SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant
This article needs more medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (December 2021) |
| Omicron | |
 | |
| General details | |
|---|---|
| WHO Designation | Omicron |
| Lineage | B1.1.529 |
| First detected | South Africa |
| Date reported | 24 November 2021 |
| Status | Variant of concern |
| Symptoms | |
| Cases map | |
 Cumulative confirmed Omicron variant cases by country and territory
| |
| SARS-CoV-2 variants | |
| |
| Part of a series on the |
| COVID-19 pandemic |
|---|
 |
|
|
|
The Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) is a variant of SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) that was first reported to the World Health Organization (WHO) from South Africa on 24 November 2021.[12][13]
Omicron multiplies around 70 times faster than the Delta variant in the bronchi (lung airways) but evidence suggests it is less severe than previous strains, especially compared to the Delta variant.[14][15] Omicron might be less able to penetrate deep lung tissue.[16] Omicron infections are 91 percent less fatal than the delta variant, with 51 percent less risk of hospitalization.[17] However, the estimated difference in the intrinsic risk of hospitalization largely decreases to 0–30 percent when reinfections are excluded.[18] Overall, the extremely high rate of spread, combined with its ability to evade both double vaccination and the body's immune system, means the total number of patients requiring hospital care at any given time is still of great concern.[16]
Vaccines continue to provide protection against severe disease and hospitalisation especially after a third dose of an mRNA vaccine is given.[19][20] Early figures suggest that double vaccination offers 30 to 40 percent protection against infection and around 70 percent protection against hospitalization. A recent third vaccine dose boosts effectiveness against infection to around 75 percent, and 88 percent for severe disease.[21]
Classification

Nomenclature
On 26 November, the WHO's Technical Advisory Group on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Evolution declared PANGO lineage B.1.1.529 a variant of concern and designated it with the Greek letter omicron.[12][22] Greek letters are used to identify variants of SARS-CoV-2. The WHO skipped the preceding letters nu and xi in the Greek alphabet to avoid confusion with the similarities of the English word "new" and the Chinese surname Xi.[22][23][24] The previous designation was for the "variant of interest" Mu.[25][26]
Possibly due to a lack of familiarity with the Greek alphabet among some English speakers and the relative frequency of the Latin prefix "omni" in other common speech, the name of the variant has also occasionally been mispronounced and misspelled as "Omnicron".[27][28]
The GISAID project has assigned it the clade identifier GR/484A,[29] and the Nextstrain project has assigned it the clade identifiers 21K and 21L, both belonging to a larger Omicron group 21M.[30]
Mutations
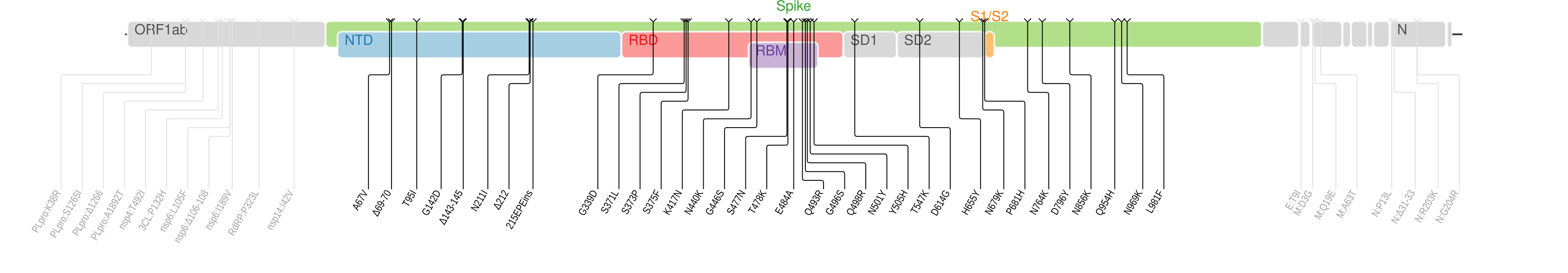
The genomic sequence of the Omicron variant is pictured above.
| Gene | Amino acid |
|---|---|
| ORF1ab | nsp3: K38R |
| nsp3: V1069I | |
| nsp3: Δ1265 | |
| nsp3: L1266I | |
| nsp3: A1892T | |
| nsp4: T492I | |
| nsp5: P132H | |
| nsp6: Δ105-107 | |
| nsp6: A189V | |
| nsp12: P323L | |
| nsp14: I42V | |
| Spike | A67V |
| Δ69-70 | |
| T95I | |
| G142D, | |
| Δ143-145 | |
| Δ211 | |
| L212I | |
| ins214EPE | |
| G339D | |
| S371L | |
| S373P | |
| S375F | |
| K417N | |
| N440K | |
| G446S | |
| S477N | |
| T478K | |
| E484A | |
| Q493R | |
| G496S | |
| Q498R | |
| N501Y | |
| Y505H | |
| T547K | |
| D614G | |
| H655Y | |
| N679K | |
| P681H | |
| N764K | |
| D796Y | |
| N856K | |
| Q954H | |
| N969K | |
| L981F | |
| E | T9I |
| M | D3G |
| Q19E | |
| A63T | |
| N | P13L |
| Δ31-33 | |
| R203K | |
| G204R | |
| Sources: UK Health Security Agency[31] CoVariants[30] | |
The variant has many mutations, some of which have concerned scientists.[32] The Omicron variant has a total of 60 mutations compared to the reference / ancestral variant: 50 nonsynonymous mutations, 8 synonymous mutations, and 2 non-coding mutations.[33] Thirty-two mutations affect the spike protein, the main antigenic target of antibodies generated by infections and of many vaccines widely administered. Many of those mutations had not been observed in other strains.[34][35] The variant is characterised by 30 amino acid changes, three small deletions, and one small insertion in the spike protein compared with the original virus, of which 15 are located in the receptor-binding domain (residues 319–541). It also carries a number of changes and deletions in other genomic regions. Additionally, the variant has three mutations at the furin cleavage site.[36] The furin cleavage site increases SARS-CoV-2 infectivity.[37] The mutations by genomic region are the following:[38][39]


- Spike protein: A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, Δ211, L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F
- Half (15) of these 30 changes are located in the receptor binding domain-RBD (residues 319–541)
- ORF1ab
- nsp3: K38R, V1069I, Δ1265, L1266I, A1892T
- nsp4: T492I
- nsp5: P132H
- nsp6: Δ105-107, A189V
- nsp12: P323L
- nsp14: I42V
- Envelope protein: T9I
- Membrane protein: D3G, Q19E, A63T
- Nucleocapsid protein: P13L, Δ31-33, R203K, G204R
A link with HIV infection may explain a large number of mutations in the sequence of the Omicron variant.[41][citation needed] Indeed, in order to be affected by such a high number of mutations, the virus must have been able to evolve a long time without killing its host, nor being eliminated. One such situation occurs in people with a weakened immune system but receiving enough medical care to survive.[42] This is the case in HIV patients in South Africa, who represent more than 20% of the population.[43] Due to lack of access to clinics, fear of stigmatisation and disrupted healthcare, millions living with HIV in the region are not on effective HIV therapy. HIV prevention could be key to reducing the risk of uncontrolled HIV driving the emergence of Covid variants.[44]
In addition, it is believed that one of these many mutations, comprising a 9-nucleotide sequence, may have been acquired from another coronavirus (known as HCoV-229E), responsible for the common cold.[45] This is not entirely unexpected — at times, viruses within the body acquire and swap segments of genetic material from each other, and this is one common means of mutation.[45]
One hypothesis to explain the novel mutations is that SARS-CoV-2 was transmitted from humans to mice and mutated in a population of mice sometime between mid-2020 and late 2021 before reinfecting humans.[46]
Sublineages and BA.2 subvariant
Researchers have established the existence of three sublineages of Omicron. The 'standard' sublineage is now referred to as BA.1 (or B.1.1.529.1), and the two other sublineages are known as BA.2 (or B.1.1.529.2) and BA.3 (or B.1.1.529.3).[47] They share many mutations, but also significantly differ. In general, BA.1 and BA.2 share 32 mutations, but differ by 28.[48] This makes them as different as some other major variants,[49] and it has been suggested that BA.2 should receive its own Greek-letter name.[48] BA.1 has itself been divided in two, the original BA.1 and BA.1.1, where the main difference is that the latter has a R346K mutation.[50][51]
Detection
Ordinary COVID-19 tests, both PCR and rapid, can detect all Omicron subvariants as COVID-19, but further tests are necessary to distinguish the subvariants from each other and from other COVID-19 variants.[52]
A notable difference between the 'standard' Omicron subvariant and BA.2 is that the latter lacks the characteristic S-gene target failure (SGTF)-causing deletion (Δ69-70) by which many qPCR tests are able to rapidly detect a case as an Omicron (or Alpha) variant, from the previously dominant Delta variant.[53][54] Thus, countries that primarily rely on SGTF for detection may overlook BA.2,[53] and British authorities consider SGTF alone as insufficient for monitoring the spread of Omicron.[55] This has resulted in it having been nicknamed 'Stealth Omicron'.[55] Because BA.2 still can be separated from other variants through normal full sequencing, or checks of certain other mutations, the nickname is however inaccurate.[48][52] Some countries, such as Denmark and Japan, use a variant qPCR that tests for several mutations, including L452R.[56][57] It can also distinguish Delta, which has L452R,[58] and all Omicron sublineages, which do not have L452R.[59][60] As Omicron became dominant and the Delta variant became rare, the SGTF mutation that had made Delta and BA.2 similar in qPCR tests could now be used for easily separating BA.1 and BA.2 from each other. As a consequence, BA.2 could now be regarded as decidedly un-stealthy.[61]
The third Omicron sublineage, BA.3, is very rare. It has the same SGTF deletion (Δ69-70) as BA.1.[62][63]
Affected countries and transmissibility
According to early research, BA.2 is roughly 30% more transmissible than BA.1.[64] As a consequence, it may prolong a COVID-19 wave when it overtakes BA.1.[65]
The first known sequence of BA.2 was in a sample from 15 November 2021.[66] In mid-December 2021, BA.2 still appeared to be rare with relatively few sequences from half a dozen countries having been uploaded to GISAID, but subsequently numbers rapidly increased. As of 17 January 2022, BA.2 had been detected in at least 40 countries and in all continents except Antarctica.[60][67] By 31 January, it had been detected in at least 57 countries.[68] In global samples collected from 4 February to 5 March and uploaded to GISAID, BA.2 accounted for c. 34%, compared to 41% for BA.1.1, 25% for BA.1 and less than 1% for BA.3.[69] Based on GISAID uploads, BA.1 peaked in early January 2022, after which it was overtaken by both BA.1.1 and BA.2.[70] In North America, parts of Europe and parts of Asia, BA.1 was first outcompeted by BA.1.1. For example, in the United States, France and Japan, BA.1.1 became the dominant subvariant in January 2022.[71][72][73]
By late December 2021/early January 2022, BA.2 appears to have become dominant in at least parts of India (already making up almost 80 percent in Kolkata in late December 2021[74]) and the Philippines, had become frequent in Scandinavia, South Africa and Singapore, and was showing signs of growth in Germany and the United Kingdom.[75][76][77][78] In Japan, which has quarantine and detailed screening of all international travellers, as of 24 January, the vast majority of BA.2 had been detected in people that had arrived from India or the Philippines with cases going back at least to 1 December 2021 (far fewer BA.1 or other variants were detected among arrivals from the two countries in that period), but small numbers had also been detected in people arriving from other countries.[57][79][80]
In Denmark, the first BA.2 was in a sample collected on 5 December 2021 and extremely few were found in the directly following period.[81] By week fifty (13–19 December) it had started to increase, with BA.2 being at around 2 percent of sequenced cases compared to 46 percent BA.1 (remaining Delta). The frequency of both Omicron subvariants continued to increase throughout the last half of December; in week fifty-two (27 December–2 January), BA.2 had reached 20 percent and BA.1 peaked at 72 percent. In January 2022, BA.1 began decreasing, whereas BA.2 continued its increase. By the second week (10–16 January) of 2022, the frequency of the two was almost equal, both being near 50 percent (around one percent was the rapidly disappearing Delta).[81] In the following week, BA.2 became clearly dominant in Denmark with 65 percent of new cases being the BA.2 subvariant.[82] Trends from the other Scandinavian countries, India, South Africa and the United Kingdom also showed that BA.2 was increasing in proportion to the original BA.1.[83][84] In early February 2022, it had become the dominant subvariant in South Africa, in late February it had become dominant in Germany and in early March it had become dominant in the United Kingdom.[85][86][87] In early March, BA.1.1 was still heavily dominant in the United States (having overtaken BA.1 in January), but BA.2 was increasing in frequency.[71]
Severity and immunity
The risk of hospitalization is the same in BA.1 and BA.2 based on reviews from Denmark, India, South Africa and the United Kingdom.[55][69][82][88] Norwegian studies show that the amount of virus in the upper airways is similar in those infected with BA.1 and BA.2.[84] In general, Omicron (all subvariants) have a higher reinfection rate than other COVID-19 variants. Studies from Denmark and Qatar found that after an infection with BA.1, the vast majority of people were well-protected against a BA.2 infection, although it is unknown how long this protection lasts.[69][89][90] Laboratory studies also show that antibodies for BA.1 generally protect against BA.2.[90] In Denmark, preliminary data found breakthrough rates in people that had been vaccinated that were similar to the breakthrough rates seen for BA.1.[82] An initial study by the UK Health Security Agency found that vaccines afford similar levels of protection against symptomatic disease by BA.1 and BA.2, and in both it is considerably higher after two doses and a booster than two doses without booster.[91][92] Because of the gradually waning effect of vaccines, further, booster vaccination may later be necessary.[87]
Possible consequences
The WHO is concerned that the large number of mutations in Omicron compared to earlier variants may reduce immunity in people who were previously infected and in vaccinated people. It is also possible the Omicron variant might be more infective in this regard than prior variants. The effects of the mutations, if any, are unknown as of late November 2021. The WHO warns that health services could be overwhelmed especially in nations with low vaccination rates where mortality and morbidity rates are likely to be much higher, and urges all nations to increase COVID-19 vaccinations.[93]
Professor Paul Morgan, immunologist at Cardiff University, also recommends vaccination. Morgan said, "I think a blunting rather than a complete loss [of immunity] is the most likely outcome. The virus can't possibly lose every single epitope on its surface, because if it did that spike protein couldn't work any more. So, while some of the antibodies and T cell clones made against earlier versions of the virus, or against the vaccines may not be effective, there will be others, which will remain effective. (...) If half, or two-thirds, or whatever it is, of the immune response is not going to be effective, and you're left with the residual half, then the more boosted that is the better."[94]
Professor Francois Balloux of the Genetics Institute at University College London said, "From what we have learned so far, we can be fairly confident that – compared with other variants – Omicron tends to be better able to reinfect people who have been previously infected and received some protection against COVID-19. That is pretty clear and was anticipated from the mutational changes we have pinpointed in its protein structure. These make it more difficult for antibodies to neutralise the virus."[95]
On 15 December 2021, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control assessed that, even if the variant turns out to be milder than Delta, its spread will very likely increase hospitalizations and fatalities due to the exponential growth in cases caused by increased transmissibility.[96]
On 23 December 2021, Nature indicates that, though Omicron likely weakens vaccine protection, reasonable effectiveness against Omicron may be maintained with currently available vaccination and boosting approaches.[97][98]
In non-human animals
In February 2022, the first confirmed case infecting a wild animal was confirmed by researchers at Pennsylvania State University in white-tailed deer in Staten Island, N.Y.[99]
Signs and symptoms
A unique reported symptom of the Omicron variant is night sweats.[8] Also, loss of taste and smell seem to be uncommon compared to other strains.[6][7]
A study performed between 1 and 7 December by the Center for Disease Control found that: "The most commonly reported symptoms [were] cough, fatigue, and congestion or runny nose" making it difficult to distinguish from a less damaging variant or other virus.[100]
Research published in London on 25 December 2021 suggested the most frequent symptoms stated by users of the Zoe Covid app were "a running nose, headaches, fatigue, sneezing and sore throats."[11]
Characteristics
Many of the mutations to the spike protein are present in other variants of concern and are related to increased infectivity and antibody evasion. Computational modeling suggests that the variant may also escape cell-mediated immunity.[35] On 26 November, the ECDC wrote that an evaluation of the neutralizing capacity of convalescent sera and of vaccines is urgently needed to assess possible immune escape, saying these data are expected within two to three weeks.[39]
Although transmission via fomites is rare, preliminary data indicate that the variant lasts for 194 hours on plastic surfaces and 21 hours on skin, compared with just 56 and 7 hours, respectively, for the ancestral Wuhan strain.[101][102]
Contagiousness
It was not known in November 2021 how the variant would spread in populations with high levels of immunity. It was also not known if the Omicron variant causes a milder or more severe COVID-19 infection. According to pharmaceutical companies, vaccines could be updated to combat the variant "in around 100 days" if necessary.[103]
Relating to naturally acquired immunity, Anne von Gottberg, an expert at the National Institute for Communicable Diseases, believed at the beginning of December 2021 that immunity granted by previous variants would not protect against Omicron.[104]
On 15 December 2021 Jenny Harries, head of the UK Health Security Agency, told a parliamentary committee that the doubling time of COVID-19 in most regions of the UK was now less than two days despite the country's high vaccination rate. She said that the Omicron variant of COVID-19 is "probably the most significant threat since the start of the pandemic", and that the number of cases in the next few days would be "quite staggering compared to the rate of growth that we've seen in cases for previous variants".[105]
In January 2022, William Schaffner, professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, compared the contagiousness of the Omicron variant to the contagiousness of the measles.[106]
Immune evasion
A study suggests that mutations that promote breakthrough infections or antibody-resistance "like those in Omicron" could be a new mechanism for viral evolution success of SARS-CoV-2 and that such may become a dominating mechanism of its evolution.[107] A preprint supports such an explanation of Omicron's spread, suggesting that it "primarily can be ascribed to the immune evasiveness rather than an inherent increase in the basic transmissibility".[108][109] Studies showed the variant to escape the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies, including of sera from vaccinated and convalescent individuals.[110][111][112][113] Nevertheless, current vaccines are expected to protect against severe illness, hospitalizations, and deaths due to Omicron[114] and, on an individual level, the Omicron variant is milder than earlier variants that evolved when the antibody/vaccination share was lower than it was when Omicron emerged.[15]
Virulence
As of 28 November 2021 the World Health Organization's update states "There is currently no information to suggest that symptoms associated with Omicron are different from ... other variants". Increased rates of hospitalization in South Africa may be due to a higher number of cases, rather than any specific feature of the Omicron variant.[115]
On 4 December 2021, the South African Medical Research Council reported that from 14 to 29 November 2021 at a hospital complex in Tshwane, inpatients were younger than in previous waves and the ICU and oxygen therapy rates were lower than in earlier waves. These observations are not definitive and the clinical profile could change over the following two weeks, allowing for more accurate conclusions about disease severity.[116] Excess deaths nearly doubled in the week of 28 November, suggesting under-reporting, but the level was still much lower than that seen in the second wave in mid-January 2021.[117]
On 12 December, director-general of the World Health Organization Tedros Adhanom asserted that it was wrong for people to consider Omicron as mild
. This is because high exposure to previous infections in South Africa likely affects the clinical course of the new infections.[118]
On 20 December, a report by the Imperial College COVID-19 Response Team, based on data from England, found that hospitalisation and asymptomatic infection indicators were not significantly associated with Omicron infection, suggesting at most limited changes in severity compared with Delta.
