Sophoradin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
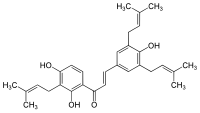
| Preferred IUPAC name
2′,4,4′-Trihydroxy-3,3′,5-tris(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)chalcone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H36O4 | |
| Molar mass | 460.614 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sophoradin is an isoprenyl chalconoid,[1] a type of polyphenolic compound, found in Sophora tonkinensis, an herb used in traditional Chinese medicine.
Sofalcone is an oral gastrointestinal medication and a synthetic analog of sophoradin.[2]
References[]
- ^ Synthesis of Isoprenyl Chalcone “Sophoradin” Isolated from Sophora subprostrata. Kazuaki Kyogoku, Katsuo Hatayama, Sadakazu Yokamori, Teruya Seki and Ichiro Tanaka, Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, Vol.39 , No.1(1975) pp.133-138
- ^ Konturek SJ, Mrzozowski T, Drozdowicz D, Pawlik W, Sendur R (August 1987). "Gastroprotective and ulcer healing effects of solon, a synthetic flavonoid derivative of sophoradin". Hepatogastroenterology. 34 (4): 164–70. PMID 3478294.
Categories:
- Chalconoids
- Aromatic compound stubs