South Coast railway line, New South Wales
| South Coast railway line | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 View of the South Coast line as it runs past the Illawarra Coke Company at Coalcliff | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | Transport Asset Holding Entity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Termini | Illawarra Junction Bomaderry | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stations | 56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator(s) | NSW TrainLink Sydney Trains Pacific National | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rolling stock | H set (OSCar) T set (Tangara) Endeavour railcars | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opened | 1887 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track length | 153 kilometres (95 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification | 1,500 V DC overhead between Illawarra Junction and Kiama | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The South Coast railway line (also known as the Illawarra railway line) is a commuter and goods railway line in New South Wales, Australia. Beginning at the Illawarra Junction, the line primarily services the Illawarra and South Coast regions of New South Wales, and connects Sydney and Bomaderry through Wollongong and Kiama.
Opening in segments between 1884 and 1893, the South Coast railway line was built as an economic link between Wollongong and Sydney, connecting the industrial works at Port Kembla to the greater metropolitan freight railway network in Sydney. The line also serves as a public transport link for residents in St George, Sutherland and the Illawarra. The 56-station, 153-kilometre line is owned by the NSW government's Transport Asset Holding Entity, with passenger services on the line provided by Sydney Trains' Eastern Suburbs & Illawarra Line service in suburban Sydney and by NSW TrainLink's South Coast Line service in the Illawarra.
History[]
Initial proposal[]
The idea for a railway between Sydney and the Illawarra area was first raised in the 1870s. At that time, railways to the north, west and southwest of Sydney had already been constructed, and a committee of prominent citizens formed to investigate the idea felt that a railway might help to develop agricultural and mining potentials in the Illawarra. In 1873, the committee asked the Government Surveyor, R. Stephens, to examine the area between Sydney and Bulli for a suitable route. The suggested route led from Rozelle in inner-western Sydney (at the site of the former Balmain Power Station), crossing the Georges River at Tom Uglys Point, climbing the Gwawley Range on a steep gradient, then following the Port Hacking River towards Stanwell Park. The railway would connect to the main line at Petersham station.[1] When Stephens went to survey the route, he encountered many difficulties with terrain, especially between Gymea Bay and the Port Hacking River, as well as along the river itself. Stephens noted his concerns about the Gymea Bay-Port Hacking route in a letter to the Engineer-in-Chief of the New South Wales Government Railways, John Whitton:[1]
[The country] consists of a sort of plateau or tableland about 200 ft (61 m) above sea-level, and deeply indented with numerous deep chasms and narrow ravines, the bed of whose creek is, to all intents and purposes, on the same level as the sea... Mr Carver, previous to my arrival, attempted to overcome the difficulty by heading up all the creeks, and he ran a trial line upwards of eight miles (13 km) in length, but this brought him to the summit of the range from which there was no getting down.
Similar things were written about the route along the River itself:[1]
[There was] a confused jumble of huge boulders and rocks covered with thick brushwood closely interwoven with vines and creepers... a quarter of a mile per day of setting out is the most I can manage..."
Besides the terrain, problems were also found with the proposed descent from Bulli to Wollongong. Stephens found that any proposed railway would have required a series of zig zags to enable trains to climb the Illawarra escarpment. The committee presented the route to Parliament in 1876, but despite a pledge of £740,000 by Parliament towards construction costs, and petitions from Kiama coal-miners, it was rejected.
