Stato da Màr
| State of the Sea Stato da Màr (vec) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overseas colonies of the Republic of Venice | |||||||||||||||||
| ca. 992–1797 | |||||||||||||||||
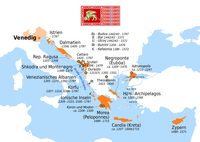
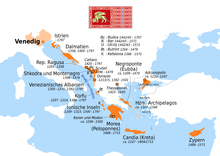 Map of the Venetian overseas domains | |||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||||||||||
• Pietro II Orseolo's expedition | Late 10th century | ||||||||||||||||
• Fourth Crusade | 1202–04 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1463–79 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1645–69 | |||||||||||||||||
• Morean War | 1684–99 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1714–18 | |||||||||||||||||
| 12 May 1797 | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
The Stato da Màr or Domini da Mar ("State/Domains of the Sea") was the name given to the Republic of Venice's maritime and overseas possessions from around 1000 to 1797, including at various times parts of what are now Istria, Dalmatia, Montenegro, Albania, Greece and notably the Ionian Islands, Peloponnese, Crete, Cyclades, Euboea, as well as Cyprus.[1]
It was one of the three subdivisions of the Republic of Venice's possessions, the other two being the Dogado, i.e. Venice proper, and the Domini di Terraferma in northern Italy.
The overseas possessions, particularly islands such as Corfu, Crete and Cyprus, played a critical role in Venice's commercial and military leadership. In his landmark study on the Mediterranean world in the 16th century, historian Fernand Braudel described these islands as "Venice's motionless fleet".[2]
History[]
The creation of Venice's overseas empire began around the year 1000 with the defeat of the Narentines by Doge Pietro II Orseolo and recognition of Venetian rule by Dalmatian city-states, allowing the Doge to call itself "Duke of Dalmatia" for the next few decades. Control over the latter, however, would not be stabilized until the early 15th century.
In the 12th and 13th centuries, Venice gradually established its rule over Istria, which lasted until the end of the Republic.
Venice's overseas domains reached its greatest nominal extent at the conclusion of the Fourth Crusade in 1204, with declaration of the acquisition of three octaves of the Byzantine Empire. However, most of this territory was never controlled by Venice, being held by the Greek Byzantine successor states, namely the Despotate of Epirus and especially the Empire of Nicaea. Venice remained an important player in Constantinople, holding the key position of Podestà until its Byzantine reconquest in 1261, and more broadly in the region during the politically complex period known as the Frankokratia. Of its Fourth Crusade acquisitions, it kept Euboea until the 15th century, the Cyclades until the 16th, and Crete until the 17th.
The aftermath of the War of Chioggia in the late 14th century saw another period of rapid growth of the Venetian empire. Corfu came under permanent Venetian rule in 1386, Argos and Nauplia in 1388–1394, the Adriatic ports of Durazzo and Alessio on the Albanian coast in 1392, followed by Scutari in 1396 and Drivasto in 1397.[3] In 1402, the Battle of Ankara temporarily reversed the rise of the Ottoman Empire in the east, and the death of Duke of Milan Giangaleazzo Visconti created a power vacuum in northern Italy that enabled expansion of the Domini di Terraferma. The changed climate created by the Ottoman Interregnum and the ensuing Treaty of Gallipoli in 1403 led to a growth of commerce and the acquisition of a new string of fortresses in Greece: Lepanto in 1407, Patras in 1408, Navarino in 1410, and temporarily Thessalonica in 1423.[3] In Dalmatia, where Venice had been forced to cede its possessions to the Kingdom of Hungary by the Treaty of Zadar (1358), it took advantage of the conflict between Ladislaus of Naples and Sigismund over the Hungarian Crown, and in 1409 secured the cession by Ladislaus of several of his Dalmatian domains —Cres, Rab, Pag, Zadar, Vrana and Novigrad— for 100,000 ducats.[4]
In 1489, Venice also acquired Cyprus, which it kept until Ottoman conquest in 1570–1571.
