Sigilmassasaurus
| Sigilmassasaurus Temporal range: Cenomanian
~ | |
|---|---|

| |
| Middle neck vertebra, specimen CMN 50791 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Spinosauridae |
| Tribe: | †Spinosaurini |
| Genus: | †Sigilmassasaurus Russell 1996 |
| Species: | †S. brevicollis
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Sigilmassasaurus brevicollis Russell 1996
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Sigilmassasaurus (/siːdʒɪlˌmɑːsəˈsɔːrəs/ see-jil-MAH-sə-SOR-əs; "Sijilmassa lizard") is a controversial genus of spinosaurid dinosaur that lived approximately 100 to 94 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now northern Africa. Named in 1996 by Canadian paleontologist Dale Russell, it contains a single species, Sigilmassasaurus brevicollis. The identity of the genus has been debated by scientists, with some considering its fossils to represent material from the closely related species Spinosaurus aegyptiacus, while others have classified it as a separate taxon, forming the clade Spinosaurini with Spinosaurus as its sister taxon.
Sigilmassasaurus was a moderately-built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore, like most other theropods. It may have had strong neck musculature as evidenced by the morphology of its vertebrae (backbones). Sigilmassasaurus may have had semiaquatic habits and a partially piscivorous diet. It coexisted with other large theropods in the Kem Kem Group.
History of research[]
Fossils of this dinosaur were recovered at the Kem Kem Formation in the Tafilalt Oasis region of Morocco, near the site of the ancient city of Sijilmassa, for which it was named. Canadian paleontologist Dale Russell named Sigilmassasaurus in 1996, from the ancient city and the Greek word sauros ("lizard"). A single species was named, S. brevicollis, which is derived from the Latin brevis ("short") and collum ("neck"), because the neck vertebrae are very short from front to back.[1] Sigilmassasaurus comes from red sandstone sediments in southern Morocco, which are known by various names, including the Grès rouges infracénomaniens, Continental Red Beds, and lower Kem Kem Beds. These rocks date back to the Cenomanian, the earliest stage of the Late Cretaceous Period, approximately 100 to 94 million years ago.[2]
The holotype, or original specimen, of S. brevicollis, CMN 41857, is a single posterior neck vertebra, although Russell referred about fifteen other vertebrae found in the same formation to the species. Other material had been found in Egypt, and was referred to by German paleontologist Ernst Stromer as "Spinosaurus B".[3] Russell in 1996 considered this Egyptian specimen, IPHG 1922 X45, to belong to Sigilmassasaurus or a closely related animal, naming it as a Sigilmassasaurus sp. A second Sigilmassasaurus sp. was by him based on specimen CMN 41629, an anterior dorsal vertebra. "Spinosaurus B" would be intermediate in build between this latter Sigilmassasaurus sp. and S. brevicollis. Russell created the family Sigilmassasauridae for these animals.[1] The neck vertebrae of these dinosaurs are wider from side to side, about 50%, than they are long from front to back. Whether the neck as a whole was particularly short, is unknown: the holotype vertebra is a cervicodorsal, from the transition between the neck and the back, which would not be long anyway. The exact position of Sigilmassasaurus within the theropod family tree is unknown, but it belongs somewhere inside the theropod subgroup known as Tetanurae and most likely was a member of the family Spinosauridae.[4]
Disputed validity[]
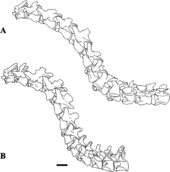
The validity of Sigilmassaurus, however, did not go unchallenged shortly after it was named. In 1996, Paul Sereno and colleagues described a Carcharodontosaurus skull (SGM-Din-1) from Morocco, as well as a neck vertebra (SGM-Din-3) which resembled that of "Spinosaurus B," which they therefore synonymized with Carcharodontosaurus.[5] A 1998 study went further, calling Sigilmassasaurus itself a junior synonym of Carcharodontosaurus.[6]
In 2005, however, Argentine paleontologist Fernando Novas and colleagues found that SGM-Din-3, which was used to synonymize Carcharodontosaurus and "Spinosaurus B" was not actually associated with SGM-Din-1, the Carcharodontosaurus skull described in 1996, and shows clear differences with the holotype of Carcharodontosaurus. Other features of "Spinosaurus B" also differed from Carcharodontosaurus, lending support to the notion that it (and therefore Sigilmassasaurus) is a separate taxon. The same study claimed that the tail vertebrae by Russell assigned to the species were in fact those of iguanodonts.[7] A study in 2013 by Bradley McFeeters and colleagues considered Sigilmassasaurus as valid and an indeterminate member of the Tetanurae.[8]
In 2014, German-Moroccan paleontologist Nizar Ibrahim and colleagues referred the specimens of Sigilmassasaurus to Spinosaurus aegyptiacus, together with "Spinosaurus B" and created a neotype for S. aegyptiacus, Spinosaurus maroccanus was considered a nomen dubium following the conclusions of previous papers.[9][10][11] In a 2015 re-description of Sigilmassasaurus by Serjoscha Evers and his team, it was considered a valid genus within the Spinosauridae. These authors also proposed Spinosaurus maroccanus as a junior synonym of Sigilmassasaurus, and rejected the proposal of a Spinosaurus aegyptiacus neotype.[4]
