Ragdoll
hideThis article has multiple issues. Please help or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
| Ragdoll | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Origin | Riverside, California, United States |
| Breed standards | |
| CFA | standard |
| Domestic cat (Felis catus) | |


The Ragdoll is a cat breed with a color point coat and striking blue eyes. Their form is large and muscular and their coat is silky soft and semi-longhair. Ragdolls were developed by American breeder Ann Baker in the 1960s. They are best known for their docile and placid temperament and affectionate nature. The name 'Ragdoll' is derived from the tendency of individuals from the original breeding stock to go limp and relaxed when picked up.[1]
Particularly popular in both the United Kingdom and the breed's native United States, Ragdolls are often known as 'dog-like cats' or 'puppy-like cats'. This is due to their tendency to follow people around, their ease when physically handled, and their relative lack of aggression toward other pets.[2]
Ragdolls are powerful, large and heavy cats that are distinguishable by their V-shape markings on their forehead, large round blue eyes, soft thick coat, thick limbs, long tail and soft bodies. Their color rings are commonly tri-colour or bi-color. [3]
Cats of the Ragdoll breed have bold personalities, a relaxed nature and a strong tolerance for pain (though this can, at times, be mistaken for lack of pain). These features allow Ragdolls to tolerate children's play and makes the breed an ideal family pet. [4]
History[]
In the 1960s, a regular, non-pedigreed, white domestic longhaired cat named Josephine produced several litters of typical cats. It originated in Riverside, California with a woman named Ann Baker.[5] Josephine was of a Persian/Angora type and had litters sired by several unknown male Birman or Burmese-like cats, one of which had the Siamese point coloration. Josephine later produced kittens with a docile, placid temperament, affectionate nature, and a tendency to go limp and relaxed when picked up.[6]
When a subsequent litter produced more of the same, Ann Baker purchased several kittens from her neighbor who lived behind her and, believing that she had something special, set out to create what is now known as the ragdoll. The breed was selectively bred over many years for desirable traits, such as large size, gentle demeanor, pointed coloration, and a tendency to go limp when picked up.[6]
Out of those early litters came Blackie, an all black Burmese-like male, and Daddy Warbucks, a seal point with white feet. Daddy Warbucks sired the founding bi-color female Fugianna, and Blackie sired Buckwheat, a dark brown/black Burmese-like female. Both Fugianna and Buckwheat were daughters of Josephine. All Ragdolls are descended from Baker's cats through matings of Daddy Warbucks to Fugianna and Buckwheat.[7][8]
Baker, in an unusual move, spurned traditional cat-breeding associations. She trademarked the name Ragdoll, set up her own registry – the International Ragdoll Cat Association (IRCA) – around 1971, and enforced stringent standards on anyone who wanted to breed or sell cats under that name.[6] The Ragdolls were also not allowed to be registered by other breed associations.[9][10] The IRCA is still in existence today but is quite small, particularly since Baker's death in 1997. IRCA cats are not recognized in any major cat breed organization or cat show.
In 1975, a group led by a husband-and-wife team, Denny and Laura Dayton, broke ranks with the IRCA with the aim of gaining mainstream recognition for the Ragdoll. Beginning with a breeding pair of IRCA cats, this group eventually developed the Ragdoll standard currently accepted by major cat registries such as the CFA and the FIFe.[11]
During or after the spread of the Ragdoll breed in America during the early 1960s, a breeding pair of Ragdolls was exported to the UK. This pair was followed by eight more cats to fully establish the breed in the UK, where it is recognised by the Governing Council of the Cat Fancy.[12]
In 1994, a second group decided to leave the IRCA and form its own group, owing to increasingly strict breeding restrictions. This group later established the Ragamuffin breed. Because Baker owned the rights to the name "Ragdoll", no offshoot groups were legally able to call their cats Ragdolls until 2005, when the trademark on "Ragdoll" was not renewed.[13]
The largest international Ragdoll breed club is the Ragdoll Fanciers' Club International (RFCI).[14]
Breed description[]
Temperament[]