Construction[]
The Government undertook no further surveys until 1880, when a new route was approved. This route originated near the inner-city locality of Macdonaldtown and ran to Kiama via the locality of "Bottle Forest", a distance of 109 kilometres (68 mi). The route selected comprises the present-day route,[2] although minor deviations were made between Waterfall and Coal Cliff between 1915 and 1920.[3] On 6 April 1881, Governor Augustus Loftus assented to Act 44 Vic. No. 28, which provided £1,020,000 for the construction of this railway, and proposed that the first section of 37 kilometres (23 mi), constituting approximately the present suburban route, be completed by 30 September 1884.[2][4] Almost immediately, concerns were raised about the new route's viability, most specifically over the cost of tunnelling between Waterfall and Otford to reach Wollongong. Construction of the various sections was awarded by tender and commenced in October 1882.[4] Work was suspended past the 24 kilometre point at Como, and Government surveyors were instructed to re-survey Stephens' work on the original route. Their work allayed concerns about the new route: although the new route had more tunnelling, excavation and sharp curves, the total cost of the "Bottle Forest" route was estimated at £130,175 less than the original Port Hacking route. The Minister for Works eventually agreed on this new route, although construction was again briefly halted when the contractors refused to recommence work on the disputed section.[5] With new contractors hired, the line was completed to Hurstville in 1884, Sutherland in 1885, Waterfall in 1886 and Clifton through to Wollongong and North Kiama (Bombo) in 1887.[6] The missing Waterfall to Clifton section comprised four large brick-arch culverts (and many small ones) and eight tunnels with a total length of over 4 km, delaying its opening until 1888.[4] The section between Kiama and Bomaderry (servicing Nowra) opened in 1893.[6]
According to the official papers on the line's construction, when the line first opened for trains between Sydney and Sutherland construction was not quite complete, so excursion services initially ran on weekends only until the entire line was handed over. The first official train ran within the modern-day suburban area on 9 December 1885, although the line was closed once again between December 1885 and January 1886 to permit testing on the new bridge over the Georges River.[5]
Track amplification[]

The line was originally constructed as double track between Illawarra Junction (near Macdonaldtown) and Hurstville with single track thereafter; however, its rising use meant that the line required duplication soon afterwards. The line was duplicated between Hurstville and Loftus Station (with the exception of the Como bridge over the Georges River) in April 1890, then southward to Waterfall by 12 December 1890. The section of track between Illawarra Junction and Hurstville was quadruplicated between 1913 and 1925.[7]
After duplication in 1890, the original lattice-girder Como Bridge across the Georges River was laid as gauntlet track.[8] This arrangement remained in place for many decades, causing a notorious bottleneck on the line, until the New South Wales Government commissioned John Holland & Co to build a new bridge in 1969. Construction of the new bridge, made of prestressed concrete box girders, commenced in 1969 and was first used by the 18:17 service from Como on 19 November 1972.[9] The old bridge, as well as a former alignment of the line between Mortdale and Oatley replaced in 1905, is now used as a rail trail for pedestrians and cyclists.[10]
Duplicated track now continues to Coniston, except for the section through the Clifton Tunnel.
Deviation[]

Many goods trains were routinely divided at Stanwell Park and taken through to Waterfall in stages, effectively increasing the number of train movements on the line. The increasing congestion and steepness led to construction of a double track deviation, which opened between Waterfall and Helensburgh in 1914, Helensburgh and Otford in 1915, and Otford and Coalcliff (bypassing the by now infamous Otford Tunnel) in 1920. The deviation avoided the steep grades with a more winding route featuring sharp curves, deep cuttings, new tunnels and a curved viaduct over Stanwell Creek that required three million bricks in its construction. The old route's ruling grade of 1 in 40 was faced by up (Sydney bound) trains almost all the way between Stanwell Park station and Otford. Although the new route was 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) longer it reduced the ruling grade from 1 in 40 to around 1 in 80.[4] Many stations in this section were closed or rebuilt on the new alignment
The Helensburgh Tunnels refer to a series of seven, now abandoned, tunnels between Waterfall and Otford. These tunnels, approximately 3,257 metres (10,686 ft) in total, were built between 1884 and 1886 and were part of the original alignment of the rail line. They were abandoned by 1920 when the new line was built.[11][12]
The main problem was the 1,550-metre-long (5,090 ft) Otford Tunnel, which took the railway through Bald Hill from the coast at Stanwell Park to the Hacking River valley. The steep grade and tight clearances meant that soot, smoke and heat could become unbearable, especially when a south-easterly wind blew into the southern portal or when a train stalled in the tunnel.[4][13]
A Mr B. Chamberlain wrote about a stalled passenger train in 1890:[4]
Even with the windows closed, the carriages were filled with smoke and steam, women fainted and children screamed until the train backed down to Stanwell Park, and was finally staged up to Otford in two trips.
Regarding the crew, Chamberlain wrote:[4]
While the passenger with closed windows in an up train had an unpleasant journey... the unfortunate enginemen underwent a shocking ordeal. On tender engines both knelt on the footplate, coats over heads, to breathe the air coming from under the engine, the apron plate being raised for this purpose. Though the air was hot from passing around or through the ash pan, it was nonetheless welcome.
