Triarchy of Negroponte
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2007) |
Triarchy of Negroponte Nigropont[citation needed] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1204–1470 | |||||||||
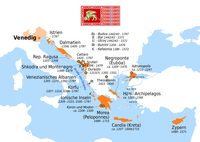
 Negroponte and the other Greek and Latin states of southern Greece, ca. 1210 | |||||||||
| Status | Protectorate of the Republic of Venice (1209-1390) Colony of the Republic of Venice (1390-1470) | ||||||||
| Capital | Chalkis | ||||||||
| Common languages | Venetian officially, Greek popularly | ||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholic officially, Greek Orthodox | ||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||
• Principality established | 1204 | ||||||||
• Ottoman Conquest | 1470 | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• Total | 3,660 km2 (1,410 sq mi) | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Triarchy of Negroponte was a crusader state established on the island of Euboea (Venetian: Negroponte) after the partition of the Byzantine Empire following the Fourth Crusade. Partitioned into three baronies (terzieri, "thirds") (Chalkis, Karystos and Oreos) run by a few interrelated Lombard families, the island soon fell under the influence of the Republic of Venice. From circa 1390, the island became a regular Venetian colony as the Realm of Negroponte (Venetian: Regno di Negroponte).
History[]
Establishment[]
According to the division of Byzantine territory (the Partitio terrarum imperii Romaniae), Euboea was awarded to Boniface of Montferrat, King of Thessalonica. Boniface in turn ceded the island as a fief to the Flemish noble Jacques II of Avesnes, who fortified the capital Chalkis.
After his death in mid-1205 however, the island was ceded to three Veronese barons: Ravano dalle Carceri, Giberto dalle Carceri and Pecoraro da Mercanuovo. They divided the island into three triarchies (terzieri, "thirds"): the northern, based at Oreos (Italian: terzero del Rio), the southern, ruled from Karystos (Italian: terzero di Caristo) and the central portion, ruled from Chalkis (Italian: terzero della Clissura). The city of Chalkis or Negroponte (città de' Lombardi, "city of the Lombards") however was not under the latter's control, but served as overall capital of the island and joint residence of the Lombard rulers and their families. By 1209 however, Ravano had established himself as sole master of Euboea, styling himself as dominus insulae Nigropontis.
Having allied himself with an unsuccessful Lombard rebellion against the Latin Emperor, Henry of Flanders, Ravano was eager to find a powerful protector. Thus, in March 1209, he signed an alliance with Venice, which recognized Venetian overlordship and gave the Venetians significant commercial privileges. In May, however, in an act of political balancing, Ravano also acknowledged his vassalage to the Latin Empire.
Succession disputes[]

However, already after the death of Ravano in 1216, his heirs disagreed over the succession, allowing the Venetian bailo to intervene as a mediator. He partitioned the three baronies in two, creating thus six hexarchies (sestieri). The northern triarchy of Oreos was divided between Ravano's nephews, and ; the southern triarchy of Karystos was divided between his widow, Isabella, and his daughter, ; and the central triarchy was divided between Giberto's heirs, and . Provisions were also made that in the case someone among the sestieri died, his inheritor would be the other sestiere of the respective triarchy, and not his children. In fact, most sestieri were succeeded by their brothers, sons or nephews, keeping the baronies within the tight circle of the original Lombard families.
In 1255 however, the death of Carintana dalle Carceri, hexarch of Oreos and wife to William II of Villehardouin, nominal overlord of Negroponte, led to the so-called "War of the Euboeote Succession", which involved the Principality of Achaea and Venice. William claimed for himself his wife's inheritance, while the Lombard barons were unwilling to concede it. On 14 June 1256, Guglielmo of Verona and Narzotto dalle Carceri, the other two triarchs, repudiated their allegiance to William and pledged themselves to Venice. William responded by capturing Chalkis, which the Venetians retook in early 1258. The war ended in the battle of Karydi in May/June 1258, where William defeated the Duke of Athens, Guy I de la Roche, who had allied himself with the rebellious triarchs. Finally, in August 1259, Doge Reniero Zeno negotiated a peace, followed by a treaty in 1262, which recognized William's suzerainty over the island, but not his possession of the triarchy of Oreoi.