The Ragdoll has been known to have a very floppy and calm nature, with claims that these characteristics have been passed down from the Persian and Birman breeds. Opinions vary as to whether this trait might be the result of genetic mutation.[15][16] The extreme docility of some individuals has led to the myth that Ragdolls are pain-resistant. Some breeders in Britain have tried to breed away from the limpness owing to concerns that extreme docility 'might not be in the best interests of the cat'.[15][17]
Breed standard marketing and publicity material describes the Ragdoll as affectionate, intelligent, relaxed in temperament, gentle, and an easy-to-handle lap cat.[18][19] The animals are often known as 'puppy cats', 'dog-like cats', 'cat-dogs', etc., because of their placid nature and affectionate behaviour, with the cats often following owners from room to room as well as seeking physical affection akin to certain dog breeds. Ragdolls can be trained to retrieve toys and enjoy doing so.[2] They have a very playful nature that often lasts well into their senior years.[20]
Physical characteristics[]
The Ragdoll is one of the largest domesticated cat breeds. A fully-grown female weighs from 8 to 15 pounds (3.6 to 6.8 kg). Males are substantially larger, ranging from 12 to 20 pounds (5.4 to 9.1 kg), or more.[6] It can take up to four years for a Ragdoll to reach mature size.[8]
They have a sturdy body, large frame, and proportionate legs. Their heads are broad with a flat top and wide space between the ears. They have long, muscular bodies with broad chests and short necks. Their tails are bushy and long in length, their paws are large round and tufted and their coats are silky, dense and medium to long length. Adults develop knickerbockers on their hind legs and a ruff around their necks. The breed is often known for their large round deep blue eyes.[21][22] The genes for point coloration are also responsible for these distinctive blue eyes. More intense shades of blue are favoured in cat shows. Although the breed has a plush coat, it consists mainly of long guard hairs, while the lack of a dense undercoat results, according to the Cat Fanciers' Association, in 'reduced shedding and matting'.[23]
Ragdolls come in six different colors: red, seal, chocolate and the corresponding 'dilutes', including blue, lilac, and cream. This also includes the lynx and tortoiseshell variations[24] in all colours and the three patterns. Ragdoll kittens are born white; they have good color at 8–10 weeks and full color and coat at 3–4 years. The three different patterns are:
- Colorpoint – One color darkening at the extremities (nose, ears, tail, and paws).
- Mitted – Same as pointed, but with white paws and abdomen. With or without a blaze (a white line or spot on the face), but must have a 'belly stripe' (white stripe that runs from the chin to the genitals) and a white chin. Mitted Ragdolls, which weren't allowed titling in CFA until the 2008–2009 show season, are often confused with Birmans. The easiest way to tell the difference is by size (the Ragdoll being larger) and chin color (Mitted Ragdolls have white chins,[25] while Birmans have colored chins), although breeders recognise the two by head shape and boning.[citation needed]
- Bicolour – White legs, white inverted V on the face, white abdomen and sometimes white patches on the back (excessive amounts of white, or 'high white', on a bicolor are known as the Van pattern, although this does not occur nearly as often as the other patterns.)
- Blue Point - This cat is named after its dark bluish-grey, that is, its points are bluish-grey. A Blue Point Ragdoll's body is a light platinum tone. It must be stated that the area of its chest and stomach has a bluish-grey color.[26][27]
Variations:
- Lynx – A variant of the above type having tabby markings.[28]
- Tortoiseshell or "tortie"- A variant noted for mottled or parti-colored[29] markings in the above patterns

Gallery[]

A female tortoiseshell ragdoll kitten

A female blue bicolor ragdoll

A male blue bicolor ragdoll

A female black bicolor ragdoll

A blue-pointed ragdoll with darkened extremities

The mitted pattern is like the pointed, but has white paws, chin and abdomen

Blue-eyed kitten. The white patch in the shape of an inverted 'V' on the face indicates a "bicolor" pattern.