Attempts were made to overcome the problem with a ventilation shaft and chimney in the early 1890s and a blower system installed in 1909.[4]
List of tunnels[]
The full list of the Helensburgh Tunnels is:
| Tunnel name | Length[14][15][16] | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|
| m | ft | ||
| Waterfall | 221 | 725 | Modified in 1915 to a cutting during track duplication |
| Cawley | 381 | 1,250 | Closed January 1914 |
| Helensburgh | 80 | 260 | Closed May 1915 |
| Metropolitan | 624 | 2,047 | Closed May 1915 |
| Lilyvale No. 1 | 80 | 260 | Closed May 1915 |
| Lilyvale No. 2 | 322 | 1,056 | Closed May 1915 |
| Otford | 1,549 | 5,082 | Closed October 1920 |
The Clifton Tunnel is an eighth tunnel in this section and built around the same time as the Helensburgh Tunnels. Unlike the others it remains in use and is the only single track section between Sydney and Unanderra.
The Metropolitan Tunnel features the first Helensburgh railway station at its northern end. The station was opened on 1 January 1889 and closed in 1915 when a new station was built on the current line. In May 1928, the colliery completed the conversion of the Metropolitan tunnel to a reservoir by plugging the southern end with concrete and used by the Metropolitan Colliery as a reservoir until town water was connected. It now features a glow worm population.[12]
Electrification[]
The Illawarra line was the first railway electrified in New South Wales, and was built in conjunction with the construction of the City Railway between Central and St James, opening on 1 March 1926, a few months before the line was connected to the new underground railway.[7][17] By November 1926 the electric overhead had passed Sutherland and continued to the branch line constructed to the Royal National Park.[7] The line between Loftus and Waterfall remained unelectrified until 1980 and was serviced by steam and then CPH railcars. The Government decided to continue electrification to Wollongong, and the wires were extended to Waterfall on 20 July 1980 and on to Wollongong in January 1986.[7][17] Further works saw electrification extended to Dapto in 1993 and Kiama in 2001. The Kiama to Nowra section remains unelectrified. With the cessation of electrically hauled freight trains in the late 1990s, the Port Kembla freight lines have been dewired although the masts remain in place.
Other modifications[]
New stations that opened along the line include Coledale in 1902, North Wollongong in 1915, Coniston in 1916, Wombarra in 1917, and Towradgi in 1948. Stations to have closed include Clifton in 1915,[18] Yallah and Toolijooa in 1974, Omega and Jaspers Brush in 1982, and Lilyvale in 1983.[19] Dunmore was also closed in November 2014, replaced by Shellharbour Junction, after rising commercial and residential development in Flinders and Shell Cove and their distance from Dunmore station, prompted the Government of New South Wales to build a replacement station closer to the area of urban growth.[20]
In 1917 the Thirroul Locomotive Depot opened to service the steam trains on the South Coast line and it closed in 1965.
Major structural problems with the Stanwell Creek viaduct were identified in late 1985, with one span close to collapsing and another badly cracked, requiring substantial repairs and stabilising work.[4]
Description of route[]

The Illawarra line commences at the Illawarra Junction just south of Redfern station. Here, a dive-under allows inter-city services from the Illawarra line to cross underneath the main suburban railway lines to access Sydney Terminal.[21] From the Illawarra junction, four tracks head south through the stations of Erskineville and St Peters to Sydenham. Immediately north of Erskineville, the Illawarra lines are connected to the Illawarra Relief Lines which emerge from underground. These lines form the Eastern Suburbs line which opened in 1979. Heading south from Erskineville, the easternmost pair of tracks are the Up and Down Illawarra lines which usually carry the T4 Illawarra Line passenger services.
The westernmost pair of tracks are the Up and Down Illawarra local tracks which usually carry T3 Bankstown Line services and T8 Airport & South Line express trains operating via Sydenham. To the west of the four tracks between Erskineville and Sydenham there is a reservation for a further pair of tracks with partially constructed platforms at Erskineville and St Peters stations.
At Sydenham, six platforms are provided, with T3 Bankstown Line services generally using the westernmost pair (platforms 1 and 2), T8 Airport & South Line peak hour services using the inner pair (platforms 3 and 4) and T4 Illawarra Line services using the easternmost pair of platforms (platforms 5 and 6). South of Sydenham, the Bankstown railway line branches off in a westwards direction. The Botany Goods Line crosses over the Illawarra line via a flyover. The line then reaches Tempe station, before crossing the Cooks River.
