–321
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 202–203.
- ^ McCullough, David (1977). The Path Between the Seas: The Creation of the Panama Canal, 1870–1914. New York, New York: Simon & Schuster. pp. 505–508. ISBN 0-671-24409-4.
- ^ "This Day In History: 1906-Teddy Roosevelt travels to Panama". history.com. A+E Networks. Retrieved October 24, 2018.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 82–84.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 84–85.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 173–174.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 173–176.
- ^ Greg Russell, "Theodore Roosevelt's Diplomacy and the Quest for Great Power Equilibrium in Asia," Presidential Studies Quarterly 2008 38(3): 433-455
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 180–182.
- ^ William Michael Morgan, "The anti-Japanese origins of the Hawaiian Annexation treaty of 1897." Diplomatic History 6.1 (1982): 23-44.
- ^ James K. Eyre Jr, "Japan and the American Annexation of the Philippines." Pacific Historical Review 11.1 (1942): 55-71 online.
- ^ Michael J. Green, By More Than Providence: Grand Strategy and American Power in the Asia Pacific Since 1783 (2019) pp 78–113.
- ^ Lucie Cheng (1984). Labor Immigration Under Capitalism: Asian Workers in the United States Before World War II. University of California Press. p. 186. ISBN 9780520048294.
- ^ Louis Morton, "Military And Naval Preparations for the Defense of the Philippines during the War Scare of 1907." Military Affairs (April 1949) 13#2 pp 95-104
- ^ "President Theodore Roosevelt and Prince Iyesato Tokugawa worked together to improve U.S. Japan relations and combat anti-Asian Racism". TheEmperorAndTheSpy.com.
- ^ Katz, Stan S. (2019). The Art of Peace. Horizon Productions.
- ^ Howard K. Beale, Theodore Roosevelt and the Rise of America to World Power (1956)
- ^ Raymond A. Esthus, "The Taft-Katsura Agreement – Reality or Myth?" Journal of Modern History 1959 31(1): 46–51 in JSTOR.
- ^ Raymond Leslie Buell, "The Development of the Anti-Japanese Agitation in the United States," Political Science Quarterly (1922) 37#4 pp. 605–638 part 1 in JSTOR and Buell, "The Development of Anti-Japanese Agitation in the United States II," Political Science Quarterly (1923) 38#1 pp. 57–81 Part 2 in JSTOR
- ^ Carl R. Weinberg, "The 'Gentlemen's Agreement' of 1907–08," OAH Magazine of History (2009) 23#4 pp 36–36.
- ^ A. Whitney Griswold, The Far Eastern Policy of the United States (1938). pp 354–360, 372–379
- ^ Charles E. Neu, An Uncertain Friendship: Theodore Roosevelt and Japan, 1906–1909 (Harvard University Press, 1967), p. 319 online.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 182–184.
- ^ Gould 2011, p. 185.
- ^ Raymond A. Esthus, Theodore Roosevelt and the International Rivalries (1970) pp 66–111
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, pp. 122–123.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 95–96
- ^ Morris (2001) pp 299–300
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 124–127.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Miller 1992, p. 437–438.
- ^ Brands 1997, p. 504.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 339–340
- ^ Chambers 1974, pp. 215–217.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 135–136.
- ^ Brands 1997, pp. 513–14.
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 139–140.
- ^ Miller 1992, pp. 483–485.
- ^ Gould 2003, pp. 163–164.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 506–507
- ^ Morris (2001) p. 520
- ^ Miller 1992, pp. 488–489.
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 533-536
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 528–529
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 534–535
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 537–539
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 554–555
- ^ Morris (2001) pp. 548–552
- ^ Gould 2011, pp. 292–293.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gould 2011, pp. 293–294.
- ^ Gould 2011, p. 295.
- ^ Rottinghaus, Brandon; Vaughn, Justin S. (February 19, 2018). "How Does Trump Stack Up Against the Best — and Worst — Presidents?". New York Times. Retrieved February 19, 2018.
- ^ Dalton 2002, pp. 4–5.
- ^ "Impact and Legacy", Biography, American President, The Rector and Visitors of the University of Virginia, 2005.
- ^ "Legacy", T Roosevelt, PBS.
Works cited[]
- Brands, Henry William (1997), TR: The Last Romantic (full biography), New York: Basic Books, ISBN 978-0-465-06958-3, OCLC 36954615.
- Chambers, John W. (1974), Woodward, C. Vann (ed.), Responses of the Presidents to Charges of Misconduct, Delacorte Press, pp. 207–237, ISBN 0-440-05923-2
- Chessman, G Wallace (1965), Governor Theodore Roosevelt: The Albany Apprenticeship, 1898–1900, ISBN 9780674732933
- Dalton, Kathleen (2002), Theodore Roosevelt: A Strenuous Life (full scholarly biography), ISBN 0-679-76733-9.
- Gould, Lewis L. (2003). Grand Old Party: A History of the Republicans. Random House. ISBN 0-375-50741-8.