Blue bicolor ragdoll cleaning her paw
A seal lynx pointed Ragdoll, about three years old

A female blue bicolor ragdoll

An 8-month-old blue bicolor ragdoll
A seal-mitted ragdoll

A 10-week-old blue-pointed male ragdoll

A 15-year-old female tortoiseshell ragdoll
Health[]
One study utilizing Swedish insurance data showed that of the common cat breeds, the Ragdoll and Siamese have the lowest survival rate. They live 12 to 15 years.[30] This study indicates the Ragdoll may have a significantly higher number of cats that die of urinary problems, mainly from kidney/ureter issues, but also partly from lower urinary issues. Whether this is an issue outside Finland, Sweden, or Denmark is unclear.[citation needed] The coat of the Ragdoll cat is thick and extremely soft. The length of the hairs can range from medium to long. Fortunately, its coat does not mat easily, but it can occur. Caring for Ragdoll cats should include brushing the coat at least twice a week to help prevent mats, tangles and excessive shedding. Ragdolls enjoy grooming and will often show their enjoyment with all the special attention.[31]
Loneliness[]
Ragdolls are not demanding and do not require constant attention[8] but they are very social and require companionship. They can develop depression when they do not receive adequate attention and affection from their owners or are left alone for long periods of time. It is often recommended that they have a feline companion to prevent or treat this issue before it develops into a severe health problem. Signs that a ragdoll is experiencing depression can include - destructive behaviour (e.g: scratching furniture, knocking things over, etc.), clinginess or over-excitement when you return home, over-sleeping, over or under-grooming, over or under-eating, a general low mood in which they act depressed or lethargic.[32][33] However, these symptoms should be discussed with a vet before any decision is made as they may also be signs of an underlying illness.
Inbreeding[]
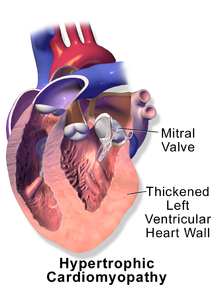
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy[]
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a common heart disease in all cats and is most commonly genetic in cause. The disease causes thickening of the heart wall, which makes the heart pump less efficiently. It can, in some instances, lead to sudden death. In Ragdolls that are homozygous positive for the disease (having two copies of the HCM gene), the condition can present early (as young as six months) and tends to be severe, with most cats dying by age 3. Heterozygous (one copy of HCM gene) cats tend to have later onset and slower progression of the disease with less severe impact.[34][35]
A DNA test was developed in 2007 to identify the gene that causes HCM in Ragdolls. Breeding only from Ragdolls that are free from this gene (homozygous negative) will ensure that they will not develop the form of HCM associated with it.[34][35]
The allelic frequencies of the Ragdoll HCM mutation R820W were 0.17 in cats from Italy and 0.23 in cats from the US in 2013.[36] This reference states that the R820W prevalence is 30% in UK.[37] The HCM prevalence was found to be 2.9% (95% CI = 2.7–8.6% ) in this study.[36]
References[]
- ^ Marty Becker, D. V. M.; Becker, Marty; Spadafori, Gina (16 September 2006). Why Do Cats Always Land on Their Feet?: 101 of the Most Perplexing Questions ... – Marty Becker, Gina Spadafori – Google Books. ISBN 9780757305733. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Benjamin L. Hart; Lynette A. Hart (2013). Your Ideal Cat: Insights Into Breed and Gender Differences in Cat Behavior. Purdue University Press. pp. 99–101. ISBN 9781557536488.
- ^ "Ragdoll". Petplan. Retrieved 14 May 2021.
- ^ "Ragdoll". Petplan. Retrieved 14 May 2021.
