Sharpe's grysbok
| Sharpe's grysbok | |
|---|---|

| |

| |
| Male and female in the Kruger National Park | |
Conservation status
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Bovidae |
| Subfamily: | Antilopinae |
| Genus: | Raphicerus |
| Species: | R. sharpei
|
| Binomial name | |
| Raphicerus sharpei Thomas, 1897
| |
| |
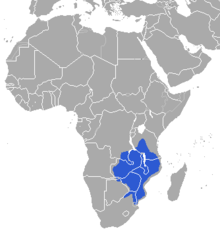
| range | |
Sharpe's or northern grysbok (Raphicerus sharpei) is a small, shy, solitary antelope that is found from tropical to south-eastern Africa.
Range[]
They are found in Transvaal (South Africa), Caprivi Strip (Namibia), Botswana, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Zambia, Malawi and Tanzania to Lake Victoria.
Description[]
It is similar in size to the gray duiker, but has a stockier body and elongated fur over the hindquarters. It stands about 20" (45–60 cm) at the shoulders and weighs only 7–11.5 kg. Its coat is reddish-brown which is streaked with white; eye-rings, around mouth, throat and underside are off-white. The males have stubby horns, which are widely spaced. Sharpe's grysbok has a short deep muzzle with large mouth and heavy molar (grinding) teeth. The short neck and face on a long-legged body result in a high-rump posture when browsing.
Habits[]
Although its territorial range is large, Sharpe's grysbok is infrequently seen. Males and females seem to form brief associations, but the species is usually encountered singly. Territory is marked with dung middens. Their habitat is rocky hill country, but preferring fertile zones on the lower slopes. They are nocturnal browsers and spend the day in the protective cover of tall grass or shrubs. They are extremely timid and will run away at the first sign of anything unusual, although this flight is accompanied "short stamping hops";[2] they move well away from where the disturbance occurred before stopping (unlike steenbok, which stop and look back).[3] Sharpe's Grysbok are reported to take refuge in aardvark burrows, like steenbok.
Sharpe's grysbok browse on leaves, buds, herb and fruits—in the dry season, their food is typically tough (for which their teeth and jaws are adapted). Grazed grass makes up about 30% of their diet.[2] Like the Cape grysbok they use a communal latrine and mark sticks in its vicinity with pre-orbital gland secretions.[4]
Taxonomy[]
The closely related Cape (or southern) grysbok (R. melanotis) occurs in the western Cape region. Haltenorth and Diller[5] consider R. sharpei as a subspecies of R. melanotis.
References[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Raphicerus sharpei. |
- ^ IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2016). "Raphicerus sharpei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T19307A50193414. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T19307A50193414.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ a b Kingdon, Jonathan. 1997. The Kingdon Field Guide to African Mammals. Academic Press, San Diego & London. Pp. 386-387. (ISBN 0-12-408355-2)
- ^ Smithers, Reay H.N. 1971. The Mammals of Botswana. Museum Memoir No. 4. The Trustees of the National Museum of Rhodesia, Salisbury [Harare], Rhodesia [Zimbabwe]. Pp. 221–222.
- ^ Chris; Stuart, Tilde (2000). A field guide to the tracks and signs of Southern and East African wildlife (3rd ed.). Cape Town: Struik. p. 142. ISBN 1868725588. Retrieved 30 July 2015.
- ^ Haltenorth, Theodor and Helmut Diller. 1980. A Field Guide to the Mammals of Africa including Madagascar. Collins, London. Pp. 53–54. (ISBN 0-00-219778-2)
- Ellerman, J.R., T.C.S. Morrison-Scott and R.W. Hayman. 1953. Southern African Mammals 1758 to 1951: A Reclassification. British Museum (Natural History), London. P. 186.
External links[]
- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Dwarf antelopes
- Mammals of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Mammals of South Africa
- Mammals of Namibia
- Mammals of Botswana
- Mammals of Zambia
- Mammals of Zimbabwe
- Mammals of Eswatini
- Mammals of Mozambique
- Fauna of East Africa
- Mammals of Tanzania
- Mammals described in 1897
- Mammals of Malawi
- Taxa named by Oldfield Thomas