The Venetian hold over navigation in the Adriatic sea was maintained for centuries, to the extent that it was labeled "Mare di Venezia" (sea of Venice) on maps of the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries.[citation needed]
From the 15th century onwards, the history of Venice's overseas empire is dominated by successive Ottoman–Venetian wars. Venice lost many territories but also occasionally gained some, most notably the Peloponnese from the late 1680s to 1715 and the Dalmatian Hinterland also in the 1680s. After that date, the remaining overseas domains, kept until the Fall of the Republic of Venice to Napoleon I in 1797, were all in Istria, Dalmatia, and the Ionian Islands, with none left east of Kythira and Antikythera.
Domains[]
The locations are listed broadly from closest to farthest from Venice. Where there is a difference between the name in Venetian language and standard Italian, the Venetian version is indicated first. Feudal lordships held by Venetians, such as Andrea Ghisi in Tinos and Mykonos, are included.
In today's northeastern Italy, Slovenia and Croatia[]



Following the Treaty of Zadar in 1358, Venice lost its presence in Dalmatia for half a century
- Venetian Istria:
- Trieste, 1283–1287, 1368–1372 and 1508–1509
- Muja/Muggia, 1420–1797
- Koper (Capodistria), 1145–1797
- Izola (Isola), 1145–1797
- Piran (Piràn/Pirano), 1283–1797
- Umag (Umago), 1269–1797
- Motovun (Montona d'Istria), 1278–1797
- Novigrad (Cittanova d'Istria), 1270–1797
- Poreč (Parenzo), 1267–1797
- Rovinj (Rovigno), 1283–1797
- Sveti Lovreč (San Lorenso del Paxenadego/San Lorenzo del Pasenatico), 1271–1797
- Bale (Vale/Valle d'Istria), 1331–1797
- Vodnjan (Dignano), 1330–1797
- Pula (Pola), 1145–1291 and 1331–1797
- Labin (Albona) and Plomin (Fianona), 1420–1797
- Plomin (Fianona), ?–1797
- Pazin (Pisino), 1508–1509
- Kvarner Gulf (Quarnaro):
- Rijeka (Fiume), 1508–1509
- Cres Island (Cherso) and Lošinj Islands (Lusin/Lussino), 15C–1797 except brief Ottoman occupation of Cres during the Cretan War (1645–1669)
- Krk Island (Vegia/Veglia), 1480–1797 except brief Ottoman occupation during the Cretan War (1645–1669)
- Rab Island (Arbe), 1409–1797
- Pag Island (Pago), 1420–1797 except brief Ottoman occupation during the Cretan War (1645–1669)
- Novigrad (Novegradi), 1409–1797 except Ottoman occupation in 1646–1647
- Nin (Nona), 1328–1358 and 1409–1797
- Zadar (Zara), 998–1186, 1202–1358 and 1409–1797
- Biograd (Zaravecia/Zaravecchia after 1204), early 11C, 1115–1124, 1125, 1409–1797
- Vrana (Aurana or Laurana Arauzona), 1409–1538, 1647 and 1683–1797
- Ugljan Island (Ugliano) and Dugi Island (Isola Lunga or Isola Grossa), 13C–1358 and 1409–1797
- Šibenik (Sebenego/Sebenico), 1116–1133, 1322–1358 and 1412–1797
- Trogir (Traù), 1125–1133 and 1420–1797
- Split (Spàlato), 998–1019, 1116–1117, 1118–1124, 1127–1141 and 1420–1797
- Fortress of Klis (Clissa), 1648–1797
- Omiš (Almissa), 1444–1797
- Vis Island (Lissa), ca. 1409–1797