[119] On 22 December, the team reported an approximately 41% (95% CI, 37–45%) lower risk of a hospitalization requiring a stay of at least 1 night compared to the Delta variant, and that the data suggest that recipients of 2 doses of the Pfizer–BioNTech, the Moderna or the Oxford–AstraZeneca vaccine remain substantially protected from hospitalization.[120]
In January, the CDC confirmed that the variant causes less severe disease than previously dominant variants.[121] The novel Omicron subtype 'BA.2' did not initially show an increase over this lower virulence,[122][123][124] albeit one preprint found that "infection experiments using hamsters show that BA.2 is more pathogenic than BA.1".[125] Nevertheless, in the U.S., the daily new COVID-19 deaths were higher during Omicron dominance than during Delta's during fall[126] and high volumes of hospitalizations due to the variant's other characteristics can cause indirect harm via local health care system strains,[121] beyond less severe but often non-mild disease effects.[126]
Diagnosis
PCR testing
The FDA has published guidelines on how PCR tests will be affected by Omicron.[127] Tests that detect multiple gene targets will continue to identify the testee as positive for COVID-19. S-gene dropout or target failure has been proposed as a shorthand way of differentiating Omicron from Delta. The variant can also be identified by sequencing and genotyping.[128]
Rapid antigen testing
In January 2022 the medicine and therapeutic regulatory agency Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) of the Australian Government states that only one of their 23 approved COVID-19 rapid antigen tests (RAT) detected Omicron in their review.[129]
Prevention
As with other variants, the WHO recommended that people continue to keep enclosed spaces well ventilated, avoid crowding and close contact, wear well-fitting masks, clean hands frequently, and get vaccinated.[12][130]
- Response by vaccine producers
On 26 November 2021, BioNTech said it would know in two weeks whether the current vaccine is effective against the variant and that an updated vaccine could be shipped in 100 days if necessary. AstraZeneca, Moderna and Johnson & Johnson were also studying the variant's impact on the effectiveness of their vaccines.[131] On the same day, Novavax stated that it was developing an updated vaccine requiring two doses for the Omicron variant, which the company expected to be ready for testing and manufacturing within a few weeks.[132][133] On 29 November 2021, The Gamaleya Institute said that Sputnik Light should be effective against the variant, that it would begin adapting Sputnik V, and that a modified version could be ready for mass production in 45 days.[134] Sinovac said it could quickly mass-produce an inactivated vaccine against the variant and that it was monitoring studies and collecting samples of the variant to determine if a new vaccine is needed.[135] On 7 December 2021, at a symposium in Brazil with its partner Instituto Butantan, Sinovac said it would update its vaccine to the new variant and make it available in three months.[136] On December 2, the Finlay Institute was already developing a version of Soberana Plus against the variant.[137] Pfizer hopes to have a vaccine targeted to immunize against Omicron ready by March 2022.[138]
- WHO
On 29 November 2021, the WHO said cases and infections are expected among those vaccinated, albeit in a small and predictable proportion.[139]
- Vaccine efficacy
In December, studies, some of which using large nationwide datasets from either Israel and Denmark, found that vaccine effectiveness of multiple common two-dosed COVID-19 vaccines is substantially lower against the Omicron variant than for other common variants including the Delta variant, and that a new (often a third) dose – a booster dose – is needed and effective, with it i.a. substantially reducing deaths from the disease compared to cohorts who received no booster but two doses.[140][141][142][143][144][145]
On 7 December 2021, preliminary results from a laboratory test conducted at the Africa Health Research Institute in Durban with 12 people who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine found a 41-fold reduction in neutralizing antibody activity against the variant in some of the samples. This is a big reduction, but it does not mean that the variant can escape vaccines completely, so vaccination with current vaccines is still recommended. Neutralizing antibody activity against the variant was greater in those fully vaccinated after being infected about a year earlier. Effectiveness estimates will likely change as more data is collected, as antibodies generated by vaccination vary widely between individuals and the sample was small.[146][147][148] On 8 December 2021, Pfizer and BioNTech reported that preliminary data indicated that a third dose of the vaccine would provide a similar level of neutralizing antibodies against the variant as seen against other variants after two doses.[149]
On 10 December 2021, the UK Health Security Agency reported that early data indicated a 20- to 40-fold reduction in neutralizing activity for Omicron by sera from Pfizer 2-dose vaccinees relative to earlier strains and a 20-fold reduction relative to Delta. The reduction was greater in sera from AstraZeneca 2-dose vaccinees, falling below the detectable threshold. An mRNA booster dose produced a similar increase in neutralising activity regardless of the vaccine used for primary vaccination. After a booster dose (usually with an mRNA vaccine),[150] vaccine effectiveness against symptomatic disease was at 70%–75%, and the effectiveness against severe disease was expected to be higher.[151]
- WHO recommendations for epidemiology
On 26 November 2021, the WHO asked nations to do the following:
- Enhance surveillance and sequencing efforts to better understand circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants.
- Submit complete genome sequences and associated metadata to a publicly available database, such as GISAID.
- Report initial cases/clusters associated with virus-of-concern infection to WHO through the IHR mechanism.
- Where capacity exists and in coordination with the international community, perform field investigations and laboratory assessments to improve understanding of the potential impacts of the virus of concern on COVID-19 epidemiology, severity, and the effectiveness of public health and social measures, diagnostic methods, immune responses, antibody neutralization, or other relevant characteristics.[152]
Treatment
Corticosteroids such as dexamethasone and IL6 receptor blockers such as tocilizumab (Actemra) are known to be effective for managing patients with the earlier strains of severe COVID-19. The impact on the effectiveness of other treatments was being assessed in 2021.[153][154]
Relating to monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) treatments, similar testing and research is ongoing. Preclinical data on in vitro pseudotyped virus data demonstrate that some mAbs designed to use highly conserved epitopes retain neutralizing activity against key mutations of Omicron substitutions.[155] Similar results are confirmed by cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray data, also providing the structural approach and molecular basis for the evasion of humoral immunity exhibited by Omicron antigenic shift as well as the importance of targeting conserved epitopes for vaccine and therapeutics design. While 7 clinical mAbs or mAb cocktails experienced loss of neutralizing activity of 1-2 orders of magnitude or greater relative to the prototypic virus, the S309 mAb, the parent mAb of sotrovimab, neutralized Omicron with only 2-3-fold reduced potency.[156] Further data suggest Omicron would cause significant humoral immune evasion, while neutralizing antibodies targeting the sarbecovirus conserved region remain most effective.[157] Indeed, most receptor-binding motif (RBM)-directed monoclonal antibodies lost in vitro neutralizing activity against Omicron, with only 3 out of 29 mAbs examined in another study retaining unaltered potency. Furthermore, a fraction of broadly neutralizing sarbecovirus mAbs neutralized Omicron through recognition of antigenic sites outside the RBM, including sotrovimab (VIR-7831), S2X259 and S2H97.[158]
Epidemiology
On 26 November 2021, the South African National Institute for Communicable Diseases announced that 30,904 COVID-tests (in one day) detected 2,828 new COVID infections (a 9.2% positivity rate).[159] One week later, on 3 December 2021, the NICD announced that 65,990 COVID tests had found 16,055 new infections (5.7 times as many as seven days before; positive rate 24.3%) and that 72 percent of them were found in Gauteng.[160][161] This province of South Africa is densely populated at about 850 inhabitants per km2. Gauteng's capital Johannesburg is a megacity (about 5.5 million inhabitants in the city itself plus 9.5 million in the urban region).
In November 2021 the transmissibility of the Omicron variant, as compared to the Delta variant or other variants of the COVID-19 virus, was still uncertain.[162] Omicron is frequently able to infect previously Covid-positive people.[163][164]
It has been estimated the Omicron variant diverged in late September or early October 2021, based on Omicron genome comparisons.[165] Sequencing data suggests that Omicron had become the dominant variant in South Africa by November 2021, the same month where it had been first identified in the country.[166][167]
Phylogeny suggests a recent emergence. Data from South Africa suggests that Omicron has a pronounced growth advantage there. However, this may be due to transmissibility or immune escape related, or both."[168] Also the serial interval plays a role in the growth.
Detectable changes in levels of COVID-19 in wastewater samples from South Africa's Gauteng province were seen as early as 17–23 October (week 42).[169] The National Institute for Communicable Diseases reports that children under the age of 2 make up 10% of total hospital admissions in the Omicron point of discovery Tshwane in South Africa.[170] Data on the S gene target failure (SGTF) of sampled cases in South Africa indicates a growth of 21% per day relative to Delta, generating an increased reproduction number by a factor of 2.4.[a] Omicron became the majority strain in South Africa around 10 November.[171][172] Another analysis showed 32% growth per day in Gauteng, South Africa, having become dominant there around 6 November.[173]
In the UK, the logarithmic growth rate of Omicron-associated S gene target failure (SGTF) cases over S gene target positive (SGTP) cases was estimated at 0.37 per day,[b] which is exceptionally high.[174] Furthermore, by 14 December it appears to have become the most dominant strain.[c][175] Without presuming behavior change in response to the variant, a million infections per day by December 24 are projected for a 2.5 days doubling time.[d][128] In Denmark, the growth rate has been roughly similar with a doubling time of about 2–3 days, it having become the most prevalent strain on 17 December.[176][177][178] Switzerland is not far behind.[179] In Germany Omicron became the most prevalent variant on January 1.[180] In Scotland, Omicron apparently became the most prevalent variant on 17 December.[181][182] In the Canadian province of Ontario it became the most prevalent strain on 13 December.[183] In the US, the variant appears to have become the most prevalent strain on December 18, growing at 0.24 per day.[184] In Portugal, Omicron had reached 61.5% of cases on 22 December.[185] In Belgium, the strain has become the most prevalent on 25 December,[186] and in the Netherlands on 28 December.[187] In Italy, it had reached 28% of cases on 20 December and was doubling every two days,[188] while it became the dominant variant in Norway on 25 December.[189] In France, it made up about 15% of COVID-19 cases in mid-December, but around 27 December it had increased to more than 60%.[190][191] Researchers recommend sampling at least 5% of COVID-19 patient samples in order to detect Omicron or other emerging variants.[192]
During January 2022, in Denmark the BA.2 variant grew at ~0.10 per day (+11% per day) as a ratio to BA.1 (the legacy Omicron variant), and became the dominant strain in week 2, 2022.[81] In the United Kingdom, the BA.2 variant was growing at ~0.11 per day (+12% per day) as a ratio to BA.1.[193]
On 13 January 2022, the BBC reported that the hospitalization rate was higher in the US and Canada than in Europe and South Africa. This was attributed to a combination of a greater number of elderly people than in South Africa, greater prevalence of comorbidities such as hypertension and obesity than in Europe, higher indoor transmission due to the winter, lower vaccination rate in the US than in Europe and Canada, and a possible still high prevalence of the Delta variant, which more often leads to hospitalization.[194]
Statistics

- 100,000–999,999
- 10,000–99,999
- 1,000–9,999
- 100–999
- 10–99
- 1–9
- 0
The chance of detecting a case particularly depends on a country's sequencing rate. For example, South Africa sequences far more samples than any other country in Africa, but at a considerably lower rate than most Western nations.[195][196] Furthermore, it can take up to two weeks to return a viral sequence in places with the technical capability, hence solid statistics on confirmed cases lag the actual situation.[197] Denmark and Norway regard cases found by their variant qPCR test, which is relatively fast and checks several genes,[56] as sufficient for counting it as an Omicron, also before full sequencing.[198][199]
| Country/Territory | Confirmed cases (PANGOLIN)[200] as of 11 February |
Confirmed cases (GISAID)[201] as of 11 February |
Confirmed cases (other sources) as of 11 February |
Suspected cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 123,729 | 422,945 | 246,780[202] | 600,041[202] | |
| 18,660 | 69,789 | 66,563[203] | – | |
| 91,721 | 356,079 | 62,480[204] | – | |
| 8,509 | 14,538 | 2,113[205] | – | |
| 3,679 | 24,190 | 69,264[206] | – | |
| 3,511 | 48,855 | 268,661[207] | – | |
| 694 | 5,131 | 45,296[198] | – | |
| 17 | 2,642 | 290,378[208][209] | – | |
| 3,513 | 26,484 | 5,591[210] | – | |
| 3,057 | 5,045 | 3,779[211] | – | |
| 276 | 2,177 | 5,397[212] | – | |
| 715 | 1,723 | 4,322[213][214][215][216] | – | |
| – | 507 | 3,857[217][218][219] | – | |
| 5,130 | 11,453 | 11,071[220] | – | |
| 604 | 10,776 | 8,209[221][222] | – | |
| 1,485 | 12,915 | 1,741[223][224] | 861[223] | |
| 2,224 | 5,532 | 1,095[225] | 19,070[226] | |
| 68 | 822 | 1,318[227] | – | |
| 2,289 | 9,927 | 51[207][228] | – | |
| 1,963 | 8,560 | 121[208][228] | – | |
| 1,322 | 5,471 | 28,583[229] | – | |
| 2,282 | 11,534 | 19,269[208][230] | – | |
| 121 | 1,057 | 455[231][232] | 80[233] | |
| 493 | 1,187 | 23[234] | – | |
| 1,606 | 8,010 | 123[235][228] | – | |
| 2,552 | 5,203 | 7,780[236] | – | |
| 112 | 122 | 24[237] | – | |
| – | – | 84[238] | – | |
| 2,321 | 9,087 | 84[239] | – | |
| 332 | 2,642 | 684[240][241][242] | – | |
| 594 | 2,569 | 69[243][228] | 6[244][208] | |
| 29 | 33 | 76[245] | 246[245] | |
| 163 | 218 | 50[246] | – | |
| 60 | 67 | 33[234] | – | |
| 574 | 9,598 | 203[247] | – | |
| 233 | 923 | 523[248][249] | – | |
| – | – | 31[250][251] | – | |
| 208 | 193 | 27[252] | – | |
| 152 | 311 | 8,239[253] | – | |
| – | – | 44[254] | 59[254] | |
| 11 | 32 | 25[255][256] | – | |
| 1,473 | 5,940 | 1[257] | – | |
| 170 | 1,030 | 116[258] | – | |
| – | 178 | 18[259] | – | |
| 76 | 216 | 102[260][261] | – | |
