Straight sinus
| Straight sinus | |
|---|---|
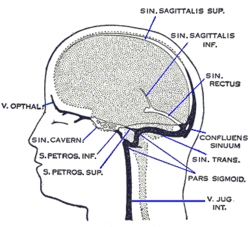 Dural veins (Straight sinus labeled as 'SIN. RECTUS' at center right.) | |
 Dura mater and its processes exposed by removing part of the right half of the skull, and the brain. (Straight sinus visible as blue line at center left.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | inferior sagittal sinus, great cerebral vein |
| Drains to | confluence of sinuses |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sinus rectus |
| TA98 | A12.3.05.112 |
| TA2 | 4853 |
| FMA | 50769 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The straight sinus, also known as tentorial sinus or the sinus rectus, is an area within the skull beneath the brain that receives venous blood. The straight sinus receives blood from the superior cerebellar veins and inferior sagittal sinus and drains into the confluence of sinuses.
Structure[]
The straight sinus is situated within the dura mater, where the falx cerebri meets the midline of tentorium cerebelli.[1] In cross-section it is triangular, contains a few transverse bands across its interior, and increases in size as it proceeds backward.[citation needed]
Function[]
It forms from the confluence of the inferior sagittal sinus and great cerebral vein.
The straight sinus is an unpaired area beneath the brain which allows blood to drain from the inferior center of the head outwards posteriorly. It receives blood from the inferior sagittal sinus, great cerebral vein, , superior cerebellar veins and veins from the falx cerebri.[1]
Additional images[]
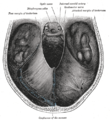
Tentorium cerebelli from above.
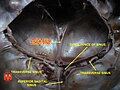
Straight sinus
See also[]
References[]
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 655 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 655 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. p. 795. ISBN 978-0-443-06612-2.
External links[]
- http://neuroangio.org/venous-brain-anatomy/venous-sinuses/[full citation needed]
- Wikipedia articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Veins of the head and neck

