Prostatic venous plexus
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2011) |
| Prostatic venous plexus | |
|---|---|
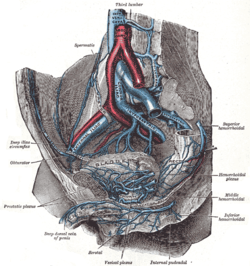 The veins of the right half of the male pelvis. (Prostatic plexus labeled at bottom right.) | |
| Details | |
| Drains from | Prostate |
| Source | Deep dorsal vein of the penis |
| Drains to | Vesical venous plexus and Pudendal plexus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plexus venosus prostaticus |
| TA98 | A12.3.10.013M |
| TA2 | 5043 |
| FMA | 29711 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The prostatic veins form a well-marked prostatic plexus which lies partly in the fascial sheath of the prostate and partly between the sheath and the . It communicates with the pudendal and vesical plexuses.
The prostatic venous plexus drains into the internal iliac vein which connects with the vertebral venous plexus, this is thought to be the route of bone metastasis of prostate cancer.[1]
It is sometimes known as "Santorini's plexus," named for the Italian anatomist Giovanni Domenico Santorini.
References[]
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 676 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 676 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ "Male Genitals - Prostate Neoplasms". Pathology study images. University of Virginia School of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2011-07-20. Retrieved 2011-04-28.
There are many connections between the prostatic venous plexus and the vertebral veins. The veins forming the prostatic plexus do not contain valves and it is thought that straining to urinate causes prostatic venous blood to flow in a reverse direction and enter the vertebral veins carrying malignant cells to the vertebral column.
External links[]
- Anatomy photo:44:05-0103 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Male Pelvis: The Prostate Gland"
Categories:
- Wikipedia articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Veins of the torso
- Prostate
- Cardiovascular system stubs