South of the Cooks River lies Wolli Creek station, constructed by the NSW State government in 2000 to provide an interchange between the Illawarra line and the newly privately built Airport Link to the east, an extension of the East Hills line, connecting via a new tunnel under the Illawarra line, which then branches off to the west. The Illawarra line continues south as four tracks through a rock cutting to the stations of Arncliffe, Banksia and Rockdale. Rockdale station has five platforms, platform 1 (the most westerly platform) is currently unelectrified and disused but was previously a terminating point for electric passenger trains. South of Rockdale, the line passes through Kogarah which has a shopping centre built overhead. The line then makes a westerly turn, heading through Carlton and Allawah.
The next station is Hurstville, which is where the four-track section ends and terminating facilities are provided. Like Kogarah, Hurstville has a shopping centre built above the platforms. South of Hurstville, the line becomes two tracks with bidirectional signalling. The line passes through Penshurst and Mortdale. At Mortdale is the Mortdale Maintenance Depot which lies on the eastern side of the tracks with access points from the south of the station. The line then continues to Oatley which has a set of points allowing trains to be turned-back. The line then crosses the Georges River over the Como bridge, which opened in November 1972 replacing an older single track iron lattice bridge which still exists to the east of the present structure and is used as a cycleway.[22][23] The line enters the Sutherland Shire, passing through Como station (which was moved to its present, new site with the opening of the new bridge in 1972), and Jannali before reaching Sutherland.
At Sutherland, three platforms are provided. The Cronulla line branches off in an eastwards direction south of the station. The former short branch line to Woronora Cemetery branched in a westerly direction at the south of the platforms. The line opened on 28 July 1900 and closed on 27 August 1944.[24] The line then continues south through Loftus, Engadine, and Heathcote. South of Loftus, the former Royal National Park line branched off, this has now been converted into a tram line connecting to the Sydney Tramway Museum, and connections to the mainline have been severed. The final station for the operation of suburban services is Waterfall station. At Waterfall, there is a train stabling yard and a train turnback (shunting road) south of the station. South of Waterfall is the site of the 2003 Waterfall train disaster.

The line then heads south through the challenging terrain of the Royal National Park and Illawarra escarpment. The line makes a steep descent down to Wollongong. The original alignment through the towns of Helensburgh and Lilyvale which opened in 1888 was bypassed by a new route in 1915. A new station at Helensburgh was subsequently opened with the new alignment.[25] A set of points allows the turnback of trains at Helensburgh. The line then proceeds through several tunnels down the Illawarra escarpment through the hamlets of Otford, Stanwell Park and Coalcliff.
South of Coalcliff, the line becomes single track as it passes through the Clifton Tunnel, before becoming double track again near Scarborough station. The line then proceeds south through the northern suburbs of Wollongong, then Wollongong and its southern suburbs. A terminating platform is provided at Thirroul, which is used to terminate peak hour services from Sydney, as well as local services.
At Coniston the double track ends with an electrified branch line heads east to Port Kembla. At Unanderra, the line to Moss Vale branches off to head west over the Illawarra escarpment to join the Main South line. The line continues south through Kembla Grange Racecourse where a simple platform serves the adjoining racecourse. The line then reaches Dapto where a passing loop is provided. Dapto was the southern extent of electrification until 2001.[26]
The line passes south through Albion Park (where another crossing loop is provided) to reach Kiama the extent of electrification. South of Kiama, the line continues as a single track non-electrified line through rolling dairy pastures via several tunnels to the towns of Gerringong and Berry before arriving at its terminus at Bomaderry on the northern bank of the Shoalhaven River. At Bomaderry, sidings connect to the Manildra Group's starch mill.[27]
An extension of the line to the Jervis Bay area had been proposed as early as 1911.[28] In April 1971, the State Government announced the line would be extended to Jervis Bay if a proposed steelworks were built.[29]
Branch lines[]
Bankstown line[]
The Bankstown line was initially opened as a branch line from the Illawarra Line to Belmore Station in February 1895, although it was soon extended through to Sefton to the Main South line on 16 July 1928.[30]
East Hills line[]
The East Hills Line was first recommended to the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Public Works in 1916, as an alternative route when the Bankstown Line was being constructed,[31] the line opened to Kingsgrove on 21 September 1931, and to East Hills three months later on 21 December 1931.[32] It was connected to the Main Southern line near Glenfield station on 21 December 1987.[31] The East Hills line experienced a major change in 2000 when the Airport line opened. This saw most East Hills trains using the new line to access the city, providing relief to the section of the Illawarra line between Sydenham and the city.
