Pushyabhuti dynasty
Pushyabhuti dynasty (Vardhana dynasty) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6th century–7th century | |||||||||||||||
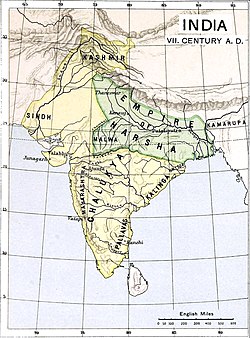
![The original territory of the Pushyabhutis was located around modern Thanesar. (Top map) The Empire of Harsha at its maximum extent. (Bottom map)[1]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5b/South_Asia_historical_AD590_EN.svg/250px-South_Asia_historical_AD590_EN.svg.png) | |||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital | Sthanvishvara (modern Thanesar) Kanyakubja (modern Kannauj) | ||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||
• Established | 6th century | ||||||||||||||
• Disestablished | 7th century | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
The Pushyabhuti dynasty (IAST: Puṣyabhūti), also known as the Vardhana dynasty, ruled parts of northern India during 6th and 7th centuries. The dynasty reached its zenith under its last ruler Harsha-Vardhana, whose empire covered much of north and north-western India, and extended till Kamarupa in the east and Narmada River in the south. The dynasty initially ruled from Sthanvishvara (modern KURUKSHETRA, Haryana), but Harsha eventually made Kanyakubja (modern Kannauj, Uttar Pradesh) his capital, from where he ruled until 647 CE.
Etymology and name[]
According to Harsha-charita, composed by the court poet Bana, the family was known as Pushyabhuti dynasty (IAST: Puṣyabhūti-vaṃśa),[2] or Pushpabhuti dynasty (IAST: Puṣpabhūti-vaṃśa). The manuscripts of Harsha-charita use the variant "Pushpabhuti", but Georg Bühler proposed that this was a scribal error, and that the correct name was Pushyabhuti.[3] Several modern scholars now use the form "Pushpabhuti", while others prefer the variant "Pushyabhuti".[4]
Some modern books describe the dynasty as "Vardhana", because the names of its kings end with the suffix "-vardhana". However, this may be misleading as the names of kings of other dynasties also end with this suffix.[2]
Origins[]
No concrete information is available about the origins of the dynasty. Harshacharita by the 7th century poet Bana gives a legendary account of their origin, naming Pushyabhuti as the dynasty's founder. According to this legend, Pushyabhuti lived in the Srikantha janapada (modern Kurukshetra district), whose capital was Sthanvishvara (modern Thanesar). A devotee of Shiva, Pushyabhuti became involved in a tantric ritual at a cremation ground, under the influence of Bhairavacharya, a teacher from "the South". At the end of this ritual, a goddess (identified with Lakshmi) anointed him the king and blessed him as the founder of a great dynasty.[5] The Pushyabhuti mentioned in Bana's account appears to be a fictional character, as he is not mentioned in the dynasty's inscriptions or any other source.[6]
The writings of Xuanzang and Arya-manjushri-mula-kalpa suggest that the dynasty belonged to the baisKshatriya varna.[7][8]
History[]
The Pushyabhuti dynasty originally ruled a small area around their capital Sthaneshvara (Thanesar). According to Hans T. Bakker, their ruler Aditya-Vardhana (or Aditya-Sena) was probably a feudatory to Sharva-varman, the Maukhari king of Kannauj. His successor Prabhakara-Vardhana may have also been a feudatory to the Maukhari king Avanti-Varman in his early days. Prabhakara's daughter Rajyashri married Avanti-Varman's son Graha-Varman. As a result of this marriage, Prabhakara's political status increased significantly, and he assumed the imperial title Parama-bhattaraka Maharajadhiraja. ("the one to whom the other kings bow because of his valour and affection").[9]
According to the Harshacharita, after Prabhakara's death, the king of Malava attacked Kannauj, supported by the ruler of Gauda. The Malava king killed Graha-Varman, and captured Rajyashri.[11] Bana does not mention this king, but historians speculate him to be a ruler of the Later Gupta dynasty.[12] Prabhakara's elder son Rajya-Vardhana defeated the Malava ruler, but was killed by the Gauda king.[13]