| – | 90 | 3[262] | – | |
| 22 | 83 | 2[263] | 2[204] | |
| 6 | 324 | 17[208][264] | – | |
| – | 20 | 144[265][266] | – | |
| – | 407 | 644[267][228][268] | – | |
| 82 | 880 | 25[269][270][271] | – | |
| 212 | 732 | 245[272] | – | |
| 38 | 48 | 11[273] | – | |
| 146 | 676 | 6[274] | – | |
| 109 | 3,588 | 10[208][275][228] | – | |
| – | 11 | 9[276] | – | |
| 308 | 4,686 | 1,418[277][228][278][279] | – | |
| 4 | 4 | 433[280][281] | 16[280] | |
| 6 | 1,214 | 2[282] | – | |
| 8 | 74 | 7[204] | – | |
| 235 | 14,467 | 1[283] | – | |
| – | 14 | 6[283] | – | |
| 242 | 4,078 | 6[284] | – | |
| 11 | 15 | 5[285] | – | |
| 46 | 350 | 31[286] | – | |
| 36 | 599 | 2551[287] | – | |
| 25 | 33 | 832[288] | – | |
| 10 | 10 | 4[289][290][291] | – | |
| – | – | 92[292][293][294] | – | |
| 10 | 3,805 | 3[208] | – | |
| – | 26 | 3[283] | – | |
| 73 | 91 | 3[295] | – | |
| – | – | 126[296][297] | – | |
| – | 4 | 89[298] | – | |
| 113 | 548 | 2[299] | – | |
| 131 | 1,364 | 3[300] | ||
| 47 | 894 | 3[301] | – | |
| 6 | 119 | 1[302] | – | |
| 460 | 1,319 | 1[303] | – | |
| – | – | 2[304] | – | |
| 27 | 100 | 2[305] | – | |
| – | 5 | 4[306] | – | |
| 34 | 1,145 | 535[307][308][309][310][311][312] | – | |
| – | – | 9[313] | – | |
| 33 | 235 | 10[314] | – | |
| 24 | 72 | 1[315] | 3[204] | |
| – | 28 | 61[316][228][317] | – | |
| 9 | 10 | 2[318] | – | |
| 28 | 73 | 75[319][320] | – | |
| 43 | 451 | 1[321] | – | |
| 110 | 361 | 600[322] | – | |
| – | 2 | 1[283] | – | |
| – | – | 1[323] | – | |
| 65 | 351 | 1[324] | – | |
| – | – | 1[325] | – | |
| 208 | 2,687 | 1[208] | – | |
| 18 | 199 | 5[326][327] | – | |
| – | 1 | 1[328] | – | |
| – | 30 | 1[329] | – | |
| – | 1 | 1[330] | – | |
| – | 1 | 1[331] | – | |
| – | 69 | 467[332] | – | |
| – | 2 | 1[333] | – | |
| – | 1 | 1[334] | – | |
| 62 | 499 | 1[335] | – | |
| 17 | 44 | 1[336] | – | |
| – | 4 | 9[337][338] | – | |
| – | 175 | 108[339] | – | |
| 12 | 158 | 8[340] | – | |
| 48 | 124 | 2[341] | – | |
| 2 | 2 | 7[342] | – | |
| 133 | 299 | 20[343] | – | |
| – | 27 | 1[344] | – | |
| – | 95 | 4[345] | – | |
| – | 72 | 3[346] | – | |
| – | – | 2[347] | – | |
| – | 212 | 1[348] | – | |
| – | 4 | 2[349] | – | |
| – | – | 2[350] | – | |
| – | – | 1[351] | – | |
| – | 1 | 1[352] | – | |
| – | 49 | 1[353] | – | |
| – | 1 | 1[354] | – | |
| – | – | 1[355] | – | |
| – | 33 | 1[356] | – | |
| – | 3 | 1[357] | – | |
| – | – | 5[358] | – | |
| – | – | 4[359] | – | |
| 14 | 89 | 10[360] | – | |
| – | 1 | 16[361] | – | |
| – | 50 | 1[362] | – | |
| – | 353 | 12[363] | – | |
| 3 | 106 | 1[364] | – | |
| – | 57 | 1[365] | – | |
| – | 85 | 26[366] | – | |
| – | – | – | – | |
| – | 36 | 2[367] | – | |
| – | – | 1[368] | – | |
| 4 | 55 | 5[369] | – | |
| – | – | 14[370] | – | |
| – | – | 41[371] | – | |
| – | – | 78[372] | – | |
| – | – | 175[373] | – | |
| – | 9 | 1[374] | – | |
| – | – | 1[375] | – | |
| – | – | 1[376] | – | |
| 16 | 45 | 29[377] | – | |
| 6 | 6 | 8[378] | – | |
| 4 | 78 | 1[379] | – | |
| 12 | 12 | 12[380] | – | |
| 13 | 15 | – | – | |
| – | 296 | – | – | |
| – | 22 | – | – | |
| – | 2 | – | – | |
| – | 4 | – | – | |
| – | 226 | – | – | |
| – | – | 14[381] | – | |
| – | – | 1[382] | – | |
| – | – | 12[383] | – | |
| – | – | 24[384] | – | |
| – | – | 1[385] | – | |
| – | 1 | – | – | |
| – | 1 | – | – | |
| – | 6 | – | – | |
| – | 16 | – | – | |
| – | 19 | – | – | |
| – | 59 | – | – | |
| – | 93 | – | – | |
| – | 133 | – | – | |
| – | 155 | – | – | |
| World total (170 countries and territories) | 279,752 | 1,150,309 | 964,777 | 620,384 |
History
On 26 November 2021, WHO designated it as a variant of concern and named it "Omicron" after the fifteenth letter in the Greek alphabet.[22] Omicron was first detected on 22 November 2021 in laboratories in Botswana and South Africa based on samples collected on 11–16 November.[386][387] The first known sample was collected in South Africa on 8 November.[167][388] The first known case, outside of South Africa, was a person arriving in Hong Kong from South Africa via Qatar on 11 November, and another person who arrived in Belgium from Egypt via Turkey on the same date.[389][390] As of 7 January 2022, the variant has been confirmed in 135 countries.[391] Omicron has an unusually large number of mutations compared to previous variants.[392][33][46][13] Several of the mutations are novel and involve changes to the spike protein reducing the ability for COVID-19 vaccines to prevent symptomatic disease.[20]
A December 2021 article in Science[393] observes Omicron did not evolve from any other variant of note, but instead on a distinct track diverging in perhaps mid-2020. The article expounds on three theories that might explain this surprising genetic lineage:
- The virus could have circulated and evolved in a population with little surveillance and sequencing.
- It could have gestated in a chronically infected COVID-19 patient.
- It might have evolved in a nonhuman species, from which it recently spilled back into people.
Reported cases
On 24 November 2021, the variant was first reported to the WHO from South Africa,[12] based on samples that had been collected from 14 to 16 November.[394] South African scientists were first alerted by samples from the very beginning of November where the PCR tests had S gene target failure (occurs in a few variants, but not in Delta which dominated in the country in October) and by a sudden increase of COVID-19 cases in Gauteng; sequencing revealed that more than 70 percent of samples collected in the province between 14 and 23 November were a new variant.[395][396] The first confirmed specimens of Omicron were collected on 8 November 2021 in South Africa,[167][388] and on 9 November in Botswana.[35] Likely Omicron (SGTF) samples had occurred on 4 November 2021 in Pretoria, South Africa.[397]
When WHO was alerted on 24 November, Hong Kong was the only place outside Africa that had confirmed a case of Omicron; one person who traveled from South Africa on 11 November, and another traveler who was cross-infected by this case while staying in the same quarantine hotel.[396][398][399]
On 25 November, one confirmed case was identified in Israel from a traveler returning from Malawi,[400] along with two who returned from South Africa and one from Madagascar.[401] All four initial cases reported from Botswana occurred among fully vaccinated individuals.[402]
On 26 November, Belgium confirmed its first case; an unvaccinated person who had travelled from Egypt via Turkey on 11 November.[389][403][404] All three initial confirmed and suspected cases reported from Israel occurred among fully vaccinated individuals,[400] as did a single suspected case in Germany.[405]
On 27 November, two cases were detected in the United Kingdom, another two in Munich, Germany and one in Milan, Italy.[406]
On 28 November, 13 cases were confirmed in the Netherlands among the 624 airline passengers who arrived from South Africa on 26 November.[407] Confirmation of a further 5 cases among these passengers followed later.[408] Entry into the Netherlands generally required having been vaccinated or PCR-tested, or having recovered. The passengers of these two flights had been tested upon arrival because of the newly imposed restrictions (which were set in place during their flight), after which 61 tested positive for SARS-CoV-2.[409] A further two cases were detected in Australia. Both people landed in Sydney the previous day, and travelled from southern Africa to Sydney Airport via Doha Airport. The two people, who were fully vaccinated, entered isolation; 12 other travellers from southern Africa also entered quarantine for fourteen days, while about 260 other passengers and crew on the flight have been directed to isolate.[410] Two travellers from South Africa who landed in Denmark tested positive for COVID-19; it was confirmed on 28 November that both carried the Omicron variant.[411][412] On the same day, Austria also confirmed its first Omicron case.[413] A detected Omicron case was reported in the Czech Republic, from a traveler who spent time in Namibia.[414] Canada also reported its first Omicron cases, with two from travelers from Nigeria, therefore becoming the first North American country to report an Omicron case.[415]
On 29 November, a positive case was recorded in Darwin, Australia. The person arrived in Darwin on a repatriation flight from Johannesburg, South Africa on 25 November, and was taken to a quarantine facility, where the positive test was recorded.[416] Two more people who travelled to Sydney from southern Africa via Singapore tested positive.[417] Portugal reported 13 Omicron cases, all of them members of a soccer club.[418] Sweden also confirmed their first case on 29 November,[419] as did Spain, when a traveler came from South Africa.[420]
On 30 November, the Netherlands reported that Omicron cases had been detected in two samples dating back as early as 19 November.[421] A positive case was recorded in Sydney from a traveller who had visited southern Africa before travel restrictions were imposed, and was subsequently active in the community.[422] Japan also confirmed its first case.[423] Two Israeli doctors have tested positive and have entered isolation. Both of them had received three shots of the Pfizer vaccine prior to testing positive.[424] In Brazil, three cases of the Omicron variant were confirmed in São Paulo.[425] Another five are under suspicion.[426][427] A person in Leipzig, Germany with no travel history nor contact with travellers tested positive for Omicron.[428]
On 1 December, the Omicron variant was detected in three samples in Nigeria that had been collected from travelers from South Africa within the last week.[429][430] On the same day, public health authorities in the United States announced the country's first confirmed Omicron case. A resident of San Francisco who had been vaccinated returned from South Africa on 22 November, began showing mild symptoms on 25 November[431] and was confirmed to have a mild case of COVID-19 on 29 November.[432] Ireland and South Korea also reported their first cases.[433] South Korea reported its cases from five travelers arriving in South Korea from Nigeria.[434]
On 2 December, Dutch health authorities confirmed that all 14 passengers with confirmed Omicron infection on 26 November had been previously vaccinated.[435] The same day, the Norwegian Institute of Public Health confirmed that 50 attendees of a company Christmas party held at a restaurant in Norway's capital, Oslo, were infected with the Omicron variant.[436] France has confirmed only 25 cases of the new Omicron variant but officials say the number could jump significantly in the coming weeks.[437]
By 6 December, Malaysia confirmed its first case of the variant. The case was a South African student entering to study at a private university.[438] In Namibia, 18 cases out of 19 positive COVID-19 samples that had been collected between 11 and 26 November were found to be Omicron, indicating a high level of prevalence in the country.[439] Fiji also confirmed two positive cases of the variant. They travelled from Nigeria arriving in Fiji on November 25.[440]
On 8 December, WHO announced the variant had been detected in 57 countries.[441]
On 9 December, Richard Mihigo, coordinator of the World Health Organisation's Immunisation and Vaccine Development Programme for Africa, announced that Africa accounted for 46% of reported cases of the Omicron variant globally.[442]
On 13 December, the first death of a person with Omicron was reported in the UK.[443]
On 16 December, New Zealand confirmed its first case of the Omicron variant, an individual who had traveled from Germany via Dubai.[444]
The first death of a person with Omicron was reported in Germany on 23 December[445] and in Australia on 27 December.[446]
On 3 January 2022, South Korea reported the first two deaths of people who tested positive post mortem for Omicron.[447]
Market reactions
Worry about the potential economic impact of the Omicron variant led to a drop in global markets on 26 November, including the worst drop of the Dow Jones Industrial Average in 2021, led by travel-related stocks. The price of Brent Crude and West Texas Intermediate oil fell 10% and 11.7%, respectively.[448] Cryptocurrency markets were also routed.[449][450] The South African rand has also hit an all-time low for 2021, trading at over 16 rand to the dollar, losing 6% of its value in November.[451][452][453]
In early December 2021, the chairman of the Federal Reserve, Jerome Powell, testified before the U.S. Senate Committee on Banking that "The recent rise in COVID-19 cases and the emergence of the Omicron variant pose downside risks to employment and economic activity and increased uncertainty for inflation."[454]
International response
On 26 November 2021, WHO advised countries not to impose new restrictions on travel, instead recommending a "risk-based and scientific" approach to travel measures.[455] On the same day, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) reported modeling indicating that strict travel restrictions would delay the variant's impact on European countries by two weeks, possibly allowing countries to prepare for it.[39]
After the WHO announcement, on the same day, several countries announced travel bans from southern Africa in response to the identification of the variant, including the United States, which banned travel from eight African countries,[456] although it notably did not ban travel from any European countries, Israel, Canada, or Australia where cases were also detected at the time the bans were announced. Other countries that also implemented travel bans include Japan, Canada, the European Union, Israel, Australia, the United Kingdom, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Morocco, and New Zealand.[457][458]
The Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency recommended flight restrictions regarding the new variant.[459] The state of New York declared a state of emergency ahead of a potential Omicron spike, although no cases had yet been detected in the state or the rest of the United States.[460] On 27 November, Switzerland introduced obligatory tests and quarantine for all visitors arriving from countries where the variant was detected, which originally included Belgium and Israel.[461]
In response to the various travel bans, South African Minister of Health Joe Phaahla defended his country's handling of the pandemic and said that travel bans went against the "norms and standards" of the World Health Organization.[462]
Some speculate that travel bans could have a significant impact on South Africa's economy by limiting tourism and could lead to other countries with economies that are reliant on tourism to hide the discovery of new variants of concern. Low vaccine coverage in less-developed nations could create opportunities for the emergence of new variants, and these nations also struggle to gain intellectual property to develop and produce vaccines locally.[463] At the same time, inoculation has slowed in South Africa due to vaccine hesitancy and apathy, with a nationwide vaccination rate of only 35% as of November 2021.[464]
On 29 November, the WHO warned countries that the variant poses a very high global risk with severe consequences and that they should prepare by accelerating vaccination of high-priority groups and strengthening health systems. WHO director-general Tedros Adhanom described the global situation as dangerous and precarious and called for a new agreement on the handling of pandemics, as the current system disincentivizes countries from alerting others to threats that will inevitably land on their shores.
