Sinophoneus
| Sinophoneus Temporal range: Middle Permian,
| |
|---|---|
| |
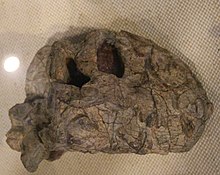
| Skull, Paleozoological Museum of China | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Suborder: | †Dinocephalia |
| Family: | †Anteosauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Anteosaurinae |
| Genus: | †Sinophoneus Cheng and Ji, 1996 |
| Species: | †S. yumenensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Sinophoneus yumenensis Cheng and Ji, 1996
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Sinophoneus is an extinct genus of dinocephalian therapsids in the family Anteosauridae. A single fossilized skull (GMV 1601) has been found from the Middle Permian Xidagou Formation of China.[1]
Description[]


Sinophoneus is characterized by a wide snout and by a ridge that runs along the midline of the skull between the eye sockets. The anteosaur Stenocybus acidentatus has also been named from the Xidagou Formation on the basis of a skull (IGCAGS V 361) and fragmentary jaw bones, but likely represents a juvenile form of Sinophoneus. Juvenile features include its smaller size, larger eye sockets and taller skull. Both GMV 1601 and IGCAGS V 361 have large rounded snouts, distinguishing them from most other anteosaurs and suggesting that they are closely related.[2]
References[]
- ^ "Dolichorhynchops - Facts and Pictures". 12 October 2016.
- ^ Kammerer, C.F. (2011). "Systematics of the Anteosauria (Therapsida: Dinocephalia)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 9 (2): 261–304. doi:10.1080/14772019.2010.492645. S2CID 84799772.
- Anteosaurs
- Prehistoric therapsid genera
- Permian synapsids of Asia
- Guadalupian synapsids
- Fossil taxa described in 1996
- Guadalupian genus first appearances
- Guadalupian genus extinctions
- Prehistoric therapsid stubs