A study by British paleontologist Thomas Arden and colleagues in 2018 concluded that Sigilmassasaurus was a valid genus and formed a tribe with Spinosaurus termed Spinosaurini. The largest specimen of Spinosaurus cf. aegyptiacus, MSNM V4047, was tentatively assigned to S. brevicollis. On the basis of vertebrae, the researchers suggested that Sigilmassasaurus may have grown larger than Spinosaurus. Although in the absence of associated material, it is difficult to be certain what material belongs to which genus. Below is a cladogram based on the analysis by Arden and colleagues:[12]

| Spinosauridae |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A 2020 study by British paleontologist Symth and colleagues suggested that Sigilmassasaurus is synonymous with Spinosaurus and the Brazilian spinosaurine genus Oxalaia, with both genera falling into the Spinosaurus hypodigm. If supported by future research, both Sigilmassasaurus and Oxalaia would be rendered junior synonyms of Spinosaurus and expand its range, which would further support the theory of faunal interchanges between Africa and South America during the Cretaceous.[13]
A 2021 study conducted by Bradley McFeeters of Carleton University; shed further light for the controversial existence of a second spinosaurid within northern Africa. The study concluded that, although limited, the new data could lend support to the controversial hypothesis that two spinosaurid taxa are represented in the Kem Kem Group. This study focused on an unusual mid-cervical vertebra belonging to a large spinosaurid from the Cenomanian Kem Kem Group of Morocco is described.[14]
It is compared to the characteristic morphology of each reconstructed cervical position in Spinosaurus aegyptiacus, based on a recent composite reconstruction that incorporates most previously referred material from this unit. Rather than conforming to any of the previously identified cervical positions in its morphology, the specimen displays a unique combination of mid-cervical characters, with the relatively compact centrum suggesting a position as C4, and the form of the neural arch laminae suggesting a position as C5 or C6. Furthermore, it displays two characters that are previously unknown in spinosaurid mid-cervicals from the Kem Kem Group: a rounded hypapophyseal tuberosity that is not continuous with a ventral keel, and a moderately developed, dorsally oriented epipophysis that does not overhang the postzygapophysis posteriorly. This revelation leads to the diagnostic value of positionally variable cervical vertebral characters in spinosaurid systematics is discussed.[14]
A quadrate bone from the Kem Kem beds was putatively assigned to Sigilmassasaurus and clearly show the occurrence of two spinosaurid species in Morocco.[15]
Paleobiology[]

On the bottoms of its cervical vertebrae, Sigilmassasaurus bore a series of highly rugged bony structures. These were suggested by Evers and colleagues as being possible evidence for substantial neck musculature, since the attachment sites of muscles and ligaments are often indicated by scarring on the bone surface. The neck muscles inferred from Sigilmassasaurus in particular would have enabled it to rapidly snatch fish out of the water, as indicated by the use of similarly placed musculature in modern birds and crocodilians.[4] This has also been proposed for the related genus Irritator, on account of the prominent sagittal crest running towards the back of its head.[16] However, Evers and colleagues noted that a more thorough biomechanical analysis is required for confirmation of this condition in Sigilmassasaurus.[4]
Several large theropods (more than one tonne) are known from the Cenomanian of northern Africa, raising questions about how such animals would have coexisted. Species of Spinosaurus, the longest known theropod, have been found in both Morocco and Egypt, as has the huge Carcharodontosaurus. Two smaller theropods, Deltadromeus and Bahariasaurus, have also been found in Morocco and Egypt, respectively, and may be closely related or possibly the same genus. Sigilmassasaurus, from Morocco, and "Spinosaurus B", from Egypt, represent a fourth type of large predator. This situation resembles that in the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation of North America, which boasts up to five theropod genera over one tonne in weight, as well as several smaller genera.[17][18] Differences in head shape and body size among the large North African theropods may have been enough to allow niche partitioning as seen among the many different predator species found today in the African savanna.[19]
See also[]
- Sigilmassasauridae
References[]
- ^ a b Russell, D.A. (1996). "Isolated Dinosaur bones from the Middle Cretaceous of the Tafilalt, Morocco". Bulletin du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Section C. 18: 349–402.