CEPI CEO Richard Hatchett said that the variant fulfilled predictions that transmission of the virus in low-vaccination areas would accelerate its evolution.[139]
In preparation for the Omicron variant arriving in the United States, President Joe Biden has stated that the variant is "cause for concern, not panic" and reiterated that the government is prepared for the variant and will have it under control. He also stated that large-scale lockdowns, similar to the ones in 2020 near the beginning of the pandemic, are "off the table for now."[465]
In mid-December, multiple Canadian provinces reinstated restrictions on gatherings and events such as sports tournaments, and tightened enforcement of proof of vaccination orders. British Columbia expressly prohibited any non-seated "organized New Year's Eve event",[466][467][468] while Quebec announced a partial lockdown on 20 December, ordering the closure of all bars, casinos, gyms, schools, and theatres, as well as imposing restrictions on the capacity and operating hours of restaurants, and the prohibition of spectators at professional sporting events.[469]
On 18 December, the Netherlands government announced a lockdown intended to prevent spread of the variant during the holiday period.[470]
In late December, some countries shortened the typical six-month interval for a booster dose of the vaccine to prepare for a wave of Omicron, as two doses are not enough to stop the infection. UK, South Korea and Thailand reduced to three months; Belgium, four months; France, Singapore, Taiwan, Italy and Australia, five months. Finland reduced it to three months for risk groups. Other countries continued with a six-month booster schedule. While antibody levels begin to drop at four months, a longer interval usually allows time for the immune system's response to mature.[471]
See also
- Timeline of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant
- COVID-19 pandemic in Africa
- COVID-19 vaccination in Africa
- COVID-19 vaccination in Botswana
- COVID-19 vaccination in South Africa
- Variants of SARS-CoV-2
Notes
- ^ With a presumed identical person-to-person serial interval of log_e(2.4)/0.21 ~ 4.2 days, or a distribution thereof to the same effect.
- ^ Logarithmic growth rate of 0.37/day means that the log odds loge(SGTF/SGTP) is increasing by 0.37 in a day. So SGTF/SGTP was increasing by a multiplicative factor of exp(0.37) ~ 1.45. This is substantially higher than a naive increase to 100%+37%. The difference is mathematically due to compound growth within the day, which does not imply that epidemically people are already infectious within a day. Rather, simplified (non-delay) differential equations are used for convenience for the modeling. This also indicates a doubling time of log_e(2)/(0.37/day) ~ 1. days for the Omicron to Delta prevalence ratio.
- ^ Referring to ref 12 in the reference, where the x-axis is crossed at 14 December.
- ^ A doubling time of 2.5 days corresponds to an exponential growth rate of ln(2)/(2.5 days) ~ 0.28/day. Direct comparison to the logistic growth rate needs to take the growth/decline of Delta into account.
References
- ^ a b c Yadav PD, Gupta N, Potdar V, Mohandas S, Sahay RR, Sarkale P, et al. (January 2022). An in vitro and in vivo approach for the isolation of Omicron variant from human clinical specimens. pp. 2022–01.02.474750. doi:10.1101/2022.01.02.474750. Archived from the original on 16 January 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ^ a b Padin, Malvika (17 January 2022). "Feeling light-headed may be an early indication you have Omicron Covid variant". mirror. Archived from the original on 28 January 2022. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- ^ Poudel S, Ishak A, Perez-Fernandez J, Garcia E, León-Figueroa DA, Romaní L, et al. (December 2021). "Highly mutated SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant sparks significant concern among global experts – What is known so far?". Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease. 45: 102234. doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2021.102234. PMC 8666662. PMID 34896326.
- ^ "How Omicron Symptoms Compare with Other Variants". Healthline. 14 January 2022. Archived from the original on 21 January 2022. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- ^ a b Omicron’s cold-like symptoms mean UK guidance ‘needs urgent update’ Archived 25 December 2021 at the Wayback Machine The Guardian
- ^ a b "Omicron Symptoms: Here's How They Differ From Other Variants". NBC Chicago. Archived from the original on 24 January 2022. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- ^ a b Slater, Jack (23 January 2022). "Is a change to your taste or smell a sign of Omicron?". Metro. Archived from the original on 26 January 2022. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- ^ a b Scribner H (21 December 2021). "Doctor reveals new nightly omicron variant symptom". Deseret News. Archived from the original on 2 January 2022. Retrieved 1 January 2022.
- ^ "Does Omicron cause less damage to the lungs?". www.medicalnewstoday.com. 14 January 2022.
- ^ Murrison, Pip (18 January 2022). "Omicron symptoms: Three distinctive rashes to watch for". Express.co.uk. Archived from the original on 12 January 2022. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- ^ a b Omicron’s cold-like symptoms mean UK guidance ‘needs urgent update’ Archived 25 December 2021 at the Wayback Machine The Guardian
- ^ a b c d e "Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern". World Health Organization. 26 November 2021. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ a b Gowrisankar A, Priyanka TM, Banerjee S (10 January 2022). "Omicron: a mysterious variant of concern". The European Physical Journal Plus. 137 (1): 100. Bibcode:2022EPJP..137..100G. doi:10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-02321-y. ISSN 2190-5444. PMC 8743750. PMID 35036269.
- ^ Harvard Medical School (6 January 2022). "Coronavirus Resource Center – Harvard Health". Harvard Health Publishing. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
Lab studies, animal studies, and epidemiological data all indicate that Omicron may cause less severe disease than previous variants.
- ^ a b David Leonhardt (5 January 2022). "Omicron Is Milder". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 6 January 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
A few weeks ago, many experts and journalists were warning that the initial evidence from South Africa — suggesting that Omicron was milder than other variants — might turn out to be a mirage. It has turned out to be real.
- ^ a b "Lung tissue study sheds light on fast Omicron spread". CIDRAP. Archived from the original on 16 December 2021. Retrieved 25 December 2021.
- ^ Lewnard, Joseph A.; Hong, Vennis X.; Patel, Manish M.; Kahn, Rebecca; Lipsitch, Marc; Tartof, Sara Y. (11 January 2022). "Clinical outcomes among patients infected with Omicron (B.1.1.529) SARS-CoV-2 variant in southern California": 2022.01.11.22269045. doi:10.1101/2022.01.11.22269045. S2CID 245851556. Archived from the original on 16 January 2022. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Some reduction in hospitalisation for Omicron v Delta in England: early analysis". Imperial College London. Archived from the original on 22 January 2022. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- ^ Ahmed SF, Quadeer AA, McKay MR (January 2022). "SARS-CoV-2 T Cell Responses Elicited by COVID-19 Vaccines or Infection Are Expected to Remain Robust against Omicron". Viruses. 14 (1): 79. doi:10.3390/v14010079. PMC 8781795. PMID 35062283.
- ^ a b Al Jurdi A, Gassen RB, Borges TD, Lape IT, Morena L, Efe O, et al. (6 January 2022). "Diminished antibody response against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant after third dose of mRNA vaccine in kidney transplant recipients": 2022.01.03.22268649. doi:10.1101/2022.01.03.22268649. S2CID 245739956. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "How Effective Are COVID-19 Vaccines Against Omicron?". Healthline. 7 January 2022. Archived from the original on 16 January 2022. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ a b c Parekh M, Platt P, Barnes J, et al. (Global Health Security Team) (26 November 2021). "Coronavirus latest news: EU suspends all flights to southern Africa over omicron Covid variant fears". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ Patel V (27 November 2021). "How Omicron, the New Covid-19 Variant, Got Its Name". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ "There are several COVID-19 variants you haven't heard of". NewsNation Now. 27 November 2021. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ "Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 18 June 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ "Countries are scrambling to stop a new covid variant". The Economist. 26 November 2021. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ Tcholakian D (15 December 2021). "'Omni is everywhere': why do so many people struggle to say Omicron?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 23 December 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ Zimmer B (2 December 2021). "'Omicron': Greek's 'Little O' Will Loom Larger Now". Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. Archived from the original on 3 December 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
President Joe Biden stumbled over the pronunciation in a press conference on Monday, calling the variant “omnicron” with an extra “n” sound. It has also been frequently misspelled that way online. The confusion is understandable, since we’re more familiar with words that have the Latin prefix “omni-” meaning “all,” as in “omnipresent” or “omnivore.”
- ^ "In focus". gisaid.org. GISAID. 28 November 2021. Archived from the original on 21 January 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
The unique mix of spike amino acid changes in Omicron GR/484A (B.1.1.529) is of interest as it comprises several that were previously known to affect receptor binding and antibody escape.
- ^ a b "Variant: 21K (Omicron)". covariants.org. CoVariants. 28 November 2021. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
Variant 21K (Omicron) appears to have arisen in November 2021, possibly in South Africa.
- ^ "SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England – Technical briefing 29" (PDF). gov.uk. UK Health Security Agency. 26 November 2021. p. 18. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ Hurst L (26 November 2021). "What we know so far about the B.1.1.529 'Omicron' COVID variant causing concern". Euronews. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ a b William A. Haseltine (2 December 2021). "Omicron Origins". Forbes. Archived from the original on 3 December 2021. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ Cookson C, Barnes O (26 November 2021). "What we know about Omicron variant that has sparked global alarm". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ a b c Callaway E (December 2021). "Heavily mutated Omicron variant puts scientists on alert". Nature. 600 (7887): 21. Bibcode:2021Natur.600...21C. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-03552-w. PMID 34824381. S2CID 244660616. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ Zimmer C (26 November 2021). "New Virus Variant Stokes Concern but Vaccines Still Likely to Work". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ Zhang L, Mann M, Syed ZA, Reynolds HM, Tian E, Samara NL, et al. (November 2021). "Furin cleavage of the SARS-CoV-2 spike is modulated by O-glycosylation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 118 (47): e2109905118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2109905118. PMC 8617502. PMID 34732583. S2CID 242937417.
- ^ SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England, technical briefing 29 (PDF) (Briefing). Public Health England. 26 November 2021. GOV-10481. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ a b c "Implications of the emergence and spread of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 variant of concern (Omicron) for the EU/EEA" (PDF). ecdc.europa.eu. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, Wall A, McGuire AT, Veesler D (April 2020). "Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein". Cell. 181 (2): 281–292.e6. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058. PMC 7102599. PMID 32155444.
- ^ "The birth of Omicron: Did HIV play a role?". www.medicalnewstoday.com. 6 December 2021. Archived from the original on 15 December 2021. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ^ "The mystery of where omicron came from — and why it matters". NPR. 1 December 2021. Archived from the original on 9 December 2021. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ "HIV and AIDS in South Africa". Avert. 21 July 2015. Archived from the original on 16 October 2015. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ Sample I (11 December 2021). "Why uncontrolled HIV may be behind the emergence of Omicron". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- ^ a b "Fact Check-Omicron is not the common cold 'rebranded'". Reuters. 10 December 2021. Archived from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 25 December 2021 – via www.reuters.com.
- ^ a b Wei C, Shan KJ, Wang W, Zhang S, Huan Q, Qian W (December 2021). "Evidence for a mouse origin of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant". Journal of Genetics and Genomics = Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 48 (12): 1111–1121. doi:10.1016/j.jgg.2021.12.003. PMC 8702434. PMID 34954396.
- ^ "Lineage B.1.1.529". PANGOLIN. 19 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ a b c McGregor G (21 January 2022). "What is 'stealth Omicron'? The rise of the subvariant is alarming some scientists who say it needs its own Greek letter". Fortune. Archived from the original on 23 January 2022. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ^ "En subvariant af omikron, BA.2, udgør nu knap halvdelen af alle danske omikrontilfælde" [A subvariant of Omicron, BA.2., now comprises almost half of all Danish Omicron cases] (in Danish). Statens Serum Institut. 19 January 2022. Archived from the original on 20 January 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Statement on Omicron sublineage BA.2". World Health Organization. 22 February 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ "Research identifies differences between Omicron lineages BA.1 and BA.2". News Medical Life Sciences. 16 February 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ a b Rajeshuni, N (26 January 2022). "Scientists monitoring new omicron subvariant BA.2". ABC News. Archived from the original on 1 February 2022. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ a b Sample I, Walker P (7 December 2021). "Scientists find 'stealth' version of Omicron that may be harder to track". www.theguardian.com. Archived from the original on 7 December 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ "Stealth Omicron: What is The Fast Spreading Omicron BA.2 Sub-Variant That Can Escape RT-PCR Test?". india.com. 23 January 2022. Archived from the original on 23 January 2022. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ^ a b c Parker C (21 January 2022). "Government scientists monitoring new BA.2 variant of Omicron". Yahoo News. Archived from the original on 21 January 2022. Retrieved 21 January 2022.
- ^ a b "Variant-PCR-testen (tidl. Delta-PCR-testen)" (in Danish). Statens Serum Institut. 21 December 2021. Archived from the original on 7 February 2021. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ a b "SARS-CoV-2の変異株B.1.1.529系統(オミクロン株)について(第6報)" (in Japanese). National Institute of Infectious Diseases (Japan). 14 January 2022. Archived from the original on 20 January 2022. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- ^ "Delta Variant Report". outbreak.info (Scripps Research). 13 December 2021. Archived from the original on 19 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ "BA.1 Lineage Report". outbreak.info (Scripps Research). 19 December 2021. Archived from the original on 16 December 2021. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ a b "BA.2 Lineage Report". outbreak.info (Scripps Research). 21 January 2022. Archived from the original on 13 December 2021. Retrieved 21 January 2022.
- ^ Zimmer C, Lyons, PJ (24 February 2022). "Is the BA.2 version of Omicron worse? Here's what you need to know". New York Times. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ "Lineage BA.3". PANGOLIN. 25 January 2022. Archived from the original on 27 January 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "BA.3 Lineage Report". outbreak.info (Scripps Research). 19 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ Goodman B (24 February 2022). "New studies bring BA.2 variant into sharper focus". CNN. p. 1.
- ^ Sample I (10 March 2022). "UK Covid cases rising among those aged 55 and over". The Guardian. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ "BA.2 Lineage Report, India". outbreak.info (Scripps Research). 4 February 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2022.
- ^ "COVID-19 variants identified in the UK". UK Health Security Agency. 21 January 2022. Archived from the original on 23 January 2022. Retrieved 21 January 2022.
- ^ "COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update, Edition 77" (PDF). World Health Organization. 1 February 2022. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 February 2022. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ a b c "COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update, Edition 82". World Health Organization. 8 March 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ "COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update, Edition 80". World Health Organization. 22 February 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ a b "Variant Proportions". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ Carassio J (7 February 2022). "BA.1.1, un nouveau sous-variant d'Omicron déjà très répandu en France". Le Progrès. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ "BA.1.1 Lineage Report, United States, France and Japan". outbreak.info (Scripps Research). 12 March 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ Yengkhom S (11 January 2022). "BA.2 'stealth' variant makes up 80% of Kolkata's Omicron infections". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 16 January 2022. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ "Omicron 'sub-lineage' BA.2 designated as COVID variant under investigation, says UKHSA". Sky News. 21 January 2022. Archived from the original on 21 January 2022. Retrieved 21 January 2022.
- ^ "SARS-CoV-2 Sequencing Update 14 January 2022" (PDF). Network for Genomic Surveillance in South Africa. 14 January 2022. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 January 2022. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ "Omicron sub-variant BA.2 'under investigation' by UK health officials". The Independent. 23 January 2022. Archived from the original on 23 January 2022. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ^ Österman H (11 January 2022). "Undergrupp av omikron ökar: "Kan vara ännu mer smittsam"" (in Swedish). Aftonbladet. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ "新型コロナウイルス感染症(変異株)の患者等の発生について(空港検疫))" (in Japanese). National Institute of Infectious Diseases (Japan). 20 January 2022. Archived from the original on 20 January 2022. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- ^ "新型コロナウイルス感染症(変異株)の患者等の発生について(空港検疫)" (in Japanese). National Institute of Infectious Diseases (Japan). 24 January 2022. Archived from the original on 24 January 2022. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- ^ a b c "Genomic overview of SARS-CoV-2 in Denmark". Danish Covid-19 Genome Consortium. 29 January 2022. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 29 January 2022.