Byzantine interlude[]
By that time, however, the Empire of Nicaea had established itself as the foremost power in the area of the former Byzantine Empire, reconquering several territories from the Latins. Its successes culminated in the recapture of Constantinople in 1261 and the reestablishment of the Byzantine Empire, whose energetic ruler, Michael VIII Palaeologus, sought to reconquer the remaining Latin principalities in southern Greece. To this end, he accepted the services of Licario, an Italian renegade, who had his base near Karystos. Under Licario's command, Byzantine troops soon conquered most of Euboea, except Chalkis.
After the departure of Licario sometime after 1280 however, with Venetian aid, the island gradually returned to Latin control.[1] By 1296, Boniface of Verona had completely expelled the Byzantines from Euboea.
Later history[]
In 1317 however, Karystos fell to the Catalan Company of Don Alfonso Fadrique, royal vicar-general (governor) of the duchy of Athens and illegitimate son of Frederick III of Sicily. In 1319, a peace treaty was signed between Venice and Don Alfonso, whereby he retained Karystos, which the Venetians acquired in 1365.
When the last triarchs, Niccolò III dalle Carceri and , died in 1383 and 1390 respectively, they left their territories to Venice, which thus established complete predominance over the island. Nevertheless, the triarchic system was maintained, with Venetian families appointed to the positions of terzieri, while the Venetian podestà (magistrate) resided at Chalkis.
Venice's rule lasted until 1470, when, during the Ottoman–Venetian War of 1463–1479, Sultan Mehmed II campaigned against Chalkis. With the fall of the city on 12 July, the whole island came under Ottoman control. The city's fall is the subject of the Rossini opera Maometto II.
List of rulers of Negroponte[]
Note: The sequence of rulers during the 13th century, as well as the familial relations between them, are not very clear, as information about Euboea's internal history is scarce to non-existent, especially for the period 1216–1255.[2] According to the rules of succession laid down on the island's division into thirds and sixths in 1216, on the death of a hexarch, he was succeeded in his domain by his fellow hexarch within their third, and not by the former's heirs.[3]
| Barony of Karystos[note 1] | Karystos Southern Triarchy |
Chalkis Central Triarchy |
Oreos Northern Triarchy | ||||
| Jacques d'Avesnes (1204–1205) | |||||||
| Ravano dalle Carceri (1205-1208) | (1205-1208) | (1205-1209) | |||||
| Ravano dalle Carceri (1208-1209) | |||||||
| Ravano dalle Carceri (1209-1216)[4] | |||||||
| (1216-1278),[5] with Othon de Cicon (1216-1264)[note 2], (jure uxoris) or Othon de Cicon (1250[6] with his wife Agnese Ghisi[7]-1264) (1264-1278), under his mother's regency, Agnese Ghisi (1266-1269).[8] He was made prisoner in 1278.[9] |
(1216-1240),[4][10] daughter of Ravano. | (1216-1220),[4][10] widow of Ravano. | Guglielmo da Verona I (1216-1220),[4][10] son of Giberto I, recovered his father's triarchy. | (1216-1220),[4][10] son of Giberto I, recovered his father's triarchy. | (1216-1247),[4] nephew of Ravano. | (1216-1220),[4][5] nephew of Ravano. | |
| (1220-1236[5]/1240[10]) and/or (1220[4]/1236[5]-1247)[note 3] |
Guglielmo da Verona I (1220-1256)[4][10] | (1220-1236[5]/1247[10])[note 4] or Carintana dalle Carceri (1220[4][note 5]/1236[5]/1247[10]-1255[note 6]) | |||||
| Carintana dalle Carceri (1240-1255)[5][note 7] Vice-hexarch: [5][note 8] |
Narzotto dalle Carceri (1247-1255),[4][5] son of Marino. | Narzotto dalle Carceri (1247-1256)[4][5] | |||||
| Narzotto dalle Carceri (1255-1256)[5][note 9] | [note 10] | ||||||
| Guillaume II de Villehardouin[12] (1256[13]-c.1260[5]) Vice-triarch in Karystos: Othon de Cicon[5][note 11] | |||||||
