Samar cobra
This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: most material can probably be sourced to the provided sources, but for whatever reason they are all bunched up in the lede. Need to be distributed to the sections they actually belong to. (April 2021) |
| Samar cobra | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Elapidae |
| Genus: | Naja |
| Species: | N. samarensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Naja samarensis | |
| |
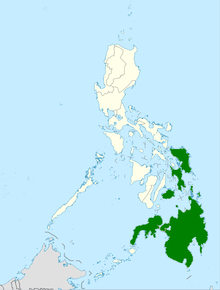
| Distribution of the Samar cobra | |
The Samar cobra (Naja samarensis) also called Peters' cobra, southern Philippine cobra or Visayan cobra, is a highly venomous species of spitting cobra native to the Visayas and Mindanao island groups of the Philippines.[4][5][6][7][8][9][10]
Description[]
The Samar cobra is a species of spitting cobra that can grow up to 1.4 meters in length. Their coloring varies from a black and yellow to green.[citation needed]
Scalation[]
There are 17-25 scale rows around the hood, 17-19 ahead of mid-body; 161-184 ventrals, 41-52 subcaudals, basal pairs sometimes undivided.[11]
Reproduction[]
The Samar cobra, or southeastern Philippines cobra, is oviparous, laying clutches of up to eight eggs.
Distribution and habitat[]
The Samar cobra is endemic to the southern Philippines. Specifically, the Visayas and Mindanao island groups.[citation needed]
Habitat can vary widely from mountainous jungle to tropical plains. They can live close to human settlements.[citation needed]
The Samar cobra typically lives at an elevation of 0 - 1,000 m (0 - 3,280 feet) asl.
Behavior and diet[]
Like the Philippine cobra (Naja philippinensis), the Samar cobra feeds mostly on small rodents such as rats and mice. They will also prey upon frogs and smaller reptiles. Since their main food source is attracted to rice paddies and human settlements, this species often comes into conflict with people.[citation needed]
Venom[]
The Samar cobra's venom is a potentially deadly neurotoxin, with cytotoxic properties as well. Envenomations can result in respiratory distress and paralysis, as well as considerable tissue necrosis around the bite site.[citation needed] They are noted for their nervous behavior, and are quick to strike as well as to spray venom, which they generally aim towards the face and eyes. However, the cobra is more reluctant to spit venom than its northern relative, the Philippines Cobra. If venom gets in the eyes, it causes extreme pain and mechanical damage to the eyeball. If not properly flushed out, it can result in permanent blindness due to its tissue destroying properties. Antivenin for the Samar cobra is produced in the Philippines, but is not widely available due to this species' restricted distribution and thus, relatively low numbers of individuals.
References[]
- ^ "Naja samarensis (Samar Cobra, Southeastern Philippine Cobra)". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 2017-09-28.
- ^ "Naja samarensis". ITIS Standard Report Page. ITIS.gov. Retrieved 10 January 2012.
- ^ "Naja samarensis PETERS, 1861". Taxonomy of Elapids. Reptile-Database. Retrieved 10 January 2012.
- ^ "Naja samarensis, General Details, Taxonomy and Biology, Venom, Clinical Effects, Treatment, First Aid, Antivenoms". WCH Clinical Toxinology Resource. University of Adelaide. Retrieved 10 January 2012.
- ^ "Naja samarensis - Southeastern Philippine Cobra". Asiatic Naja. Bangor University. Retrieved 5 November 2013.
- ^ Dart, Richard C (2003). Medical Toxicology. USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 3 edition. p. 1569. ISBN 0-7817-2845-2.
- ^ Brown, John H. (1973). Toxicology and Pharmacology of Venoms from Poisonous Snakes. Springfield, IL USA: Charles C. Thomas. pp. 81. ISBN 0-398-02808-7.
- ^ Zug, George R. (1996). Snakes in Question: The Smithsonian Answer Book. Washington D.C., USA: Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press. ISBN 1-56098-648-4.
- ^ "Naja samarensis". University of Adelaide.
- ^ Wüster, W.; Thorpe, R. S. (1991). "Asiatic cobras: Systematics and snakebite". Experientia. 47 (2): 205–9. doi:10.1007/BF01945429. PMID 2001726. S2CID 26579314.
- ^ http://pages.bangor.ac.uk/~bss166/Taxa/AsNaja.htm
- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Naja
- Reptiles of the Philippines
- Endemic fauna of the Philippines
- Fauna of Samar
- Fauna of Leyte
- Fauna of Bohol
- Fauna of Dinagat Islands
- Fauna of Mindanao
- Reptiles described in 1861