- ^ "Ragdoll – The Cat Fanciers' Association, Inc". cfa.org. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Helgren, J. Anne (2006). "Ragdoll". Iams. Telemark Productions. Archived from the original on 13 November 2014.
- ^ "Ragdoll History-The Beginning". Ragdoll Historical Society. Archived from the original on 18 February 2015. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Mattern, Joanne (2001). The Ragdoll Cat. Mankato, Minnesota: Capstone. pp. 5–16. ISBN 0736808973.
- ^ "Ragdoll". Iams. Archived from the original on 28 September 2007.
- ^ Robbins, Nancy (14 February 2012). Domestic Cats: Their History, Breeds and Other Facts. CreateSpace. p. 220. ISBN 9781470075385.
- ^ "Raistrick Ragdolls". Raistrickragdfolls.co.uk. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 15 November 2014.
- ^ "Welcome to the Governing Council of the Cat Fancy". Archived from the original on 8 December 2012. Retrieved 14 December 2010.
- ^ U.S. trademark number 1,026,916.
- ^ "Ragdoll Fanciers Club International- Ragdoll Cat Breeders Club – Welcome". Rfci.org. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Understanding Cat Behavior: The Complete Feline Problem Solver Roger Tabor (2003). P 33.
- ^ Do cats always land on their feet Gina Spadafori, Marty Becker
- ^ The Cat: Its Behavior, Nutrition & Health Linda P. Case, Kerry Helms, Bruce Macallister (2003). P 31.
- ^ Ragdoll Breed standard Governing Council of Cat Fancy
- ^ Ragdoll Breed standard Cat Fanciers' Association
- ^ Dina (2019-02-02). "Are Ragdoll Cats Playful? | Purr Craze". Retrieved 2021-06-24.
- ^ "Ragdoll Cat Breed Information | Purina". www.purina.co.uk. Retrieved 2021-06-24.
- ^ "Ragdoll Cats - A Complete Guide To The Ragdoll Cat Breed". The Happy Cat Site. 2019-05-14. Retrieved 2021-06-24.
- ^ Breed Profile Archived 14 July 2009 at the Wayback Machine Cat Fanciers' Association
- ^ "Ragdoll Introduction". Tica.org. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ Mattern, Joanne. The Ragdoll Cat. capstone press. p. 19.
- ^ "Blue Point Ragdoll". Ragdoll World. 14 June 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ "Ragdoll Breed Standards" (PDF).
- ^ "Ragdoll International Patterns and Colors". Ragdollinternational.org. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- ^ "Ragdoll : POINT SCORE" (PDF). Cfa.org. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ Egenvall, A.; Nødtvedt, A.; Häggström, J.; Ström Holst, B.; Möller, L.; Bonnett, B. N. (2009). "Mortality of Life-Insured Swedish Cats during 1999–2006: Age, Breed, Sex, and Diagnosis". Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine. 23 (6): 1175–1183. doi:10.1111/j.1939-1676.2009.0396.x. PMC 7167180. PMID 19780926.
- ^ "Grooming Tips for a Ragdoll Cat". Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- ^ Pierre (2019-01-18). "Should You Get A Companion For Your Ragdoll Cat? | Purr Craze". Retrieved 2021-06-24.
- ^ "Ragdoll Cats - A Complete Guide To The Ragdoll Cat Breed". The Happy Cat Site. 2019-05-14. Retrieved 2021-06-24.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Minutes of Executive Council Meeting No: 28 (doc)". New Zealand Cat Fancy. 25 September 2011. Retrieved 8 February 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Frequently Asked Questions about the HCM Genetic Mutation Predominantly Found in Ragdoll Cats". NC State College of Veterinary Medicine. Retrieved 8 February 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Myosin-Binding Protein C DNA Variants in Domestic Cats (A31P, A74T, R820W) and Their Association with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy" (PDF). Vetogene.it. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) in cats". Fabcats.org. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ragdoll cats. |
- Cat breeds
- Cat breeds originating in the United States
- Inbred animals