- ^ Sereno, PC; Dutheil, DB; Iarochene, M; Larsson, HCE; Lyon, GH; Magwene, PM; Sidor, CA; Varricchio, DJ; Wilson, JA (1996). "Predatory dinosaurs from the Sahara and Late Cretaceous faunal differentiation". Science. 272 (5264): 986–991. Bibcode:1996Sci...272..986S. doi:10.1126/science.272.5264.986. PMID 8662584. S2CID 39658297.
- ^ Stromer, E. (1934). "Ergebnisse der Forschungsreisen Prof. E. Stromers in den Wüsten Ägyptens. II. Wirbeltier-Reste der Baharije-Stufe (unterstes Cenoman). 13. Dinosauria". Abhandlungen der Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften Mathematisch-naturwissenschaftliche Abteilung. Neue Folge (in German). 22: 1–79.
- ^ a b c d Evers, S. W.; Rauhut, O. W. M.; Milner, A. C.; McFeeters, B.; Allain, R. (2015). "A reappraisal of the morphology and systematic position of the theropod dinosaur Sigilmassasaurus from the "middle" Cretaceous of Morocco". PeerJ. 3: e1323. doi:10.7717/peerj.1323. PMC 4614847. PMID 26500829.
- ^ Sereno, Paul C.; Dutheil, Didier B.; Iarochene, M.; Larsson, Hans C. E.; Lyon, Gabrielle H.; Magwene, Paul M.; Sidor, Christian A.; Varricchio, David J.; Wilson, Jeffrey A. (1996). "Predatory Dinosaurs from the Sahara and Late Cretaceous Faunal Differentiation". Science. 272 (5264): 986–991. Bibcode:1996Sci...272..986S. doi:10.1126/science.272.5264.986. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 8662584. S2CID 39658297.
- ^ Sereno, Paul C.; Beck, Allison L.; Dutheil, Didier B.; Gado, Boubacar; Larsson, Hans C. E.; Lyon, Gabrielle H.; Marcot, Jonathan D.; Rauhut, Oliver W. M.; Sadleir, Rudyard W. (1998). "A Long-Snouted Predatory Dinosaur from Africa and the Evolution of Spinosaurids". Science. 282 (5392): 1298–1302. Bibcode:1998Sci...282.1298S. doi:10.1126/science.282.5392.1298. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 9812890.
- ^ Novas, Fernando; de Valais, Silvina; Vickers Rich, Patricia; Rich, Tom (2005). "A large Cretaceous theropod from Patagonia, Argentina, and the evolution of carcharodontosaurids". Die Naturwissenschaften. 92 (5): 226–30. Bibcode:2005NW.....92..226N. doi:10.1007/s00114-005-0623-3. PMID 15834691. S2CID 24015414.
- ^ McFeeters, Bradley; Ryan, Michael J.; Hinic-Frlog, Sanja; Schröder-Adams, Claudia (2013). "A reevaluation of Sigilmassasaurus brevicollis (Dinosauria) from the Cretaceous of Morocco". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 50 (6): 636–649. Bibcode:2013CaJES..50..636M. doi:10.1139/cjes-2012-0129.