Cronulla line[]


A single track tramway line between Sutherland and Cronulla, with four stations and a goods siding, opened on 12 June 1911.[33] By 1932 the tramway had closed. Competing bus services had begun to run with unrestricted competition, and the tram line by this time was so full with services that trams often ran late due to holdups at the crossing loops and passengers missed their connections at Sutherland. The line suffered large losses in its later years, and the effect of the Great Depression at the time forced it to cease its services, the last passenger service operating on 3 August 1931. The goods service continued until 12 January of the next year.[34]
Although the closure of the tramway allowed planning to go ahead for a railway, the planning for the replacement railway line suffered various delays in the 1930s due to funding issues: the line's construction competed with a proposal to electrify the Illawarra Line to Waterfall, and there were disputes over the point at which the line would connect to the main line. Two early proposals to join the line at Como and north of Sutherland station were rejected.[35] Local residents were also concerned that the railway would increase Council rates in the Cronulla area.[36] Despite the delays, Parliament finally gave approval to the line on 2 March 1936, and a route with five new stations was surveyed that would connect with the main line at the southern side of Sutherland station. The new line was opened on 16 December 1939[37] by the Governor, Baron Wakehurst at a large ceremony at Cronulla station.[38]
Although a crossing loop was installed at Caringbah and Gymea when the line was opened, the single track line prevented the expansion of services to the Cronulla peninsula, and so in the 1980s it was decided to duplicate a 3.5 kilometre section of the line between Gymea and Caringbah, with Gymea, Miranda and Caringbah all receiving island platforms. The new section was opened on 15 July 1985.[39] In the 2000s, the remaining single track sections were duplicated. These opened on 19 April 2010.[40]
Woronora Cemetery line[]
In 1897, land was set aside near Sutherland Station for a denominational cemetery; it was an alternative to a site at Kurnell, which would have required a long branch line. A single track line 822 metres (2,697 ft) long was constructed next to the station and opened on 13 June 1900.[41] A single 134-metre (440 ft) platform and a loop for engines were included. The first funeral had taken place earlier that year, with the casket arriving by train from Mortuary station in the city. Due to the advent of the motor car and motorised funerals, funerals by train became rare, and the line eventually closed on 23 May 1947, with no funeral having taken place for some years beforehand. The line and platform were subsequently demolished and removed, and no remains, apart from the original formation coming from the main line, are visible today.[34]
Royal National Park line[]

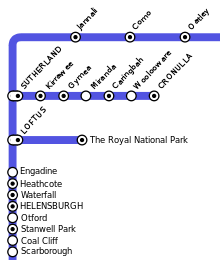
The large area of Crown Land now comprising the Royal National Park was gazetted as a National Park in 1879, only the second such area in the world.[42] In 1886 the need for a training ground for the New South Wales infantrymen, riflemen and artillery, prompted the construction of a short branch line into the National Park. It opened on 9 March 1886 along with the extension of the Illawarra Line from Sutherland to Waterfall,[43] and first served passengers at an army camp open day around a month later. The station featured a single station, originally called Loftus, with two terminal roads, several goods sidings and a loading bank to cope with the heavy artillery equipment.[34] A regular service to the Park serving tourists commenced in May 1886, and a short section of the line was duplicated in 1899 to service the multiple trains that travelled there on weekends. When the Illawarra Line was electrified in 1926, this branch was included being the southern extremity until 1980.[7][17]
Although the army camp closed after the Federation of Australia, the line continued to serve park visitors throughout the 20th century. There was also access to nearby Grays Point. In 1946 a second platform was added on the branch to serve the New South Wales State Scout Jamboree held between December 1946 and January 1947. The terminus was renamed The Royal National Park by June 1955, at the request of the Park's trustees.[34]
The opening of the Cronulla Branch, the building of more roads to the area and other factors led to a decline of services on the branch. Despite a resurgence of passengers in 1978, when the station was rebuilt following the relocation of the Park's Visitors' Centre to the site of the original station, patronage declined to approximately three passengers per train.[43] Until 1990 the line continued to receive regular trains on weekends[44] but when passenger services were temporarily suspended in 1991 due to signalling problems on the branch, CityRail and the State Government decided to close the branch altogether, citing the lack of passengers. Although the branch lay dormant for some time, Parliamentary approval was subsequently given to the Sydney Tramway Museum to operate the line.[45] The Museum converted the branch to light rail standards in order to run their trams on it, and the line was reopened on 1 May 1993,[17] marketed as the ParkLink service. Trams run on the branch on Sundays and public holidays at hourly intervals.[46]
Port Kembla line[]
At Coniston, an electrified branch line proceeds east to Port Kembla with three intermediate stations.