- Brač Island (Braza/Brazza), 1268–1358 and 1420–1797
- Makarska (Macarsca), 13C–1326 and 1646–1797
- Hvar Island (Łexina/Lesina), 1331–1358 and 1409–1797
- Korčula Island (Curzola), 1255–1358 and 1409–1797
- Dalmatian Hinterland, mostly conquered during the Morean War:
- Obrovac (Obrovazzo), Benkovac (Bencovazzo), Skradin (Scardona), Vrlika (Verlicca) and Sinj (Signo), 1686–1797
- Knin (Tenin), 1647 and 1688–1797
- Imotski (Imoschi), 1717–1797
- Vrgorac (Vergoraz/Vergorazzo), 1694–1797
- Metković (Porto Narenta), 1685–1797
- Dubrovnik (Raguxa/Ragusa), 1000–1030 and 1205–1358
In today's Montenegro and Albania[]

- Herceg Novi (Castelnuovo), 1687–1797
- Risan (Risano), 1688–1797
- Kotor (Càtaro/Cattaro) and Perast (Perasto), 1420–1797
- Sveti Stefan (Santo Stefano), 1423–1797
- Budva (Budua) and Sutomore (Spizza), 1420–1797
- Bar (Antivari), 1443–1571
- Ulcinj (Dulcigno), 1405–1571
- Shkodër (Scutari), 1396–1479
- Drisht (Drivasto), 1393–1423 and 1442–1478
- Lezhë (Alessio), 1386–1478 and 1501–1506
- Durrës (Durazo/Durazzo), 1205–1213 and 1392–1501
- Vlorë (Valona) and Kaninë Castle (Canina), 1690–1691
- Butrint (Butrinto), 1350 and 1386–1797
In today's Southern Italy (Venetian Apulian ports)[]

- Trani, 1496–1509
- Mola di Bari and Polignano a Mare, 1495–1509 and 1528–1530
- Monopoli, 1484–1509 and 1528–1530
- Brindisi and Otranto, 1496–1509
- Gallipoli, 1484
In today's Greece and Cyprus[]




- Kerkyra Island (Corfù) and Paxi Island (Passo), 1207–1214 and 1386–1797
- Parga (Parga), 1401–1797 with several brief Ottoman occupations
- Preveza (Prevesa), 1401–1463, 1684–1699, 1717–1797
- Arta (Arta), 1717–1797
- Vonitsa (Vonizza), 1684–1797
- Lefkada Island (Santa Maura), 1362–1479, 1502–1503, 1684–1797
- Cephalonia Island (Cefalonia), 1500–1797
- Ithaca Island (Itaca), 1503–1797
- Zakynthos Island (Zante), 1479–1797
- Nafpaktos (Lepanto), 1390 and 1407–1499
- Amfissa (Salona), 1687–1697
- Peloponnese (Morea): various outposts until Ottoman conquest in the 15th-16th centuries, then region–wide Venetian rule 1688–1715 as Realm of the Morea
- Patras (Patraso/Patrasso), 1408–1430 and 1687–1715
- Pylos (Navarino), 1417–1501 and 1686–1715
- Methoni (Modon/Modone), 1207–1500 and 1686–1715
- Koroni (Coron/Corone), 1207–1500 and 1685–1715
- Mani Peninsula (Braccio della Maina), 1487–1499
- Monemvasia (Malvasia), 1464–1540 and 1690–1715
- Argos (Argo), 1394–1462 and 1687–1715
- Nafplio (Napoli di Romània), 1388–1540 and 1686–1715
- Kythira Island (Cerigo) and Antikythera Island (Cerigotto), 1238–1715 and 1718–1797
- Crete, known to Venice as the Realm of Candia:
- Chania (La Canea), ca. 1210–1263 and 1285–1645
- Rethymno (Retimo), ca. 1210–1646
- Sitia (Sitia), ca. 1210–1651
- Heraklion (Candia), ca. 1210–1669
- Gramvousa Island (Grabusa), ca. 1210–1691
- Souda Islet (Suda) and Spinalonga Island (Spinalonga), ca. 1210–1715
- In the Dodecanese:
- Karpathos (Scarpanto) and Kasos (Caso), 1306–1538
- Halki (Calchi), 1204–?