| Narzotto dalle Carceri (1260-1264),[10][5] restored to his triarchy. | Guglielmo da Verona I (1260-1263),[10][5] restored to his triarchy. | (1260-1264),[10][5] restored to his triarchy. | |||||
| (1264-1278),[10][5], son of Narzotto, under his mother's regency, .[14] | Guglielmo da Verona II (1263-1275)[10][5] | (1264-1278),[10][5] nephew of Guglielmo II da Verona. Vice-hexarch: [5][15] |
(1264-1278),[10][5] nephew of Guglielmo II da Verona. Vice-hexarch: [5][16] | ||||
| (1275-1278)[10][5] | |||||||
| Occupation of the Nicaean Empire (1278-1285/96) Vice-governor: Licario[5] | |||||||
| (1296-1317),[5] with Bonifacio da Verona,[17] (jure uxoris) | (1285-1313),[10][5], daughter of Narzotto, with Giorgio Ghisi I (1299-1311) (jure uxoris) | (1285-1328),[10][5] daughter of Giberto II,[18] with (1303-1326) (jure uxoris) Vice-triarch: [5][19] |
Maria dalle Carceri (da Verona) (1285-1323),[10][5] daughter of Gaetano, with Alberto Pallavicini (1285-1311) and Andrea Cornaro (1311-1323) (both jure uxoris) | ||||
| Marulla da Verona (1317-1326),[5], daughter of the previous, with Alfonso Fadrique of Sicily (1317-1338), (jure uxoris) | Bartolomeo Ghisi II[20](1313-1341), son of the previous. | Pietro dalle Carceri (1285[4][21]/1323[10][5]-1340), son of Grapozzo and Beatrice, recovered in 1323 his father's triarchy and united it to his mother's after her death in 1328. | |||||
| Bonifacio Fadrique of Sicily (1338-1365),[5] son of the previous. In 1365 he sold the barony to the Republic of Venice. | Giorgio Ghisi II (1341-1358) | Giovanni dalle Carceri (1340-1358),[10][5] son of the previous, under regency of his mother, .[22] | |||||
| Part of the Republic of Venice[23] | (1358-1384) (1384-1390) |
Niccolò dalle Carceri (1358-1383),[10][5][24] son of the previous, under regency of his mother, Fiorenza Sanudo.[25] | |||||
| Between the 1270 and 1280, Venice gained even more influence over the island's government, to the point that, in this period, Venice redistributed the powers on the island, returning to it the original triachy form of government. Venice appointed new families for the Northern and Southern Triachies, where its ruling families had been extinguished, and kept the central triarchy to Maria Sanudo, maternal half-sister of Niccolò dalle Carceri. | |||||||
| , , and (1390-1402) (1402-1406) |
(1383-1426),[10][5] with Gaspare Sommaripa (1383-1402) (jure uxoris) | (1385–1394) (1394-c.1425) (c.1425–1434) | |||||
| Niccolò II Zorzi (1406-1436) Niccolò III Zorzi (1436-1440) (1440-1447) (1447-1470) |
Crusino I Sommaripa (1426-1462) Domenico Sommaripa (1462-1466) Giovanni Sommaripa (1466-1468) Crusino II Sommaripa (1468-1470) | ||||||
Notes[]
- ^ The barony of Karystos was a separate territory from the namesake triarchy. Cf. Rodd (1907)
- ^ Othon supported the island's occupation of the Achaean prince in 1256, and this fact may have spared the barony from said occupation.
- ^ Cawley states that Berta and Isabella were, at some point, deposed for unknown reasons.
- ^ According to 1216 rules, Marino would be the legitimate heir of his brother Rizzardo. However, Rodd argues that, around 1236, Marino renounced his brother's hexarchy and took his aunt Isabella's, ceded by his cousin Berta.
- ^ Cawley states Carintana may have taken her father's place as hexarch immediately after his death.
- ^ It's undisputed that, at least at the time of her death in 1255, Carintana was ruling her father's hexarchy.
- ^ Rodd refers that Carintana may have taken Berta's hexarchy after her death. This way, Marino and his niece Carintana controlled two hexarchies each, in different triarchies.
- ^ Carintana appointed a vice-hexarch to Berta's hexarchy, and the chosen was Berta's widower, Michele.
