Soviet occupation of Manchuria
Soviet occupation of Manchuria | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1945–1946[a] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
 Flag of the Soviet Union (1936-1955) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
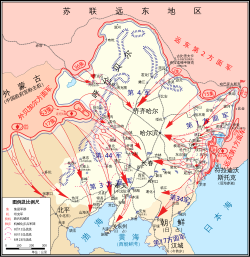 Soviet gains in North East Asia, August 1945. | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Soviet occupation | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Shenyang (Command Station) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Chinese (Northeastern Mandarin) Japanese Russian | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Military occupation | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Soviet commander | |||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1946 | Rodion Malinovsky | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||
• Soviet troops invaded Manchuria | 9 August 1945 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Withdrawal of all Soviet troops in Manchuria | 3 May 1946[a] | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | yuan | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | China Russia | ||||||||||||||||||||||
The Soviet occupation of Manchuria took place after the Red Army invaded the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo in August 1945; the occupation would continue until Soviet forces withdrew in May 1946.
History[]
On 11 February 1945, the Big Three (Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin) signed the Yalta Agreement. Yalta obligated the Soviet Union to enter the war against Japan within three months after Germany's surrender, in exchange for territorial concessions and Soviet influence in post-war Manchuria.

Stalin would order the invasion of Manchukuo on 9 August 1945, according to conditions of Tehran Conference and inaugurated in one of the largest campaigns in the Second World War. The massive Red Army steamrolled into Manchuria, brushing aside scattered Japanese resistance, and they liberated Mengjiang (Inner Mongolia), southern Sakhalin, and the northern half of the Korean peninsula as well. The rapid defeat of the Kwantung Army in Manchuria, along with the recent atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki by the Americans, contributed significantly to the Japanese surrender on the 15th.[1][2][3][4]
The invasion, along with the surrender, prompted the Kuomintang to jockey for position vis-a-vis the Chinese Communists in mainland China. The Kuomintang signed the Treaty of Friendship and Alliance with the Soviet Union on 14 August 1945, which affirmed Chinese sovereignty over Manchuria in exchange for Chinese recognition of the Soviet-aligned Mongolian People's Republic. The Soviets began withdrawing from Manchuria within three weeks of Japan's surrender, although they would delay the process several times. The resumption of the Chinese Civil War in early 1946 prompted the Red Army to finish the withdrawal, but not before secretly turning Manchuria over to the Chinese Communists in March in violation of the Agreement. [5]
See also[]
- Soviet invasion of Manchuria
- Soviet occupation of Mongolia
- Soviet occupations
References[]
Note[]
- ^ Occupation of Lüshun base until 1955
Citations[]
- ^ Robert Butow, Japan's Decision to Surrender, Stanford University Press, 1954 ISBN 978-0-8047-0460-1.
- ^ Richard B. Frank, Downfall: The End of the Imperial Japanese Empire, Penguin, 2001 ISBN 978-0-14-100146-3.
- ^ , Hiroshima in History: The Myths of Revisionism, University of Missouri Press, 2007 ISBN 978-0-8262-1732-5.
- ^ Tsuyoshi Hasegawa, Racing the Enemy: Stalin, Truman, and the Surrender of Japan, Belknap Press, 2006 ISBN 0-674-01693-9.
- ^ 作者:劉向上 (20 April 2009). "张莘夫事件"与苏军撤出东北 (in Chinese). 揚子晚報網. Archived from the original on 1 November 2013. Retrieved 20 April 2009.
- World War II occupied territories
- Aftermath of World War II in the Soviet Union and Russia
- Soviet military occupations
- China–Soviet Union relations