- ^ a b c Bernstein L (25 January 2022). "There's a new version of omicron but so far it doesn't appear to be more dangerous". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 25 January 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "Enhancing response to Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variant: Technical brief and priority actions for Member States" (PDF). World Health Organization. 21 January 2022. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 January 2022. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- ^ a b "COVID-19 Ukerapport – uke 2" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Norwegian Institute of Public Health. 19 January 2022. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 January 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "Omicron BA.2 sub-variant dominant in S.Africa, says CDC". Reuters. 10 February 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ "Wöchentlicher Lagebericht des RKI zur Coronavirus-Krankheit-2019 (COVID-19)" (PDF). Robert Koch Institute. 10 March 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ a b "Covid infections rising again across UK - ONS". BBC News. 11 March 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ Larsen JA (21 January 2022). "Ny Omikron-variant tager over i Danmark – det ved vi om den" (in Danish). TV2. Archived from the original on 22 January 2022. Retrieved 21 January 2022.
- ^ "Reinfections with Omicron subvariants are rare, Danish study finds". Reuters. 22 February 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ a b "Had Omicron? You're unlikely to catch its rising variant". Nature. 25 February 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ "Boosters increase protection against death from Omicron in over-50s to 95% – UKHSA". The Guardian. 27 January 2022. Archived from the original on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ^ "COVID-19 vaccine surveillance report Week 4" (PDF). UK Health Security Agency. 27 January 2022. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 January 2022. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ^ Gregory A (29 November 2021). "Omicron Covid variant poses very high global risk, says WHO". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 29 November 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ Geddes L (29 November 2021). "What does appearance of Omicron variant mean for the double-vaccinated?". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 29 November 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ Omicron: what do we know about the new Covid variant? Archived 5 December 2021 at the Wayback Machine The Guardian
- ^ Assessment of the further emergence and potential impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant of concern in the context of ongoing transmission of the Delta variant of concern in the EU/EEA, 18th update (Technical report). Stockholm: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 15 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ Cele S, Jackson L, Khoury DS, Khan K, Moyo-Gwete T, Tegally H, et al. (COMMIT-KZN Team) (December 2021). "Omicron extensively but incompletely escapes Pfizer BNT162b2 neutralization". Nature. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04387-1. PMID 35016196. S2CID 245879254.
- ^ Callaway E (December 2021). "Omicron likely to weaken COVID vaccine protection". Nature. 600 (7889): 367–368. Bibcode:2021Natur.600..367C. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-03672-3. PMID 34880488. S2CID 245007078. Archived from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- ^ "Why Omicron-infected white-tailed deer pose an especially big risk to humans". Fortune.
- ^ CDC COVID-19 Response Team (December 2021). "SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) Variant – United States, December 1-8, 2021". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Center for Disease Control. 70 (50): 1731–1734. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7050e1. PMC 8675659. PMID 34914670. S2CID 245071514. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ^ "Omicron survives longer on plastic, skin than prior variants; nose swabbing found best for rapid tests". Reuters. 24 January 2022. Archived from the original on 28 January 2022. Retrieved 28 January 2022.
- ^ Hirose R, Itoh Y, Ikegaya H, Miyazaki H, Watanabe N, Yoshida T, et al. (19 January 2022). "Differences in environmental stability among SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: Omicron has higher stability". bioRxiv 10.1101/2022.01.18.476607.
- ^ New Covid variant: Will new measures against Omicron work? Archived 28 November 2021 at the Wayback Machine BBC
- ^ AFP (2 December 2021). "S. Africa expert: Previous infection doesn't protect against Omicron, but shots do". The Times of Israel. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "LIVE – Covid: 'Staggering' Omicron case numbers expected – top health official". BBC News. 15 December 2021. Archived from the original on 22 December 2021. Retrieved 15 December 2021. See entry for 10:05
- ^ Rozsa M, Karlis N (28 January 2022). "Omicron variant of COVID-19 may be the most contagious virus to ever exist". Salon. Archived from the original on 28 January 2022. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- ^ Wang, Rui; Chen, Jiahui; Wei, Guo-Wei (16 December 2021). "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Evolution Revealing Vaccine-Resistant Mutations in Europe and America" (PDF). The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. 12 (49): 11850–11857. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c03380. PMC 8672435. PMID 34873910. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 December 2021. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ^ "Study findings suggest spread of Omicron can be ascribed to immune evasiveness rather than an increase in transmissibility". News-Medical.net. 5 January 2022. Archived from the original on 21 January 2022. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ Lyngse, Frederik Plesner; Mortensen, Laust Hvas; Denwood, Matthew J.; Christiansen, Lasse Engbo; Møller, Camilla Holten; Skov, Robert Leo; Spiess, Katja; Fomsgaard, Anders; Lassaunière, Maria Magdalena; Rasmussen, Morten; Stegger, Marc; Nielsen, Claus; Sieber, Raphael Niklaus; Cohen, Arieh Sierra; Møller, Frederik Trier; Overvad, Maria; Mølbak, Kåre; Krause, Tyra Grove; Kirkeby, Carsten Thure (27 December 2021). "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron VOC Transmission in Danish Households": 2021.12.27.21268278. doi:10.1101/2021.12.27.21268278. S2CID 245536365. Archived from the original on 26 January 2022. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Yunlong Cao et al. (23 December 2021). "Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies". Nature. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-03796-6. S2CID 245455422.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ^ Wilhelm, Alexander; Widera, Marek; Grikscheit, Katharina; Toptan, Tuna; Schenk, Barbara; Pallas, Christiane; Metzler, Melinda; Kohmer, Niko; Hoehl, Sebastian; Helfritz, Fabian A.; Wolf, Timo; Goetsch, Udo; Ciesek, Sandra (8 December 2021). "Reduced Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant by Vaccine Sera and Monoclonal Antibodies". doi:10.1101/2021.12.07.21267432. S2CID 244950946.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Liu, Lihong; Iketani, Sho; Guo, Yicheng; Chan, Jasper F-W.; Wang, Maple; Liu, Liyuan; Luo, Yang; Chu, Hin; Huang, Yiming; Nair, Manoj S.; Yu, Jian; Chik, Kenn K-H.; Yuen, Terrence T-T.; Yoon, Chaemin; To, Kelvin K-W.; Chen, Honglin; Yin, Michael T.; Sobieszczyk, Magdalena E.; Huang, Yaoxing; Wang, Harris H.; Sheng, Zizhang; Yuen, Kwok-Yung; Ho, David D. (23 December 2021). "Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2". Nature. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-03826-3. PMID 35016198. S2CID 245462866.
- ^ Rössler, Annika; Riepler, Lydia; Bante, David; Laer, Dorothee von; Kimpel, Janine (11 December 2021). "SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 variant (Omicron) evades neutralization by sera from vaccinated and convalescent individuals". doi:10.1101/2021.12.08.21267491. S2CID 245019954.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Omicron Variant: What You Need to Know". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 20 December 2021. Archived from the original on 27 January 2022. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ^ "Update on Omicron". World Health Organization. 28 November 2021. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- ^ Abdullah F (4 December 2021). "Tshwane District Omicron Variant Patient Profile – Early Features". South African Medical Research Council. Archived from the original on 7 December 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ "Omicron Wave Sees South Africa's Weekly Excess Deaths Almost Double". Bloomberg. 8 December 2021. Archived from the original on 19 December 2021. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ^ "South Africa: previous infections may explain Omicron hospitalisation rate". The Guardian. 14 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2021.
- ^ Ferguson N, Ghani A, Cori A, Hogan A, Hinsley W, Volz E (20 December 2021). Growth, population distribution and immune escape of the Omicron in England (Technical report). WHO Collaborating Centre for Infectious Disease Modelling, MRC Centre for Global Infectious Disease Analysis. Imperial College London. doi:10.25561/93038. Report 49. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 December 2021.
- ^ Ferguson N, Ghani A, Hinsley W, Volz E (22 December 2021). Hospitalisation risk for Omicron cases in England (Technical report). WHO Collaborating Centre for Infectious Disease Modelling, MRC Centre for Global Infectious Disease Analysis. Imperial College London. doi:10.25561/93035. Report 50. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 December 2021.
- ^ a b Iuliano, A. Danielle (2022). "Trends in Disease Severity and Health Care Utilization During the Early Omicron Variant Period Compared with Previous SARS-CoV-2 High Transmission Periods — United States, December 2020–January 2022". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 71. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7104e4. ISSN 0149-2195.
- ^ "What to know about BA.2, the newest Covid omicron variant". NBC News. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ "Omicron BA.2: What we know about the Covid sub-variant". BBC News. 2 February 2022. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ "There's a new version of omicron but so far it doesn't appear to be more dangerous". Washington Post. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ Yamasoba, Daichi; Kimura, Izumi; Nasser, Hesham; Morioka, Yuhei; Nao, Naganori; Ito, Jumpei; Uriu, Keiya; Tsuda, Masumi; Zahradnik, Jiri; Shirakawa, Kotaro; Suzuki, Rigel; Kishimoto, Mai; Kosugi, Yusuke; Kobiyama, Kouji; Hara, Teppei; Toyoda, Mako; Tanaka, Yuri L.; Butlertanaka, Erika P.; Shimizu, Ryo; Ito, Hayato; Wang, Lei; Oda, Yoshitaka; Orba, Yasuko; Sasaki, Michihito; Nagata, Kayoko; Yoshimatsu, Kumiko; Asakura, Hiroyuki; Nagashima, Mami; Sadamasu, Kenji; Yoshimura, Kazuhisa; Kuramochi, Jin; Seki, Motoaki; Fujiki, Ryoji; Kaneda, Atsushi; Shimada, Tadanaga; Nakada, Taka-aki; Sakao, Seiichiro; Suzuki, Takuji; Ueno, Takamasa; Takaori-Kondo, Akifumi; Ishii, Ken J.; Schreiber, Gideon; Consortium, The Genotype to Phenotype Japan (G2P-Japan); Sawa, Hirofumi; Saito, Akatsuki; Irie, Takashi; Tanaka, Shinya; Matsuno, Keita; Fukuhara, Takasuke; Ikeda, Terumasa; Sato, Kei (15 February 2022). "Virological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2 variant". pp. 2022.02.14.480335. doi:10.1101/2022.02.14.480335v1.
- ^ a b Johnson, Carla K. "Omicron drives US deaths higher than in fall's delta wave". medicalxpress.com. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ "SARS-CoV-2 Viral Mutations: Impact on COVID-19 Tests". FDA. 16 December 2021. Archived from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ a b "SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ "Only one approved rapid test in Australia explicitly states it detects Omicron". the Guardian. 27 January 2022. Archived from the original on 30 January 2022. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- ^ Nebehay S, Winning A (26 November 2021). "WHO names new COVID variant omicron, cautions against travel measures". Reuters. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ "BioNTech says it could tweak Covid vaccine in 100 days if needed". The Guardian. 26 November 2021. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ "Novavax developing vaccine that targets new COVID-19 variant". CBS Baltimore Staff. 30 November 2021. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ Maddipatla M, Roy M (26 November 2021). "Maryland-Based Vaccine Manufacturer Developing COVID-19 Vaccine That Targets Omicron Variant". Reuters. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- ^ "Sputnik V maker: Vaccine could be adapted to fight omicron". ABC News. Moscow. Associated Press. 29 November 2021. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ "Sinovac and world's Covid-19 vaccine makers 'ready' to produce Omicron jab". South China Morning Post. 29 November 2021. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ "Sinovac prevê atualização da Coronavac para variante Ômicron em até três meses" [Sinovac plans to update Coronavac to the Omicron variant within three months]. CNN Brazil (in Portuguese). 7 December 2021. Archived from the original on 9 December 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Cuba to update domestic vaccine to battle Omicron". Al Jazeera. 2 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ Spencer K (10 January 2022). "Pfizer CEO says omicron vaccine will be ready in March". CNBC. Archived from the original on 26 January 2022. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ^ a b "Omicron poses very high global risk, world must prepare -WHO". Reuters. Geneva. 29 November 2021. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- ^ Arbel, Ronen; Hammerman, Ariel; Sergienko, Ruslan; Friger, Michael; Peretz, Alon; Netzer, Doron; Yaron, Shlomit (8 December 2021). "BNT162b2 Vaccine Booster and Mortality Due to Covid-19". New England Journal of Medicine. 385 (26): 2413–2420. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2115624. PMC 8728797. PMID 34879190.
- ^ Khoury, David S.; Steain, Megan; Triccas, James A.; Sigal, Alex; Davenport, Miles P.; Cromer, Deborah (17 December 2021). "A meta-analysis of Early Results to predict Vaccine efficacy against Omicron": 2021.12.13.21267748. doi:10.1101/2021.12.13.21267748. S2CID 245130598. Archived from the original on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 28 January 2022.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Garcia-Beltran, Wilfredo F.; Denis, Kerri J. St; Hoelzemer, Angelique; Lam, Evan C.; Nitido, Adam D.; Sheehan, Maegan L.; Berrios, Cristhian; Ofoman, Onosereme; Chang, Christina C.; Hauser, Blake M.; Feldman, Jared; Gregory, David J.; Poznansky, Mark C.; Schmidt, Aaron G.; Iafrate, A. John; Naranbhai, Vivek; Balazs, Alejandro B. (14 December 2021). "mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine boosters induce neutralizing immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant". medRxiv : The Preprint Server for Health Sciences: 2021.12.14.21267755. doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.21267755. PMC 8687472. PMID 34931201. Archived from the original on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 28 January 2022.
- ^ Nicole A. Doria-Rose, Xiaoying Shen et al. (20 December 2021). "Booster of mRNA-1273 Strengthens SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Neutralization". medRxiv : The Preprint Server for Health Sciences: 2021.12.15.21267805. doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.21267805. PMC 8687471. PMID 34931200. Archived from the original on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 28 January 2022.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ^ Hansen, Christian Holm; Schelde, Astrid Blicher; Moustsen-Helm, Ida Rask; Emborg, Hanne-Dorthe; Krause, Tyra Grove; Mølbak, Kåre; Valentiner-Branth, Palle; Institut, on behalf of the Infectious Disease Preparedness Group at Statens Serum (23 December 2021). "Vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 infection with the Omicron or Delta variants following a two-dose or booster BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 vaccination series: A Danish cohort study": 2021.12.20.21267966. doi:10.1101/2021.12.20.21267966. S2CID 245352810. Archived from the original on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 28 January 2022.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Bar-On, Yinon M.; Goldberg, Yair; Mandel, Micha; Bodenheimer, Omri; Freedman, Laurence; Alroy-Preis, Sharon; Ash, Nachman; Huppert, Amit; Milo, Ron (23 December 2021). "Protection against Covid-19 by BNT162b2 Booster across Age Groups". New England Journal of Medicine. 385 (26): 2421–2430. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2115926. ISSN 0028-4793. PMC 8728796. PMID 34879188.
- ^ "Pfizer shot provides partial omicron shield, study finds". The Japan Times. Bloomberg. 8 December 2021. Archived from the original on 8 December 2021. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ "Early Lab Test Shows Omicron Weakening Vaccine Effectiveness". The Wall Street Journal. 7 December 2021. Archived from the original on 7 December 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ "Omicron coronavirus variant partly evades Pfizer vaccine's protection, study shows". CNN. 7 December 2021. Archived from the original on 8 December 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ "Pfizer And BioNTech Provide Update On Omicron Variant" (Press release). New York City and Mainz: Pfizer. 8 December 2021. Archived from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ "Coronavirus (COVID-19) booster vaccine". NHS. Government Digital Service. 17 September 2021. Archived from the original on 22 December 2021. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ^ SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England, technical briefing 31 (PDF) (Briefing). Public Health England. 10 December 2021. pp. 3–5, 20–22. GOV-10645. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ "Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern". WHO. 26 November 2021. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021.
- ^ "Update on Omicron". World Health Organization. 28 November 2021. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021.
- ^ Gordon AC, Mouncey PR, Al-Beidh F, Rowan KM, Nichol AD, Arabi YM, et al. (April 2021). "Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19". The New England Journal of Medicine. 384 (16): 1491–1502. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2100433. PMC 7953461. PMID 33631065.
- ^ Cathcart AL, Havenar-Daughton C, Lempp FA, Ma D, Schmid M, Agostini ML, et al. (2021). "The dual function monoclonal antibodies VIR-7831 and VIR-7832 demonstrate potent in vitro and in vivo activity against SARS-CoV-2". bioRxiv 10.1101/2021.03.09.434607.
