Silfra

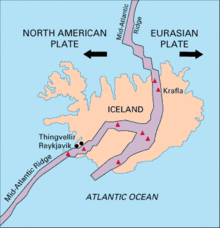
Silfra (Icelandic pronunciation: [ˈsɪl(v)ra]) is a rift formed in the divergent tectonic boundary between the North American and Eurasian plates and is located in the Þingvallavatn Lake in the Þingvellir National Park in Iceland.
Formation[]
Silfra lies in the Þingvellir valley and within the Þingvellir National Park. The valley, and Silfra itself, were formed by the divergent tectonic drift of the Eurasian and North American plates. The plates drift about 2 cm (0.79 in) farther apart every year, building up tension between the plates and the earth mass above. This tension is relieved through periodic major earthquakes at approximately ten year intervals, which have caused cracks and fissures to form in Þingvellir valley; Silfra lies at the rim of the Þingvallavatn Lake[1] and is one of the largest and deepest of these fissures. The Silfra fissure intercepts a major aquifer, which feeds multiple springs at its base.[2] Boulders and rocks falling into the widening cracks have formed caves within the fissures.[1][3]
Hydrology[]
Silfra is spring fed by groundwater originating as meltwater from Langjökull, Iceland's second largest glacier, about fifty kilometres north of the Þingvallavatn Lake. In the distant past, this Langjökull meltwater ran through a river directly and unimpeded into the Þingvallavatn Lake. This river was blocked a few thousand years ago by lava flows from the Skjaldbreiður volcano causing the meltwater to pond and seep underground into the porous lava rock to form an aquifer. This water then percolates through the aquifer for thirty to a hundred years before emerging from the fissure springs in the Þingvallavatn Lake fifty kilometres to the south. The emerging, highly filtered groundwater is exceptionally clear and potable.[2][4]
Scuba diving[]

Scuba diving and snorkeling in Silfra is popular because of its clear water and location within the continental rift.[5] There are three main dive sites: Silfra Hall, Silfra Cathedral and Silfra Lagoon. The Cathedral is a 100 metres (330 ft) long fissure with visibility almost from end to end.[6][7] Shallow at the entry points and at the ends of the fissure, Silfra descends to a maximum depth of 63 metres (207 ft) but diving to this depth is seldom done as it requires technical diving skills. The water temperature is between 2–4 °C (36–39 °F) but can be comfortably dived using a dry suit.[citation needed]
See also[]
- Geography of Iceland
- List of lakes of Iceland
- Sport in Iceland
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Geology of Silfra, Silfra.org – website
- ^ Jump up to: a b Water in Silfra, Silfra.org – website
- ^ Silfra Caves, Silfra.org – website
- ^ Top Diving Destination, Dive Iceland
- ^ Detailed information and photos of Silfra, Silfra.org – website
- ^ Three sections of Silfra, Total Iceland
- ^ Wednesday, 23 October 2019
Coordinates: 64°15′18″N 21°07′23″W / 64.255°N 21.123°W
- Geology of Iceland
- Southwest Iceland
- Rifts and grabens
- Underwater diving sites in Iceland