The line is double track as far as just west of Port Kembla North and is used by freight trains as well as local passenger services. A stabling yard is provided at Port Kembla for overnight storage of electric trains.
While the railway network at Port Kembla was built in 1916, stations and passenger trains servicing the surrounding suburbs did not operate until 5 January 1920, when the Port Kembla railway station was opened. A station at Cringila was added to the Port Kembla commuter branch in 1926, along with one at Port Kembla North, a decade later, in 1936. A railway station for workers at Port Kembla, named Lysaghts, after the nearby Lysaght steel plant, was also opened in 1938.[19]
Unanderra – Moss Vale line[]
The Unanderra – Moss Vale line is a cross country railway line, branching from the Illawarra line at Unanderra and winding west up the Illawarra escarpment to join the Main Southern line at Moss Vale. The line was first proposed in the 1880s by residents of Moss Vale and local industry keen for a connection to the port at Port Kembla. Construction began on 26 June 1925, and the line opened on 20 August 1932.[47]
Services[]

The South Coast line passenger services currently consist of electric double deck multiple unit trains that operate between Bondi Junction or Central and either Wollongong, Kiama or Port Kembla. Diesel shuttle trains connect at Kiama and operate to Bomaderry. Although electrified to Wollongong in 1985, several diesel trains operated between Sydney and Nowra until 1991, one of which was the South Coast Daylight Express, operated as a locomotive hauled train of Budd and Tulloch type passenger cars which included catering facilities.[48]
Freight traffic usually operates only to the junction with the Metropolitan line at Tempe. A large amount of coal and a lesser amount of other freight are transported by rail on the line daily to and from Port Kembla, although freight trains are restricted from using the suburban lines during peak hours.[49] South of Unanderra, freight trains serve the ballast quarries at Dunmore and Bombo while the only freight trains south of Bombo are to the Manildra Group's Bomaderry starch plant. As at October 2016, all services were operated by Pacific National. The only active coal mine on the line is served by a siding south of Otford. Most other coal trains come from the Gwabegar line in the state's Central West.
References[]
- ^ a b c Forsyth 1988–1993, pp. 169–70.
- ^ a b Forsyth 1988–1993, p. 171.
- ^ Bozier, Rolfe. "South Coast Line". Retrieved 25 January 2007.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Oakes, John (2009) [2003]. Sydney's Forgotten Illawarra Railways (2nd rev. ed.). Sydney: Australian Railway Historical Society, NSW Division. pp. 11, 12, 23, 24, 26, 54–56, 60, 73, 79–85. ISBN 978-0-9805106-6-9.
- ^ a b Forsyth 1988–1993, p. 172.
- ^ a b "South Coast line". www.nswrail.net. Retrieved 26 November 2006.
- ^ a b c d e Forsyth 1988–1993, p. 100.
- ^ Dewick, Craig. "Railzone FAQ#2: What is gauntlet track?". Archived from the original on 7 January 2006. Retrieved 11 January 2007.
- ^ Forsyth 1988–1993, p. 121.
- ^ "RailTrails Australia: Como Railway Bridge – Trail Description". Retrieved 11 January 2007.
- ^ Noone, Richard; Samandar, Lema (5 June 2015). "Helensburgh tunnels: The eerie beauty of the Sutherland to Wollongong rail network". Daily Telegraph. News Corp. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
- ^ a b "Helensburgh's Railway Tunnels". Helensburgh and District Historical Society. Helensburgh and District Historical Society.
- ^ Bailey, William A. (1974). Tunnels on Australian Railways. Austrail Publications. pp. 40–41.
- ^ Bozier, Rolfe (ed.). "NSW Railway Tunnels". NSWRail.net. Rolfe Bozier. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- ^ "The Illawarra Railway". The Maitland Mercury and Hunter River General Advertiser. Vol. XLV, no. 6310. New South Wales, Australia. 4 October 1888. p. 3. Retrieved 30 May 2016 – via National Library of Australia.
