Szilassi polyhedron
| Szilassi polyhedron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Toroidal polyhedron |
| Faces | 7 hexagons |
| Edges | 21 |
| Vertices | 14 |
| Euler char. | 0 (Genus 1) |
| Vertex configuration | 6.6.6 |
| Symmetry group | C1, [ ]+, (11) |
| Dual polyhedron | Császár polyhedron |
| Properties | Nonconvex |
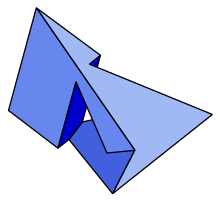
The Szilassi polyhedron is a nonconvex polyhedron, topologically a torus, with seven hexagonal faces.

Coloring and symmetry[]
Each face of this polyhedron shares an edge with each other face. As a result, it requires seven colours to colour all adjacent faces, providing the lower bound for the seven colour theorem. It has an axis of 180-degree symmetry; three pairs of faces are congruent leaving one unpaired hexagon that has the same rotational symmetry as the polyhedron. The 14 vertices and 21 edges of the Szilassi polyhedron form an embedding of the Heawood graph onto the surface of a torus.[1]
Complete face adjacency[]

The tetrahedron and the Szilassi polyhedron are the only two known polyhedra in which each face shares an edge with each other face.
If a polyhedron with f faces is embedded onto a surface with h holes, in such a way that each face shares an edge with each other face, it follows by some manipulation of the Euler characteristic that
This equation is satisfied for the tetrahedron with h = 0 and f = 4, and for the Szilassi polyhedron with h = 1 and f = 7.
The next possible solution, h = 6 and f = 12, would correspond to a polyhedron with 44 vertices and 66 edges. However, it is not known whether such a polyhedron can be realized geometrically without self-crossings (rather than as an abstract polytope). More generally this equation can be satisfied precisely when f is congruent to 0, 3, 4, or 7 modulo 12.[2][3]
History[]
The Szilassi polyhedron is named after Hungarian mathematician Lajos Szilassi, who discovered it in 1977.[4][1] The dual to the Szilassi polyhedron, the Császár polyhedron, was discovered earlier by Ákos Császár (1949); it has seven vertices, 21 edges connecting every pair of vertices, and 14 triangular faces. Like the Szilassi polyhedron, the Császár polyhedron has the topology of a torus.[5]
Is there a non-convex polyhedron without self-intersections with more than seven faces, all of which share an edge with each other?
References[]
- ^ a b Szilassi, Lajos (1986), "Regular toroids" (PDF), Structural Topology, 13: 69–80
- ^ Jungerman, M.; Ringel, Gerhard (1980), "Minimal triangulations on orientable surfaces", Acta Mathematica, 145 (1–2): 121–154, doi:10.1007/BF02414187
- ^ Grünbaum, Branko; Szilassi, Lajos (2009), "Geometric realizations of special toroidal complexes", Contributions to Discrete Mathematics, 4 (1): 21–39, doi:10.11575/cdm.v4i1.61986, MR 2541986
- ^ Gardner, Martin (1978), "In which a mathematical aesthetic is applied to modern minimal art", Mathematical Games, Scientific American, 239 (5): 22–32, doi:10.1038/scientificamerican1178-22, JSTOR 24955839
- ^ Császár, Ákos (1949), "A polyhedron without diagonals", Acta Sci. Math. Szeged, 13: 140–142
External links[]
- Ace, Tom, The Szilassi polyhedron.
- Peterson, Ivars (2007), "A polyhedron with a hole", MathTrek, Mathematical Association of America.
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Szilassi Polyhedron", MathWorld
- Szilassi Polyhedron – Papercraft model at CutOutFoldUp.com
- Nonconvex polyhedra
- Toroidal polyhedra