- ^ McCallum M, Czudnochowski N, Rosen LE, Zepeda SK, Bowen JE, Dillen JR, et al. (2021). "Structural basis of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron immune evasion and receptor engagement". bioRxiv 10.1101/2021.12.28.474380.
- ^ Cao Y, Wang J, Jian F, Xiao T, Song W, Yisimayi A, et al. (December 2021). "Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies". Nature. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-03796-6. PMID 35016194. S2CID 245455422.
- ^ Cameroni E, Saliba C, Bowen JE, Rosen LE, Culap K, Pinto D, et al. (December 2021). "Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift". bioRxiv. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-03825-4. PMC 8687478. PMID 34931194. Archived from the original on 24 December 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ Latest confirmed cases of COVID-19 in South Africa (26 November 2021) Archived 4 December 2021 at the Wayback Machine www.nicd.ac.za
- ^ Latest confirmed cases of COVID-19 in South Africa (3 December 2021) Archived 4 December 2021 at the Wayback Machine www.nicd.ac.za
- ^ see also GIS dashboard Archived 8 September 2021 at the Wayback Machine (statistical data) www.nicd.ac.za
- ^ "Update on Omicron". World Health Organization. 28 November 2021. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- ^ Pulliam JR, van Schalkwyk C, Govender N, von Gottberg A, Cohen C, Groome MJ, et al. (January 2021). "SARS-CoV-2 reinfection trends in South Africa: analysis of routine surveillance data". medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.11.11.21266068. S2CID 243983860.
- ^ "Omicron seems to carry higher Covid reinfection risk, says South Africa". The Guardian. 2 December 2021. Archived from the original on 3 December 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "'Patience is crucial': Why we won't know for weeks how dangerous Omicron is". www.science.org. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- ^ Network for Genomic Surveillance in South Africa (26 November 2021). "Proportion and number of clades by epiweek in South Africa, 2021" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ a b c "Omicron becomes dominant variant in South Africa". The Guardian. 2 December 2021. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "Risk assessment for SARS-CoV-2 variant: Omicron VOC-21NOV-01 (B.1.1.529): 3 December 2021" (PDF). GOV.UK. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 December 2021. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ McCarthy K, Rachida S, Yousif M, Ndlovu N, Iwu-Jaja C, Howard W, et al. "Wastewater-based epidemiology for SARS-CoV-2 in South Africa" (PDF). National Institute for Communicable Diseases. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19: Toddlers make up 10% of hospital cases in South Africa's Omicron epicentre". gulfnews.com. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "Omicron Spread in South Africa". p. 6. Archived from the original on 4 December 2021. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ Mandavilli A (4 December 2021). "Omicron Variant Spreading Twice as Quickly as Delta in South Africa". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 4 December 2021. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ The SARS-CoV-2 variant Omicron: a snapshot of where we are – 08.12.2021, 5 PM CET., archived from the original on 21 December 2021, retrieved 10 December 2021
- ^ "Prof. Albertsen deliberations". Twitter. Archived from the original on 14 December 2021. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ^ "SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England – Technical briefing 33" (PDF). gov.uk. UK Health Security Agency. 23 December 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 January 2022. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Covid-19 Rapport om omikronvarianten [Status of the SARS-CoV-2 variant Omicron in Denmark] (PDF) (Report) (in Danish). Statens Serum Institut. 20 December 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- ^ Ekspertrapport den 17. december 2021 – Scenarier for smittetal og nyindlæggelser med omikronvarianten [Expert report 17 December 2021 – Scenarios for infection numbers and new hospitalizations with the Omicron-variant] (PDF) (Report) (in Danish). Statens Serum Institut. 18 December 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 December 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- ^ "Variant-PCR svar fra 27. nov. og frem, Testcenter Danmark" (in Danish). Archived from the original on 27 December 2021. Retrieved 27 December 2021.
- ^ "Schweiz sitrep". Twitter. 10 December 2021. Archived from the original on 12 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ "RKI – Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 – Wochenbericht vom 13.1.2022" (PDF). www.rki.de. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 January 2022. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ "Omicron in Scotland – evidence paper". www.gov.scot. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ^ Wenseleers T (22 December 2021), tomwenseleers/newcovid_belgium, archived from the original on 22 December 2021, retrieved 22 December 2021
- ^ "Ontario Dashboard". Ontario COVID-19 Science Advisory Table. Archived from the original on 17 March 2021. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- ^ "COVID Data Tracker". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 28 March 2020. Archived from the original on 22 May 2021. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- ^ "Portugal says Omicron dominant, infections rising". NewsNine. 25 December 2021. Archived from the original on 28 December 2021. Retrieved 28 December 2021.
- ^ Wenseleers T (20 December 2021), tomwenseleers/newcovid_belgium, archived from the original on 22 December 2021, retrieved 21 December 2021
- ^ "Variants of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 in the Netherlands". Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ "COVID: Omicron accountts for 28% of cases in Italy, will soon be dominant". ANSA.en. 23 December 2021. Archived from the original on 24 December 2021. Retrieved 28 December 2021.
- ^ Oppdatert P. "Statistikk over meldte tilfeller av virusvarianten omikron" (in Norwegian). Folkehelseinstituttet. Archived from the original on 28 December 2021. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "Covid-19: Omicron is now the dominant variant in France". France24. 31 December 2021. Archived from the original on 3 January 2022. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- ^ "Omicron is now the dominant variant in France". CNN. 31 December 2021. Archived from the original on 31 December 2021. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- ^ Maxmen A (December 2021). "Omicron blindspots: why it's hard to track coronavirus variants". Nature. 600 (7890): 579. Bibcode:2021Natur.600..579M. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-03698-7. PMID 34916668. S2CID 245262198. Archived from the original on 19 December 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England, Technical briefing 38" (PDF). assets.publishing.service.gov.uk. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "The puzzle of America's record Covid hospital rate". BBC News. 13 January 2022. Archived from the original on 14 January 2022. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ Berger M (28 November 2021). "South Africa, which found the omicron variant first, leads Africa in coronavirus sequencing". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "Sequencing by country". GISAID. 2 December 2021. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ Geddes L (15 December 2021). "How big is the risk of Omicron in the UK and how do we know?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ^ a b Oppdatert, Publisert. "Statistikk over meldte tilfeller av virusvarianten omikron". Folkehelseinstituttet (in Norwegian). Retrieved 22 December 2021.
- ^ "Status på omikron-varianten (B.1.1.529) pr. 05.12.21" [Status of the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) per 05.12.21] (in Danish). Statens Serum Institut. Archived from the original on 7 December 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- ^ "Cov-Lineages". cov-lineages.org. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) Updated frequently. - ^ "Tracking of Variants". GISAID. Archived from the original on 23 June 2021. Retrieved 12 January 2022. Updated frequently.
- ^ a b "UK Health Security Agency Omicron daily overview: 31 December 2021" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Omikron (B.1.1.529)" [Omicron (B.1.1.529)] (in Danish). Statens Serum Institut. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- ^ a b c d "Newsnodes - Omicron tracker". newsnodes.com. Retrieved 24 December 2021.
- ^ "オミクロン株の国内発生状況について". www.mhlw.go.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ "Tracking variants of the novel coronavirus in Canada". CTV News. 4 February 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b "Wochenberichte zu COVID-19" (in German). Robert Koch Institute. 16 December 2021. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Omicron in Europe: Where has the new COVID variant been detected?". euronews. 13 December 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "SARS-CoV-2-Varianten in Österreich". AGES - Österreichische Agentur für Gesundheit und Ernährungssicherheit (in German). Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "Coronavirus : chiffres clés et évolution de la COVID-19 en France et dans le Monde". www.santepubliquefrance.fr (in French). Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ "Indonesia Laporkan 3.779 Kasus Omicron". CNNIndonesia.com (in Indonesian). 8 February 2022. Retrieved 8 February 2022.
- ^ "Country Has 5,397 Omicron Cases". สำนักข่าวไทย อสมท (in Thai). 10 January 2022. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
- ^ "Singapore reports 24 confirmed Omicron cases as at Thursday". www.thesundaily.my. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- ^ Auto, Hermes (22 December 2021). "More Omicron cases picked up in Singapore; community spread a matter of time: MOH | The Straits Times". www.straitstimes.com. Retrieved 22 December 2021.
- ^ Acharya, Ashutosh (29 December 2021). "Omicron most transmissible COVID-19 variant but not threatening Singapore: Experts". The Federal. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "MOH | News Highlights". www.moh.gov.sg. Retrieved 1 January 2022.
- ^ "Tänahommikuse seisuga on haiglas 274 koroonaviirusega nakatunud patsienti" [As of this morning, the hospital has 274 patients infected with the coronavirus]. terviseamet.ee (in Estonian). 13 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
Eestis on tuvastatud kokku 26 koroonapositiivset, kelle puhul viitab genotüpiseerimine omikron tüvele, nendest kuus on kinnitatud sekveneerimise käigus... A total of 26 corona-positive cases have been identified in Estonia, in which case genotyping indicates an omicron strain, six of which have been confirmed during sequencing...
- ^ "Tänahommikuse seisuga on haiglas 220 koroonaviirusega nakatunud patsienti | Terviseamet". www.terviseamet.ee (in Estonian). Retrieved 22 December 2021.
- ^ "Tänahommikuse seisuga on haiglas 231 koroonaviirusega nakatunud patsienti | Terviseamet". www.terviseamet.ee (in Estonian). Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- ^ "Variants of concern". CDGN. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- ^ India, COVID19. "INDIA WE WILL FIGHT IT TOGETHER". COVID19 India. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ "Omicron Cases in India | Coronavirus Cases in India". NDTV.com. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
- ^ a b @IsraelMOH (25 December 2021). "היום, 25/12/2021 זוהו 591 מאומתים חדשים" (Tweet) (in Hebrew) – via Twitter.
- ^ staff, T. O. I.; Schneider, Tal. "In Israel's first suspected Omicron death, vaccinated woman succumbs to virus". www.timesofisrael.com. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "Lineage B.1.1.529". cov-lineages.org. Cov-Lineages. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Omicron variant more resistant to vaccine but causes less severe covid, major South African study concludes". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
Later information provided by a Discovery Health spokeswoman put the number of total cases at 78,173, of which 19,070 tests were positive during the "omicron period" from Nov. 15 to Dec. 7.
- ^ 고병준 (3 January 2022). "(2nd LD) Daily virus cases stay below 4,000 for 2nd straight day amid tighter antivirus curbs". Yonhap News Agency. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Epidemiological update: Omicron variant of concern (VOC) – data as of 16 December 2021 (12:00)". European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 16 December 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "Statistik om SARS-CoV-2 virusvarianter av särskild betydelse — Folkhälsomyndigheten". www.folkhalsomyndigheten.se (in Swedish). Retrieved 5 January 2022.
- ^ "COVID-19 Switzerland | Coronavirus | Dashboard". www.covid19.admin.ch. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "Ómicron: the Ministry of Health confirmed the first case in Argentina". MRT. 6 December 2021. Archived from the original on 6 December 2021. Retrieved 6 December 2021.
- ^ "Córdoba confirmó 454 casos de la variante Ómicron de coronavirus" [Córdoba confirmed 454 cases of the Omicron variant of coronavirus] (in Spanish). Télam. 19 December 2021. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ "Hay más de 80 casos posibles de Ómicron en Argentina" [There are more than 80 possible cases of Ómicron in Argentina] (in Spanish). 13 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ a b "Table 1. Confirmed cases of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron VOC reported by public sources, as of 10 December 2021 (12:00)". ecdc.europa.eu. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). 10 December 2021. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ "Omikronvariant B.1.1.529". National Institute for Public Health and the Environment. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ^ "Summary of COVID-19 virus variants in Ireland – HPSC". HSE Health Protection Surveillance Centre (HPSC). 28 January 2022. p. 7. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- ^ "Travel restrictions tightened as Rock confirms 24 Omicron cases". 17 December 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Kári spáir omíkron-bylgju í janúar". ruv.is (in Icelandic). 18 December 2021. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ "Covid-19: sulla piattaforma ICoGen 84 sequenze della variante Omicron" [Covid-19: 84 sequences of the Omicron variant on the ICoGen platform] (in Italian). 18 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "ISP confirmó 30 casos de la nueva variante Ómicron a nivel nacional". CNN Chile (in Spanish). 16 December 2021. Archived from the original on 16 December 2021. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ "Autoridad sanitaria informa 73 casos confirmados con variante Ómicron en Chile". La Tercera. 20 December 2021. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- ^ Ministerio de Salud [@ministeriosalud] (3 January 2022). "'Tenemos 684 casos #ómicron en todo el país. De ellos, 661 corresponden a viajeros, 14 casos positivos con nexo de viajeros y 9 son los casos comunitarios, estos últimos, todos en la región Metropolitana'" ['We have 684 #omicron cases nationwide. Of these, 661 correspond to travelers, 14 positive cases connected to travelers and 9 are community cases, the latter, all in the Metropolitan region.'] (Tweet) (in Spanish). Retrieved 4 January 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Portugal tem 38 casos da variante ómicron. Cuidados intensivos com "tendência fortemente crescente"" [Portugal has 38 cases of the omicron variant. Intensive care shows "strongly increasing trend"]. Público. 3 December 2021. Archived from the original on 4 December 2021. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ "Monitorização das linhas vermelhas para a COVID-19" [Monitoring of red lines for COVID-19] (PDF). INSA (in Portuguese). National Health Service of Portugal. 3 December 2021. p. 14. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 December 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ a b MATIN, S. Ba , LE. "Le Matin - Omicron : 76 cas enregistrés au Maroc dont une personne admise en réanimation". Le Matin (in French). Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "Zimbabwe says country has identified 50 cases of Omicron". Reuters. Johannesburg. 3 December 2021. Archived from the original on 3 December 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Ômicron: incidência já é de 31,7% em oito estados do Brasil, mostra levantamento inédito" (in Brazilian Portuguese). Editora Globo S/A. 29 December 2021. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- ^ "THL ja STM: Etelä-Suomessa lähes kaikki tapaukset omikronia". Yle Uutiset (in Finnish). 5 January 2022. Retrieved 6 January 2022.
- ^ "53,600 COVID infections diagnosed in 1 week, 140 deaths in 2 weeks". clickittefaq. 13 January 2022. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
The total number of cases of the Omicron variant was 523 until Wednesday.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Cyprus detects first cases of COVID-19 Omicron variant". news.trust.org. Reuters. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ "Coronavirus: 28 more people found positive for Omicron | Cyprus Mail". cyprus-mail.com. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ @MOH_Kenya (18 December 2021). "Twenty-seven sequences (77%) were confirmed to belong to the newly identified Omicron variant of concern" (Tweet). Retrieved 20 December 2021 – via Twitter.
- ^ "В России выявили более 250 случаев заболевания подвидом омикрон-штамма ВA.2". TASS. 2 February 2022. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ a b "COVID-19 Update - 24 December". www.gov.ky. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- ^ Ministry of Health - Uganda [@@MinofHealthUG] (18 December 2021). "PRESS RELEASE: Update on Omicron Variant in #Uganda" (Tweet). Uganda. Retrieved 19 December 2021 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Omicron confirmed in nine African countries, say officials". ABC News. Archived from the original on 7 December 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ Guillén, Beatriz (3 December 2021). "México confirma el primer caso de ómicron en el país" [Mexico confirms the first omicron case in the country]. El País (in Spanish). Mexico. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "MidCentral hits 90% fully vaccinated milestone; 69 community cases; 62 in hospital; 7 in ICU". Ministry of Health NZ. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "Namibia detects Omicron coronavirus variant in 18 of 19 samples". Reuters. 6 December 2021. Archived from the original on 6 December 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ "HK reports 7 imported virus cases". Hong Kong's Information Services Department (in Chinese (Hong Kong)). Retrieved 24 December 2021.
- ^ "14 imported virus cases found". Hong Kong's Information Services Department (in Chinese (Hong Kong)). Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ "Senegal records first Omicron case in tourist who attended demonstration". Reuters. 5 December 2021. Archived from the original on 5 December 2021. Retrieved 5 December 2021.
- ^ "Omicron in southern Africa: Mozambique is worried for its economy, especially tourism". Bahrain News Agency. 10 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ Newsroom. "Όμικρον: 17 κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα | Η ΚΑΘΗΜΕΡΙΝΗ". www.kathimerini.gr. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ Bell, Jonathan (21 December 2021). "Omicron cases surge from one to more than 100 in two weeks". www.royalgazette.com. Retrieved 24 December 2021.