- ^ "The Illawarra Railway". The Sydney Morning Herald. No. 15, 765. New South Wales, Australia. 2 October 1888. p. 4. Retrieved 30 May 2016 – via National Library of Australia.
- ^ a b c d Lukaszyk, Anita. "Electrification". Neety's Train Page. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 11 January 2007. Table sourced from "Historic Electric Traction". Railpage Australia. Melbourne.
- ^ "Clifton Station". www.nswrail.net. Retrieved 17 May 2021.
- ^ a b Bozier, Rolfe. "South Coast Line". NSWrail.net. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ^ Humphries, Glen (6 November 2014). "New Shellharbour Junction set to open". Illawarra Mercury. Fairfax Regional Media. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ^ Railcorp track diagram (Map). 9 September 2002. § Illawarra Line.
- ^ "20 Years Ago". Railway Digest: 442. November 1992.
- ^ "Como (Georges River) Underbridge". NSW Environment & Heritage.
- ^ Neve, Peter (August 1993). "The Woronora Cemetery Branch Railway". Australian Railway Historical Society Bulletin: 187–195.
- ^ Singleton, C.C. (May 1966). "The Helensburgh Deviation". Australian Railway Historical Society Bulletin: 97–106.
- ^ "RIC Annual report 2001-2002" (PDF). Railcorp. Retrieved 8 January 2007.
- ^ "Submission of shoalhaven City, 9 May 2005" (PDF). Parliament of Australia. Retrieved 8 January 2007.
- ^ The Sydney Morning Herald (8 February 1911). "Proposed Railways". Trove. John Fairfax Holdings (Original) / National Library of Australia (Archive). Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ^ "20 Years Ago". Railway Digest: 142. April 1991.
- ^ Forsyth 1988–1993, p. 177.
- ^ a b Forsyth 1988–1993, p. 195.
- ^ Bozier, Rolfe. "East Hills Line: History". New South Wales Railways. Retrieved 11 January 2007.
- ^ Forsyth 1988–1993, pp. 208–10.
- ^ a b c d Neve, Peter (1997). ""Railways (and tramways) in the Sutherland Shire": (Sutherland Shire Studies No. 6)" (PDF). Sutherland Shire Council. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 March 2011. Retrieved 4 March 2013.
- ^ Forsyth 1988–1993, p. 211.
- ^ Forsyth 1988–1993, p. 214.
- ^ Bozier, Rolfe. "Cronulla Line: History". New South Wales Railways. Retrieved 11 January 2007.
- ^ Forsyth 1988–1993, p. 216.
- ^ Forsyth 1988–1993, p. 206.
- ^ "Timetable and platform changes on the Cronulla branch line". CityRail. Retrieved 4 March 2013.
- ^ Forsyth 1988–1993, p. 125.
- ^ New South Wales National Parks & Wildlife Service. "Royal National Park". Retrieved 13 January 2013.
- ^ a b Bozier, Rolfe. "Royal National Park Branch: Description". New South Wales Railways. Retrieved 11 January 2007.
- ^ State Rail Authority of New South Wales (29 April 1991). "Sutherland Timetable". NSW Rail Historical Timetables: CityRail. Archived from the original on 26 October 2009. Retrieved 30 December 2006.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ Downy, Christopher, MLA (25 February 1992). "Article 25 - Private Members Statements, "Sydney Tramway Museum"". Hansard: New South Wales Legislative Assembly. Retrieved 11 January 2007.
- ^ Sydney Tramway Museum. "Our Vintage Tram Routes". Railpage Australia. Melbourne. Archived from the original on 31 December 2006. Retrieved 11 January 2007.
- ^ Jacobson, O.F. (February 1972). "The Unanderra to Moss Vale Line". Australian Railway Historical Society Bulletin: 25–48.
- ^ "The last Daylight". Railway Digest: 118. April 1991.
- ^ Australian Rail Track Corporation. "Southern Sydney Freight Line: Index". Archived from the original on 11 April 2013. Retrieved 11 January 2007.
- Forsyth, J.H. (John Howard), ed. (1988–1993). Stations & Tracks Vol. 1: "Main Suburban & Branches – Illawarra & Branches". Sydney: State Rail Authority of New South Wales.
- Regional railway lines in New South Wales
- Railway lines opened in 1887
- Standard gauge railways in Australia
- Transport in Wollongong
- 1887 establishments in Australia
- City of Shellharbour
- Georges River Council
