Salix amygdaloides
| Salix amygdaloides | |
|---|---|

| |
| Peachleaf willow leaves | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Malpighiales |
| Family: | Salicaceae |
| Genus: | Salix |
| Species: | S. amygdaloides
|
| Binomial name | |
| Salix amygdaloides | |
| |
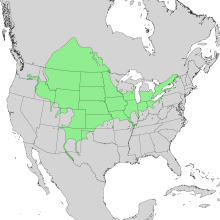
| Natural range | |
Salix amygdaloides, the peachleaf willow, is a species of willow native to southern Canada and the United States, from Quebec west to western British Columbia, southeast to eastern Kentucky, and southwest and west to Arizona and Nevada, respectively.[1]
It is a small to medium-sized deciduous tree, growing to 4–20 m (13–66 ft) tall; besides the cottonwoods, it is the largest tree native to the prairies. It has a single trunk, or sometimes several shorter trunks. The leaves are lanceolate, 3–13 cm (1+1⁄4–5 in) long and 1–4 cm (1⁄2–1+1⁄2 in) wide, yellowish green with a pale, whitish underside and a finely serrated margin. The flowers are yellow catkins, 3–8 cm (1+1⁄4–3+1⁄4 in) long, produced in the spring with the leaves. The reddish-yellow fruit matures in late spring or early summer, and the individual capsules are 4–6 mm (3⁄16–1⁄4 in) long.[2][3]
The peachleaf willow grows very quickly, but is short-lived.
It can be found on the northern prairies, often near streams, and accompanying cottonwoods. As both the common and scientific names suggest, the leaves bear some similarity to those of a peach or an almond (Latin, amygdalus).
References[]
- ^ "Salix amygdaloides". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
- ^ "Salix amygdaloides". Plants of British Columbia.
- ^ "Salix amygdaloides". Northern Prairie Wildlife Research Center. Archived from the original on 2008-03-28.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Salix amygdaloides. |
- Salix
- Trees of the Plains-Midwest (United States)
- Trees of the Western United States
- Trees of Western Canada
- Trees of the Great Lakes region (North America)
- Flora of the North-Central United States
- Flora of the Rocky Mountains
- Flora of Colorado
- Flora of Montana
- Flora of New Mexico
- Flora of Wyoming
- Trees of the North-Central United States
- Trees of the Northeastern United States