- ^ Bell, Jonathan (24 December 2021). "Two in hospital as Bermuda passes 6,000 Covid-19 cases". www.royalgazette.com. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- ^ "Latvia gets its first two Omicron cases". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. Reuters. 6 December 2021. Archived from the original on 6 December 2021. Retrieved 6 December 2021.
- ^ "Pagājušajā nedēļā par trešdaļu pieaudzis Covid-19 inficēto skaits | Slimību profilakses un kontroles centrs". www.spkc.gov.lv (in Latvian). Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- ^ "Comunicate de presa" [Press Releases]. ms.ro (in Romanian). Ministerul Sănătăţii (Health Ministry Romania). 12 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
So far, 8 cases with the Omicron variant of the SARS-Cov-2 virus have been confirmed in Romania.
- ^ "MS: Încă două cazuri de infectare cu varianta Omicron au fost confirmate în România". www.digi24.ro (in Romanian). Retrieved 18 December 2021.
Până în prezent, în România au fost confirmate 13 cazuri cu varianta OMICRON a virusului SARS-Cov-2.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Au fost descoperite încă 9 cazuri de infectare cu varianta Omicron în România". www.digi24.ro (in Romanian). Retrieved 24 December 2021.
- ^ "Covid-19: 245 Omicron cases detected so far, 157 among umrah returnees, says Khairy". The Star. 6 January 2022. Retrieved 6 January 2022.
- ^ "Zambia reports more Omicron variant COVID-19 cases". Xinhuanet.com. 11 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ Adetifa, Dr Ifedayo (7 December 2021). "Three Additional Cases of Omicron Variant Confirmed". ncdc.gov.ng. Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC). Retrieved 11 December 2021.
In addition to the three cases announced earlier on 1st December 2021, this brings the total number of confirmed cases of the Omicron variant detected in Nigeria to six (6).
- ^ "Koronavirus ONLINE: Válek smetl povinné očkování 60+. A 5982 případů za sobotu v ČR". Blesk.cz (in Czech). Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "Kosovo reports first cases of COVID-19 Omicron". Reuters. Pristina. 26 December 2021. Retrieved 28 December 2021.
Kosovo's health ministry said on Sunday it had registered its first nine cases of the Omicron coronavirus variant in the Balkan country.
- ^ "First cases of the omicron variant of coronavirus confirmed in Slovenia". GOV.SI. 14 December 2021. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ^ W3bStudio (21 December 2021). "Omicron confirmed in all Slovenian regions but one". Slovenia Times. Retrieved 22 December 2021.
- ^ "Omicron estimated to represent 40% of all coronavirus cases in Slovenia". Slovenia Times. 30 December 2021. Retrieved 1 January 2022.
The National Laboratory of Health, Environment and Food said today it had confirmed 981 omicron cases with PCR tests...
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b "Cases of Omicron variant rise to 8 in Lebanon". www.news.cn. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ "Lebanon's total Omicron cases rise to 433". ANI News. Xinhua. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Covid-19 à La Réunion : identification d'un 2ème cas positif au variant « Omicron »" [Covid-19 in Reunion Island: identification of a 2nd positive case for the "Omicron" variant]. reunion.gouv.fr (in French). Les services de l'État à La Réunion. 3 December 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ a b c d "В России впервые с октября выявили менее 200 тыс. случаев ковида за неделю". ТАСС. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "Six cases of Omicron variant detected in Turkey – minister". Reuters. 11 December 2021. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ^ "Laboratorije Odjeljenja za molekularnu dijagnostiku potvrdile 5 slučajeva infekcije Omicron sojem". Institut za javno zdravlje Crne Gore. 16 December 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ^ "Cambodia confirms 1st case of Omicron COVID-19 variant". Xinhua News Agency. 15 December 2021. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ^ "Distribución de casos por las VOC delta - ómicron" [Distribution of cases by VOC Delta - Omicron]. Instituto Nacional de Salud del Perú (in Spanish). 9 March 2022. Retrieved 9 March 2022.
- ^ الأردنية (بترا), وكالة الأنباء. "تسجيل 30 إصابة جديدة بمتحور أوميكرون في ا��مملكة". بترا -وكالة الأنباء الأردنية. Retrieved 5 January 2022.
- ^ 畅, 刘 (13 December 2021). "天津从入境人员中检出奥密克戎变异株,为中国内地首次检出" [The Omicron mutant strain was detected in Tianjin from immigrants, which is the first detection in Mainland China]. The Beijing News. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ "Guangzhou reports China's second case of Omicron variant". South China Morning Post. 14 December 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ^ "湖南长沙从入境人员中检出2例新冠病毒奥密克戎变异株感染者" [2 cases of coronavirus Omicron variant detected from incoming persons in Changsha, Hunan Province]. 18 December 2021.
- ^ MINSAP, Redacción (15 December 2021). "Nota informativa del Ministerio de Salud Pública". Sitio oficial de gobierno del Ministerio de Salud Pública en Cuba (in European Spanish). Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "Ascienden a 44 los casos de Ómicron en Cuba". Cubita Now. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ "Ascienden a 92 los casos de ómicron confirmados en Cuba" [Confirmed omicron cases in Cuba amount to 92]. Cubita Now. 4 January 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Malawi confirms 3 Omicron cases, issues strict traveling restrictions". www.news.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ "First case of Omicron coronavirus variant detected in Gaza". The Times of Israel. 26 December 2021.
- ^ "الناطق باسم وزارة الصحة د. كمال... - وزارة الصحة الفلسطينية - Facebook". Facebook. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ Chang, Ming-hsuan; Liu, Kay (1 January 2022). "Taiwan reports 21 new COVID-19 cases, confirms 2 Omicron infections". Central News Agency of the Republic of China. Focus Taiwan. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "Lithuania confirms two Omicron infections". Lithuanian National Radio and Television. 15 December 2021. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ^ @MinSaludCol (20 December 2021). "¡ATENCIÓN! Se confirma la presencia de la variante Ómicron en Colombia" (Tweet). Retrieved 21 December 2021 – via Twitter.
- ^ "First Omicron cases confirmed in Slovakia". The Slovak Spectator. 11 December 2021. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
First three Omicron cases have been confirmed in Slovakia.
- ^ Lindo, Paula (13 December 2021). "Health Ministry: Trinidad and Tobago's first omicron case breached travel protocols". Trinidad and Tobago Newsday. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
TT's first recorded case of the omicron variant is an imported one.
- ^ "Confirman primer caso positivo de variante ómicron en Puerto Rico". CNN en Español (in Spanish). 14 December 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2021.
- ^ "Two confirmed cases of Omicron variant in quarantine". Fiji Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 6 December 2021. Retrieved 6 December 2021.
- ^ "Nepal detects first two cases of Omicron variant – health ministry". Reuters. 6 December 2021. Retrieved 6 December 2021.
- ^ "Myanmar confirms four cases of Omicron variant of COVID-19". ANI News. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "Philippines detects Omicron variant from 2 international travelers". GMA News. 15 December 2021. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ^ Magsambol, Bonz (20 December 2021). "Philippines detects one more case of Omicron, total now at 3". Rappler. Retrieved 22 December 2021.
- ^ "PH detects 4th imported Omicron case". CNN Philippines. 27 December 2021.
- ^ "Philippines detects 10 new Omicron cases, including 3 local". GMA News. 31 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "Philippines detects 29 more cases of COVID-19 omicron variant". ABS-CBN News. 6 January 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- ^ "Philippines detects 492 new Omicron cases, total at 535". GMA News. 19 January 2022. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- ^ "'Omicron variant' detected in two people in TRNC!". KIBRIS POSTASI (in Turkish). Retrieved 22 December 2021.
- ^ "Bangladesh reports first Omicron cases". Business Standard. 11 December 2021. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- ^ "Epidemiological update: Omicron variant of concern (VOC) – data as of 8 December 2021 (12.00)". ecdc.europa.eu. ECDC. 8 December 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Müller Cecília: megjött Magyarországra az omikron variáns" [Cecília Müller: the omicron variant has arrived in Hungary]. Infostart. 13 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ "További 46 omikronos esetet azonosítottak". koronavirus.gov.hu (in Hungarian). 23 December 2021. Retrieved 24 December 2021.
- ^ "Recording the First Cases Of Omicron Variant #OmanVSCovid19". Twitter. Retrieved 14 December 2021.
- ^ "Coronavirus: Pakistan reports first case of Omicron variant". www.geo.tv. 9 December 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Important Public Service Information". Twitter. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "Sri Lanka reports first case of Omicron variant". The Economic Times. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Omicron Cases Rise to 600 in Georgia". bm.ge. 7 January 2022. Retrieved 8 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "The Kingdom of Bahrain detects a case of the Omicron variant in an incoming traveller with no local contact". Bahrain News Agency. 11 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ "Ecuador confirma primer caso de Ómicron". Ministerio de Salud Pública. 14 December 2021. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ^ Coronavirus: Kuwait reports first case of Omicron variant 8 December 2021
- ^ "First case of Omicron detected in Maldives". ANI News. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Maldives reports 4 new Omicron cases". The Times of Addu. 15 December 2021. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ "Public Health National Emergency Operations Center, Sierra Leone". www.facebook.com. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia detects first case of COVID-19 Omicron variant in Kingdom". Al Arabiya English. December 2021. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "Tunisia records first case of omicron variant". Arab News. 3 December 2021. Archived from the original on 8 December 2021. Retrieved 5 December 2021.
- ^ Mukherjee, Promit; Hunnicutt, Trevor (1 December 2021). "Omicron rapidly dominating in South Africa; U.S. reports first case". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "افزایش مبتلایان به اُمیکرون در کشور به ۴۶۷ مورد". ایسنا (in Persian). 7 January 2022. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
- ^ "В Україні виявили штам "Омікрон"" [Omicron strain found in Ukraine]. Ukrainian Ministry of Health (in Ukrainian). 18 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "Panama detects first case of COVID-19 Omicron variant". Reuters. 20 December 2021. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- ^ "Costa Rica Announces First Case of Omicron Variant". The Tico Times. 20 December 2021. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- ^ "First Omicron cases in Aruba". The Daily Herald. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- ^ "В Северной Македонии выявили первый случай заражения омикрон-штаммом". ТАСС. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- ^ Макфакс (5 January 2022). "Пораст на бројот на заразени од коронаворус, во Македонија активни 5.667 случаи" [Increase in the number of coronavirus infected, 5,667 active cases in Macedonia]. МАКФАКС (in Macedonian). Retrieved 9 January 2022.
Во Македонија вчера беа детектирани девет случаи на омикрон, од кои 8 од Скопје и едно лице од Кочани. (Nine cases of Omicron were detected in Macedonia yesterday, of which 8 were from Skopje and one person from Kocani.)
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ngày 19/1: Có 15.959 ca COVID-19, Hà Nội vẫn nhiều nhất; Đã ghi nhận 108 ca nhiễm biến chủng Omicron" (in Vietnamese). Retrieved 19 January 2022.
- ^ "Brunei detects another 7 Omicron cases". The Star (Malaysia). 28 December 2021. Retrieved 28 December 2021.
Another seven new Omicron cases have been detected in the Sultanate following the first case found on Dec 22...
- ^ Farrugia, Claire (3 January 2022). "Authorities keep silent on cases of Omicron". Times of Malta. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
Nothing said after the announcement that the first two cases had been detected.
- ^ Sequera, Vivian (23 December 2021). "Venezuela's Maduro says seven Omicron cases detected". Reuters. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- ^ "Covid-19 : la circulation du variant Omicron désormais avérée en Guyane, une vingtaine de cas détectés" [Covid-19: the circulation of the Omicron variant now proven in Guyana, around twenty cases detected]. Guyane la 1ère (in French). 29 December 2021. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "(COVID-19) La République du Congo enregistre une flambée des nouvelles contaminations (officiel)_French.news.cn" [(COVID-19) Republic of Congo records outbreak of new contamination (official)]. french.news.cn (in French). 5 January 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
...confirmant également pour la première fois la circulation du variant Omicron en République du Congo (...also confirming for the first time the circulation of the Omicron variant in the Republic of Congo).
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "MOPH Confirms Detection of Four Cases of Omicron COVID-19 Variant in Qatar". news.qna.org.qa. 17 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Se confirman tres casos de Ómicron en viajeros provenientes de Cancún" [Three cases of Omicron confirmed in travellers from Cancun]. mspbs.gov. 27 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Burkina Faso com dois casos de variante de covid-19 Omicron" [Burkina Faso with two cases of COVID-19 Omicron variant]. ANGOP. 18 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "Omikron-variant officieel op Curaçao" [Omicron variant officially in Curacao]. Paradise FM. 24 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ Byron, Anglina (1 January 2022). "Dr Laws confirms two cases of Omicron variant in St Kitts and Nevis". Associates Times a Caribbean News website. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "Libya reports first Omicron cases". The Libya Observer. 30 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "First Case of 'Omicron' Variant Confirmed in Albania". Albanian Daily News. 23 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ Rollock, Melissa (30 December 2021). "Chief Medical Officer: Omicron Is Here". GIS. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "One Imported Omicron Case". www.gov.vc. 27 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Sorto, Marlon (25 December 2021). "República Dominicana confirma primer caso de variante ómicron de covid-19" [Dominican Republic confirms first case of Omicron variant of COVID-19]. CNN Espanol. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "Jamaica On Alert For Omicron Variant – Jamaica Information Service". jis.gov.jm. 22 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Omikron soj stigao u Srbiju, potvrdila dr Tanja Jovanović" [Omicron strain has arrived in Serbia, Dr. Tanja Jovanović confirmed.]. Klinka. 23 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "Tanzanian president confirms spreading of Omicron variant-Xinhua". english.news.cn. 1 January 2022. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Le Togo enregistre ses premiers cas du variant Omicron" [Togo records its first cases of the Omicron variant]. Le Courrier. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
Au moins cinq cas du nouveau variant Omicron ont été identifiés au Togo. (At least five cases of the new Omicron variant have been identified in Togo).
- ^ "В Беларусь пришел новый вариант коронавируса – омикрон" [New variant of coronavirus arrives in Belarus - Omicron]. minzdrav.gov.by (in Russian). 29 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
Новый штамм выявлен у четырех минчан. (The new strain was identified in four residents of Minsk.)
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Omikron stigao i u Bosnu i Hercegovinu, novi soj potvrđen kod 10 osoba" [Omicron has also arrived in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the new strain has been confirmed in 10 people]. www.klix.ba (in Croatian). 29 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Covid-19: Angola confirms Omicron's circulation". Angola Press News Agency. 24 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "COVID-19 : Dr Muyembe révèle que le variant Omicron représente 29% soit 11% d'écart avec le variant Delta en RDC" [COVID-19: Dr Muyembe reveals that the Omicron variant represents 29% or 11% difference from the Delta variant in the DRC]. Politico.cd (in French). 15 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Covid-19 in Bulgaria: Omicron variant found in 12 samples sequenced by NCIPD". The Sofia Globe. 2 January 2022. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ^ "Covid-19 : Un premier cas de variant Omicron confirmé à Mayotte" [Covid-19: First case of the Omicron variant confirmed in Mayotte]. Mayotte la 1ère (in French). 22 December 2021. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Covid-19 : un premier cas de variant Omicron détecté en Martinique" [Covid-19: First case of the Omicron variant detected in Martinique]. Martinique la 1ère (in French). 24 December 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Ceesay, Landing (7 January 2022). "Covid-19 Update: Gambia Registers 26 Omicron Variant Cases". Gambia.com. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Covid -19 : premiers cas de variant Omicron détectés en Guadeloupe et à Saint-Martin". LEFIGARO (in French). 18 December 2021. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
Un autre cas a été confirmé, à Saint-Martin, sur une personne en provenance du Canada, indique la même source. (Another case has been confirmed in Saint-Martin, on a person from Canada, indicating the same source.)
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Laos has detected first case of Covid-19 Omicron Variant". Laotiantimes.com. 7 January 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- ^ Reuters (6 January 2022). "Iraq reports first cases of Omicron variant". Reuters. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
Iraq has identified more than five cases of the Omicron coronavirus variant...