- ^ dal Sasso, C.; Maganuco, S.; Buffetaut, E.; Mendez, M.A. (2005). "New information on the skull of the enigmatic theropod Spinosaurus, with remarks on its sizes and affinities". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 25 (4): 888–896. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2005)025[0888:NIOTSO]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634.
- ^ Ibrahim, Nizar; Sereno, Paul C.; Dal Sasso, Cristiano; Maganuco, Simone; Fabri, Matteo; Martill, David M.; Zouhri, Samir; Myhrvold, Nathan; Lurino, Dawid A. (2014). "Semiaquatic adaptations in a giant predatory dinosaur". Science. 345 (6204): 1613–6. Bibcode:2014Sci...345.1613I. doi:10.1126/science.1258750. PMID 25213375. S2CID 34421257. Supplementary Information
- ^ Sereno, P.C.; Beck, A.L.; Dutheil, D.B.; Gado, B.; Larsson, H.C.E.; Lyon, G.H.; Marcot, J.D.; Rauhut, O.W.M.; Sadleir, R.W.; Sidor, C.A.; Varricchio, D.D.; Wilson, G.P; Wilson, J.A. (1998). "A long-snouted predatory dinosaur from Africa and the evolution of spinosaurids". Science. 282 (5392): 1298–1302. Bibcode:1998Sci...282.1298S. doi:10.1126/science.282.5392.1298. PMID 9812890.
- ^ Arden, T.M.S.; Klein, C.G.; Zouhri, S.; Longrich, N.R. (2018). "Aquatic adaptation in the skull of carnivorous dinosaurs (Theropoda: Spinosauridae) and the evolution of aquatic habits in Spinosaurus". Cretaceous Research. 93: 275–284. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2018.06.013. S2CID 134735938.
- ^ Symth, R. S. H.; Ibrahim, N. & Martilla, D. M. (2020). "Sigilmassasaurus is Spinosaurus: a reappraisal of African spinosaurines". Cretaceous Research. 114: 104520. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2020.104520. S2CID 219487346.
- ^ a b McFeeters, Bradley D. (2021). "New mid-cervical vertebral morphotype of Spinosauridae from the Kem Kem Group of Morocco". Vertebrate Anatomy Morphology Palaeontology. 8: 182–193. doi:10.18435/vamp29370. S2CID 234104245. Retrieved November 7, 2021.
 This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^ Hendrickx, Christophe; Mateus, Octávio; Buffetaut, Eric (January 6, 2016). Evans, Alistair Robert (ed.). "Morphofunctional Analysis of the Quadrate of Spinosauridae (Dinosauria: Theropoda) and the Presence of Spinosaurus and a Second Spinosaurine Taxon in the Cenomanian of North Africa". PLOS ONE. 11 (1): e0144695. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0144695. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4703214. PMID 26734729.
- ^ Sues, H. D.; Frey, E.; Martill, D. M.; Scott, D. M. (2002). "Irritator challengeri, a spinosaurid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Lower Cretaceous of Brazil". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 22 (3): 535–547. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2002)022[0535:ICASDT]2.0.CO;2.
- ^ M Henderson, Donald (1998). "Skull and tooth morphology as indicators of niche partitioning in sympatric Morrison Formation theropods". Gaia. 15.
- ^ Holtz, Thomas; E. Molnar, Ralph; Currie, Philip (2004), "Basal Tetanurae", The Dinosauria: Second Edition, pp. 71–110
- ^ Farlow, James O.; Planka, Eric R. (2002). "Body Size Overlap, Habitat Partitioning and Living Space Requirements of Terrestrial Vertebrate Predators: Implications for the Paleoecology of Large Theropod Dinosaurs". Historical Biology. 16 (1): 21–40. doi:10.1080/0891296031000154687. ISSN 0891-2963. S2CID 18114585.
- Spinosaurids
- Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Africa
- Cenomanian life
- Cretaceous Morocco
- Fossils of Morocco
- Fossil taxa described in 1996
- Taxa named by Dale Russell