The Harshacharita further states that Prabhakara's younger son Harsha-Vardhana then vowed to destroy the Gauda king and their allies. [14] Again, Bana does not mention the name of the Gauda king, but historians identify him with Shashanka-Deva, a Maukhari vassal (mahasamanta). Harsha formed an alliance with Bhaskar Varman, the king of Kamarupa, and forced Shashanka to retreat. Subsequently, in 606 CE, Harsha was formally crowned as an emperor.[15] He captured a large part of northern India (see the Empire of Harsha).[16] There are different assessments of the exact extent of Harsha's empire, but he controlled major parts of northern India; his overlordship was accepted by the king of Vallabhi in the west and the Kamarupa king Bhaskaravarman in the east; in the south, his empire extended up to the Narmada River.[17]
Harsha eventually made Kanyakubja (modern Kannauj in Uttar Pradesh) his capital,[3] and ruled till c. 647 CE. He died without an heir, leading to the end of the Pushyabhuti dynasty.[16]
Rulers[]
The following are the known rulers of the Pushyabhuti or Vardhana dynasty, with estimated period of reign (IAST names in bracket):[19]
- Pushyabhuti (Puṣyabhuti), possibly mythical
- Naravardhana (c. 500–525 CE)
- Rajyavardana I (c. 525–555 CE)
- Adityavardhana (Ādityavardhana or Ādityasena), (c. 555–580 CE)
- Prabhakara-vardhana (Prabhākaravardhana), (c. 580–605 CE)
- Rajya-vardhana (Rājyavardhana II), (c. 605–606 CE)
- Harsha-vardhana (Harṣavardhana), (c. 606–647 CE)
See also[]
- Harshavardhan
- Middle kingdoms of India
- List of Hindu empires and dynasties
References[]
- ^ Schwartzberg, Joseph E. (1978). A Historical atlas of South Asia. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 146, map XIV.2 (d). ISBN 0226742210.
- ^ a b D. C. Ganguly 1981, p. 240.
- ^ a b Baijnath Sharma 1970, p. 89.
- ^ Max Deeg 2016, p. 99.
- ^ Hans Bakker 2014, pp. 78–79.
- ^ Hans Bakker 2014, p. 80.
- ^ Shankar Goyal (2007). "RELIGIOUS ANALYSIS OF HARSHA'S PERSONALITY". Indian History Congress: 137. JSTOR 44147825.
This probably explains the emergence of Pushyabhuti , a Vaisya by caste and a Saiva by faith , as its ruler
Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Y. Krishan; Indian History and Culture Society (1986). Essays in Indian History and Culture. Indian History & Culture Society. p. 167.
yuan Chwang, who remained in Inda for approximately thirteen years (c. A.DD. 630-44) tells us that Harshavardhana was of 'Fe ishe'(bais) extraction. The Āryamanjuśrimulakalpa also clearly states that the Pushyabhutis belonged to the vaisya caste. According to Tripathi , the suffix ' bhūti ' additionally indicates that Pushyabhuti , the founder of the family was a vaisya
- ^ Hans Bakker 2014, p. 79.
- ^ Sastri, Hirananda (1931). Epigraphia Indica Vol.21. pp. 74–80.
- ^ Hans Bakker 2014, p. 81.
- ^ Hans Bakker 2014, p. 82.
- ^ Hans Bakker 2014, pp. 85–86.
- ^ Hans Bakker 2014, p. 87.
- ^ Hans Bakker 2014, p. 88.
- ^ a b Sukla Das 1990, p. 2.
- ^ Upinder Singh 2008, p. 562.
- ^ CNG Coins
- ^ Ronald M. Davidson 2012, pp. 38–39.
Bibliography[]
- Baijnath Sharma (1970). Harṣa and His Times. Sushma Prakashan. OCLC 202093.
- D. C. Ganguly (1981). "Western India in the Sixth Century A.D.". In R. C. Majumdar (ed.). A Comprehensive History of India. 3, Part I: A.D. 300-985. Indian History Congress / People's Publishing House. OCLC 34008529.
- Hans Bakker (2014). The World of the Skandapurāṇa. BRILL. ISBN 978-90-04-27714-4.
- Max Deeg (2016). "The Political Position of Xuanzang: The Didactic Creation of an Indian Dynasty in the Xiyu ji". In Thomas Jülch (ed.). The Middle Kingdom and the Dharma Wheel: Aspects of the Relationship between the Buddhist Saṃgha and the State in Chinese History. BRILL. ISBN 978-90-04-32258-5.
- Ronald M. Davidson (2012). Indian Esoteric Buddhism: A Social History of the Tantric Movement. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-50102-6.
- Sukla Das (1990). Crime and Punishment in Ancient India. Abhinav Publications. ISBN 978-81-7017-054-9.
- Upinder Singh (2008). A History of Ancient and Early Medieval India: From the Stone Age to the 12th Century. Pearson Education India. ISBN 978-81-317-1120-0.
- Pushyabhuti dynasty
- States and territories established in the 6th century
- States and territories disestablished in the 7th century
- 6th-century establishments in Nepal