- Tilos (Piscopi)
- Kalymnos (Calimno), 1207–1310
- Leros (Lero), 13th century–1309
- Patmos (Patmo), 1659–1669
- Astypalaia (Stampalia), 1207–1522 and 1648–1668
- the Cyclades, most of which Venice held as the Duchy of the Archipelago:
- Syros (Siro), 1207–1522
- Paros (Paro), Antiparos (Antiparo) and Mykonos (Micono), 1207–1537
- Naxos (Nasso), Milos (Milo), Folegandros (Policandro), Andros (Andro), Ios (Io), Amorgos (Amorgo), Kimolos (Argentiera), Sikinos (Sicandro), 1207–1566
- Santorini (Santorini), 1207–ca. 1280 and 1301–1576
- Kythnos (Citno) and Sifnos (Sifanto), 1207–1617
- Tinos (Tino), 1207–1715
- Spetses (Velvina or Spezia), 1220–1460
- Hydra (Idra), 1204–1566
- Poros, together with (on the mainland) Methana, Troezen (Damala) and Epidaurus (Epidauro), 1484–1715
- Aegina (Egina), 1451–1537
- Athens (Atene), 1394–1403 and 1687–1688
- Euboea Island (Negroponte), 1211–1470
- Pteleos, 1322–1470
- the Sporades including Skiathos (Sciato), Skopelos (Scopelo), Alonnisos (Alonneso) and Skyros (Sciro), 1207–1270s and 1453–1538
- Lemnos Island (Lemno), 1464–1479 and 1656–1657
- Samothrace Island (Samotracia), 1204–1355
- Thessaloniki (Salonico/Salonicco), 1423–1430
- Gelibolu Peninsula (Gallipoli) and Tekirdağ (Rodosto), 1204–1235
- Beyoğlu (Pera) neighborhood in Constantinople, 1204–1261
- Gökçeada Island (Imbro), 1377–1462
- Bozcaada Island (Tenedo), 1377–1381, ?–1455 and 1656–1657
- Cyprus Island (Sipro/Cipro), 1489–1570
- Famagusta (Famagosta), 1489–1571
In today's Russia[]
- Tanais (Tana), 13C–1332
See also[]
- Venetian navy
- Savi agli Ordini
- Provveditore Generale da Mar
- Captain General of the Sea
- Venetian Works of Defence between the 16th and 17th centuries: Stato da Terra – western Stato da Mar
- Genoese colonies
Notes[]
- ^ Map of venetian forts & presence in the Stato da Mar of southern Balkans
- ^ "Sur le grand axe de sa puissance, ces îles sont la flotte immobile de Venise." Fernand Braudel (1949). La Méditerranée et le monde méditerranéen à l'époque de Philippe II, 1 : La part du milieu. Paris: Armand Colin. p. 149.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gullino 1996, § La politica delle annessioni.
- ^ Gullino 1996, § La conquista della Dalmazia (1409–1420).
Bibliography[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Stato da mar of the Republic of Venice. |
- Arbel, Benjamin (1996). "Colonie d'oltremare". In Alberto Tenenti; Ugo Tucci (eds.). Storia di Venezia. Dalle origini alla caduta della Serenissima (in Italian). V: Il Rinascimento. Società ed economia. Rome: Enciclopedia Italiana. pp. 947–985. OCLC 644711009.
- Crowley, Roger (2011). City of Fortune - How Venice Won and lost a Naval Empire. London: Faber and Faber. ISBN 978-0-571-24594-9.
- Da Mosto, Andrea (1937). L'Archivio di Stato di Venezia. Rome: Biblioteca d'Arte editrice.
- Gullino, Giuseppe (1996). "Le frontiere navali". In Alberto Tenenti; Ugo Tucci (eds.). Storia di Venezia. Dalle origini alla caduta della Serenissima (in Italian). IV: Il Rinascimento. Politica e cultura. Rome: Enciclopedia Italiana. pp. 13–111. OCLC 644711024.
- Mutinelli, Fabio (1851). Lessico Veneto. Venice: tipografia Giambattista Andreola.
- States and territories disestablished in 1797
- Stato da Màr
- Overseas empires
- Venetian period in the history of Greece
- 992 establishments
- 10th-century establishments in the Republic of Venice
- 1797 disestablishments in the Republic of Venice
- History of Venice