- ^ "AMI - Des membres du gouvernement commentent les résultats du conseil des ministres". fr.ami.mr. 30 December 2021. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "South Sudan confirms omicron variant in the country". Juba echo. 2 January 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ "Covid-19 Omicron: Des cas positifs de ce variant "plus transmissible mais moins virulent" enregistres en Côte d'Ivoire". gouv.ci. 4 January 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
...on a eu 78 échantillons positifs pour le variant Omicron.
- ^ "Covid 19: INSP confirma que 87% das amostras enviadas ao Instituto Pasteur revelaram presença da ómicron" [Covid 19: INSP confirms that 87% of samples sent to the Pasteur Institute revealed the presence of the omicron]. inforpress.cv. 4 January 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
Há menos de uma semana, foram enviadas para esse laboratório, cerca de trezentas amostras, das quais foram processadas 202 que confirmaram a presença da variante ómicron em 87% das amostras processadas”, avançou a mesma fonte.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ McLeod, Sheri-Kae (7 January 2022). "Antigua Confirms First Case of Omicron". Caribbean News. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ "Gabon: le variant Omicron représente de 20 à 25% des personnes contrôlées positives au Covid-19". RFI (in French). 6 January 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ "Ministerio de Salud confirma presencia de variante ómicron en Bolivia". La Nación (in Spanish). 7 January 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ ""Omicron" a pus stăpânire pe Iaşi: 29 la 0! La ATI sunt numai nevaccinati" ["Omicron" took over Laşi: 29 to 0! At ATI they are only unvaccinated]. www.ziaruldeiasi.ro. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
29 din 29 confirmaţi... (29 out of 29 confirmed...)
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "First 8 Omicron Cases Detected in Kazakhstan". see.news. 6 January 2022. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Variant Omicron: premiers cas détectés en Guadeloupe et à Saint-Martin" [Omicron variant: first cases detected in Guadeloupe and Saint-Martin]. SudOuest (in French). 18 December 2021. ISSN 1760-6454. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
- ^ "Azerbaijan detects COVID-19 Omicron variant". AzerNews.az. 10 January 2022. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
Twelve people have tested positive for the COVID-19 Omicron variant in Azerbaijan.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Bhutan reports first cases of Omicron coronavirus variant". The Economic Times. 14 January 2021. Retrieved 19 January 2022.
- ^ "Papua New Guinea reports first Omicron cases, amid fears over low vaccination rate". the Guardian. 19 January 2022. Retrieved 19 January 2022.
- ^ "12 cases of Omicron variant confirmed in Mongolia". MONTSAME News Agency. 17 January 2022. Retrieved 19 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Página12 (22 January 2022). "Covid-19 en la Antártida: Ómicron se propagó en la Base Esperanza y evacuaron a 9 personas | Se registraron 24 contagios" [Covid-19 in Antarctica: Omicron has spread at the Esperanza Base and 9 people were evacuated]. PAGINA12. Retrieved 28 January 2022.
La variante Ómicron de coronavirus llegó a la Antártida, donde se detectaron 24 casos de covid-19 en la Base Esperanza...
- ^ "Uzbekistan reports first Omicron case, tightens pandemic restrictions-Xinhua". www.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 10 February 2022.
- ^ Schrieber M (16 December 2021). "The scientist in Botswana who identified omicron was saddened by the world's reaction". Goats and Soda. NPR. Archived from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ^ "Inside the South African lab that discovered Omicron". Africanews. 9 December 2021. Archived from the original on 17 December 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ^ a b "SARS-CoV-2 Sequencing Update 1 December 2021" (PDF). South African National Institute for Communicable Diseases. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ a b Lambrecht P (29 November 2021). "Wat weten we al over de nieuwe coronavariant, de omikron?" [What do we already know about the new coronavirus variant, Omicron?]. De Tijd (in Dutch). Belgium. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ Philip Whiteside (30 November 2021). "COVID-19: how the spread of Omicron went from patient zero to all around the globe". Sky News. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ^ "Enhancing Readiness for Omicron (B.1.1.529): Technical Brief and Priority Actions for Member States". WHO. 17 December 2021. Archived from the original on 29 November 2021. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ Torjesen I (November 2021). "Covid-19: Omicron may be more transmissible than other variants and partly resistant to existing vaccines, scientists fear". BMJ. 375: n2943. doi:10.1136/bmj.n2943. PMID 34845008. S2CID 244715303. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "Where did 'weird' Omicron come from?". www.science.org. Archived from the original on 22 December 2021. Retrieved 27 December 2021.
- ^ Vaughan A (27 November 2021). "Omicron: How dangerous is the new variant first found in South Africa?". NewScientist. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ Cowan K (29 November 2021). "Inside SA leg of Omicron variant discovery: A single test result, a missing gene, and an email". News24. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ a b Whiteside P (30 November 2021). "COVID-19: How the spread of Omicron went from patient zero to all around the globe". SkyNews. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ van Vliet K (3 December 2021). "Waarom Zuid-Afrika zoveel virusvarianten ontdekt". Trouw (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 22 December 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ Covid: New heavily mutated variant B.1.1.529 in South Africa raises concern Archived 26 November 2021 at the Wayback Machine, 25 November 2021, BBC News, accessed 25 November 2021
- ^ Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants Archived 18 June 2021 at the Wayback Machine (Tables: Currently designated Variants Under Monitoring -describes 529 variant as present in 'Multiple countries'- and 'Formerly monitored variants'- B.1.523 & B.1.619 Reclassified Nov 2021). www.who.int, accessed 25 November 2021
- ^ a b @BNODesk (26 November 2021). "Statement from Israel's health ministry reporting 1 confirmed case of new coronavirus variant B.1.1.529" (Tweet). Retrieved 26 November 2021 – via Twitter.
- ^ "מחוסנת ב-3 מנות ואישה שנסעה לאילת באוטובוס: המאומתים לזן החדשt". m.ynet.co.il (in Hebrew). 26 November 2021. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
"4 מאומתים לווריאנט החדש התגלו בארץ, רה"מ יקיים מסיבת עיתונאים ב-14:30" translated: "4 verified for the new variant were discovered in the country, the prime minister will hold a press conference at 14:30
- ^ Four cases of the new COVID-19 variant recorded in Botswana Archived 26 November 2021 at the Wayback Machine, 25 November 2021, Mmegi Online, accessed 26 November 2021
- ^ "Al meer dan veertig omikron-gevallen vastgesteld in Europa" [More than 40 omicron cases identified in Europe]. De Standaard (in Dutch). Belgium. 30 November 2021. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "Belgium detects first case of new COVID-19 variant in Europe". Reuters. 26 November 2021. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ Kesselgruber K (27 November 2021). "Flughafen Frankfurt: Person mit Omikron-Verdacht war vollständig geimpft" [Frankfurt airport: Person suspected to be infected with Omicron Variant was fully vaccinated]. Frankfurter Rundschau (in German). Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ "UK, Germany and Italy detect Omicron coronavirus variant cases". Reuters. 27 November 2021. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ "Coronavirus variant Omicron found in 13 positive tests so far | RIVM". www.rivm.nl. Archived from the original on 6 December 2021. Retrieved 6 December 2021.
- ^ "Actuele informatie over COVID-19 | RIVM" [Current information about COVID-19 | RIVM]. www.rivm.nl (in Dutch). 4 December 2021. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 6 December 2021.
- ^ "61 travellers from South Africa in Netherlands positive for COVID-19 – authorities". Reuters. Amsterdam. 27 November 2021. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ "Travellers test positive to Omicron COVID-19 strain after arriving in Sydney from southern Africa, NSW Health says". ABC News. 28 November 2021. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ "To personer er indrejst i Danmark med coronavarianten Omikron" [Two people have entered Denmark with the corona variant Omicron]. www.bt.dk (in Danish). 28 November 2021. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ Af Ritzau (28 November 2021). "Nu er det bekræftet: To personer smittet med Omikron rejst ind i Danmark" [Now it has been confirmed: Two people infected with Omicron traveled into Denmark]. ekstrabladet.dk (in Danish). Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ "Austria detects suspect Omicron case as Europe battles virus surge". WION. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ "Omicron variant found in UK, Germany, Czech Republic". New York Post. 28 November 2021. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ "Canada, Netherland, Australia latest countries reporting cases of omicron COVID-19 variant". ABC13. 28 November 2021. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ Perera A (29 November 2021). "COVID-positive repatriation flight arrival to the Northern Territory tests positive to Omicron variant". ABC News. Archived from the original on 29 November 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ Nguyen K (29 November 2021). "NSW Health confirms two more Omicron COVID-19 cases in travellers from southern Africa". ABC News. Archived from the original on 29 November 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ "Live updates: Omicron variant". Cable News Network. 29 November 2021. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ "Första fallet av omikron upptäckt i Sverige" [The first case of omicron detection in Sweden]. www.aftonbladet.se (in Swedish). 29 November 2021. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ "Spain detects first Omicron case, COVID-19 infections rise". Reuters. 29 November 2021. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- ^ "Omicron variant found in two previous test samples | RIVM". www.rivm.nl. Archived from the original on 4 December 2021. Retrieved 6 December 2021.
- ^ "NSW records fifth case of Omicron COVID-19 variant as two more potential infections investigated". ABC News. 30 November 2021. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- ^ "Japan's first Omicron case may help portray PM Kishida as decisive". Reuters. 30 November 2021. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- ^ "Two Israeli doctors test positive for Omicron COVID variant". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on 31 December 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- ^ "SP confirma terceiro caso da variante ômicron" [SP confirms third case of ômicron variant]. g1 (in Brazilian Portuguese). 1 December 2021. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "O que se sabe sobre os primeiros casos confirmados da variante Ômicron no Brasil" [What is known about the first confirmed cases of the Ômicron variant in Brazil]. CNN Brasil (in Brazilian Portuguese). 30 November 2021. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "Passa para 6 o número de casos suspeitos da variante Ômicron investigados no Brasil" [The number of suspected cases of the Ômicron variant investigated in Brazil goes to 6]. CNN Brasil (in Brazilian Portuguese). 30 November 2021. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "Germany: Leipzig reports first Omicron variant case with no travel history". Free Press Journal. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ Dahir A, Ezeamalu B, Pérez-Peña R (1 December 2021). "Ghana and Nigeria are the latest African countries to detect the Omicron variant". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "Nigeria confirms first cases of Omicron among travellers from South Africa". Reuters. 1 December 2021. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ Graff A (1 December 2021). "First case of omicron in US identified in San Francisco". San Francisco Chronicle. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ Stark K, Rodriguez JF, Dillon RM (1 December 2021). "First U.S. Case of Omicron Variant Found in San Francisco Resident". San Francisco: KQED. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ O'Donnell D (1 December 2021). "Case of Omicron variant confirmed in Ireland". RTÉ News and Current Affairs. Archived from the original on 3 December 2021. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- ^ "South Korea reports five Omicron cases on flight from Nigeria". Reuters. 1 December 2021. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "Dutch say 14 air passengers from S. Africa with Omicron were vaccinated". Reuters. 2 December 2021. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "Number of confirmed omicron cases as of 3 December". Folkehelseinstituttet. 4 December 2021. Archived from the original on 4 December 2021. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ "France now has 25 Omicron Covid variant cases – minister". Reuters. 6 December 2021. Archived from the original on 6 December 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ "Omicron sudah sampai ke Malaysia". Malaysiakini. 3 December 2021. Archived from the original on 3 December 2021. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ "Namibia detects Omicron coronavirus variant in 18 of 19 samples". Reuters. 6 December 2021. Archived from the original on 6 December 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ "Fijians test positive for Omicron variant – Govt". RNZ. 7 December 2021. Archived from the original on 6 December 2021. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ "New omicron variant detected in 57 countries: WHO". www.aa.com.tr. Archived from the original on 8 December 2021. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ "Africa accounts for 46% of reported cases of Omicron, WHO official says". Reuters. 9 December 2021. Archived from the original on 10 December 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Covid: First UK death recorded with Omicron variant". BBC News. 13 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ "First Omicron case detected in New Zealand". Ministry of Healfh. 16 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ "COVID: Germany records first death from omicron variant". DW. 23 December 2021. Archived from the original on 24 December 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ "Australia: Omicron death, false negative COVID results". Al Jazeera. 27 December 2021. Archived from the original on 27 December 2021. Retrieved 27 December 2021.
- ^ Reuters (3 January 2022). "S.Korea reports first deaths linked to Omicron coronavirus variant – Yonhap". Reuters. Archived from the original on 3 January 2022. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ^ Gregg A (26 November 2021). "Dow plunges more than 900 points as new coronavirus variant sends global markets reeling". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ "'Omicron' cryptocurrency soars on new variant". www.msn.com. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ Davies P (26 November 2021). "Bitcoin's price has slumped after a new COVID variant was found. Why?". euronews. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ "South African markets sink on new Covid-19 variant". Moneyweb. 26 November 2021. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ "Rand tanks as UK red lists South Africa again amid new Covid variant". Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ "New variant sees Rand plummet | eNCA". www.enca.com. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ "Omicron raises uncertainty around inflation, says Powell". BBC News. 2 December 2021. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "WHO cautions against imposing travel restrictions due to new variant". Reuters. Geneva. 26 November 2021. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ "Covid live updates today: Omicron variant, symptoms, vaccines efficacy, restrictions..." en.as. 28 November 2021. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ "World closing its doors to African countries due to omicron". aa.com. 30 November 2011. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- ^ Yong C (26 November 2021). "Singapore bans travellers from 7 African countries; no cases of new Covid-19 variant here". The Straits Times. Singapore. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ "Anvisa recomenda restrições de voo diante de nova variante de covid-19" [Anvisa recommends flight restrictions in view of the new covid-19 variant]. agenciabrasil.ebc.com.br. 26 November 2021. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ Kennedy M, Price RD. "'It's Coming': NY Declares State of Emergency Ahead of Potential Omicron Spike". NBC New York. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ "Switzerland announces new restrictions for Israelis after the discovery of Omicron". Globally 24. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ Winning A, Cocks T (26 November 2021). "South Africa says travel bans over new variant unjustified". Reuters. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ Zwi A. "Travel bans aren't the answer to stopping new COVID variant Omicron". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ "EXCLUSIVE South Africa delays COVID vaccine deliveries as inoculations slow". Reuters. 24 November 2021. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ Kaitlan Collins and Kate Sullivan. "Biden says new Omicron variant is 'cause for concern, not a cause for panic'". CNN. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "New COVID-19 restrictions in effect for parts of Canada; some productions cancelled". CTVNews. 20 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "B.C. enacts social gathering and event capacity limits as Omicron variant spreads". Global News. Archived from the original on 19 December 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- ^ "B.C. limits indoor gatherings, cancels New Year's Eve events as Omicron picks up speed". CBC News. 17 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ^ "Quebec shutting down schools, bars, gyms tonight as COVID-19 cases soar". CTV News Montreal. 20 December 2021. Archived from the original on 20 December 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ Meijer BH, van den Berg S (18 December 2021). "Netherlands to go into strict Christmas lockdown". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2 January 2022. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "As Omicron threatens a global surge, some countries shorten COVID-19 booster timelines". Reuters. 20 December 2022. Archived from the original on 15 January 2022. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
Further reading
- WHO: Update on Omicron
- Live Omicron Variant Location Map
- Omicron variant: What have COVID vaccine makers said and are they working on new doses?
- Callaway E, Ledford H (December 2021). "How bad is Omicron? What scientists know so far". Nature. 600 (7888): 197–199. Bibcode:2021Natur.600..197C. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-03614-z. PMID 34857948. S2CID 244840636.
External links
- Corum J, Zimmer C (9 February 2021). "Coronavirus Variant Tracker". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
Constantly Updated
- Archived video:
- Mohale F, Phaahla J, Oliveira T, Lessels R, Gottberg A, Moore P, Crisp N (25 November 2021). Health Department briefs media about a new so-called super-variant (Internet video live stream). South Africa: eNCA. Retrieved 27 November 2021. Archived at the Wayback Machine and Ghostarchive.
- Oliveira T, Kamwendo S (26 November 2021). Professor Tulio de Oliviera on the new COVID-19 variant (Internet video live stream). South Africa: SABC News. Archived from the original on 29 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2021. Archived at the Wayback Machine and Ghostarchive
- Variants of SARS-CoV-2
- COVID-19 pandemic in South Africa
- 2021 in health
- COVID-19 pandemic in Botswana