- Gould, Lewis L (2011), The Presidency of Theodore Roosevelt (2nd ed.), ISBN 978-0700617746
- Greem, Michael J. By More Than Providence: Grand Strategy and American Power in the Asia Pacific Since 1783 (2019), pp 78–113.
- Herring, George (2008). From Colony to Superpower: U.S. Foreign Relations Since 1776. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0195078220.
- McGerr, Michael (2003). The Rise and Fall of the Progressive Movement in America. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-684-85975-0.
- Miller, Nathan (1992), Theodore Roosevelt: A Life, William Morrow & Co, ISBN 978-0688132200
- Morris, Edmund (2001), Theodore Rex, Random House, ISBN 978-0394555096
- Neu, Charles E. An Uncertain Friendship: Theodore Roosevelt and Japan, 1906–1909 (1967) online.</ref>}}
Further reading[]
- Beale, Howard K (1956), Theodore Roosevelt and the Rise of America to World Power (standard history of his foreign policy). online
- Blum, John Morton (1954), The Republican Roosevelt, Cambridge: Harvard University Press, OCLC 310975.
- Brinkley, Douglas (2009). The Wilderness Warrior: Theodore Roosevelt and the Crusade for America. New York: HarperCollins.online review; another online review
- Burton, D. H. "Theodore Roosevelt and the Special Relationship with Britain" History Today (Aug 1973), Vol. 23 Issue 8, pp 527-535 online.
- Coletta, Paolo E. “The Diplomacy of Theodore Roosevelt and William Howard Taft.” In American Foreign Relations: A Historiographical Review, edited by Gerald K. Haines and Samuel J. Walker, 91-114. (Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, 1981).
- Collin, Richard H. "Symbiosis versus Hegemony: New Directions in the Foreign Relations Historiography of Theodore Roosevelt and William Howard Taft." Diplomatic History 19.3 (1995): 473–497. online
- Cooper, John Milton (1983), The Warrior and the Priest: Woodrow Wilson and Theodore Roosevelt (dual scholarly biography), ISBN 978-0-674-94751-1.
- Cutright, P.R. (1985) Theodore Roosevelt: The making of a Modern Conservationist (U of Illinois Press.)
- Dalton, Kathleen. "Changing Interpretations of Theodore Roosevelt and the Progressive Era." in A Companion to the Gilded Age and Progressive Era ed. by Christopher M. Nichols and Nancy C. Unger (2017) pp: 296–307.
- Dorsey, Leroy G (1997), "The Frontier Myth and Teddy Roosevelt's Fight for Conservation", in Gerster, Patrick; Cords, Nicholas (eds.), Myth America: A Historical Anthology, II, St. James, NY: Brandywine Press, ISBN 1-881089-97-5.
- Gable, John. “The Man in the Arena of History: The Historiography of Theodore Roosevelt” in Theodore Roosevelt: Many-Sided American, eds. Natalie Naylor, Douglas Brinkley and John Gable (Interlaken, NY: Hearts of the Lakes, 1992), 613–643.
- Graff, Henry F., ed. The Presidents: A Reference History (3rd ed. 2002) online
- Greenberg, David. "Theodore Roosevelt and the image of presidential activism." Social Research 78.4 (2011): 1057–1088. online
- Hendrix, Henry J (2009), Theodore Roosevelt's Naval Diplomacy: The US Navy & the Birth of the American Century.
- Hull, Katy. "Hero, Champion of Social Justice, Benign Friend: Theodore Roosevelt in American Memory." European journal of American studies 13.13-2 (2018). online
- Juergens, George. News from the White House: The Presidential-Press Relationship in the Progressive Era (U of Chicago Press, 1981).
- Leuchtenberg, William E. (2015), The American President: From Teddy Roosevelt to Bill Clinton, Oxford University Press
- Murphey, William (March 2013), "Theodore Roosevelt and the Bureau of Corporation: Executive-Corporate Cooperation and the Advancement of the Regulatory State", American Nineteenth Century History, 14 (1): 73–111, doi:10.1080/14664658.2013.774983.
- Ponder, Stephen. “Executive Publicity and Congressional Resistance, 1905-1913: Congress and the Roosevelt Administration’s PR Men.” Congress and the Presidency 13:2 (1986): 177–186.
- Pringle, Henry F (1931), Theodore Roosevelt (full scholarly biography). Pulitzer prize. online free; 2nd edition 1956 is updated and shortened. 1956 edition online free to borrow
- Ricard, Serge (2006), "The Roosevelt Corollary", Presidential Studies Quarterly, 36 (1): 17–26, doi:10.1111/j.1741-5705.2006.00283.x.
- Swanson, Ryan A (2011), "'I Never Was a Champion at Anything': Theodore Roosevelt's Complex and Contradictory Record as America's 'Sports President'", Journal of Sport History, 38 (3): 425–46.
- Thompson, John M. Great Power Rising: Theodore Roosevelt and the Politics of US Foreign Policy (Oxford UP, 2019).
External links[]
- Presidency of Theodore Roosevelt
- Presidencies of the United States
- 1900s in the United States
- 1901 establishments in the United States
- Progressive Era in the United States
- Theodore Roosevelt
- 1900s in Washington, D.C.