- ^ According 1216 rules, it's very likely that Narzotto took his cousin Carintana's southern hexarchy, but didn't do the same in the northern one, to which he and Guglielmo da Verona I had nominated Grapello dalle Carceri (da Verona).
- ^ Albeit part of da Verona family, Grapello appears often as dalle Carceri.
- ^ Othon, lord of the barony of Karystos, supported the occupation of the Achaean prince, and the latter nominated the former as governor of the namesake triachy.[citation needed]
References[]
- ^ Fine 1994, p. 190; Setton 1976, p. 426.
- ^ Bury (1886), pp. 321ff.
- ^ Bury (1886), pp. 319–321
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m Cawley 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj Rodd 1907.
- ^ Longnon 1973, p. 77.
- ^ Setton 1976, p. 418.
- ^ Loenertz 1975, p. 36.
- ^ Setton 1976, pp. 418, 426.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x Bury 1883.
- ^ After Carintana's death, the vacancy led the other two triarchs to nominate a new one: Grapello, son of the triach of Chalkis Alberto da Verona, and nephew of the triarch Guglielmo
- ^ He probably idn't use the title of triarch, but Guillaume occupied the island in 1256 to claim the hexarchies of his wife, Carintana dalle Carceri. It's know that he ordered the arrest of the triarchs Guglielmo and Narzotto.
- ^ Lutrell 1986.
- ^ It is unknown when Felicia ended her regency.
- ^ Absent from the island, Grapozzo appointed his cousin Leone to rule in his place.
- ^ Absent from the island, Gaetano appointed his cousin Leone to rule in his place.
- ^ Bonifacio reestablished the barony in 1296.
- ^ Beatrice was also widow of her uncle, the triarch Grapozzo.
- ^ Probably absent from the island, Beatrice appointed her mother to rule in her place, as long as she lived.
- ^ The numbering II is from the familiar counting of the name. Bartolomeo Ghisi I was his grandfather, father of Giorgio Ghisi I.
- ^ Cawley argues that Pietro may have started to rule next to his cousin Maria and her spouses.
- ^ It is unknown when Balzana ended her regency.
- ^ It's likely that, with the redistribution of powers in the island, the barony merged with the triarchy. p
- ^ Also Duke of the Archipelago (1371-1383).
- ^ Fiorenza was also Duchess of the Archipelago (1362-1371), title that she passed to her son. It is unknown when she ended her regency.
Sources and bibliography[]
- Bury, John Bagnell (1886). "The Lombards and Venetians in Euboia (1205–1303)". The Journal of Hellenic Studies. 7: 309–352. doi:10.2307/623649. JSTOR 623649.
- Bury, John Bagnell (1887). "The Lombards and Venetians in Euboia (1303–1340)". The Journal of Hellenic Studies. 8: 194–213. doi:10.2307/623457. JSTOR 623457.
- Bury, John Bagnell (1888). "The Lombards and Venetians in Euboia (1340–1470)". The Journal of Hellenic Studies. 9: 91–117. doi:10.2307/623661. JSTOR 623661.
- Cawley, Charles (August 2012), Latin lordships in Greece: Euboea, Medieval Lands database, Foundation for Medieval Genealogy,[self-published source][better source needed]
- Fine, John Van Antwerp (1994) [1987]. The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08260-4.
- Koder, Johannes (1973), Negroponte: Untersuchungen zur Topographie und Siedlungsgeschichte der Insel Euboia während der Zeit der Venezianerherrschaft (in German), Vienna: Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, ISBN 3-7001-0020-5
- Miller, William (1908). The Latins in the Levant: A History of Frankish Greece (1204–1566). London: John Murray. OCLC 563022439.
- Nicol, Donald M. (1993). The Last Centuries of Byzantium, 1261–1453 (Second ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-43991-6.
- Setton, Kenneth M. (1976). The Papacy and the Levant (1204–1571), Volume I: The Thirteenth and Fourteenth Centuries. Philadelphia: The American Philosophical Society. ISBN 0-87169-114-0.
- Triarchy of Negroponte
- States of Frankish and Latin Greece
- Kingdom of Thessalonica
- Former countries in the Balkans
- 1204 establishments in Europe
- States and territories established in 1204
- 1470 disestablishments in Europe